8a- Nucleic Acids
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
What are DNA + RNA?
important information-carrying molecules
both are polymers of the biological molecule group called nucleic acids (phosphate group in the nucleus)
What is the difference between DNA + RNA?
DNA:
stores genetic information
RNA:
transfers genetic information from DNA to ribosomes
What are DNA + RNA polymers of?
nucleotides
What is a nucleotide made up of?
a pentose sugar
a nitrogen-containing organic base
a phosphate group (compromising a phosphate ion)
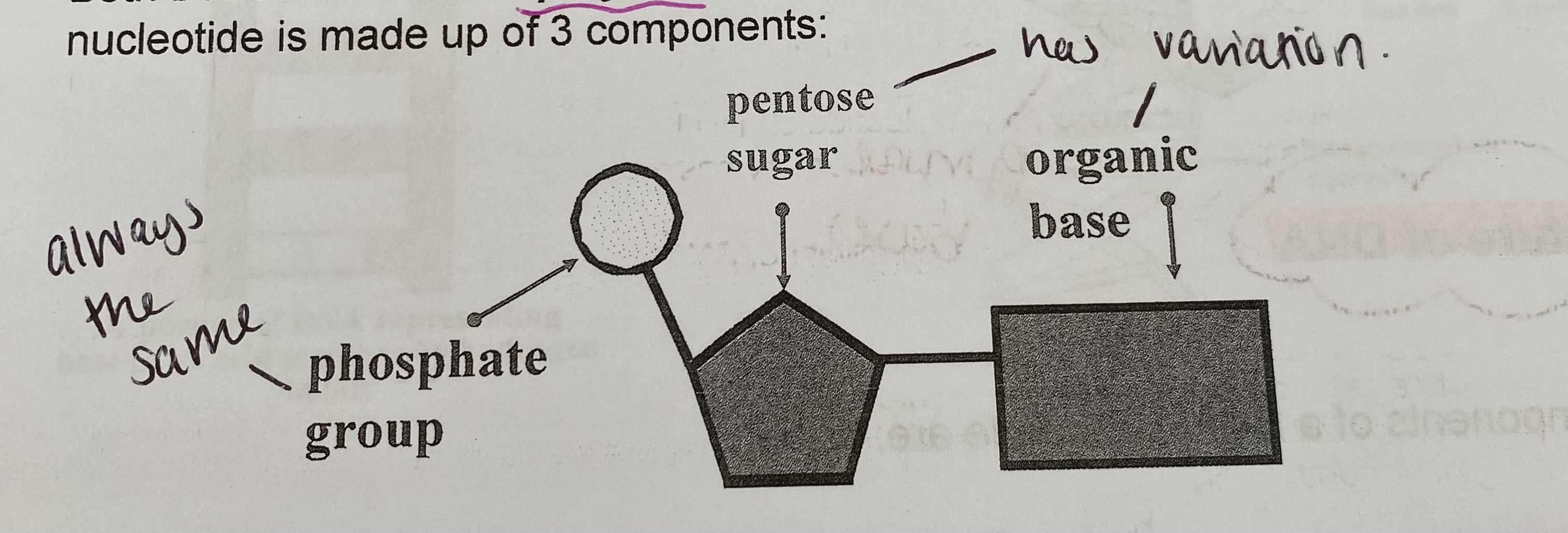
Why is a pentose sugar so called?
contains 5 carbons
What is a nucleotide?
monomers that join to form polynucleotide strands
chain held together because phosphate group is linked to the sugar of the next nucleotide by strong covalent bonds
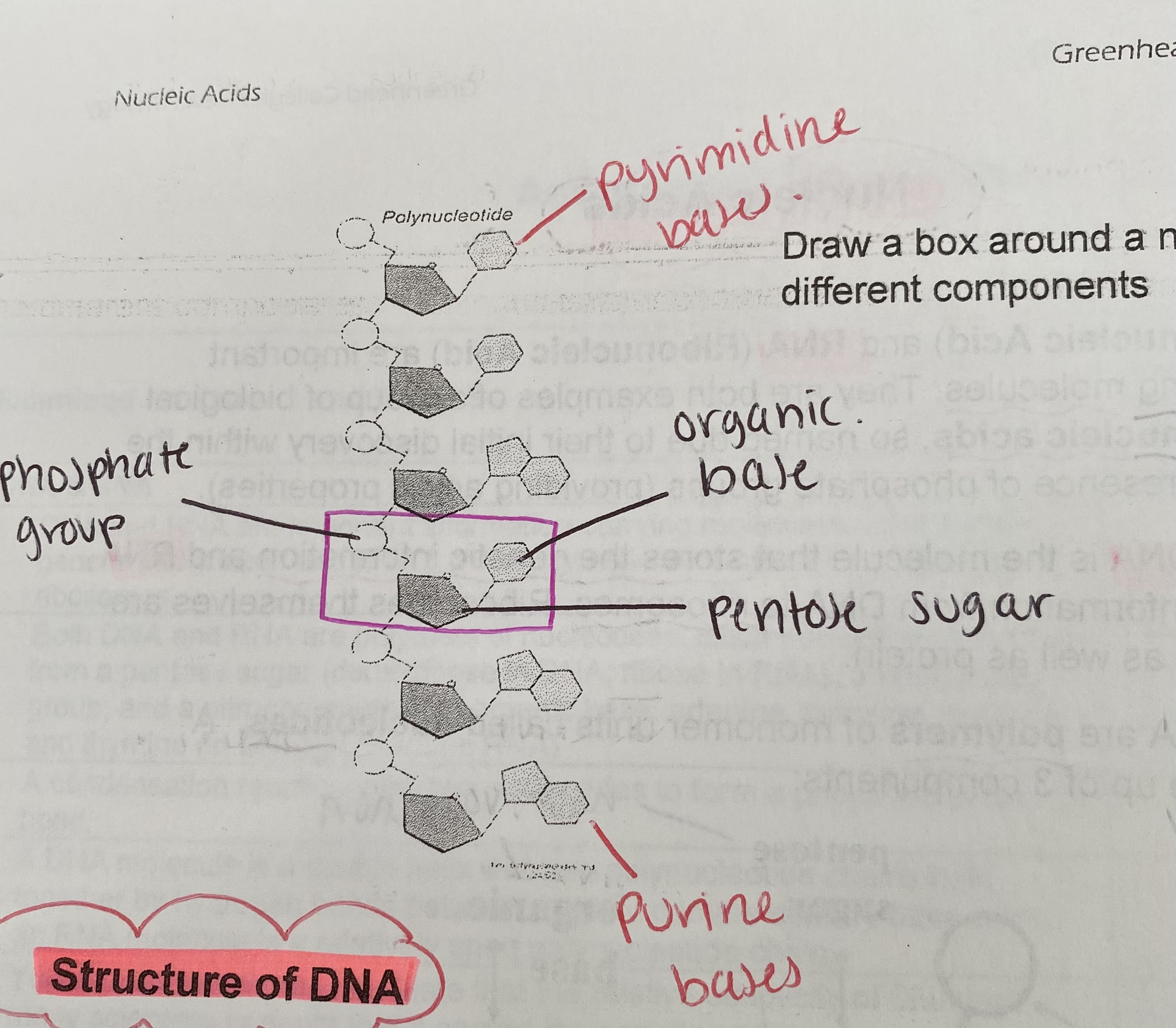
What bond forms in a nucleotide chain?
phosphodiester bonds
What is the sugar-phosphate backbone?
the phosphate group and sugar are identical throughout the chain
What type of reaction is used to join the nucleotides together?
condensation
What is the only way in which 1 polynucleotide chain can differ from another?
the sequence of nucleotides/ bases in the polynucleotide chain
What is the pentose sugar of a DNA nucleotide called?
deoxyribose
What are the components of a DNA nucleotide?
deoxyribose
a nitrogen-containing organic base
a phosphate group
What are the 4 bases in DNA nucleotides?
adenine
guanine
cytosine
thymine
What are purines?
adenine and guanine
What are pyrimidines?
thymine and cytosine
What is DNA?
two polynucleotide chains/ strands that twist to form a double helix
> the bases of each strand are held together by hydrogen bonding
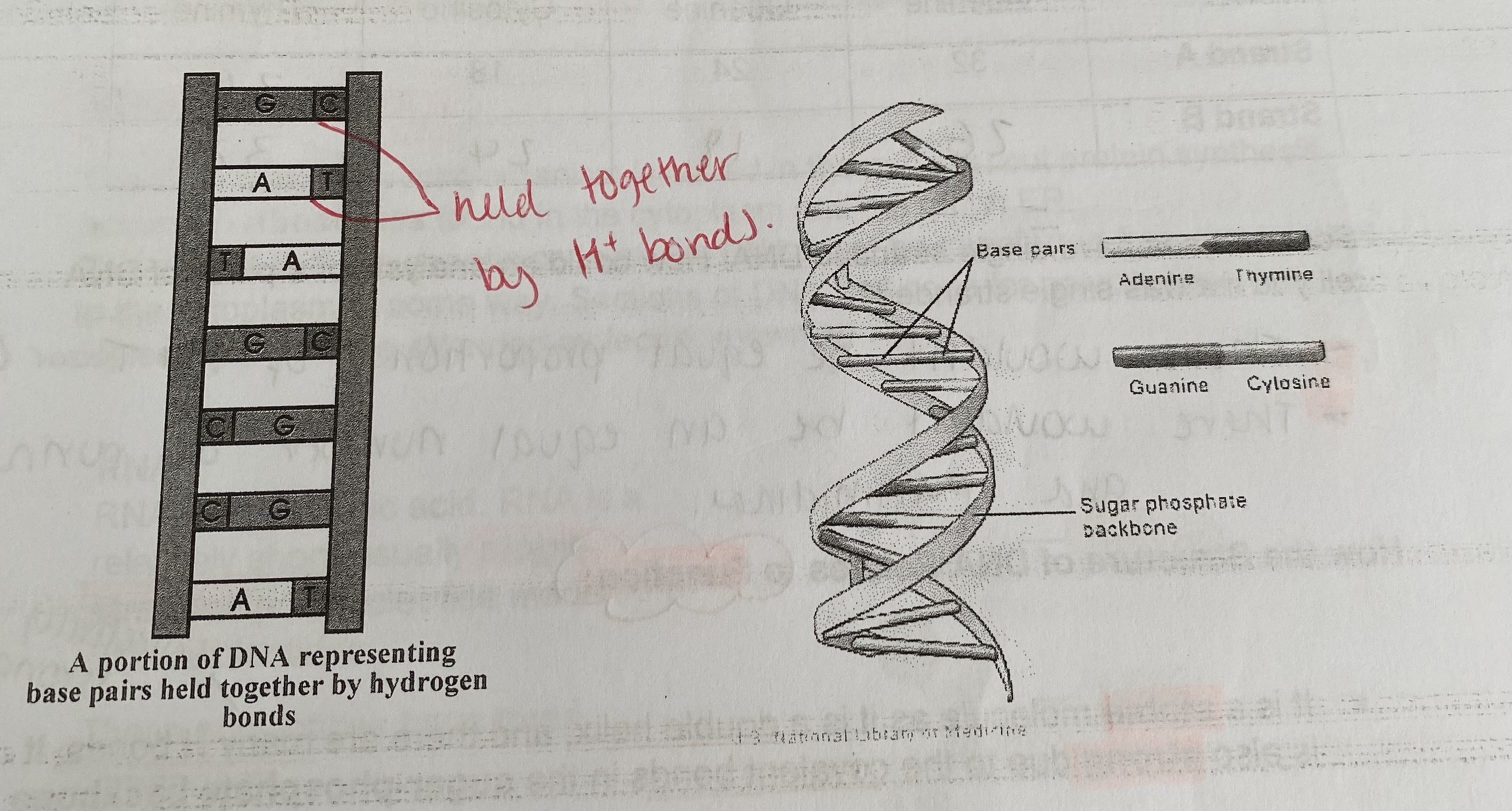
Which bases are always paired together?
Adenine + Thymine
Cytosine + Guanine
What term is used to describe the pairing bases?
complementary base pairs
How many bonds does adenine form with thymine?
2
How many bonds does cytosine form with guanine?
3
Some viruses have single stranded DNA. How could an analysis of a piece of DNA tell you if it was single stranded?
there wouldn’t be equal proportions of A+T or G+C
there wouldn’t be an equal number of purines and pyrimidines
How does the structure of DNA relate to its function?
Stable as it is a double helix and there are many H bonds
Strong due to covalent bonds in the sugar-phosphate backbone
Can replicate due to complementary base pairing
Can separate due to weak H bonds
Compact
Contain large amounts of coded information as the chain is long
Allows DNA to fit inside nucleus as it has a double helix shape
Precise genetic code determined by sequence of bases which controls protein synthesis
How many different bases are there in DNA?
4
How many different amino acids are there in proteins?
20
What is the role of DNA?
contains the genetic code
codes for production of proteins
provides diversity and variety
What is the structure of RNA?
relatively short, single stranded polynucleotide
What is the pentose sugar called in RNA?
ribose
What are the components of RNA nucleotides?
a ribose
a nitrogen-containing organic base
a phosphate group
What are the bases in RNA?
adenine
guanine
cytosine
uracil
Which base is not found in RNA?
thymine
Is uracil a purine or pyrimidine base?
pyrimidine
What is DNA replication?
new cells have the same genetic code as the parent cells
cells divide and their DNA is copied
What is the process called for DNA replication?
semi-conservative replication
Why is DNA replication termed as semi-conservative?
2 strands of the DNA molecule are separated
Both strands of the DNA molecule act as a template for the formation of a new complementary strand
Following replication each new DNA molecule consists of one original (old) strand and one ‘new’ strand
Describe semi-conservative replication
Enzyme called DNA helicase is required to unwind the DNA double helix by breaking weak hydrogen bonds between complementary bases in the polynucleotide strands. This separates the strands
Each exposed strand now acts as a template for the formation of a new strand
New DNA nucleotides are attracted to exposed bases on the template strands and attach by complementary base pairing. New hydrogen bonds form
Ezyme DNA polymerase joins the new nucleotides together to form a new polynucleotide strand. Phosphodiester bonds are formed during condensation reactions

What is some evidence for semi-conservative replication?
Experiments by Meselson and Stahl in 1958
used bacteria E.coli grown in a medium containing heavy isotope (15N)
then transferred to a medium containing normal light isotope of nitrogen (14N) and allowed to grow
After periods of time, samples were taken and the DNA was extracted and centrifuged
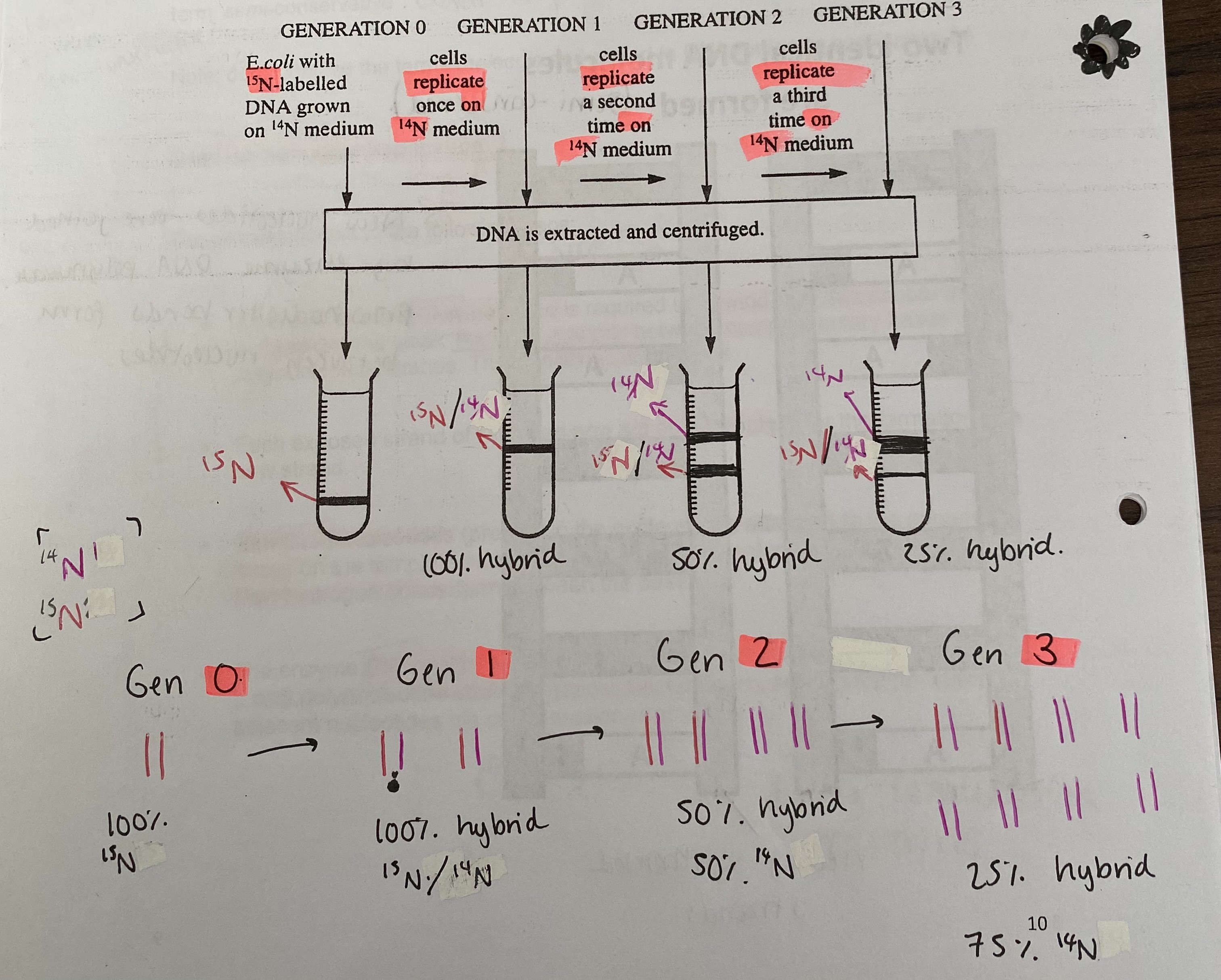
Summarise the generations from the E.coli experiment
Generation 0= DNA all heavy
Generation 1= 2 hybrid molecules of DNA
Generation 2= 2 hybrid molecules and 2 all new light DNA (50% hybrid, 50% light)
Generation 3= 2 hybrid molecules and 6 all new light DNA (25% hybrid, 75% light)
What is the full name of ATP?
Adenosine triphosphate
What is ATP?
the immediate source of energy
What do ATP molecules consist of?
the organic base adenine
ribose sugar
3 phosphate groups (ions)
W
What does ATP look like?
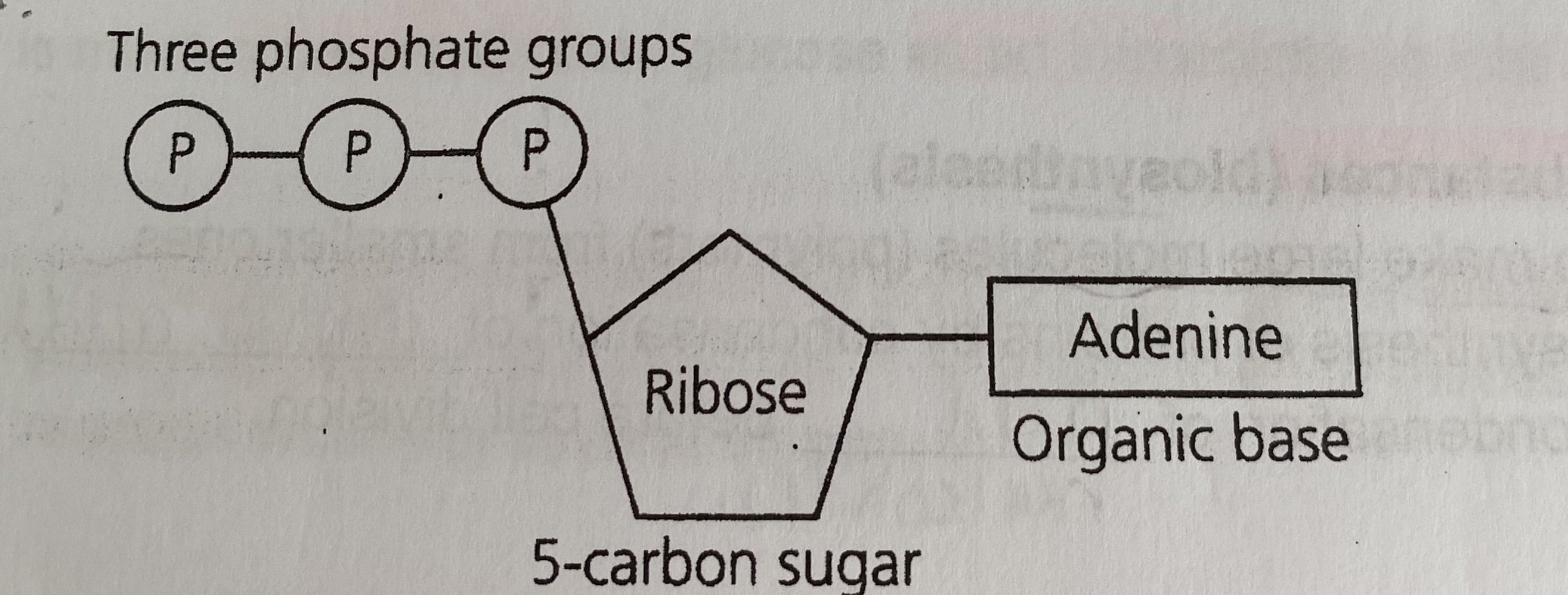
Describe the synthesis of ATP
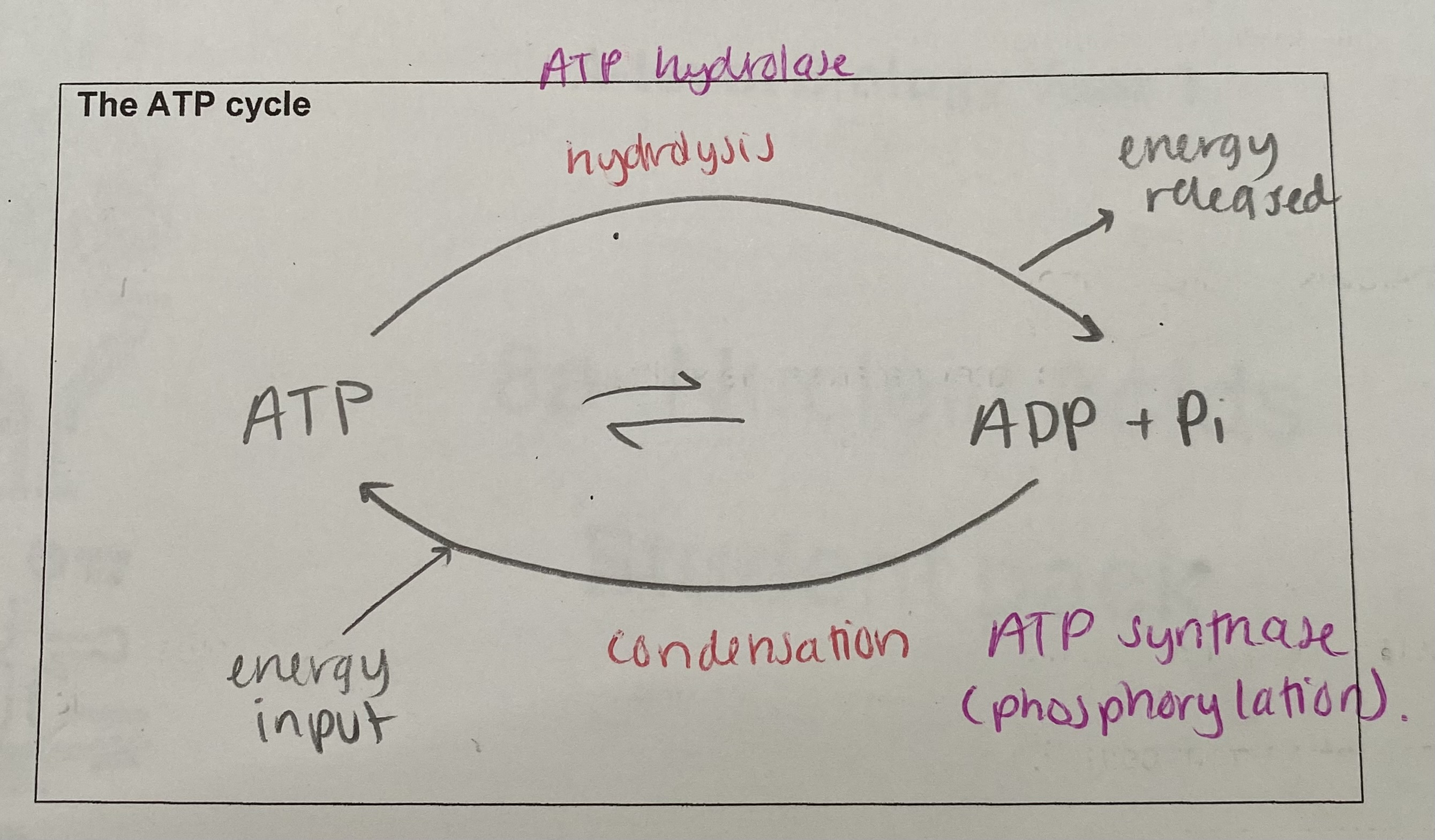
synthesized by the addition of ADP to an inorganic phosphate
condensation reaction catalysed by ATP synthase
requires input of energy from a metabolic process and occurs during respiration
What is phosphorylation?
the addition of a phosphate molecule
Describe the breakdown of ATP
the covalent bond linking the phosphate groups is unstable and easily broken by the enzyme ATP hydrolase in a hydrolysis reaction
this occurs when an inorganic phosphate group is removed
energy is released and ATP becomes ADP
What is the role of ATP?
active transport
exocytosis
synthesis of substances (biosynthesis)
movement
activation of other molecules
Describe how ATP is used for active transport
energy required to move substances against a conc gradient using carrier proteins
The protein pumps are also ATP hydrolase enzymes catalyse the splitting of ATP to ADP + Pi and use the energy released to change shape and pump the molecule
Describe how ATP is used for exocytosis
energy required to make vesicles prior to secretion from cells
energy required for the reverse process (endocytosis) used to bring large molecules into cells
Describe how ATP is used for synthesis of substances
energy required to make large molecules from smaller ones in condensation reactions
Describe how ATP is used for movement
energy required for muscle contraction
Describe how ATP is used for activation of other molecules
transfers it phosphate group to other molecules, phosphorylating them and making them more reactive
reduce the activation
Suggest how you can make a molecule more reactive
add a phosphate group to phosphorylate and make them more reactive
Describe ATP as an energy source
not a good long term energy store due to instability of its phosphate bonds
cells maintain only a few seconds supply
ATP is an immediate energy source as ATP is rapidly reformed
What is the ATP cycle?
Why is ATP more useful than glucose as an immediate source of energy?
breakdown is a single reaction making energy immediately available. Breakdown of glucose is a complex reaction
ATP is soluble and easily moved around but cannot pass through cell membranes
breakdown of ATP releases a small amount of energy whereas glucose releases more energy than required so is inefficient