Fullerenes
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
What are Fullerenes
Fullerenes are molecules of carbon atoms with hollow shapes.
How are fullerenes arranged
The structure of fullerenes is based on hexagonal rings of carbon atoms but they may also contain rings with five or seven carbon atoms.
What was the first fullerene to be discovered
Buckminsterfullerene(c60)
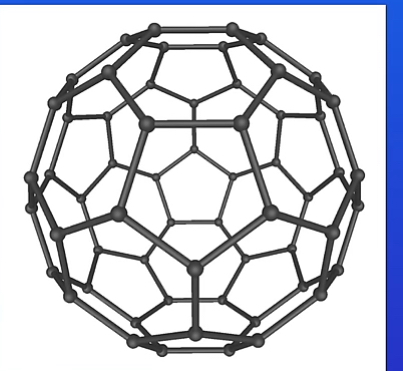
How much carbon atoms does Buckminsterfullerene contain
60
How is Buckminsterfullerene arranged
In a hollow sphere.
-The carbon atoms form rings with either 6 carbon atoms or with five
What are the uses of Fullerenes
-Used to deliver drugs such as pharmaceuticals into the body as they can cage other molecules which is then trapped inside
-Great industrial catalyst as it has a huge surface area
-Can be used as lubricants for machines to reduce direction between moving sorts
What can Fullerenes form
Carbon nanotubes
What are Carbon Nanotubes
Carbon nanotubes are cylindrical fullerenes with very high length to diameter ratios.
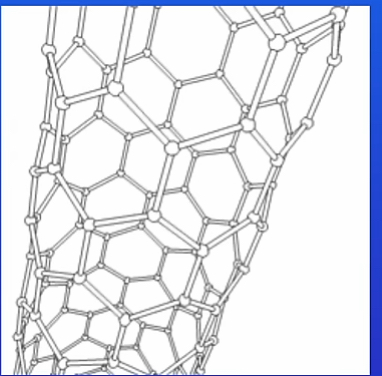
What are the properties of Carbon Nanotubes
-High tensile strength which means that we can apply a great deal of strengthens force to a carbon nanotube before it breaks
-Good conductor of electricity and heat as they have delocalised electrons
What are the uses of Carbon nanotubes
To reinforce materials without adding weight for example tennis rackets
-Used for electronics
What is Nanotechnology
Technology that uses very small particles such as nanotubes