Animal Biology
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What does monophyletic mean?
all species can be traced back to a common ancestor
What are the common characteristics shared by all organisms within Animalia?
1. multicellular
2. heterotrophic
3. dominant diploid generation
4. motile at some point in their life
5. 2-3 layers of tissue derived from embryonic development
What are the 3 types of body symmetries found in Animalia?
1. radial
2. bilateral
3. asymmetric
Which body symmetry is described by an organism having a distinct top and bottom, but no distinct right and left sides?
radial

Which body symmetry is described by an organism have a right and left side divided by a sagittal plane?
bilateral
(Note: right and
left sides are
mirror images)

Which body symmetry can be described with these anatomical phrases: dorsal-top, ventral- bottom, anterior-towards the head, posterior-towards the tail?
bilateral
Which body symmetry is described by having no definite pattern?
asymmetric

What is the term that describes when bilateral organisms have a high concentration of nerve tissue located at the anterior end?
cephalization
(Note: more complex
animals have a higher
degree of cephalization)
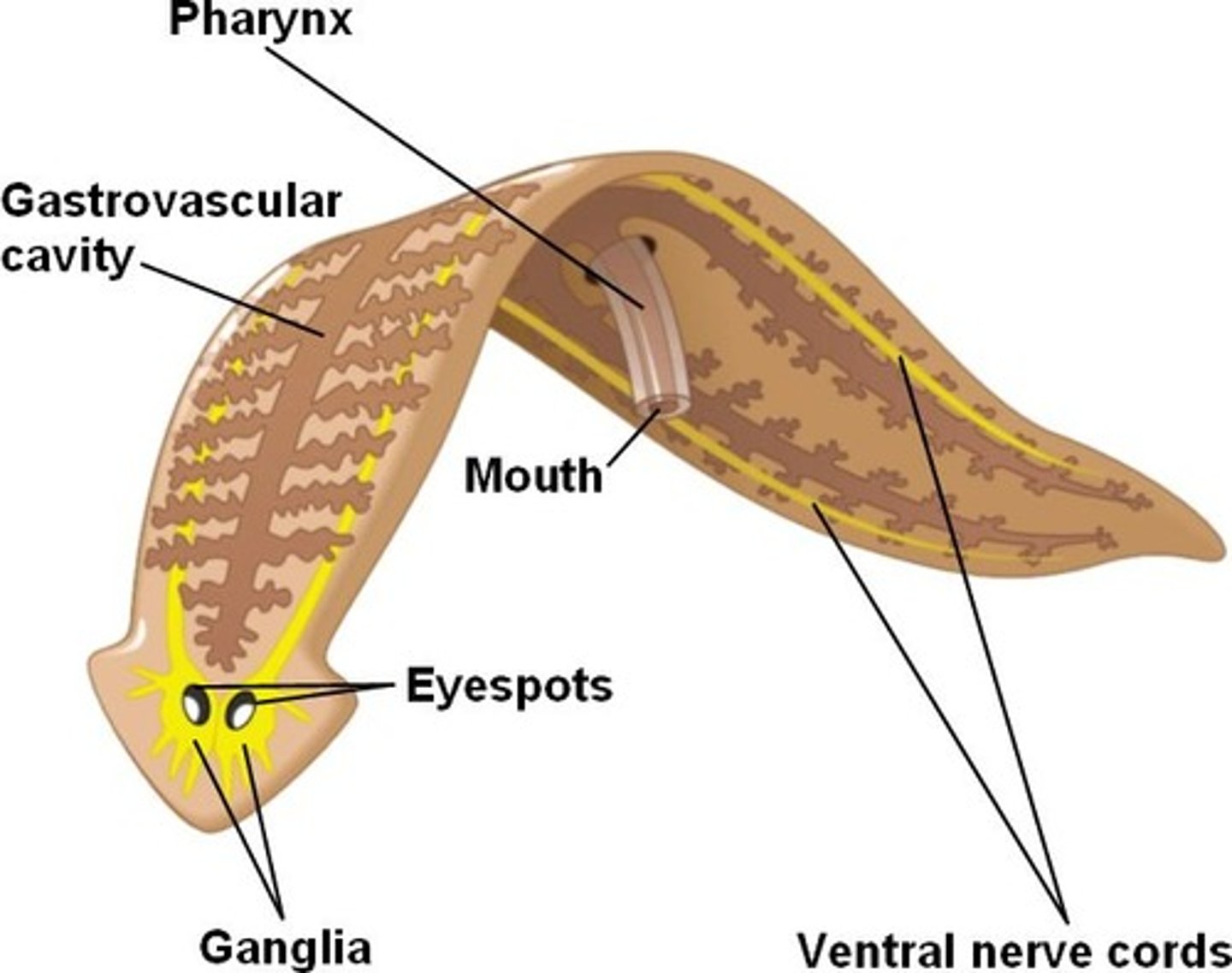
Which digestive system has one opening and is sac-like with limited processes?
gastrovascular cavity
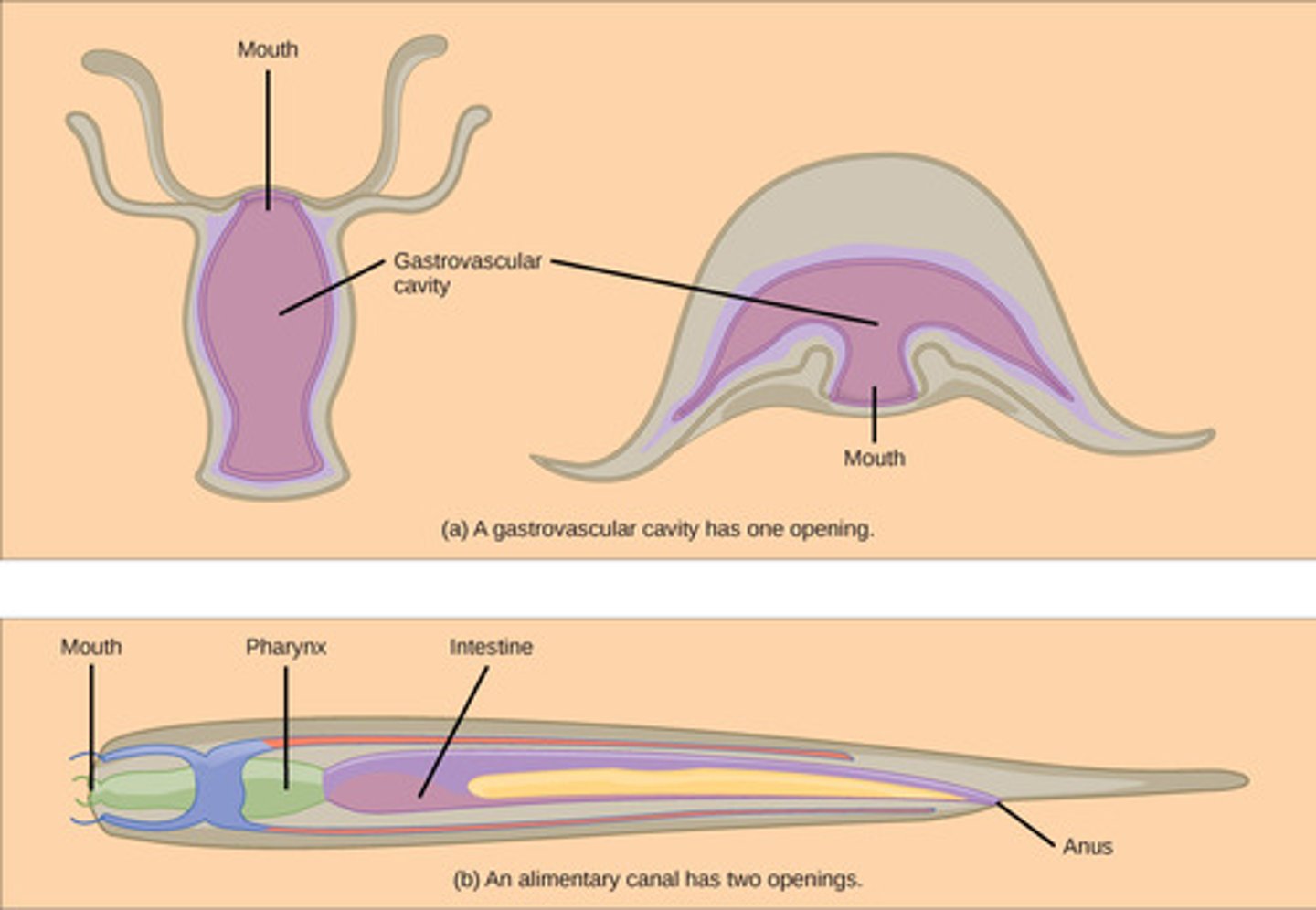
Which digestive system has two openings with specialized activities as food travels through it?
digestive tract
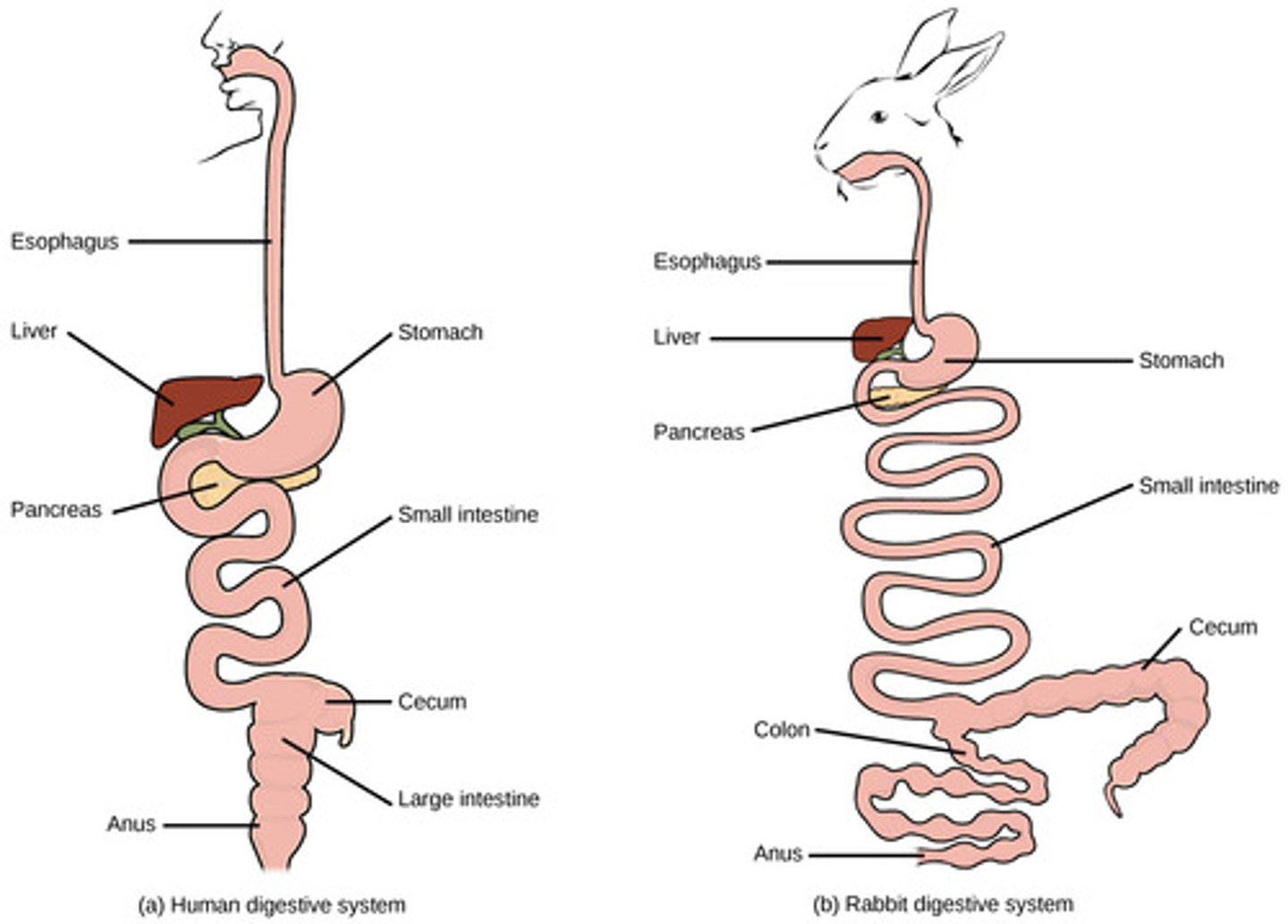
What are organisms with true tissues that are organized into germ layers?
eumetazoans
Which organisms have two embryonic cell layers?
diploblastic organisms
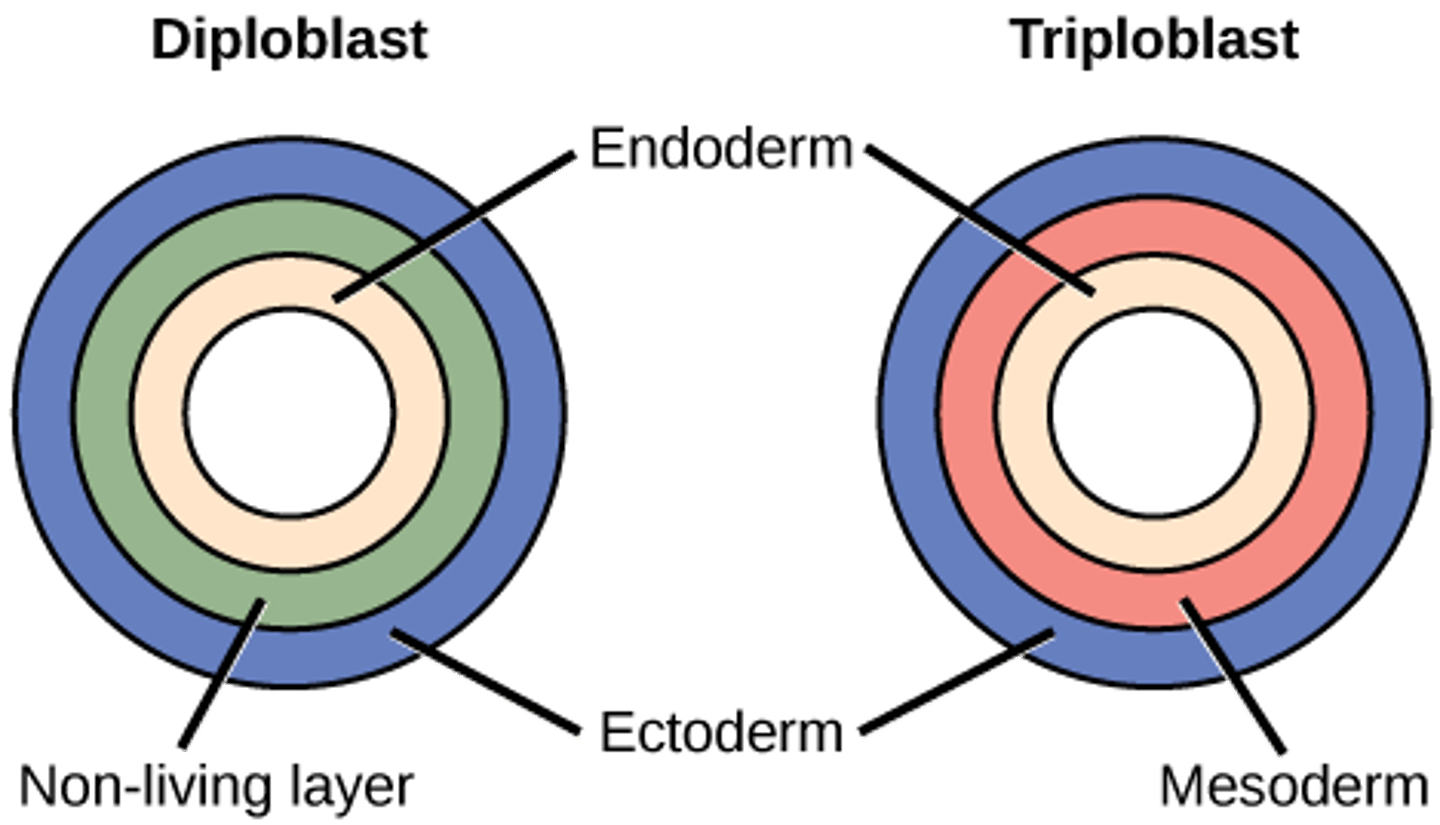
Which organisms have three embryonic cell layers?
triploblastic organisms
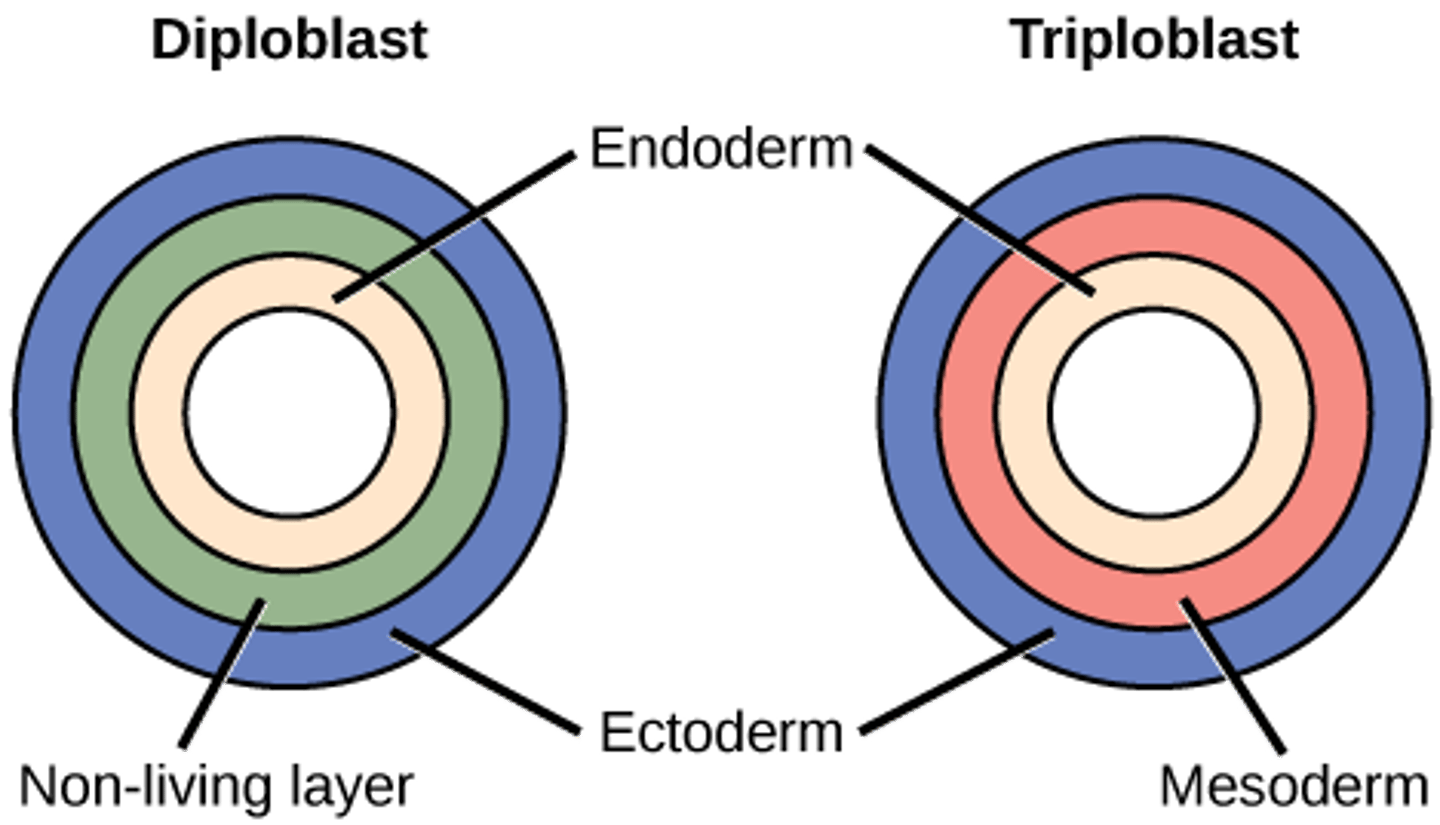
What are the 3 layers of a triploblastic organism?
1. ectoderm
2. mesoderm
3. endoderm
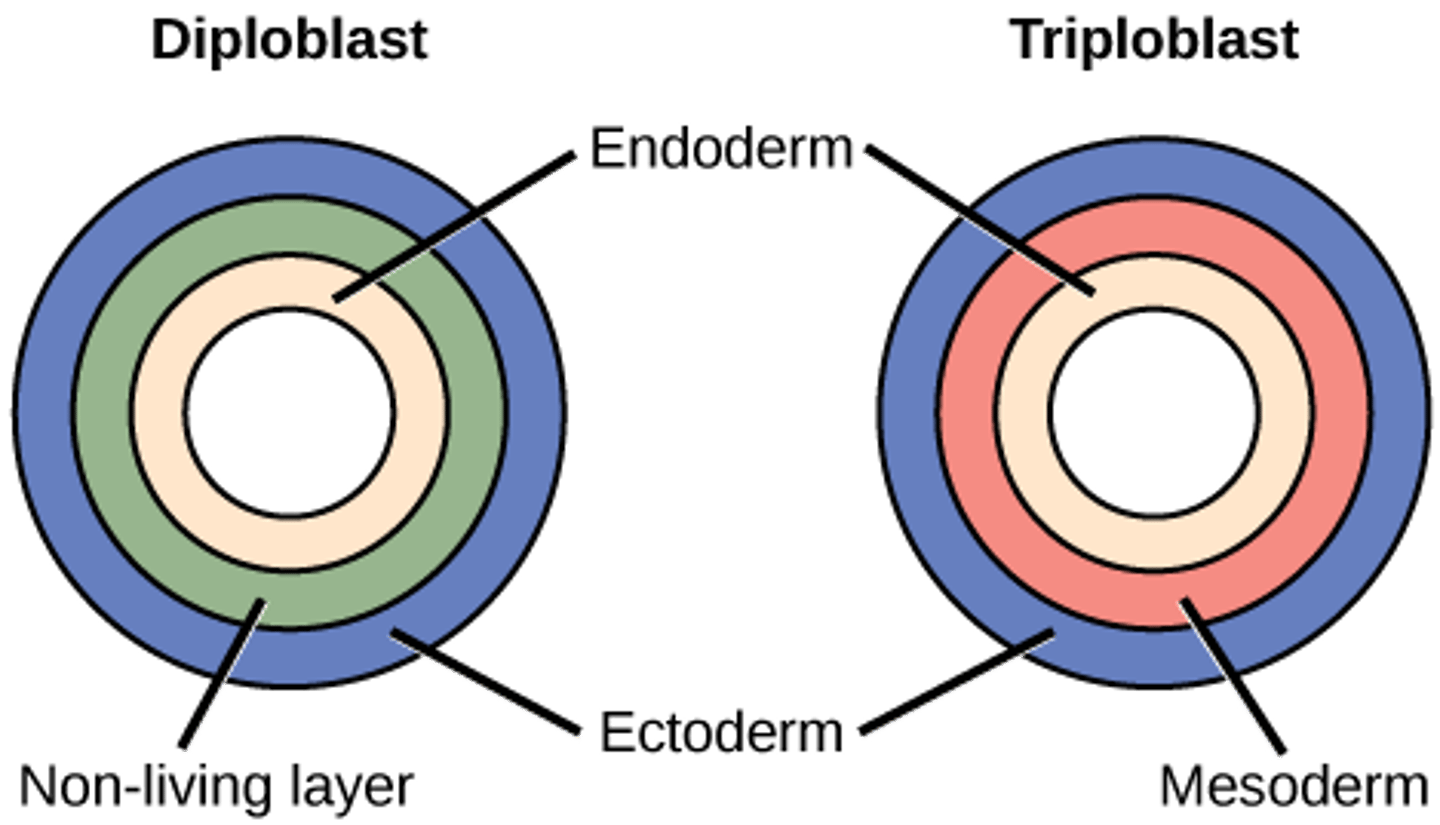
Which organisms do not have organized true tissues, and thus organs do not develop?
parazoans

What is a fluid-filled cavity that cushions the internal organs?
coelom
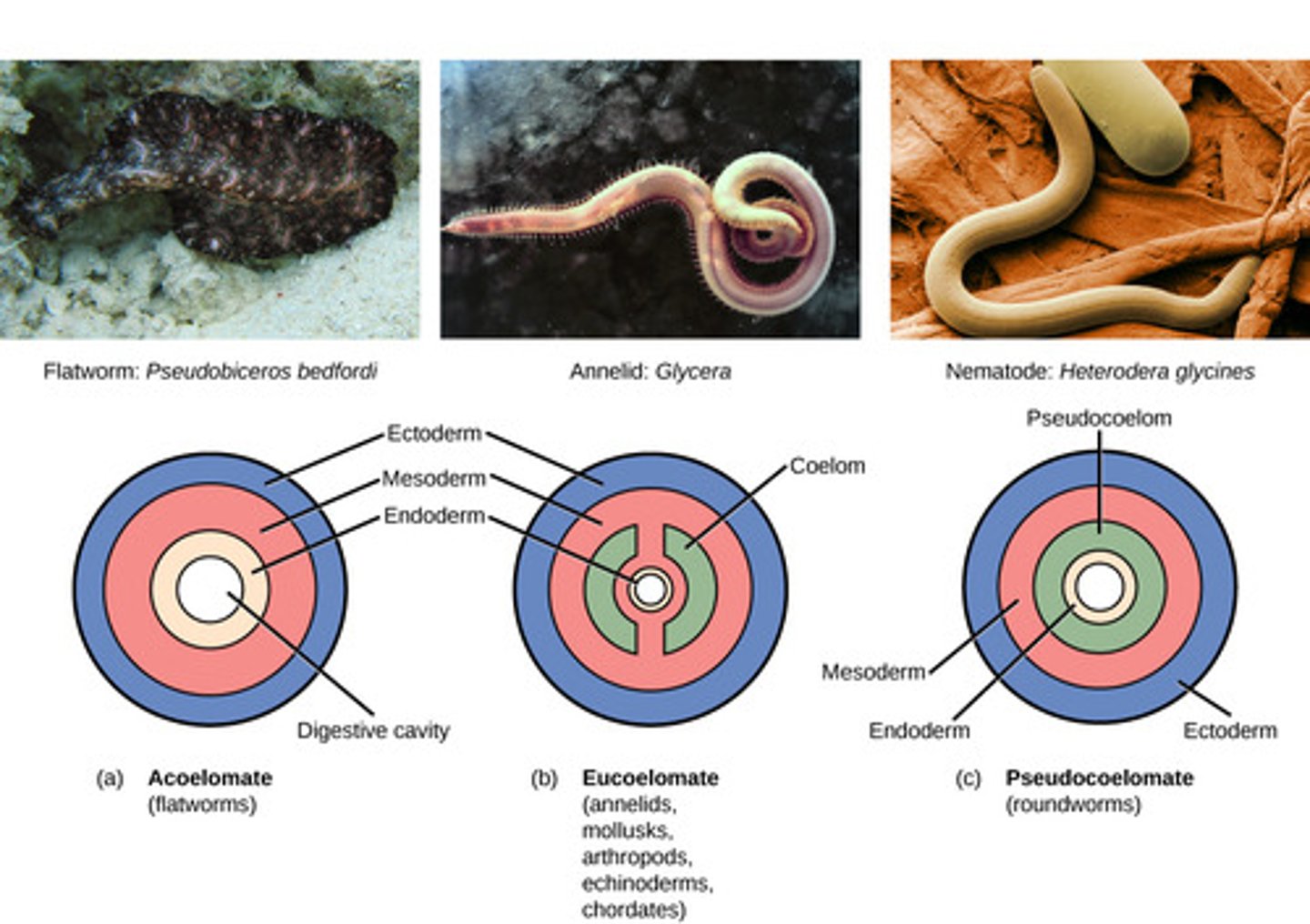
Which organisms lack a coelom?
acoelomates
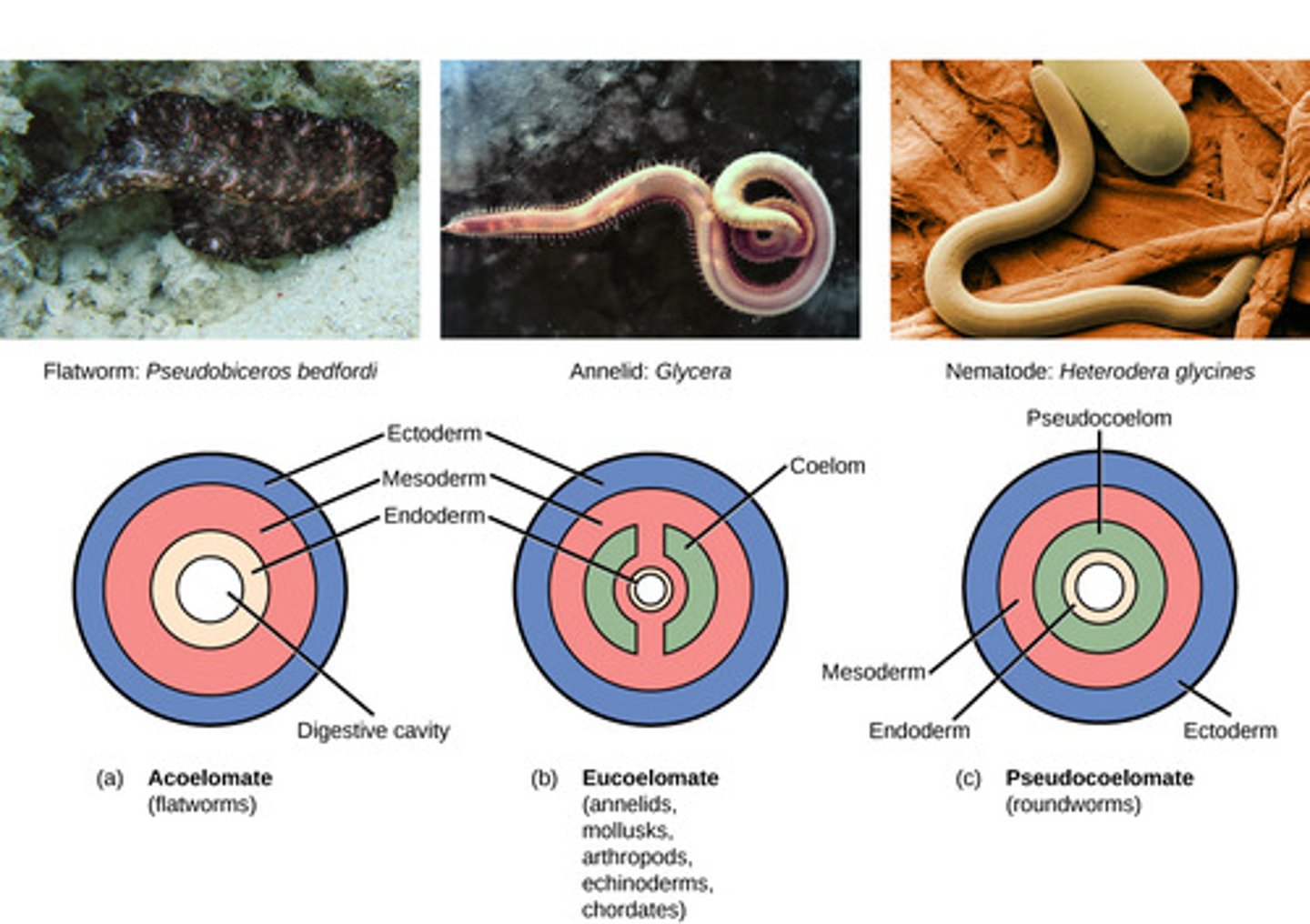
Which organisms have an internal cavity but it is not completely lined by mesoderm-derived tissue?
pseudocoelomates
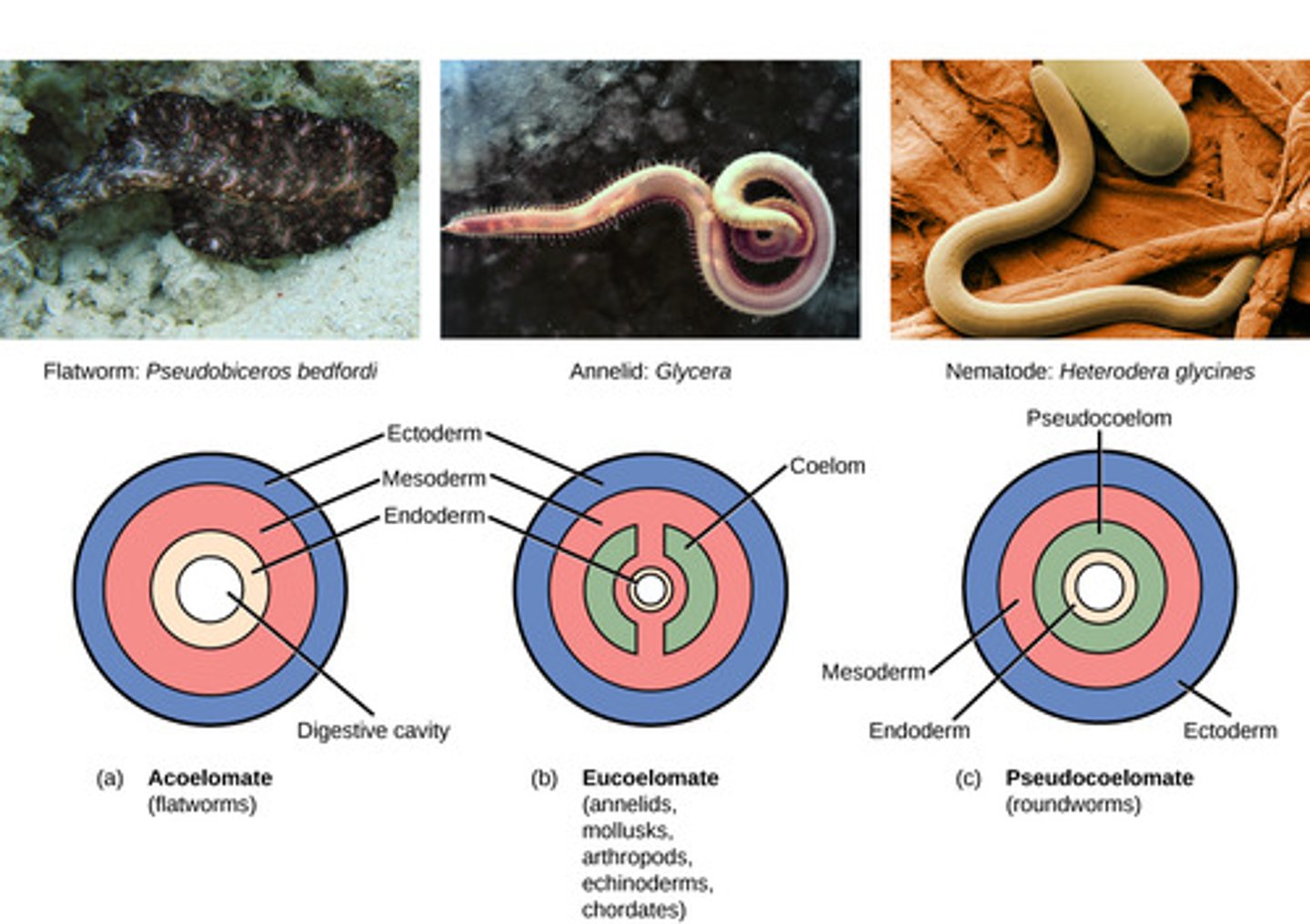
Which organisms have a coelom?
coelomates
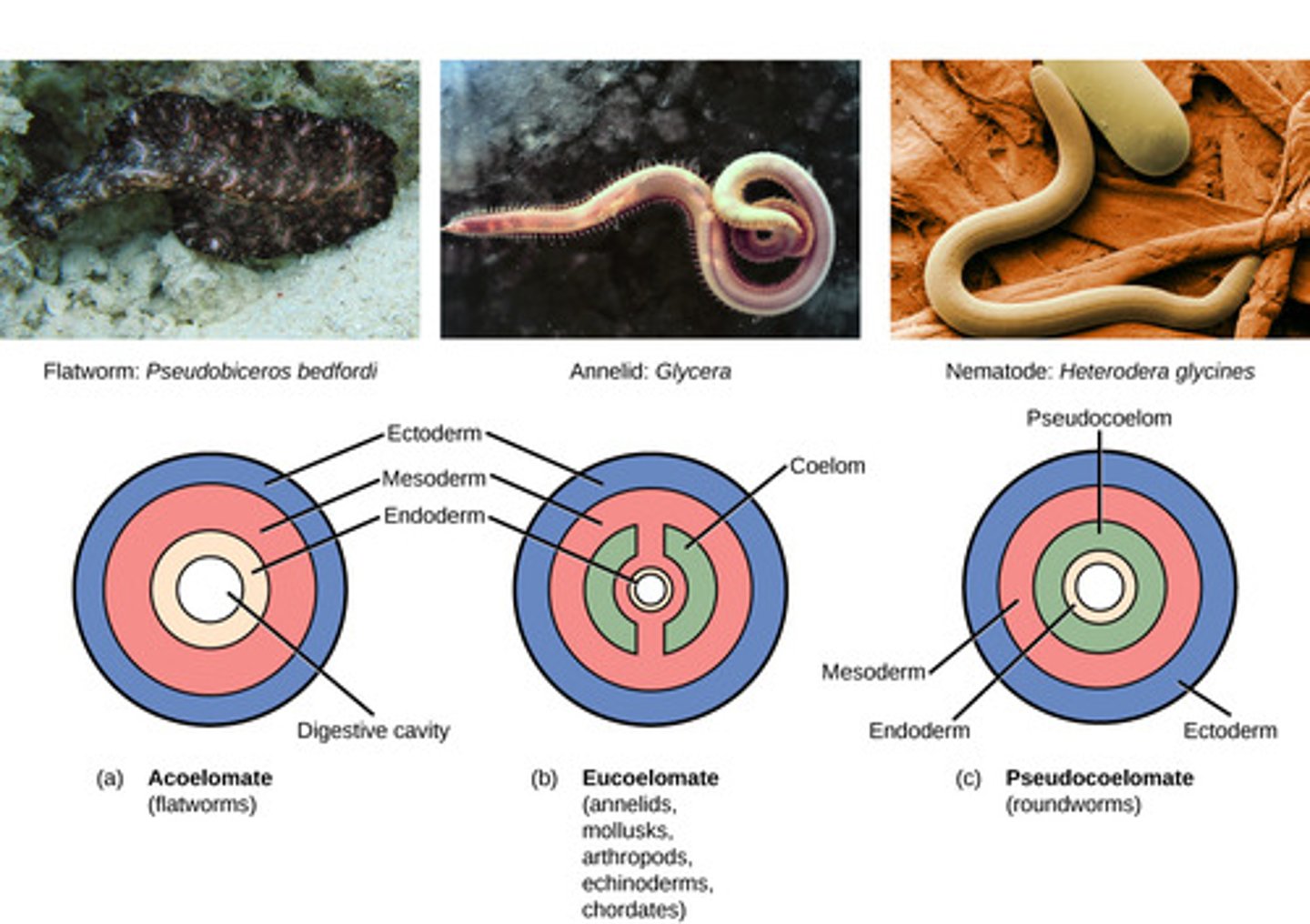
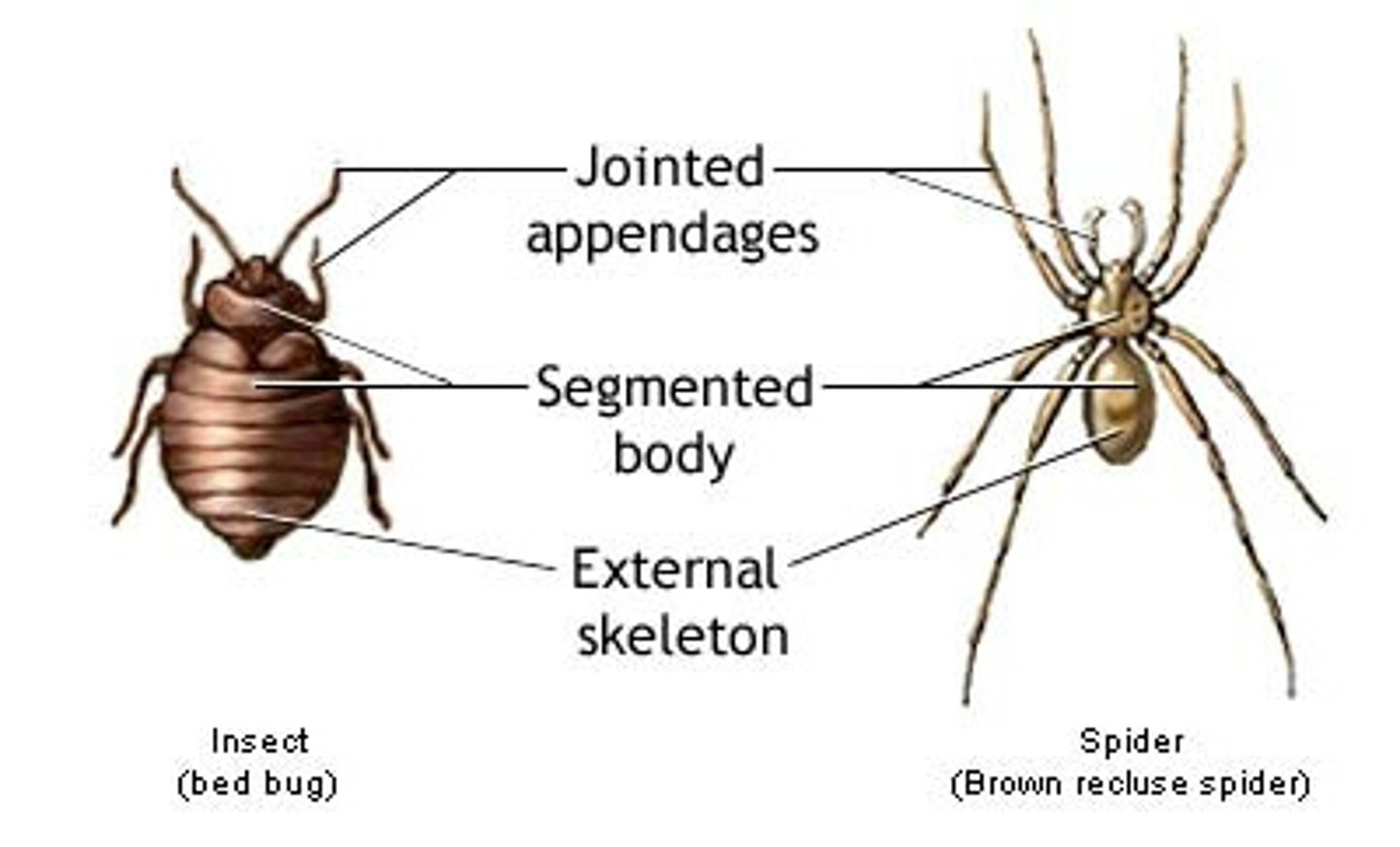
What is the term describing the degree to which organisms have segmented body structures?
segmentation

What are the 2 types of segmentation?
1. repetitive
2. specialized
In which organisms can segmentation be seen?
1. arthropods
2. annelids
3. chordates
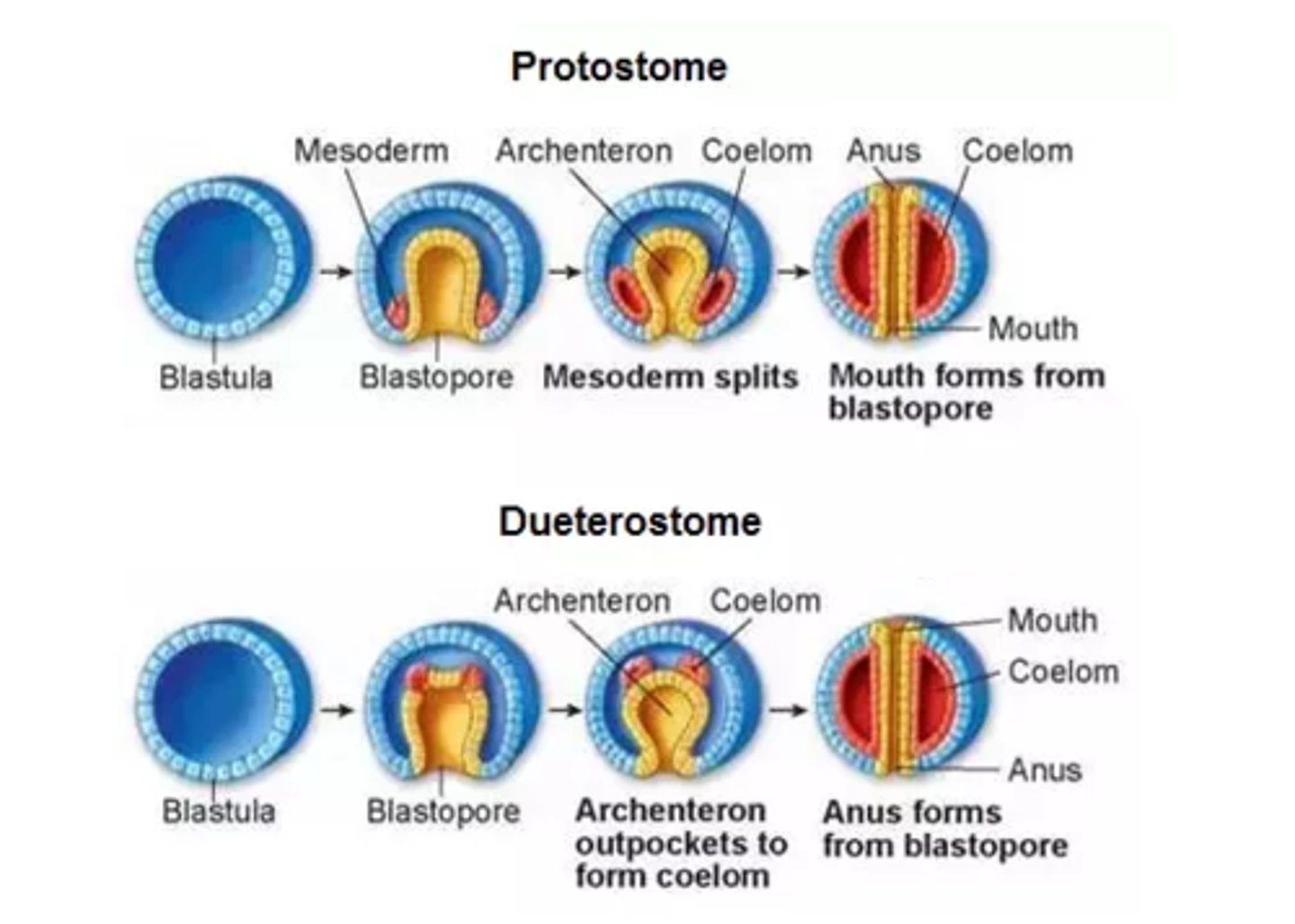
What is the primitive gut that forms during gastrulation in the developing blastula
archenteron
Into what structure does the archenteron develop in animals?
digestive tract
Which openings does the archenteron possibly develop into?
mouth or anus
(Note: depends
on the type of organism)
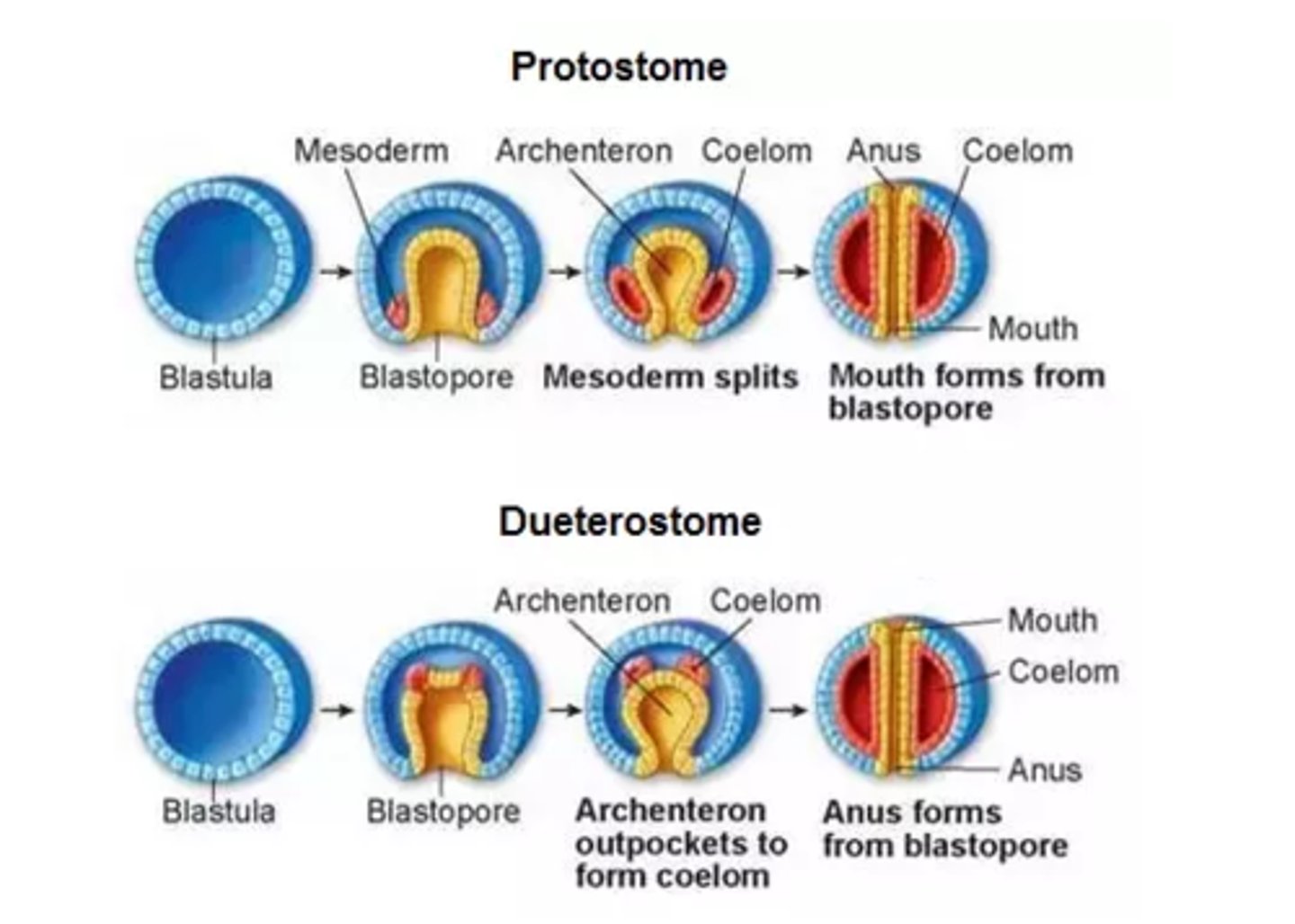
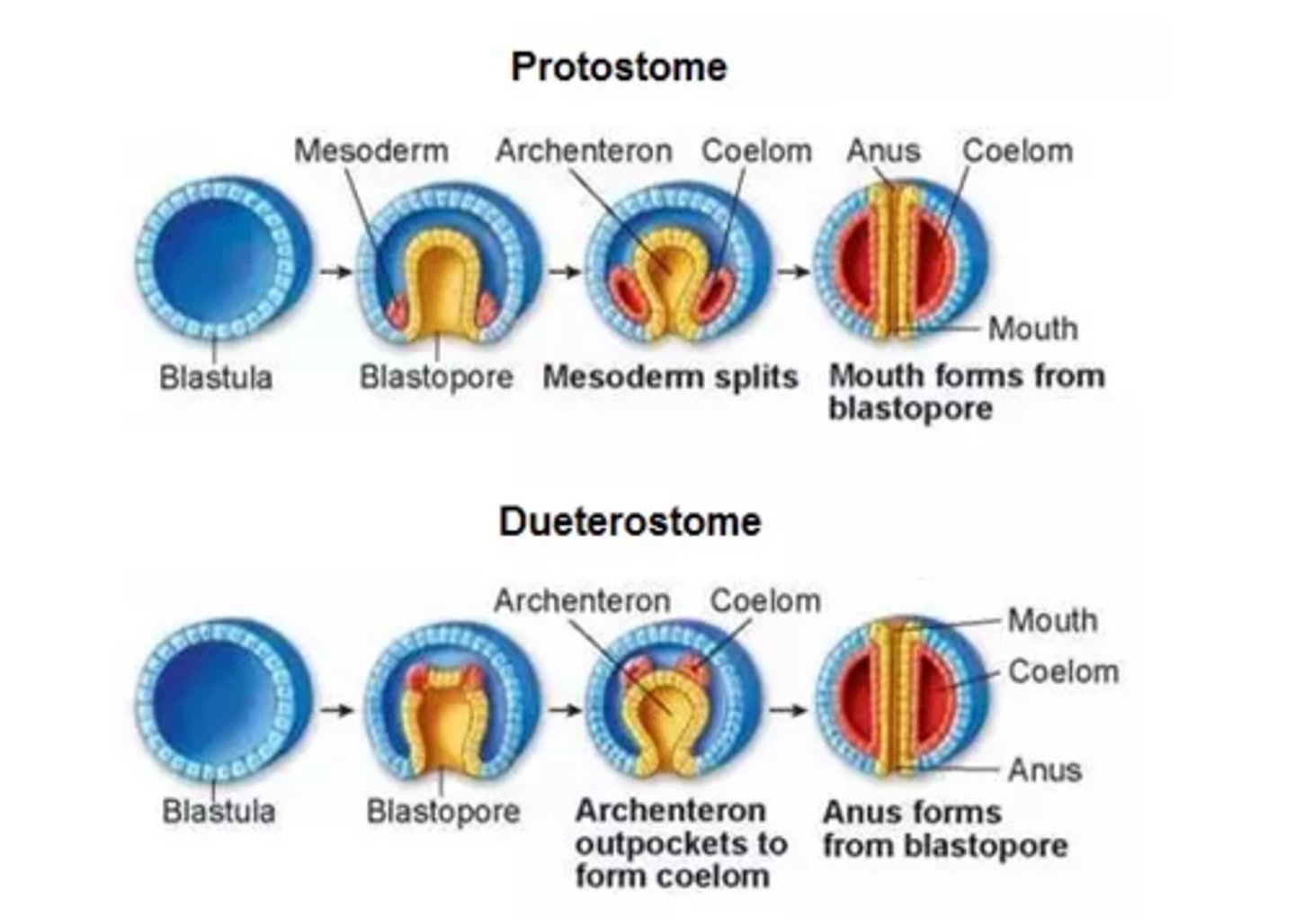
Which organisms have their mouth develop first?
protostomes
Which organisms have their anus develop first?
deuterostomes
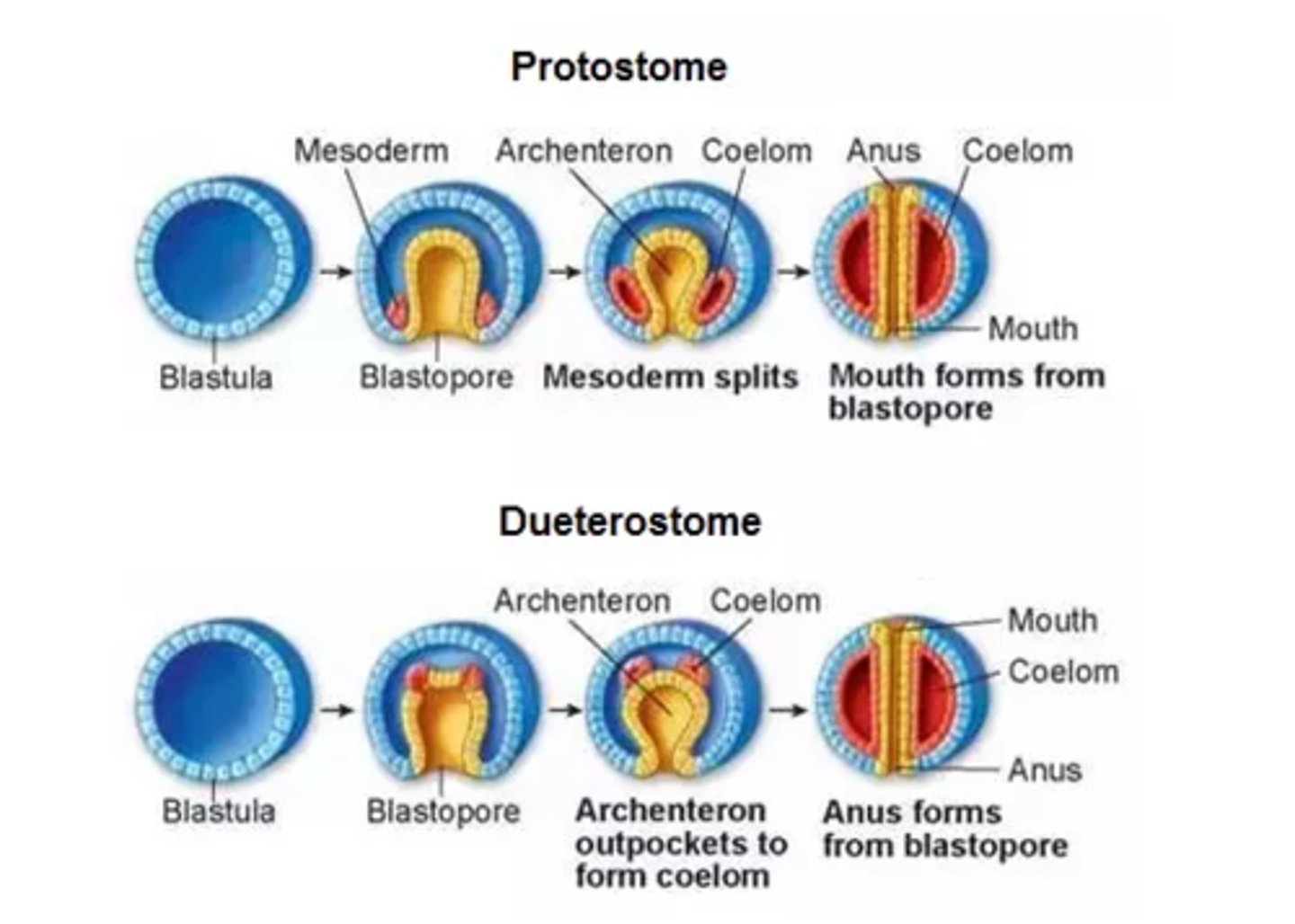
What are the 2 ways that the coelom can develop from the archenteron?
1. splitting of the
mesodermal tissue
at the sides of the
archenteron
2. directly from an
out-pouching in
the archenteron wall