Sexually Transmitted Diseases
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
syphilis is caused by what?
Treponema pallidum, a spirochete
Treatment of women before week __ of pregnancy prevents lesions of congenital syphilis, but not reliable after then
16
syphilis was first identified in 1905 and used to be treated with…?
arsenic and mercury (heavy metals!)
what are the stages of syphilis?
primary (localized)
Secondary (systemic)
Latent (asymptomatic)
Tertiary (long-term inflammation of the CNS, aorta, brain, skin, spine, eye...).
Congenital (systemic, chronic inflammation)
those with syphilis often have…?
HIV, or other STDs
what are the symptoms of primary syphilis?
negative serological test
chancres (sores/ulcers)
what are the symptoms of secondary syphilis?
systemic disease (flu-like symptoms)
macules and papules (palms, soles, face)
high bacteremia, contagious
positive serological tests
what are the sites of principal manifestation in secondary syphilis ?
skin and mucous membranes
what are the symptoms of latent (early, not primary or secondary) syphilis?
clinically well, no signs of disease
recovered from secondary disease
serological tests are positive
what are the symptoms of tertiary syphilis?
gummas, inflammation (CNS, aorta, brain, skin, spine, eye)
positive serolgoical tests
t/f: Humans are only known hosts of syphilis.
true
syphilis transmission is virtually always by …?
direct contact with infectious lesions (highest incidence in 20-30 year old sexually active adults)
Syphilis Rates in US plummeted after…?
penicillin introduction in 1940/50s
One bump up with HIV; recent increase over last dozen years
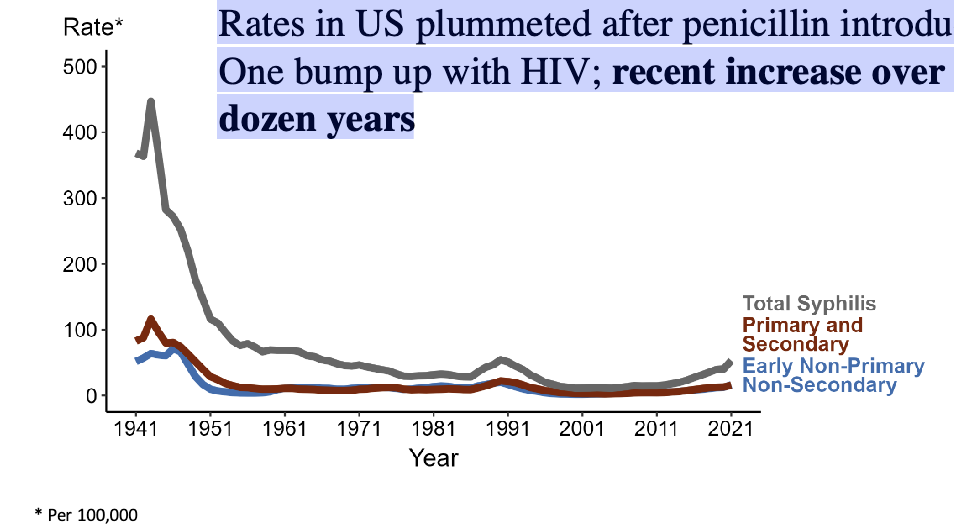
in the general population, what group is at a higher risk of contracting syphilis? syphilis also has a strong linkage to…?
MSM; HIV status
what is a chancre?
hard and indurated ulcerated lesion, highly infectious, PAINLESS in primary syphilis
in primary syphilis, there may be regional adenopathy (swelling of lymph nodes). what are the symptoms?
painless, rubbery
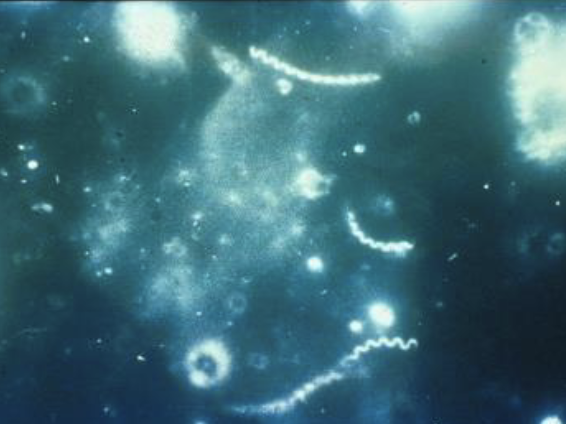
Treponema pallidum on Darkfield Microscopy
Light shines in from the side with a darkfield microscope. The light illuminates objects in the fluid sample.
Scrape the suspected chancre and put the juices on a slide -> it is teeming with spirochetes
Spirochetes twirl though the field of vision
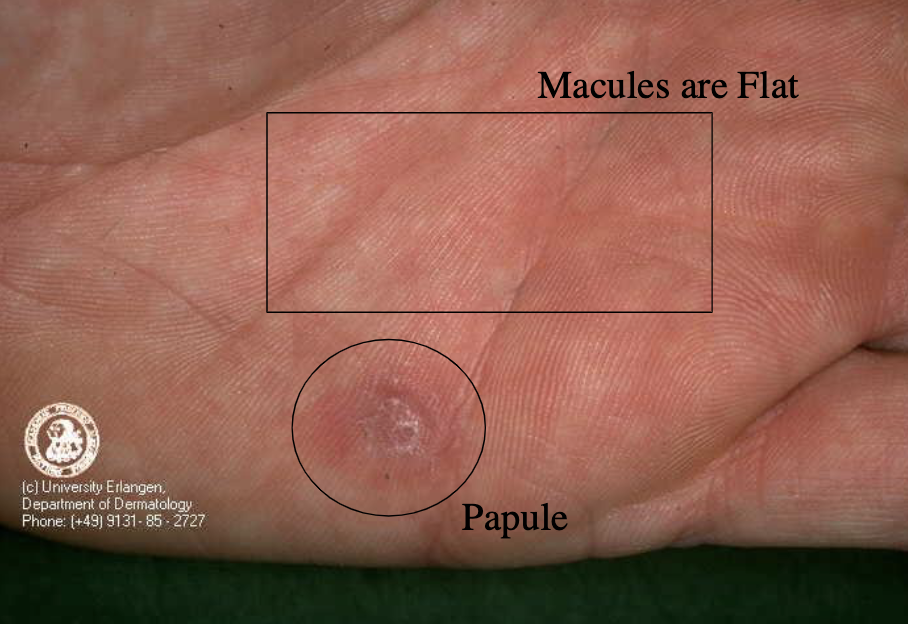
papules vs macules?
(secondary syphilis)
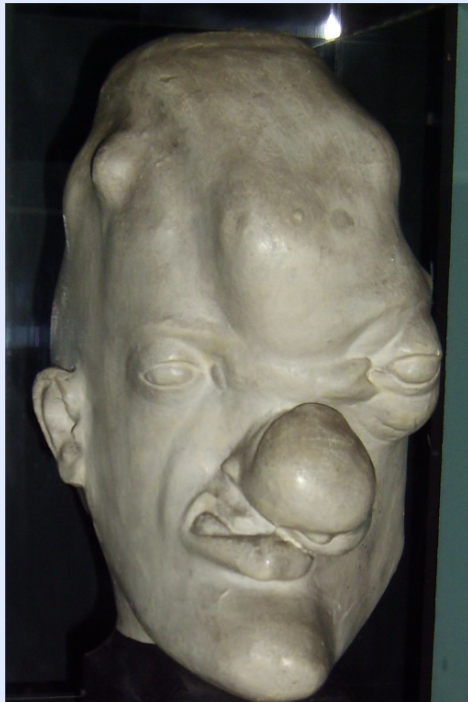
what are gummas?
nodular granulomatous lesions (soft, tumor-like masses) affecting skin/bone/live/anywhere (tertiary syphilis)
can take years to develop after infection 15-45

tertiary syphilis can cause damage to what systems?
cardiovascular
arteritis (vaculitis) results in thickening/hardening of vasa vasorum
neurosyphilis
dementia, general paresis
Most (93%) of missed opportunities to identify congenital syphilis are due to a l
lack of testing, inadequate or no treatment, or lack of recognition of positive tests
what is congenital syphilis?
If mother infective, child will be stillborn or present with fulminant syphilis
what are symptoms of congenital syphilis I?
rhinitis, sniffles followed by skin lesions
positive serologic testing
Osteochondritis (inflamed bone, cartilage).
Hepatosplenomegaly and adenopathy.
Immune-complex glomerulonephritis.
Death in first 2 years with pulmonary hemorrhages, bacterial infections, hepatitis
what is a key symptom of congenital syphilis II?
hutchinson’s teeth (notched, narrow edged incisors + mulberry molars)
rhagades lines (fissures, cracks, fine linear dermal scars especially around the mouth, and areas subjected to frequent movement)
saddle nose (deformed nasal cartilage)
which stages of syphilis can be cured with treatment?
primary or secondary
changes of tertiary syphilis (aortitis, neurological changes) are not reversible after treatment, except for gummas
how is secondary syphilis diagnosed?
T pallidum specific test
if positive → antibody titre test
how is primary syphilis diagnosed?
presenting signs/symptoms/history
darkfield exam of chancre exudate
seronegative (no positive blood test)
what are treponemal tests?
specific to syphilis
appear early after acute infection
detectable for life even after successful treatment
indicate CURRENT OR PAST infection
what are non-treponemal tests?
antibodies to a cardiolipin-cholesterol lecithin antigen (regain) that cross-react with syphilis antigens
quantitative titer
Falls in titer indicate a response (four-fold decrease)
are treponemal tests done first or non-treponemal?
treponemal test first to screen, then non-treponemal
what is the treatment for Primary, Secondary, early latent syphilis?
Penicillin
what is the regimen for Late latent, or tertiary, neurosyphilis without CSF changes?
IM penicillin
what is the regimen for syphilis during pregnancy?
Treat as appropriate for the stage of their disease. Treatment of women before16th week of pregnancy prevents lesions of congenital syphilis, but not reliable after then
what is the regimen for neurosyphilis/congenital syphilis?
IV penicillin
what treatments for syphilis are alternatives for penicillin allergies?
ceftriaxone, tetracyline, or doxycyline (but not well studied)
what is gonorrhea caused by?
Neisseria gonorrhoeae (Gram-negative diplococcus) which infects mucus-secreting epithelial vells
what are some complications that arise with gonorrhea?
pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) with abscesses,
subsequent ectopic pregnancies or sterility in women.
Can be lethal.
Gonorrheal pharyngitis;
disseminated bacteremia occurs with rash and arthritis
t/f: > 95% of men with gonorrhea are symptomatic; however, often no symptoms in women
true
A patient has, on exam, a large circular lesion on the side of the tongue that they were unaware of. It has slightly rolled edges, and
despite the erosion of the mucosa is essentially painless. The patient
is sexually active. Which of the following is the most likely
explanation for this scenario?
A. Oropharyngeal gonorrhea
B. Oropharyngeal syphilis
C. Oropharyngeal papillomavirus ("warts")
D. Tongue abscess
B. Oropharyngeal syphilis
The following statements about gonorrhea are correct EXCEPT one.
Which is the EXCEPTION?
A. Gonorrhea can be transmitted at the same time as HIV.
B. Gonorrhea can cause pharyngitis, proctitis, urethritis, and cervicitis.
C. Gonorrhea is always clinically evident (i.e., symptomatic).
D. Gonorrhea is a major cause of female sterility
C. Gonorrhea is always clinically evident (i.e., symptomatic).
The following statements regarding Chlamydiae are correct EXCEPT
one. Which is the EXCEPTION?
A. Chlamydiae infection can lead to blindness.
B. Chlamydiae can survive within phagosomes.
C. Chlamydiae can grow only inside a host cell because their small
genomes do not encode some essential enzymes.
D. The reticulate body is the form that can transit from one host cell to
another
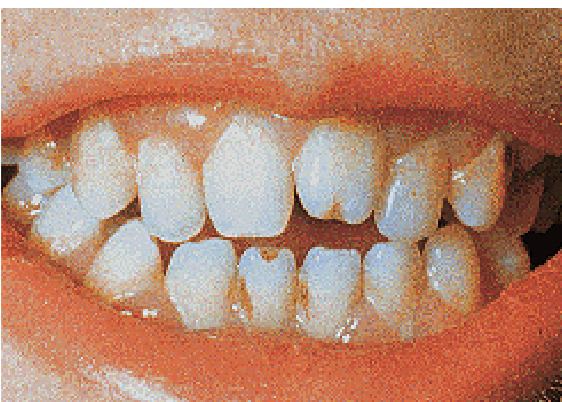
“Screwdriver” shaped incisors with notching (Hutchinson’s teeth)
congenital syphilis II
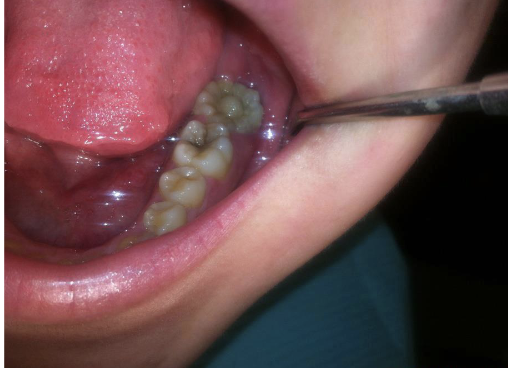
A “Mulberry” Molar (hutchinson’s teeth)
congenital syphilis II
what are symptoms of gonorrhea (men)?
epididymitis, urethritis
what are symptoms of gonorrhea (women)?
pelvic inflammatory disease with abscesses, subsequent ectopic pregnancies or sterility
both men and women with gonorrhea can have what symptom?
gonorrheal pharyngitis /tonsilitis/gingivitis
what is the 2nd most common cause after Group A Strep?
Gonorrheal pharyngitis
what is the most common cause of urethritis (men) and cervicitis (women)
in the US?
chlamydiae
chlamydiae can also cause what other complications?
trachoma, conjunctivitis, arthritis, pneumonia, and other respiratory tract infections
what are the 2 unique stages of chlamydiae?
reticulate body (active metabolism)
elementary body (transit form that goes from one cell to another)
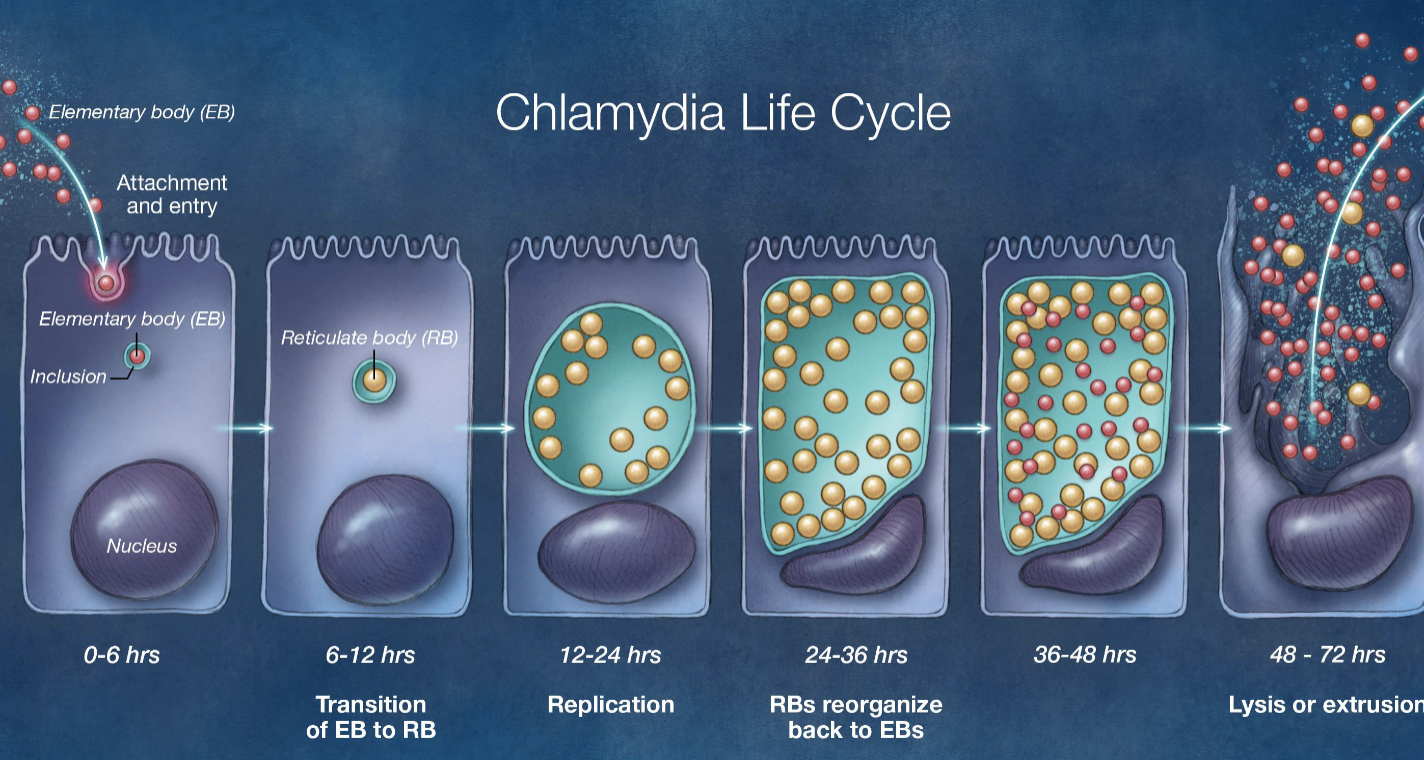
anitbiotics are only effective against which stage of chlamydiae?
reticulate
what is a key genomic characterisitcs of chlamydiae?
Strict intracellular bacteria with small genome
cannot generate ATP;
has no oxidative enzymes, flavoproteins or cytochromes;
can make own proteins
symptoms of human papilloma virus?
Cutaneous and anogenital warts, cervical cancer
juvenile onset recurrent respiratory papillomatosis (JORRP)
focal oral hyperplasia
what is the new recommended treatment for gonnorhea?
ceftriaxone 500 mg given IM
what are the 2 major STD syndromes of C. trachomatis in humans?
lymphogranuloma venereum (LGV)
urethritis
how is chalmydiae diagnosed?
direct fluorescent assays (nucleic acid amplification tests NAAT)
what are treatments for chlamydiae urethritis/cervicitis?
100 mg Doxycycline 2x daily (or azithromycin)
erythromycin (children or pregnant women)
what is respiratory papillomatosis?
death by suffocation – during vaginal delivery, infant’s oropharynx infected
what causes the majority of cervical, penile, vulvar, vaginal, anal, and oropharyngeal cancers?
HPV 16 and 18 (preventable via subunit vaccine)