Spinal Cord and Laminectomy Lab
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Right head rotation, Head, neck flexion, Left lateral flexion, Depression or elevation, protraction
what movement would stretch the right trapezius?
Left head rotation, Neck flexion, Left lateral flexion, Depression, retraction
what movement would stretch the right levator scapulae?
Depression, protraction
what movement would stretch the right rhomboid major?
Depression, protraction
what movement would stretch the right latissimus dorsi?
Trunk flexion, right lateral flexion
what movement would stretch the left iliocostalis?
head, neck and Trunk flexion, right lateral flexion
what movement would stretch the left longissimus?
Spinal column flexion
what movement would stretch the left spinalis?
Head rotation to right, head & neck flexion, right lateral flexion
what movement would stretch the left splenius capitis?
Head rotation to right, head & neck flexion, right lateral flexion
what movement would stretch the left semispinalis capitis?
Trunk flexion, right side bending
what movement would stretch the left multifundis lumborum?
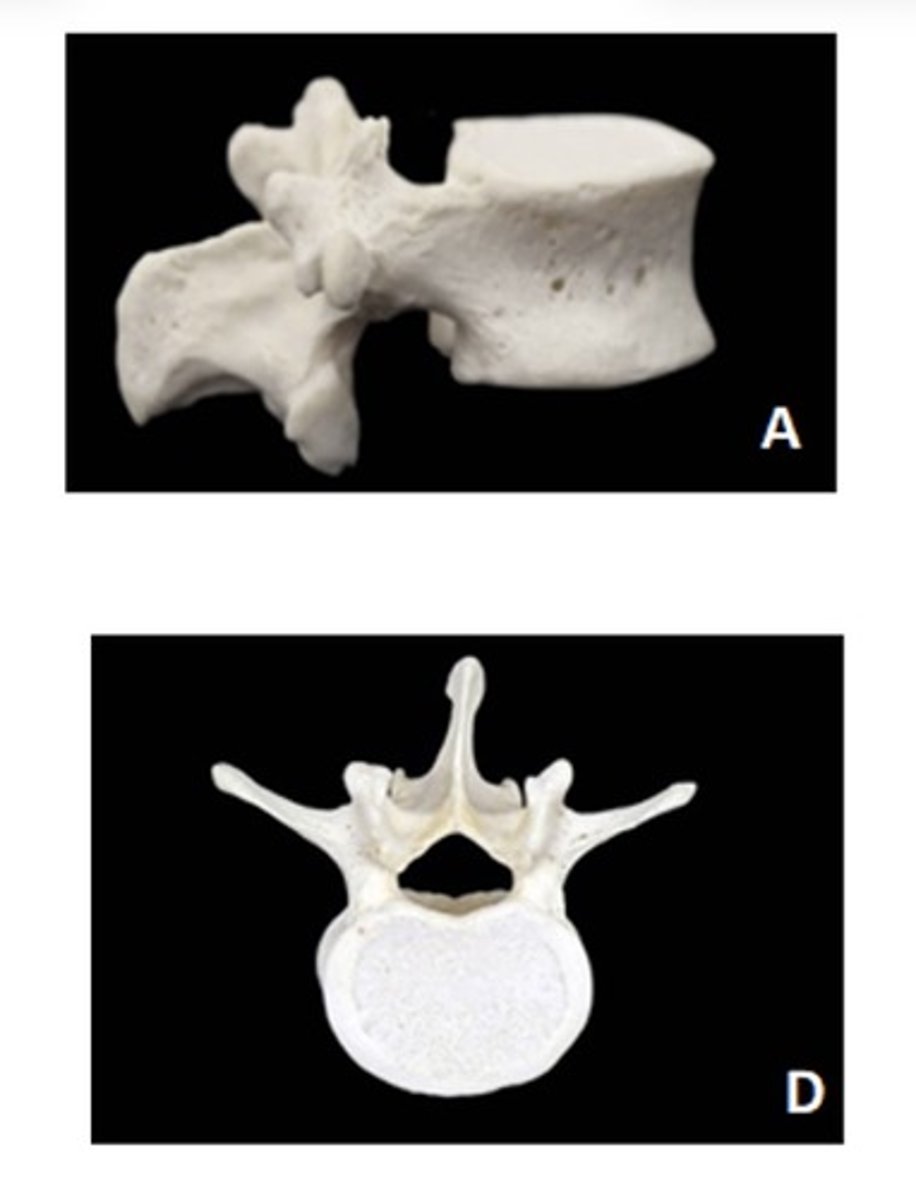
Lumbar
A - lateral
D - superior
ID the vertebra and view
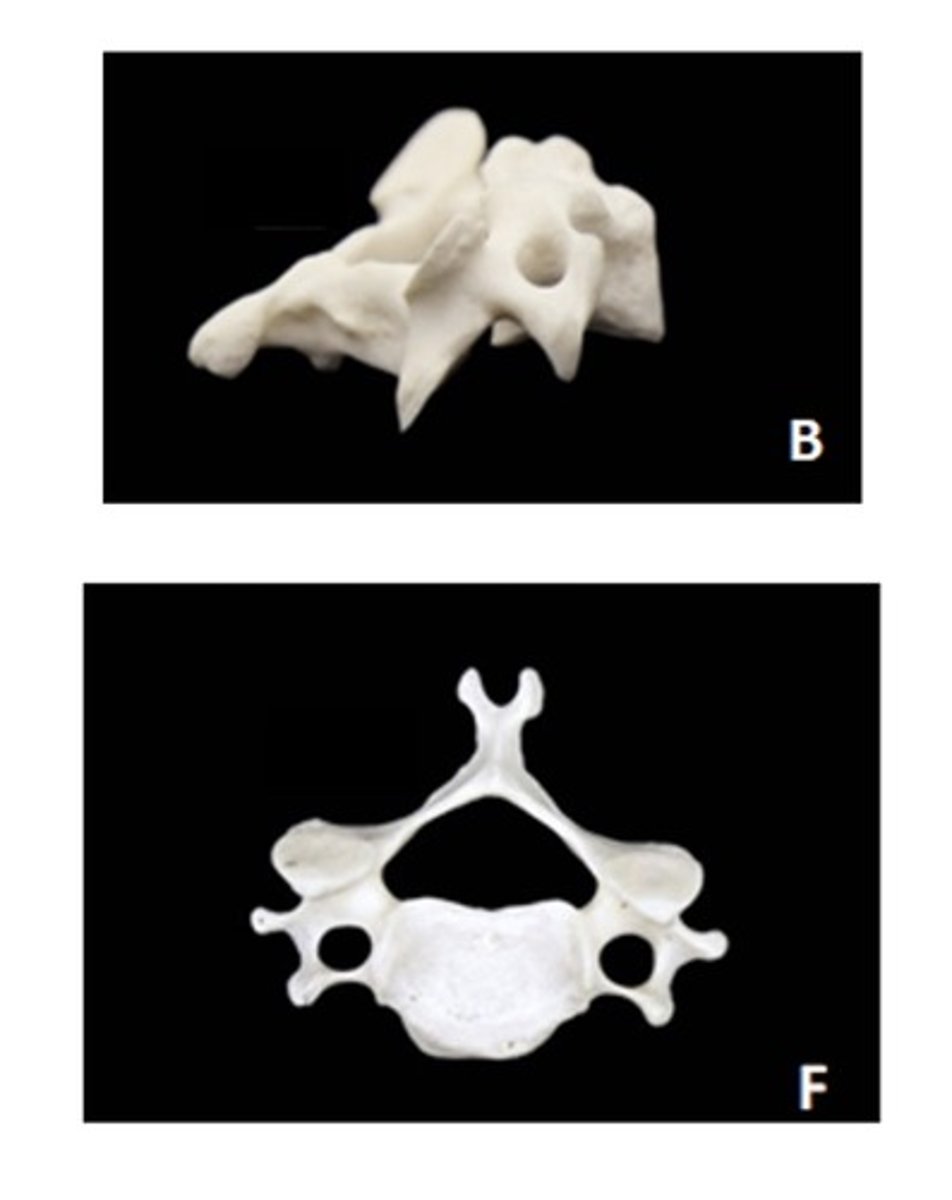
Cervical
b - lateral
f - superior
ID the vertebra and view
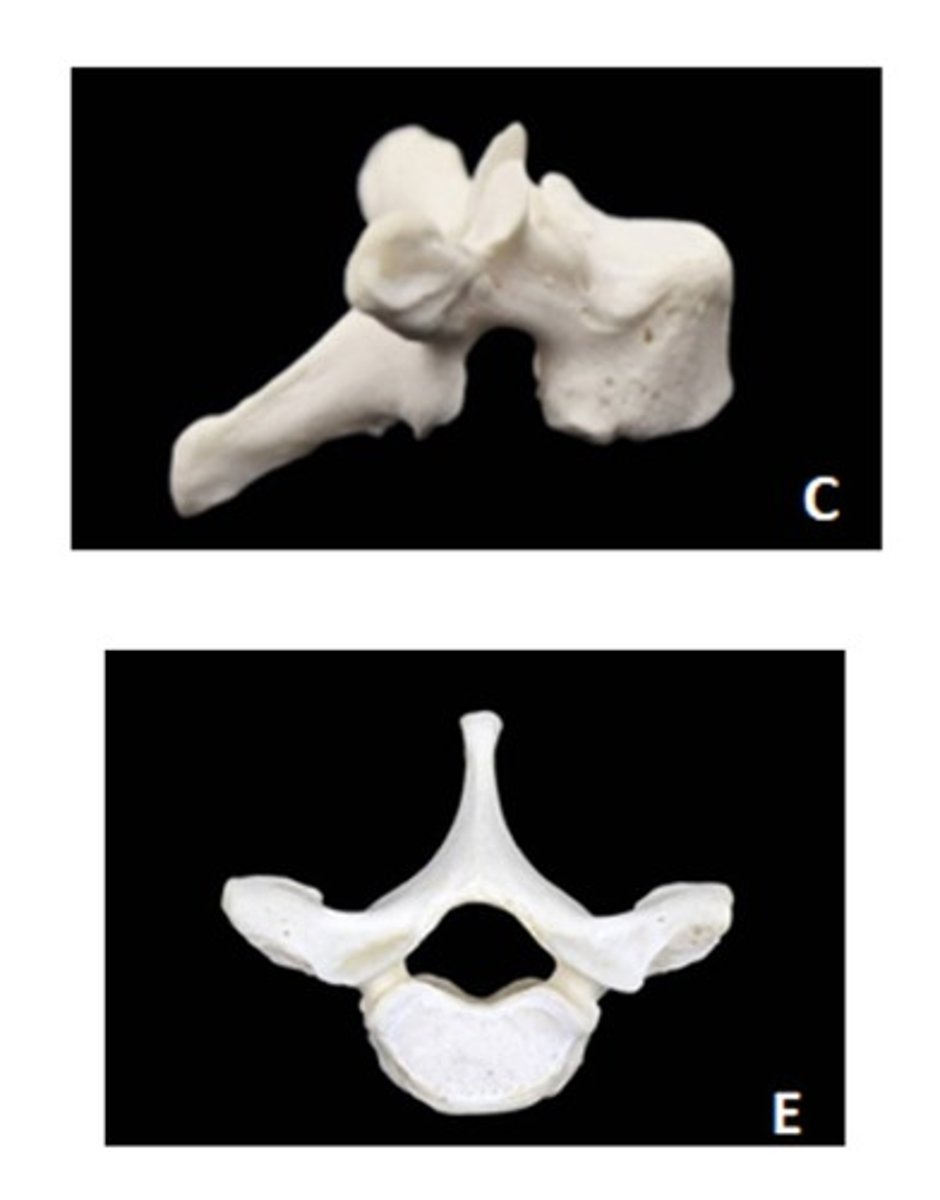
Thoracic
c - lateral
e - superior
ID the vertebra and view
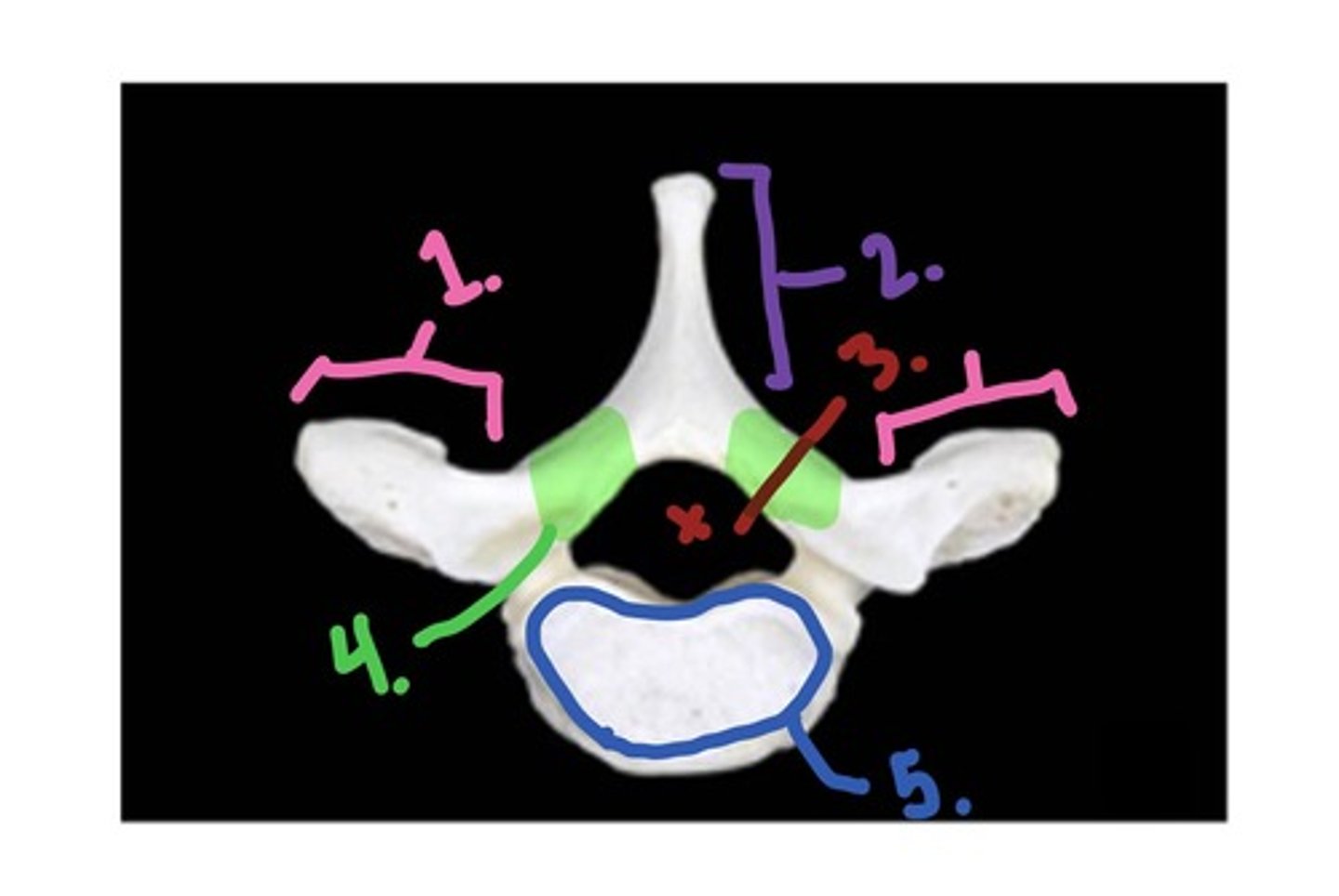
Lumbar - superior view
1. spinous process
2. transverse process
3. vertebral foramen
4. vertebral body
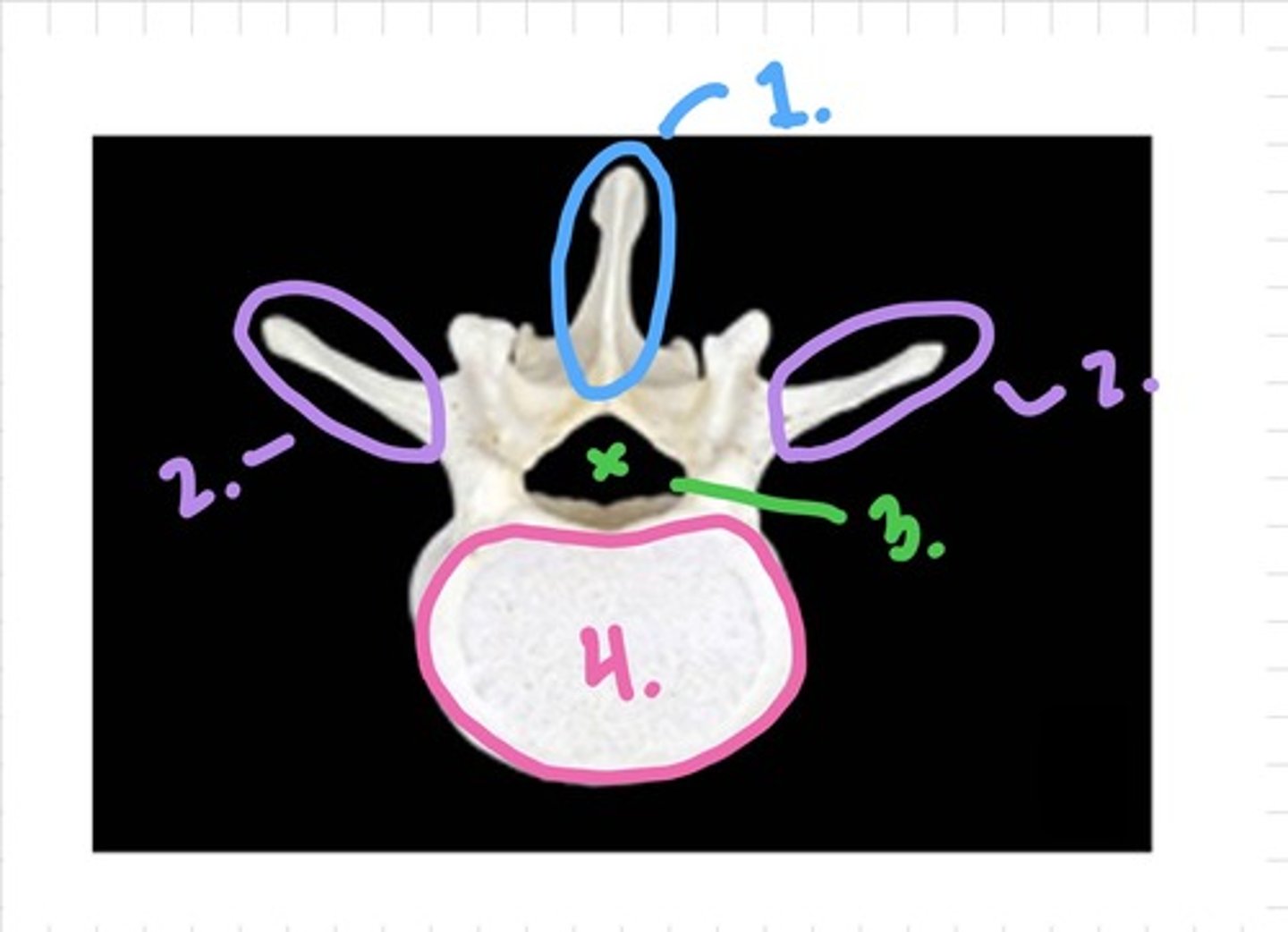
Cervical - superior view
1. spinous process
2. vertebral foramen
3. superior articular facet
4./5. Posterior/Anterior Tubercles of the transverse process
6. vertebral body
7. transverse foramen
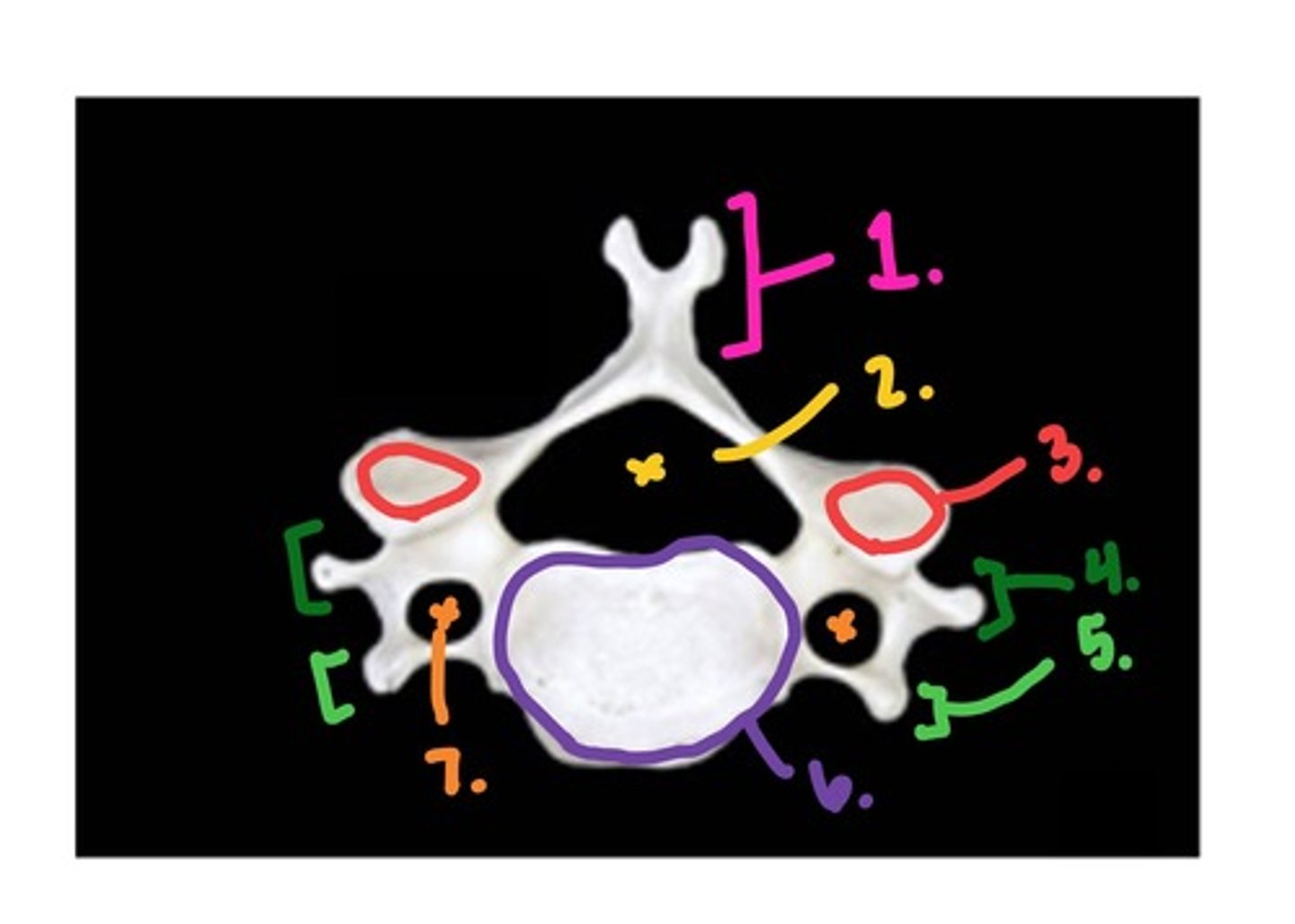
Thoracic - superior view
1. transverse process
2. spinous process
3. vertebral foramen
4. lamina
5. body
1. Joint Angle: From anterosuperior to posteroinferior
2. Superior Facet faces: Horizontal face inferiorly
3. Inferior Facet faces: Horizontal face superiorly
ROM impact: Allows some rotation and side-bending, but the two movements are coupled together (right rotation requires right side-bending)
- Flexion and extension are allowed with gliding of facets
what are the angles and positions of the following facet joints for the cervical vertebra? what is the ROM impact?
1. Joint Angle
2. Superior Facet
3. Inferior Facet
1. Joint Angle: Relative to cervical, facets are more nearly vertical, but angled from anterosuperior to posteroinferior
2. Superior Facet faces: Face posteriorly, slightly angled anteriorly
3. Inferior Facet faces: Face anterioly, slightly angled posteriorly
ROM impact: Allows some rotation and side-bending, but the two movements are limited by the ribcage
- Flexion and extension are allowed with gliding of facets, but severely limited by the ribcage
what are the angles and positions of the following facet joints for the thoracic vertebra? what is the ROM impact?
1. Joint Angle
2. Superior Facet
3. Inferior Facet
1. Joint Angle: Approximately in the sagittal plane
2. Superior Facet faces: posteromedially
3. Inferior Facet faces: posterolaterally
ROM impact: Rotation is severely limited; the axis of rotation for rotation is forced to be in the posterior part of the intervertebral disc
- Flexion and extension are allowed with gliding of facets
what are the angles and positions of the following facet joints for the lumbar vertebra? what is the ROM impact?
1. Joint Angle
2. Superior Facet
3. Inferior Facet
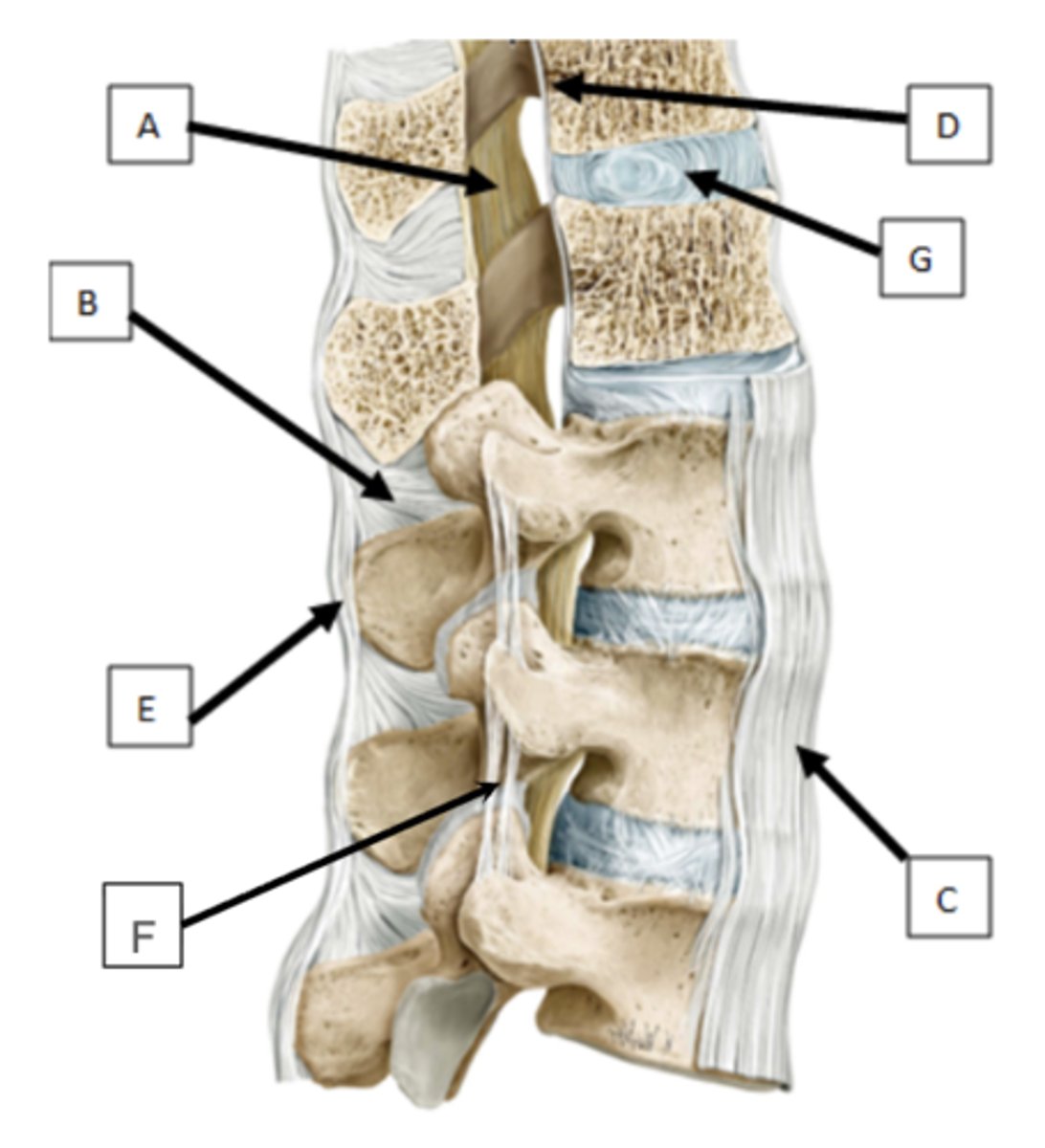
in the middle of the blue section (lamina)
indicate where the surgeon should cut through the vertebra in order to reveal the spinal cord
a. Ligamentum Flava → Limits flexion
b. interspinous ligament → Limits flexion
c. anterior longitudinal ligament → Limits extension
d. posterior longitudinal ligament → Limits flexion
e. supraspinous ligament → Limits flexion
f. intertransverse ligament → Limits sidebending
g. IV disc → Limits motion in all directions and acts as a shock absorber between vertebral bodies
ID the structures and indicate what movement it limits
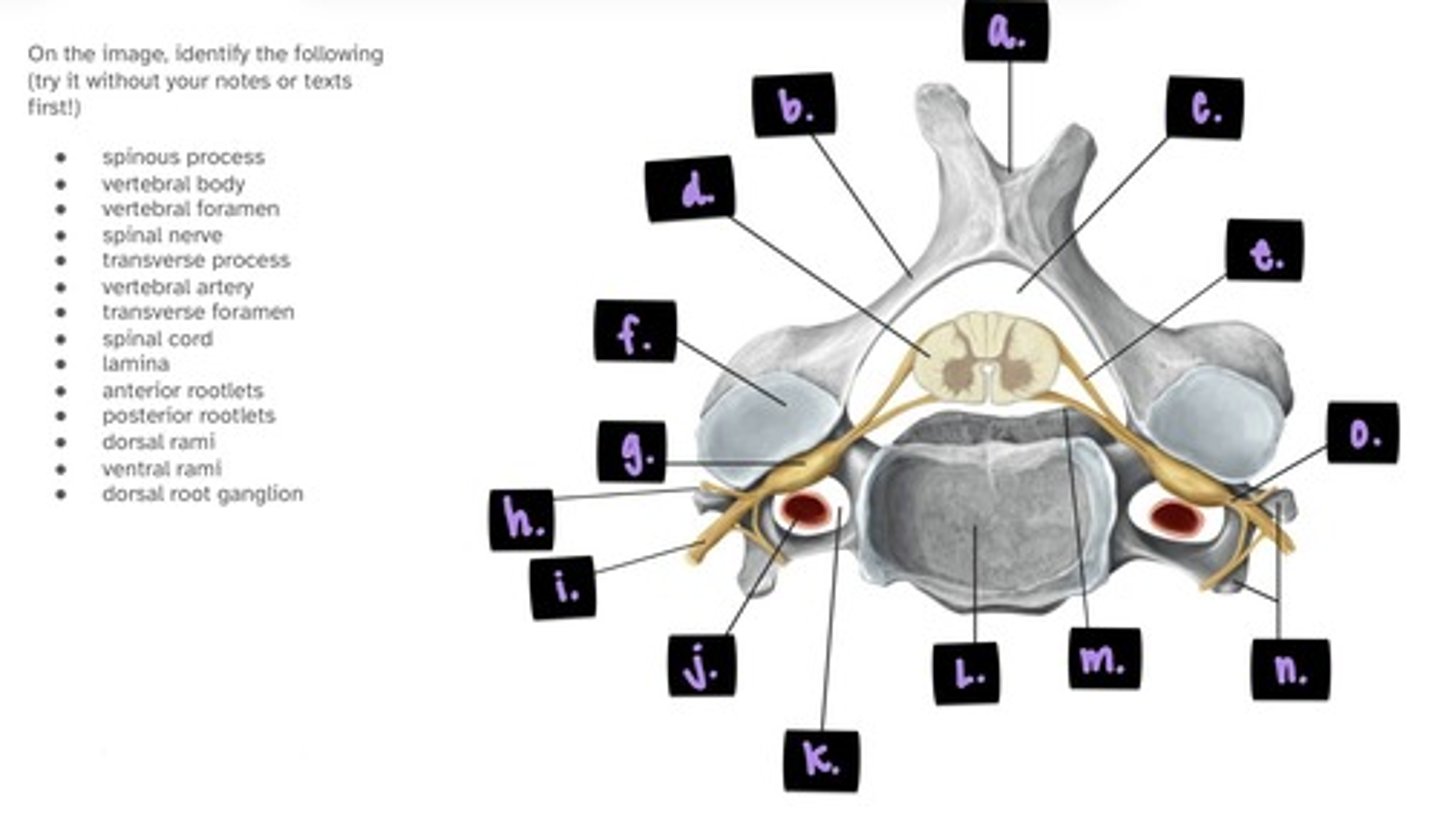
a. spinous process (bifid)
b. lamina
c. vertebral foramen
d. spinal cord
e. posterior root
f. superior articular facet
g. dorsal root/spinal ganglion
h. transverse process
label a. → h.
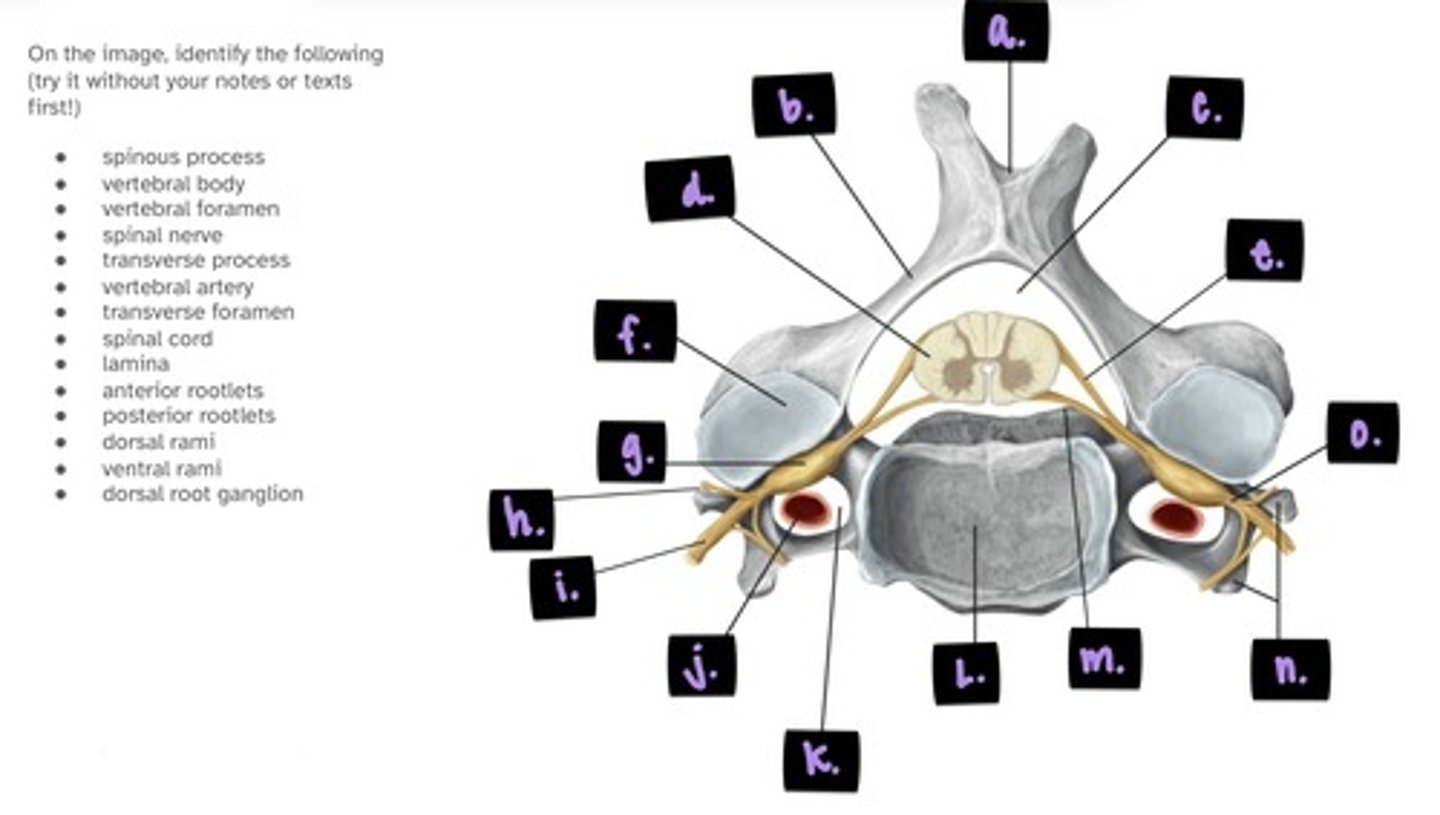
i. spinal nerve
j. vertebral artery
k. transverse foramen
l. vertebral body
m. anterior root
n. posterior/anterior tubercles
o. spinal nerve
label i. → o.
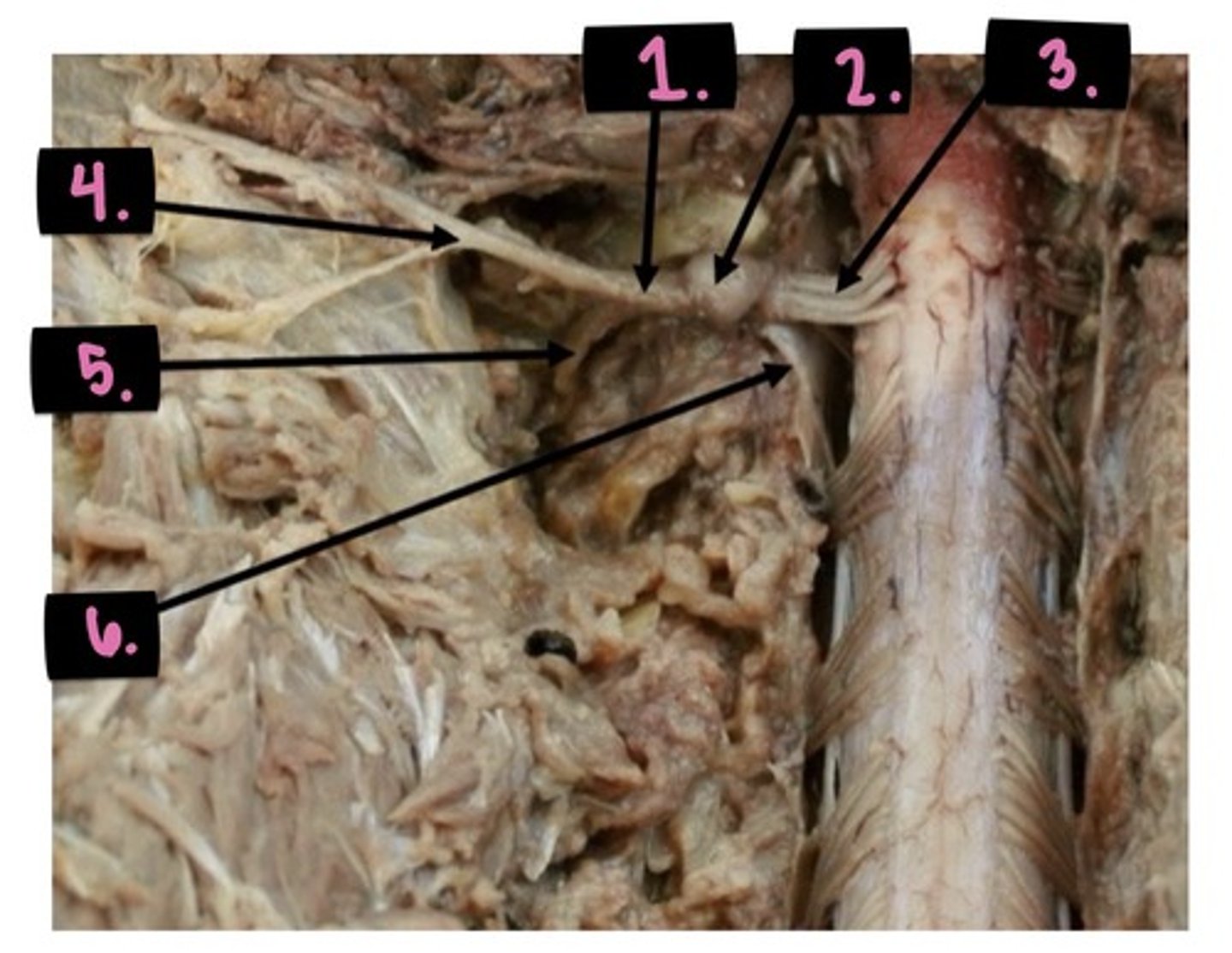
- anterior rootlets (M)
- posterior rootlets (S)
- dorsal rami (B)
- ventral rami (B)
- dorsal root ganglion (S)
For these structures, what type of fibers do they contain (Motor, Sensory, Both)
- anterior rootlets
- posterior rootlets
- dorsal rami
- ventral rami
- dorsal root ganglion
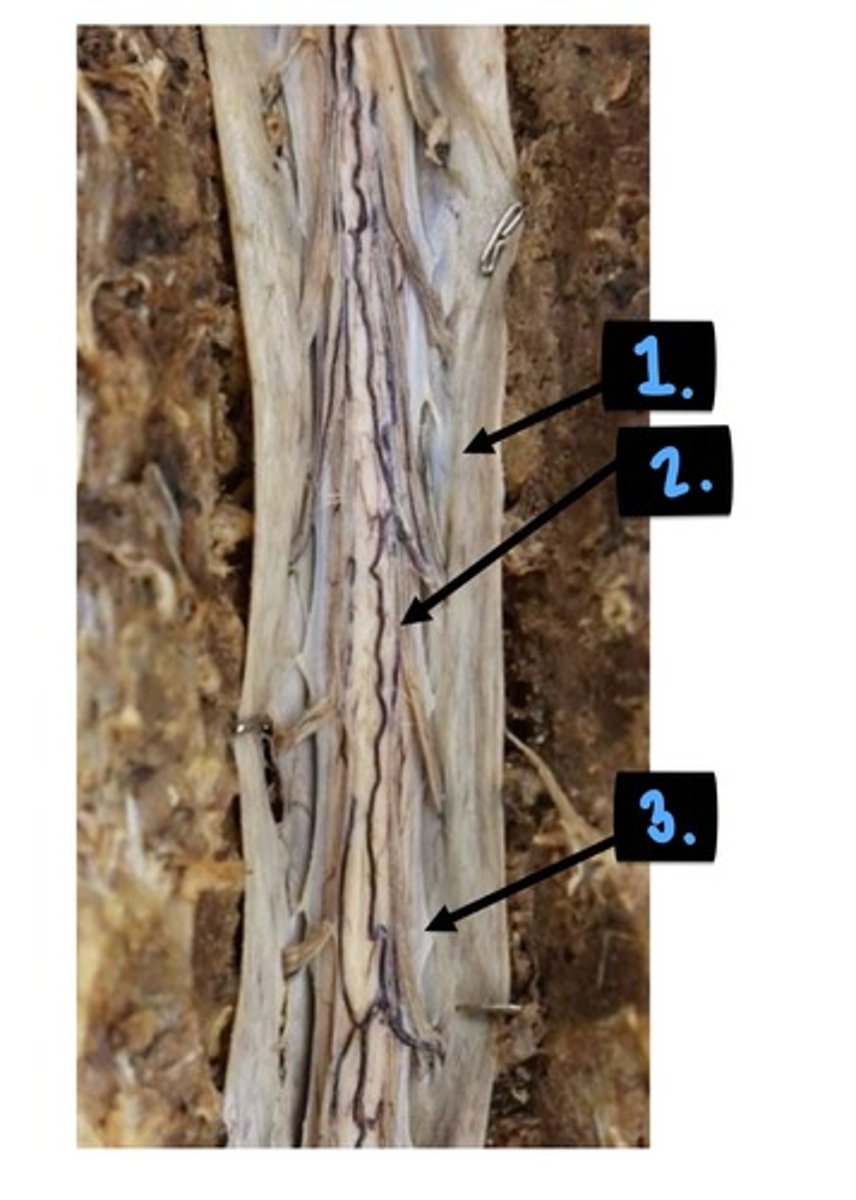
1. thecal sac
2. dorsal rootlets
3. dentate ligament

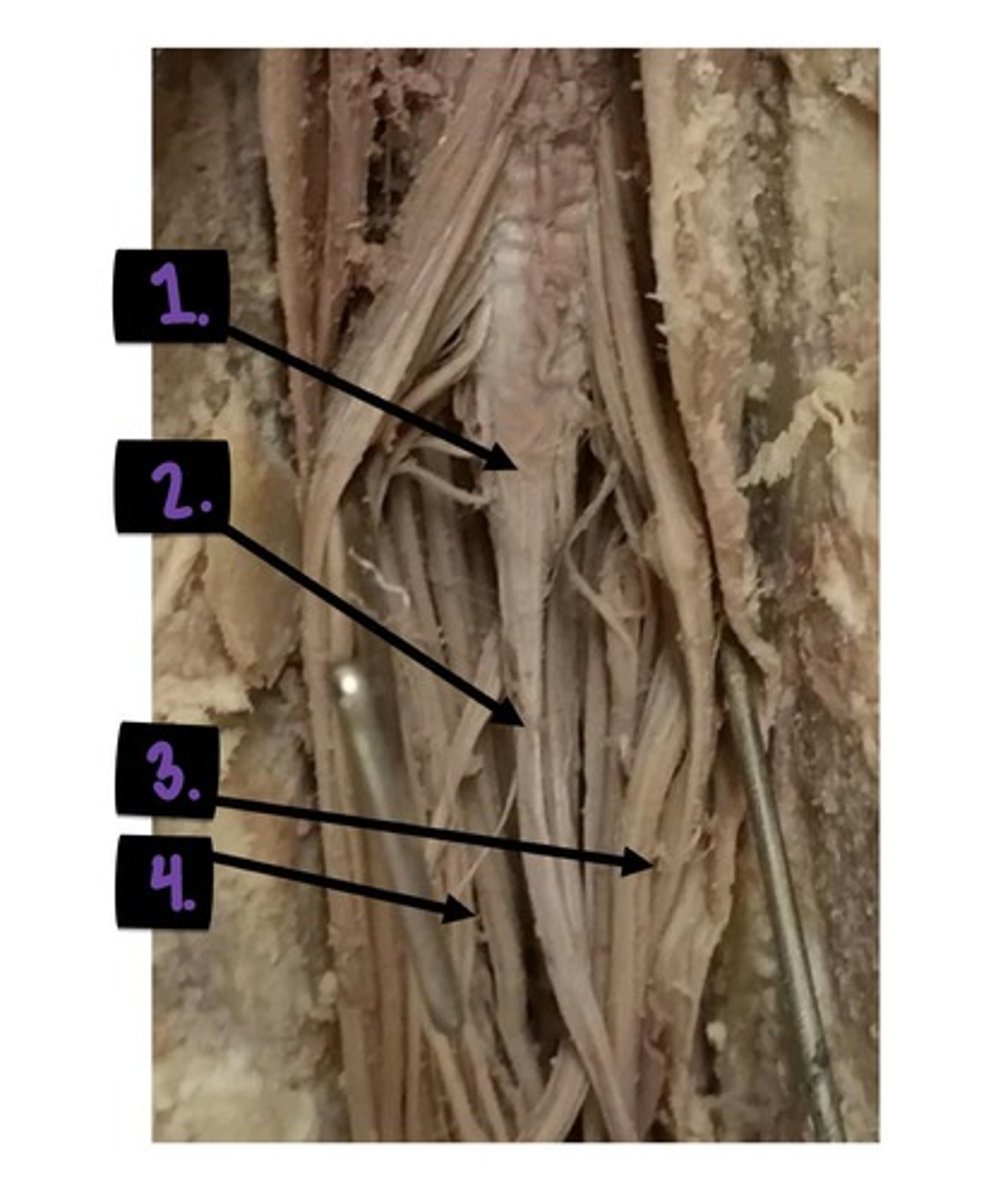
1. conus medullaris
2. filum terminale
3./4. cauda equina

1. Spinal nerve
2. DRG
3. Dorsal rootlets
4. Dorsal ramus
5. ventral ramus
6. ventral rootlets
1. lower thoracic, lumbar, sacral
2. red - anterior, pink - posterior
3. approximately midsagittal
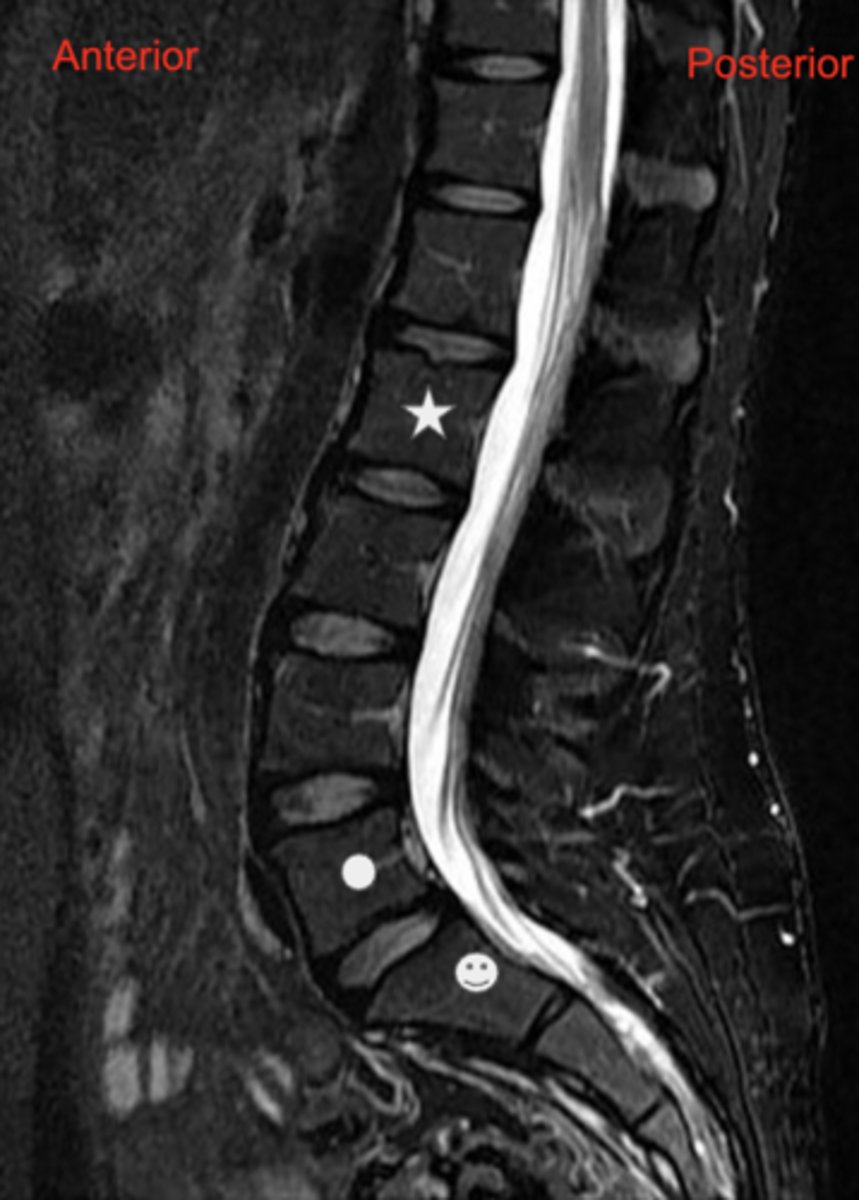
answer the following about the image:
1. Regions or parts of the spinal column that are represented?
2. Which box indicates anterior and posterior?
3. Is this an approximately midsagittal section, or is it relatively far from the midline of the body?
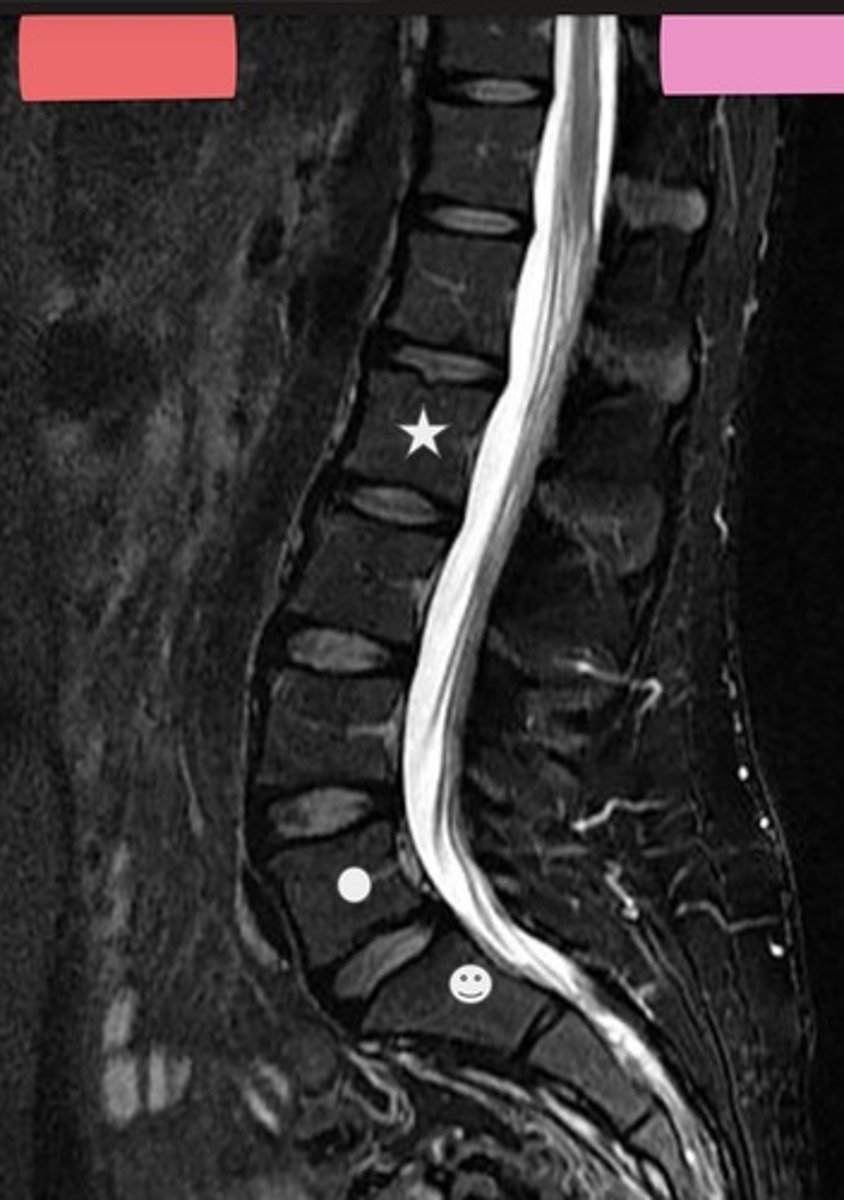
1. subarachnoid space
2. Nucleus pulposus
3.
- Star-L2
- Circle-L5
- Smiley Face-S1
answer the following about the image:
1. This MRI image was obtained with T2-weighted technique. In T2-weighted images, water that is not flowing is white. What space here is filled with relatively motionless water?
2. What features of intervertebral discs are seen?
3. What vertebra is indicated by the symbols
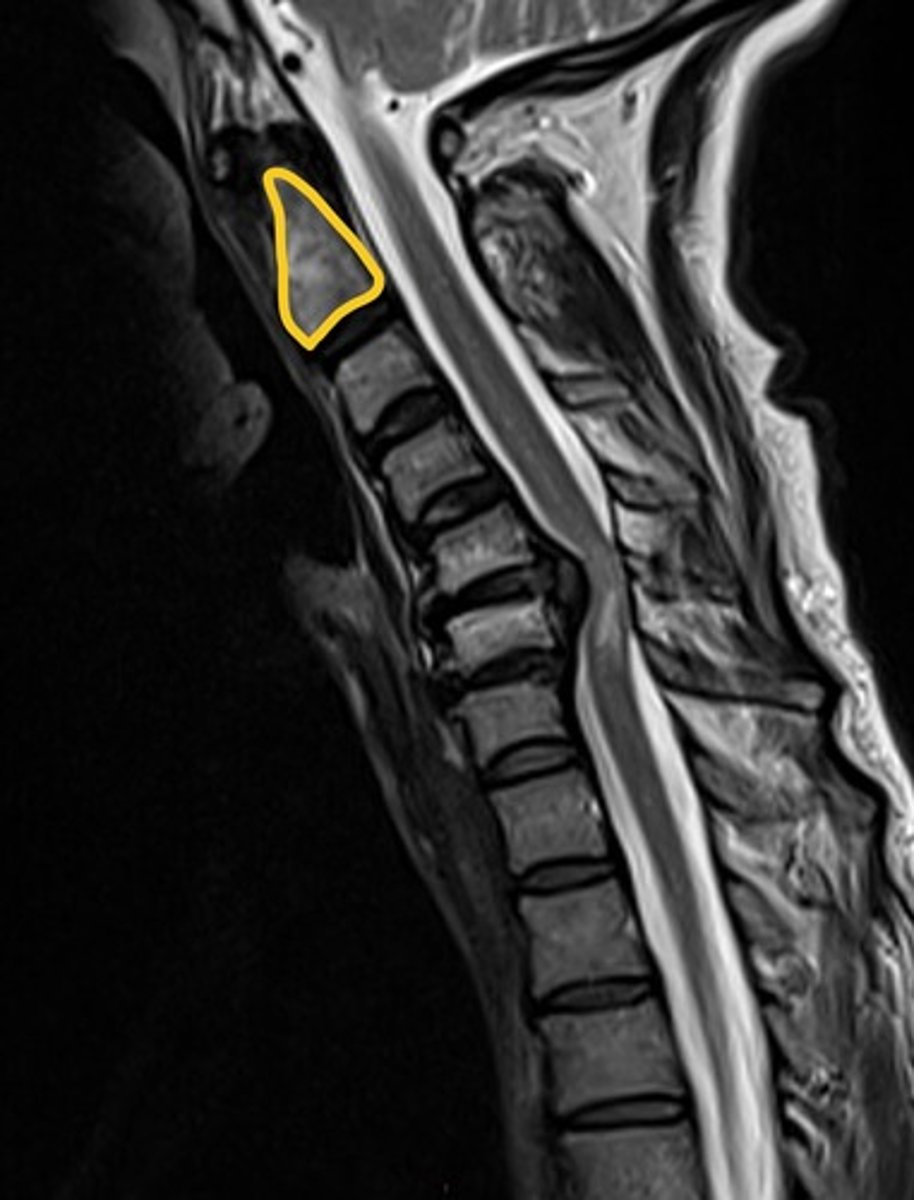
- Disc herniation at C5/6, impingement of C7 spinal nerve
- C2
- Sensory loss to C7 dermatome
Explain the anatomical deficit that is occurring. What is the circled vertebra? what might be a cutaneous deficit the patient is experiencing?