Set 9 - Predation & Foraging
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
117 Terms
Picas
Live in the mountain
Forage close to their habitat because of eagles and for the wwinter
Forage for plants with varying poison which acts like a preservative
Important Factors of Food
Energy content
Nutrational content
Cost
Humans are adapted to
Maximixe food and minimize energy expenditure
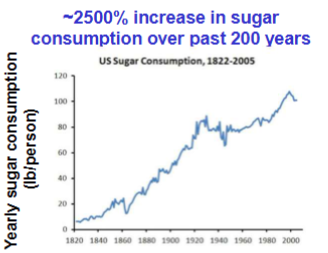
2500% increase in
Sugar consumptions over 200 years
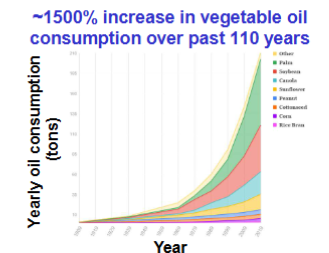
1500% increase in
Vegetable oil consumptions over 110 years
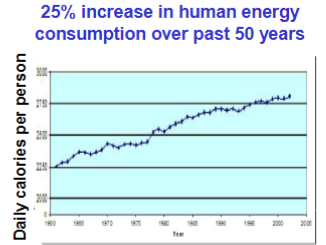
25% increase in
Human energy consumptions over 50 years
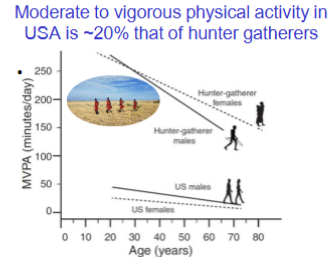
How much do US humans move compared to hunter gatherers?
20%
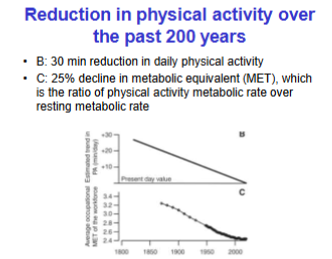
Metabolic Equivalent
Ratio of physical activity metabolic rate over resting rate, 25% decline
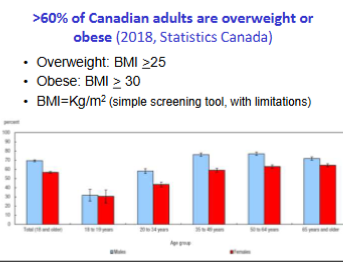
More than 60% of canadians are
Overweight or obese
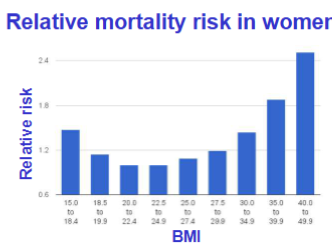
Having a BMI greater than 25
Increases death
Poor diet and exercises causes
63% of premature death
Presenteeism
Decrease productivity at ork
Ultimate Exercise Benefits
Maintain weight, health
Decrease risks of disease/metal health
Increase survival of new neurons
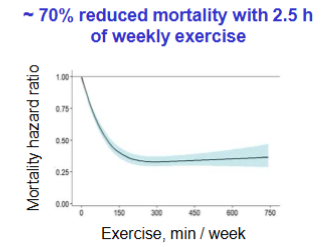
70% decrease in mortality from
2.5H of weekly exercise
Proximate Benefits of Exercise
Improves blood flow to brain
No micro strokes
Anti inflammatory effects
Decrease neurodenerative disease
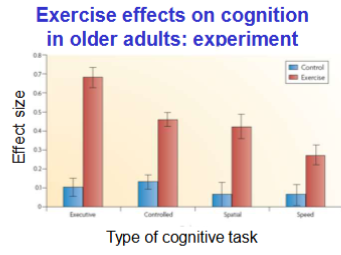
Exercise in rodents
Double new neurons
Exercise in humans
Increase blood vessel formation
What happens hen mice have an enriched and/or exercise
Neurogenesis in DG hippocampus increase
60% of strokes, 40% of dementia and 35% of late life depression decrease if
Factors such as alcohol consumptions, diet, and physical activity are improved
Men and Women have about
10-20% or 15-25% of fat
More then 60% of the brain is
Fat, myelin is 35% fat
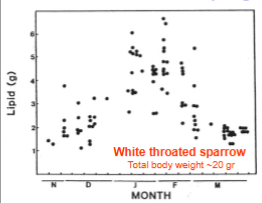
White Throated Sparro store more fat`
In the winter
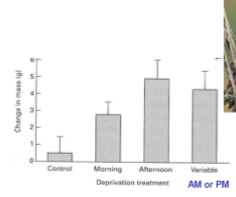
How does interuption to feeding impact Starling fat storage?
In the morning, there’s less fat storage
In the afternoon, there”s more storage because they assume they’ll need to make it through the day/night
Even though prey 1 is less common
It should be the only one eaten if above threshold
Positive correlation between
Patch residency and food intake ratio
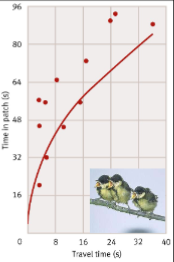
Great Tit Container Experiment
As time to open container increase, so did time in that patch
Moose Altered Theory
Mooses must spend 18% foraging for Na rich aquatic animals
Adaptations to Avoid Being Hit by a Car
Avoidance in space, time and inspection
Crown Eagles
Prey on monkeys and defend territory to have enough feed to feed offsprings
Tungara Frogs Mating Calls
Attracts flies around 284 bites per hour
Ants prefer
Safer, less rewarding patches as long as it’s not much worse (around 12%), but some are willing to go higher patches with predator
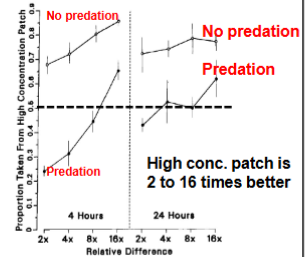
Horse Racing
1.5kg can make a difference in winning
As Starling Weight Increases
Ascent angle decreases, and less weight, ascent angle becomes steeper
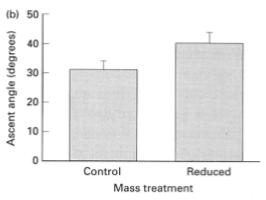
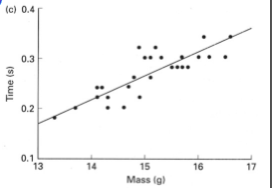
As Zebra Finch Mass Increases
Time to ascend increases
Avenue Nest
Has tall walls running down an open path, surrounded with trinkets males bowerbirds can find
Types of Nests Bowerbirds Make
Avenue or teepee nests
Bowerbirds enhancement
Perform elaborate behaviours and use optical illusions to enriched trinkets
Forced Perspecitve Illusions
Stationary observer see the shells placed by the males on the gesso in a awy that makes the items larger than they are, increasing reproductive success
Intrasexual Selection
Members of sex compete with each other for access to sex
Intersexual Selection
Individual of sex choose which individual of other sex to take as mate
Bateman’s Principles
Females should be choosier because eggs expensive and potential success limited
Females selection means more variance in reproductive success of males
Females devote more energy before
Birth if internal gestation
African Cichlid FIsh Females select
Males more dominant, aggressive mates
When African Cichild Females saw preferred males win
Increase in reproductive related genes
When African Cichild Females saw preferred males lose
Increase in anxiety/stress related genes
Secondary/Epigametic Characterisitics
Traits that attract a mate
Pulse Song
Singing with interval between pulses which affects females mate choice
Polyandrous
Females mate with numerous males
How Humans Actions influence Female Choice
Increase hybridization from pollution and poor distinction of different species colours
Closely related endangered species reared together may sexually imprint on adults of wrong species
Changes can be interpreted as danger, decreasing reproduction
Limited males causes females to breed with bad ones and invest less in offsprings
Direct Benefit Model
Selection favors females have genetic disposition to prefer mates that give them tangible resources to increase fertility, females gain something
Nuptial Gift
Prey items consumed during courtship
Scorpionflies Females
Determine mate choice based on size of nuptial gift, and how long to have sex
What’s the relationship bnetween prey size and sex time?
Positive (sex less than 7 mins = no sperm transfer)
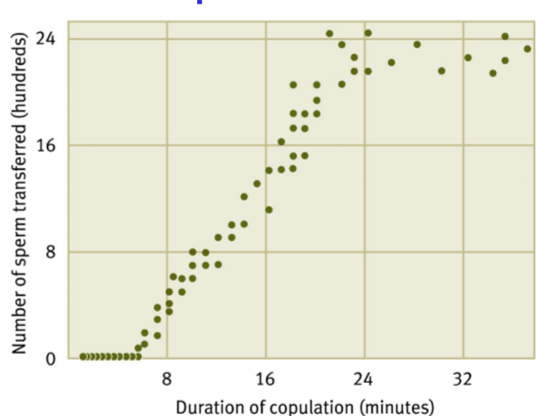
Scorpionflies Males
Will discard too small preys, and will steal from each other by micmicking females
Good Genes Model
Selection favours females to choose better males with best genes best to have superior offspring
Pronghorn Antelope Females
Search to find mates by visiting males with a harem of females and uses current harem defenses as indicator of good genes
Offspring from Attractive Pronghorn Antelope Males
Have a higher survival rate than others
Honest Indicators
Indicators of genetic quality to stop being deceived by males, the more costly the harder to fake
Hamilton-Zuk Hypothesis
Exaggerated ornaments in males evolve as honest indicators of male’s genetic resistance to parasites
Endoparasites
Parasites that live inside host and can’t be seen, females gauge health with a correlated trait
Females choose males based on different
MHC to maintain variability using odour
Stickleback Females Prefer Males with more
MHC alleles = more MHC peptides
Sticklebacks Females exposed to two water columns
When pair is less than optimal MHC peptide, synthetic one was more attractive
When pair is optimal, synthetic is less attractive
Females Sticklebacks raid nests after birth
Are repelled by very male MHC odour she was attracted to before mating to prevent her eating her own eggs
Runaway Sexual Selection
Extreme males traits evolve between genetic male trait and females preference
Females Stalk Eyes Flies were Breeded with long or short flies
Short eye breeding preferred shorter males
No evidence for long eye stalk between control
Sensory Exploitation Model
Newly emerged trait in males are preferred by females because it elicits a reswponse already in females, not associated with mating preference
Pustulosus and Coloradorum Mate Calls
Both begin with a whine, but putulosus add low frequency chuck to the end which female pustulosus prefer
Coloradorum Females also prefer
Chuck because botrh species prefer low frequency sounds
Exposure to Conditioned Sexual Stimuli
Quicker to have sex, display higher levels of courtship, make more sperm
Sexual Imprinting
Youngs remember behaviour and morphology of aprents and use characteristics to guide subsequency selection of mates
Novel Trait Approach
Offspring raised by parent with same novel trait
When mannikin birds were exposed to parents with red feathers on their head
Males raised with red feather females, preferred them too, and vice versa for females
Dendritic Spines in Neurons associated with
Learning
Decrease in Dencritic Spines after
Imprinting because learning for preferences not needed since they don’t change
Male Zebra Finch in Isolated for 2 months after a month of being born
Will imprint on the first female’s phenotype it sees after isolation, and decreased spine density after exposure
Japanese Male Quail imprinted on brown females can
Learn to associate breeding chance and changes it preferrence after imprinting
Leks
Black grouse mating arenas in bogs where males gather and defend a small territory and attract females with display
Mate Copying more common in
Younger grouse since older ones mate earlier
Unanimity of Female Sage Grouse Choice increases
As more females mates in a day
Oxytocin
Neurohormone in the pituiary gland, playing a role in social behaviour
Females with no OT gene
Learned normally but didn’t mate copy because they didn’t recognize scent of another female like OT gene females do
When SD songbirds are raised with SD adults or IN adults
Birds paired and mated weith other that have the same rearing which they were raised in, and females prefer songs alike those she was raiseed in
Male Deer Stags
Form harems in mating season and use roaring as an honest indicators of fighting abilityP
Parallel Walks
Males walks alongside each other to assess size and ability
Reed Deer Stag Males that roared more
Had harems, increased when threatened and more like to win a fight
When hearing a large stag road
Males become more attentive and increase rate of roaring
Heavier European Earwig Males
Succeed more in stopping sex between lighter males but lifting them off
Females increase male male competition to have
More chances to mate with the highest ranking male
Majority of Elephant Female Mounts are
Protested andf often interrupted by another male
As harem size increase
Female bodies stay the same
Parental Bluegill Sunfish
Light bodied with dark yellow breasts, build nests, highly territorial, fan eggs to oxygenate them and defends
Sneaker Bluegill Sunfish
Smaller, less aggressive that hide near parental males and swim into territory while breeding to shed sperm
Satelite Bluegill Sunfish
Imitates females and gets parental male to mate with both of them and the imposter will release his own sperm
Sneaker Bluegill Sunfish invest in
More sperm production with shorter lifespan, higher testes to body size ratio
Parental Bluegill Sunfish invest more in
Higher quality sperm
Spermatophore
Capsule of sperm and proteins which females selects which to put in their ovipore
In presence of males
They’ll make less spermatophores to modify number of sperm and attractiveness
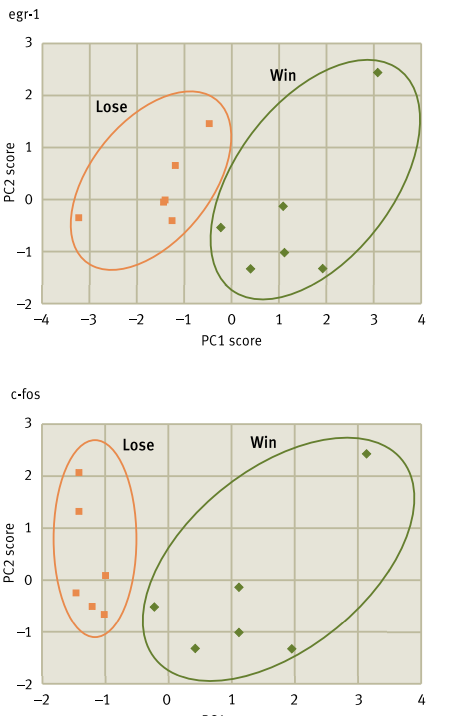
What’s the main message?
egr 1 and c fos gene expression hgiher in associated with reproduction after seeing preferred male win, and highest in areas of brain associated wwith anxiety after watching male lose
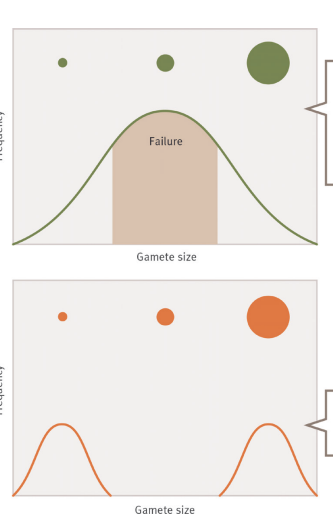
What’s the main message?
Natural selection favours large and small gamates