HBS 1.2 test
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
tendons
Flexible, but inelastic cord of strong fibrous collagen tissue attached a muscle to a bone.
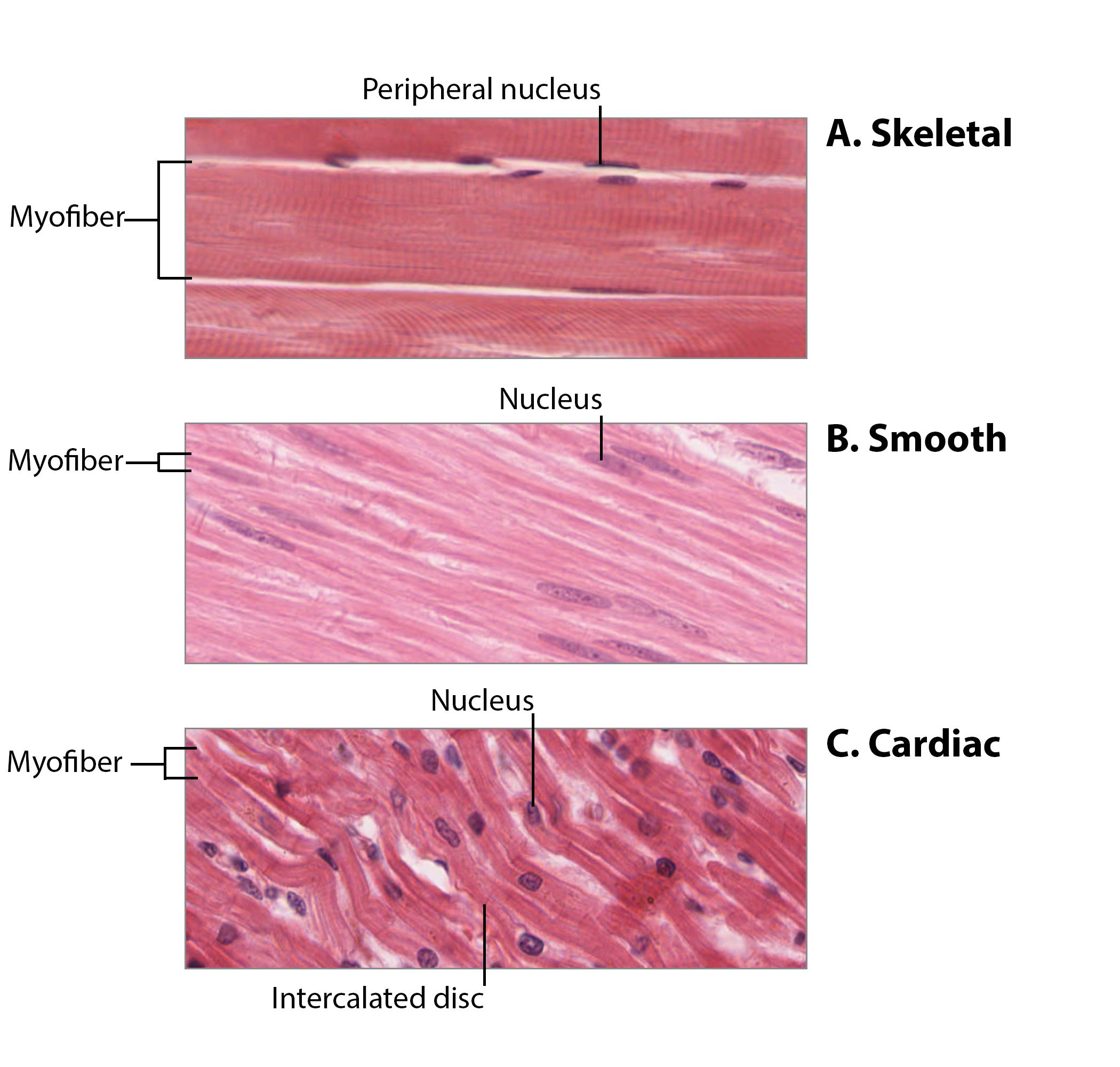
skeletal muscle
striated, voluntary, limbs, movement
smooth muscle
no striated, no voluntary, intestines, digestiong
cardiac muscle
striated, no voluntary, chest, breathing
involuntary muscle contraction
moves without you willing it too move
skeletal, cardiac, smooth pic
just look at em!
requirements for muscle contraction
ATP & salt
when the muscle fibers “shorten” what happens?
the muscle contracts
step 1
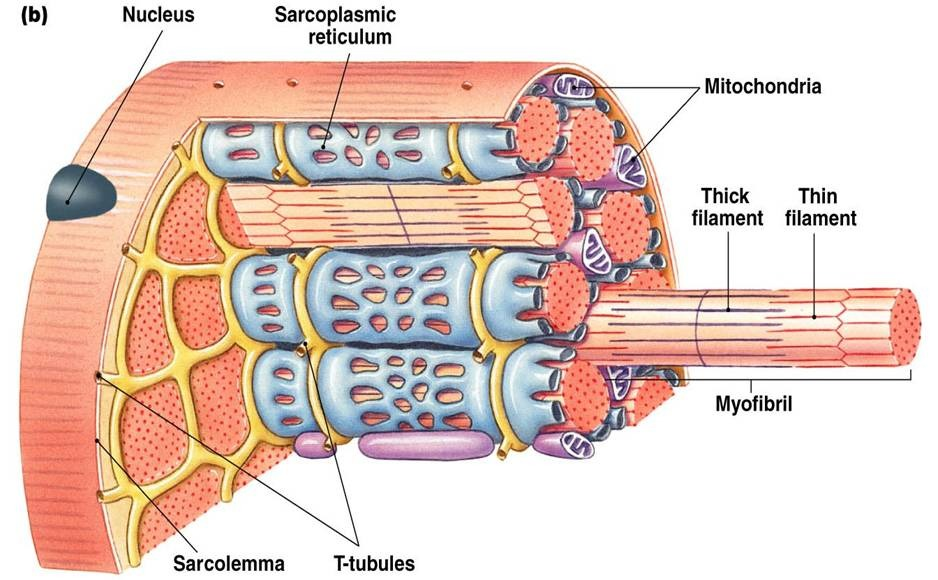
motor neuron fires an action potential. neurotransmitter acetylcholine is released at muscular junction. Acetylcholine binds to receptors on muscle fibers sarcolemma, causing depolarization.
step 2
depolarization spreads along sarcolemma. travels into the fiber via T.tubules. This triggers the gated calcium channels on the SR to open.
step 3
Ca2+ stored in the SR flood into the sarcoplasm.
step 4
Actin’s myosin binding sites are blocked by tropomyosin protein which troponin complex holds in place. calcium ions bind to the troponin which causes a conformational change and exposes the binding sites.
step 5
myosin heads powered through ATP hydrolysis bind too actin and pulls the thin filament towards the center of the sarcomere. This pulls the z discs closer together and the sarcomere shortens.
why do muscle cramps happen?
calcium stays in the muscle cell and there is not enough ATP for the head to deattach
why do muscles contract involuntarily to maintain homeostasis?
contractions release heat helping body maintain homeostasis
Your friend tried to convince you that the only reason to make sure you get enough calcium is so you can build strong bones. Can you offer them another reason?
calcium is also needed for muscle contraction because it binds to troponin and exposes binding sites
Explain how it is that actin and myosin in the sarcomere never actually shorten and yet the muscle as a whole does.
actin and myosin dont shorten but slide past eachother which shortens the sarcomere
muscle fiber diagram!!
know them!
do muscles work alone?
An abundant supply of blood vessels brings nutrients and oxygen to muscles while also removing wastes.
Nerves control when muscles contract and how strong those contractions are.
muscle rules
muscles always cross at least one joint
muscles have origin and insertion. origin is not moveable and insertion is moveable
muscles always pull in the direction of the fibers
muscles work in opposing fibers
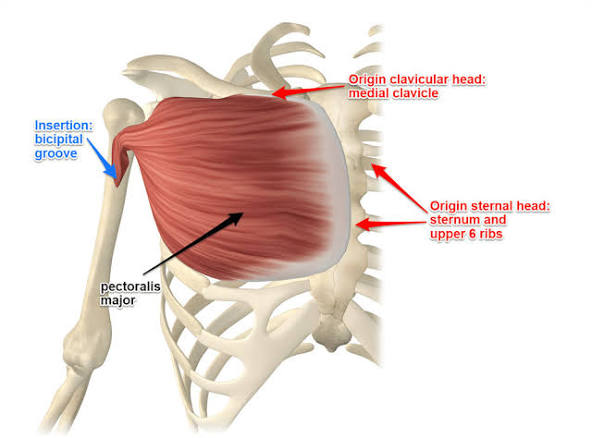
pectoralis major
origin = sternals
insertion = proximal to humerus
moves arm rotating medially, adduction
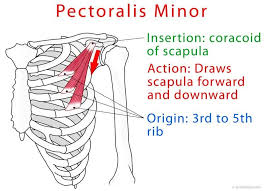
pectoralis minor
origin = ribs
insertion = scapular
pulls scapula forward and down
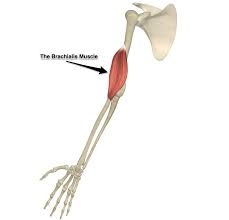
brachialis
origin = anterior brachial
insertion = ulnar side of antecubital
flexes forearm at elbow
intercostals
elevate and depress ribs for breathing
left psoas major
origin = vertebrae
insetion = trochanter of femur
action = hip flexion
activities = climbing/marching
left gluteus medius
origin = gluteal lines
insertion = trochanter of femur
action - abduction of hip
neither flexor extensor
activities: walking
what happens after cast removal?
muscle fibers shrink because they’re not being stimulated to contract or support weight (muscle atrophy)