Bio Principles Lab: Macromolecules
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Structural Molecules:
Cellulose, peptidoglycans, keratins etc.
Regulatory Molecules:
Enzymes, Hormones, etc.
Defense Molecules:
Antibodies, mucus etc.
Gene and Hereditary Molecules:
DNA, RNA
Nervous Control Molecules:
Neurotransmitters e.g. acetylcholine, dopamine, adrenaline
Monomer:
A molecule that is a building block for larger
molecules (polymers).
For example, an amino acid acts as the building blocks for proteins.
Polymer:
A large molecule made of repeating subunits
(monomers).
For example, a carbohydrate is a polymer that
is made of repeating monosaccharides.
Starch = (glucose + glucose)n
where n >100
Proteins = (amino acids + amino acids)n
where n>50
Classes of Macromolecules:
Carbohydrates
Proteins
Lipids
Nucleic acids
Carbohydrates
Are biological molecules made of carbon,
hydrogen, and oxygen in a ratio
C 2H O (one carbon atom to one water molecule)
Monosaccharides
-Just one sugar
Disaccharides
-Two sugar joined together
Polysaccharides;
-legions for they are many
Monosaccharides
(mono- = “one”)
(saccar- = “sugar”)
Simple sugars; typically contain 3-7 carbons
Classified based on # of carbons (triose, tetrose, hexose, etc.)
Ex. glucose, fructose, galactose, gulose
Aldose & Ketose
Aldose
Aldehyde Group; carbonyl C is the last one in the chain
Ketose
Ketone Group; carbonyl C is internal to the chain, so that other carbons are on both sides of it
Disaccharides
Are sugars formed by the combination of two monosaccharides
Ex. (glucose + fructose = sucrose), (galactose + glucose = lactose), (glucose + glucose = maltose)
Polysaccarides
Are long-chain polymers of monosaccharides connected by glycosidic bonds
Ex. starch, glycogen, cellulose
Benedict’s Test for Simple Sugars
Using Benedict’s Reagent
light blue (no reducing sugar)
turquoise blue (traceable)
green (low)
yellow (moderate)
red (high)
Test for Starch
Using iodine
blue-black (if starch is present)
Hydrolases
The group of enzymes that catalyze bond cleavages by reaction with water. The natural function of most hydrolases is digestive to break down nutrients into smaller units for digestion.
Breaking Glycosidic Bonds
Starch can be hydrolysed in the presence of an enzyme (boiled with dilute sulphuric acid)
Lipids
Composed mainly of carbon and hydrogen -CH- moieties
A broad group of organic compounds which include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins, monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others.
The functions of lipids include storing energy, signaling, and acting as structural components of cell membranes
They are insoluble in water
Soluble in organic solvents such as alcohol
Types of Lipids
Triglycerides: commonly known as fats.
Phospholipids: essential components of cell membranes
Sterols include compounds like cholesterol (chemical messengers)
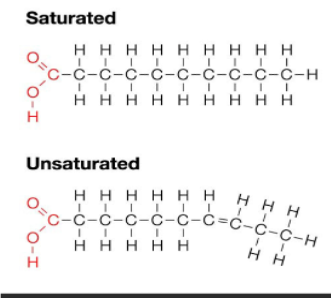
Fats: Saturated vs Unsaturated
Saturated:
Have no double bonds
“saturated” with hydrogens
Very linear
Ex. Animal Fats
Unsaturated:
Have double bonds
“kinks” in hydrocarbon chain
Monounsaturated (one double bond) or Polyunsaturated (more than one double bond)
Generally healthier
Ex. Plant Oils
Brown Paper Test for Lipids
Sudan IV Test (solution) mixed with ethanol
Proteins
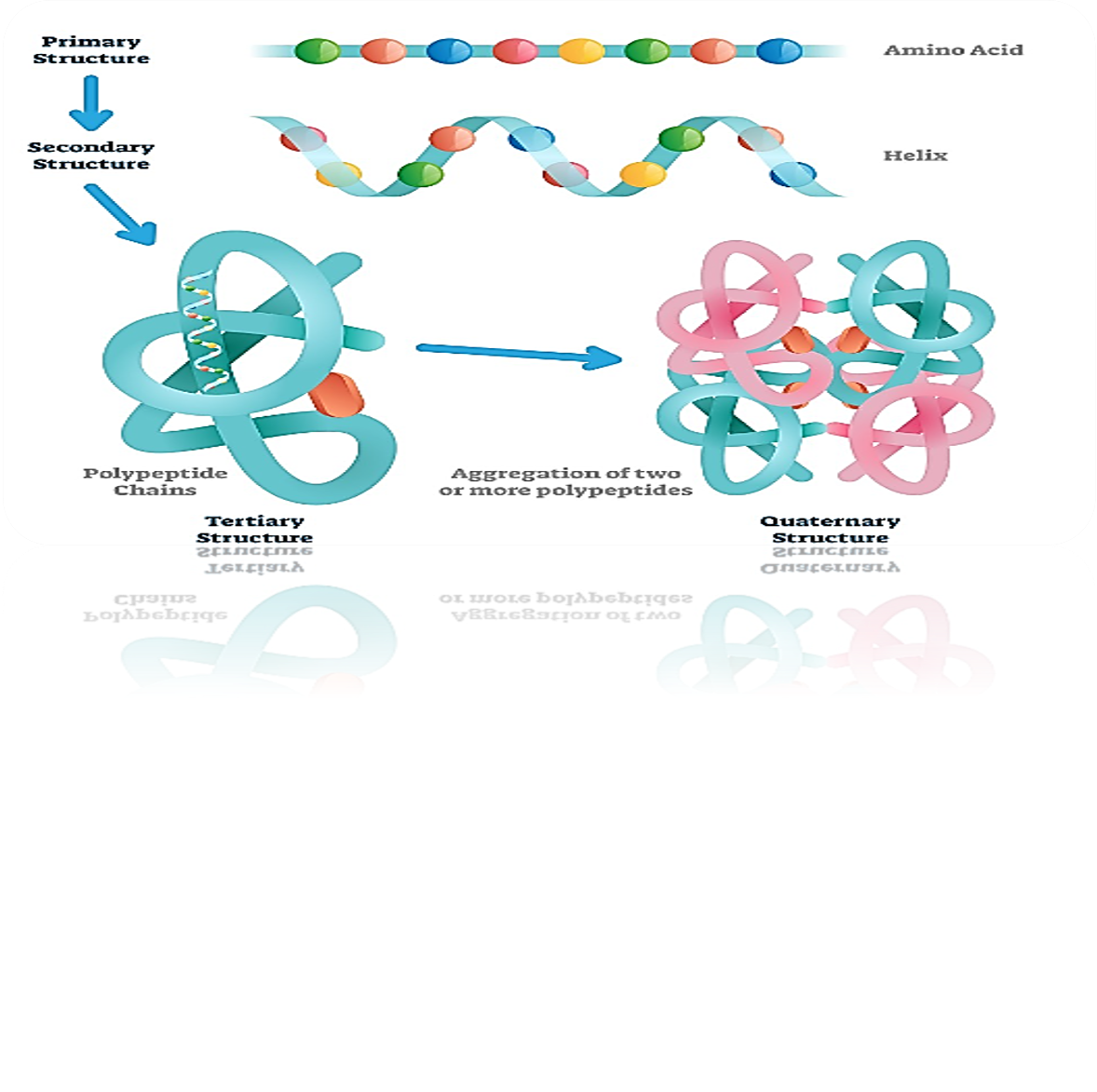
Amino acids + Peptide = Protein
Primary Structure
Secondary Structure
Tertiary Structure
Quaternary Structure
Amino acids
Amino Group + Hydrogen + Carboxyl Group
Classifications (3 examples)
Essential (Valine, Lysine, Histidine)
Conditionally Non-Essential (Glycine, Serine, Proline)
Non-Essential (Alanine, Cysteine, Glutamate)
Test for Proteins
Biuret Reagent reacts with protein source
Purple (proteins present)
Light Blue (proteins absent)
Mention a macromolecule that contains nitrogen as part of the chemical substituents of its subunit
Proteins
Mention one function of lipids
Moving and storing energy
What is a protein’s primary structure
This sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain is called the primary structure. This, in turn, determines the three-dimensional structure, including the shape of the active site.
What is the difference between a proteins tertiary structure and its quaternary structure
Aggregation of two or more polypeptides
The process of breaking down a poly-or-disaccharide into it’s constituent sugar is called
Hydrolysis
Mention one isomer of glucose
Fructose
True or false, glucose is a ketose sugar
Flase
True or false, fructose is a ketohexose sugar
True
Maltose is a disaccharide made up of ___________________ and _________________
Glucose-Glucose
What is the bond is joining two or more sugars together called
Glycosidic bond
What is the bond joining two or more amino acids together called
Peptide bonds