4.2a The Respiratory System Anatomy
5.0(1)Studied by 104 people
Card Sorting
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:01 AM on 3/9/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
1
New cards
What are the ==7 basic organs== of the Respiratory System (arranged in chronological order)?
1. Nose
2. Pharynx
3. Larynx
4. Trachea
5. Bronchi
6. Lungs (Subdivided into ==Bronchioles== and ==Alveoli==)
7. Diaphragm
2
New cards
What are 4 main functions of respiratory system?
1. ==Gas exchange:== adding O2 and removing CO2
2. ==Regulate blood pH:== more CO2 = less pH (less pH means more acidic)
3. ==Maintain homeostasis==: purify, warm and humidity the air
4. ==Produce sound==: Larynx causes it
3
New cards
The respiratory system can be divided into two major categories. Name them
Upper Respiratory Tract and Lower Respiratory Tract
4
New cards
What is the first organ in the Upper Respiratory Tract?
Nose
5
New cards
Explain how air travels through nose
Air enters the nose through the external nares (nostrils), where it is warmed, purified & humidified.
6
New cards
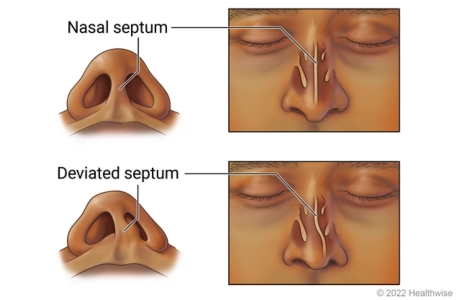
____ causes snoring if deviated
nasal septum
7
New cards
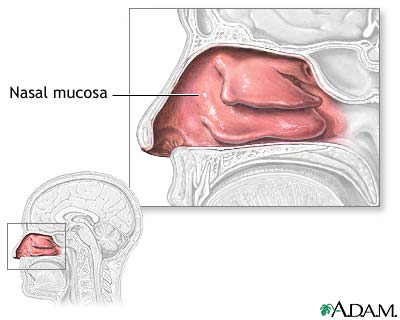
What is nasal cavity filled with and what is it function.
The nasal cavity is filled with ==Mucosa==. It moistens air and traps incoming foreign particles.
8
New cards
\---- type of receptors are located in mucosa
Olfactory Receptors
9
New cards
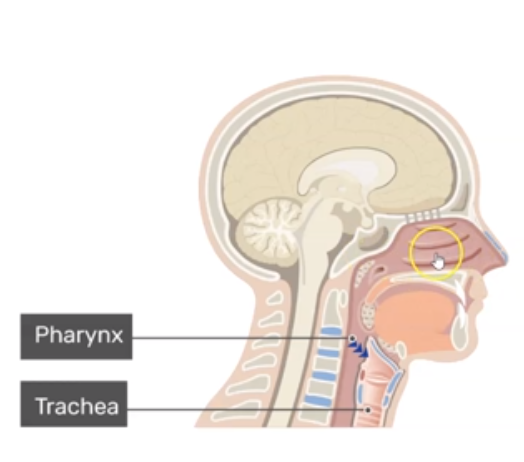
Where does air travel after the nose?
Pharynx
10
New cards
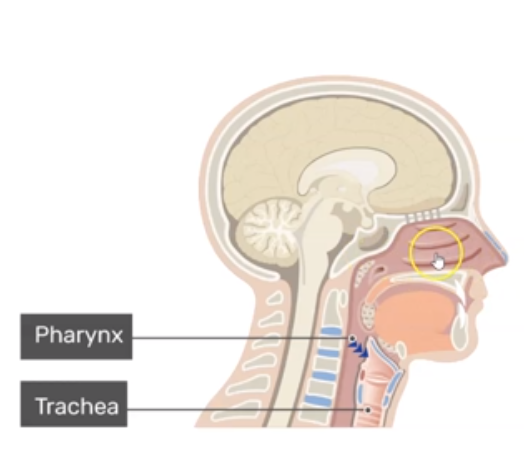
What is Pharynx?
Muscular Passage from nasal cavity to larynx
11
New cards
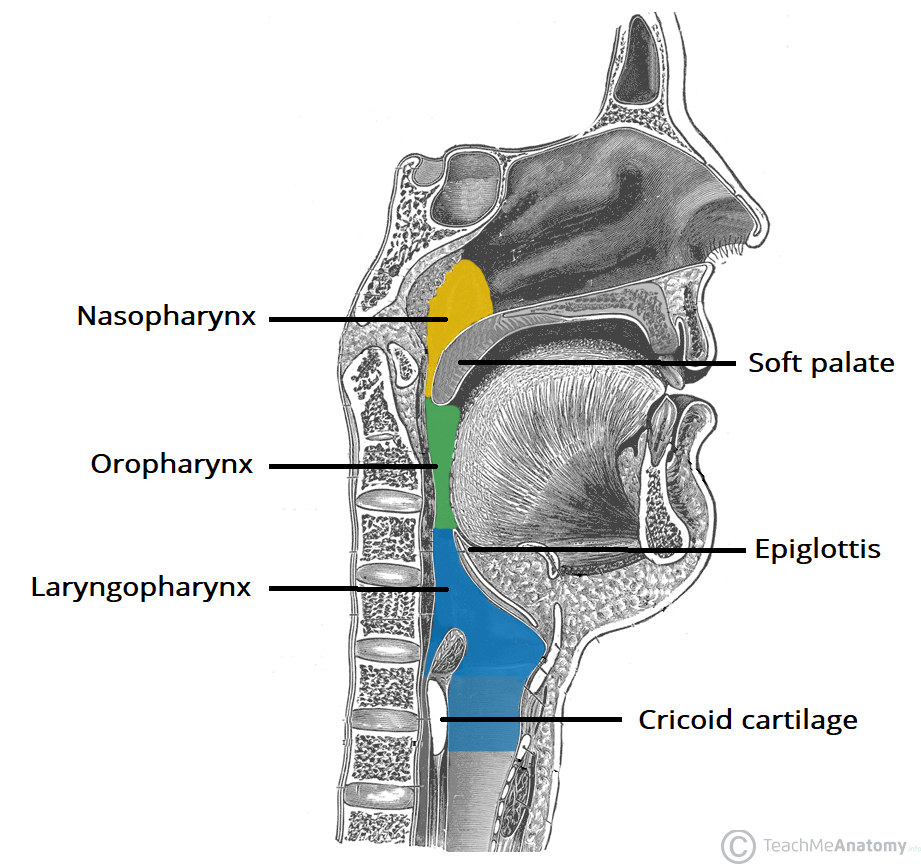
What are the 3 parts of Pharynx?
1. ==Nasopharynx==: internal nares to eustachian tubes. (it causes ears to “plug/pop”
2. ==Oropharynx==: middle region behind the mouth
3. ==Laryngopharynx==: Inferior region attached to where larynx and esophagus meet
12
New cards
Where does air go after Pharynx?
Larynx
13
New cards
What is Larynx?
Short tube of cartilage lined by mucous membrane that connects the pharynx to the trachea
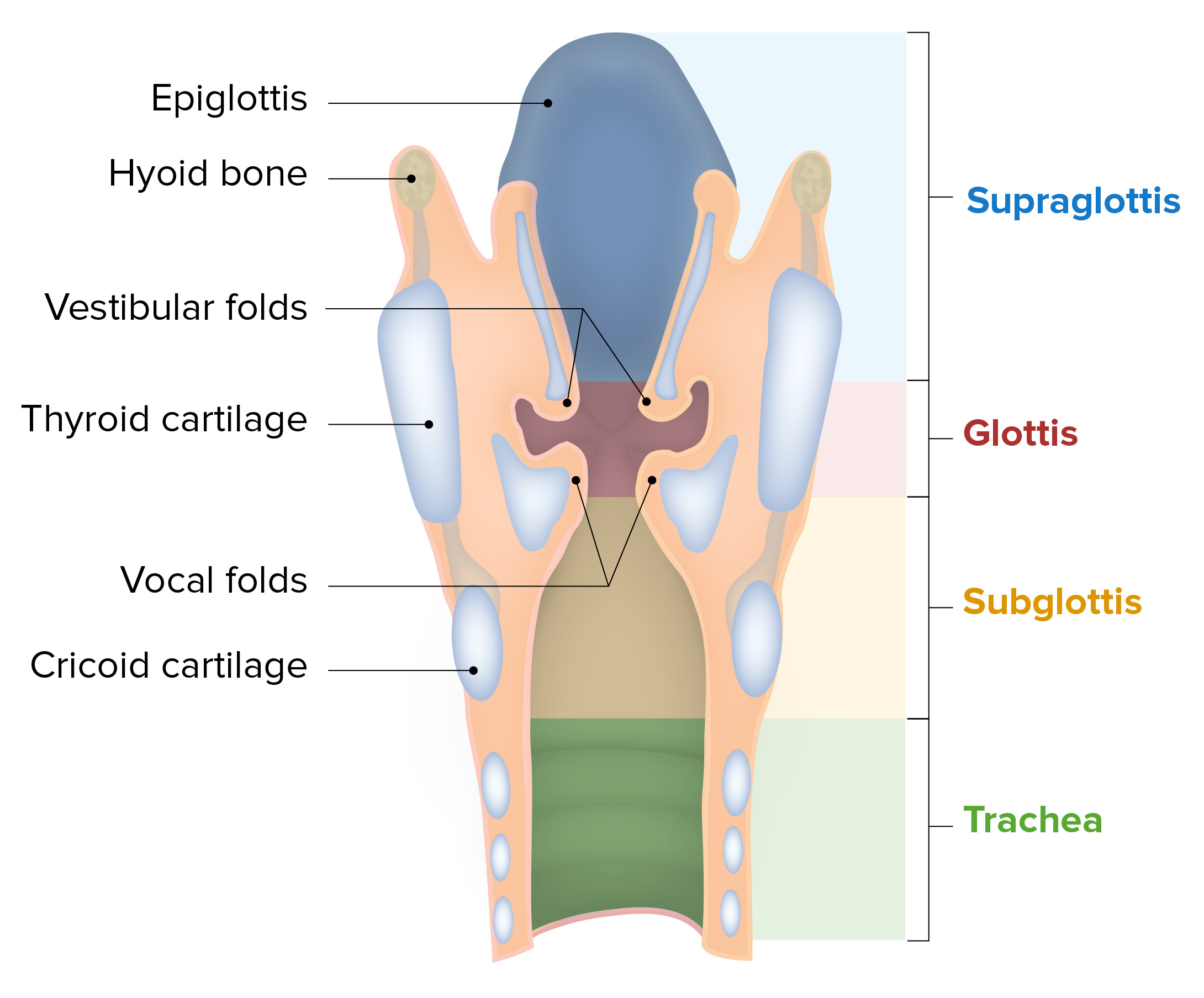
14
New cards
What are Vocal Cords and its functions?
Part of the Larynx that produces sound though vibration. Generally small & tight in females; thick & loose in males
15
New cards
Explain the parts of vocal cords
1. True Vocal Cords (TVF): Vocal cords that produce sound
2. False Vocal Cords (FVF): vestibular folds that help to close the larynx
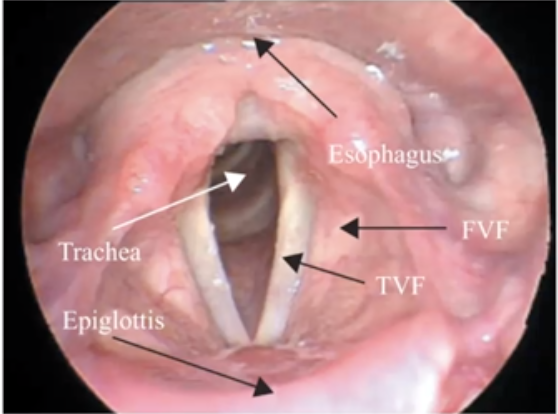
16
New cards
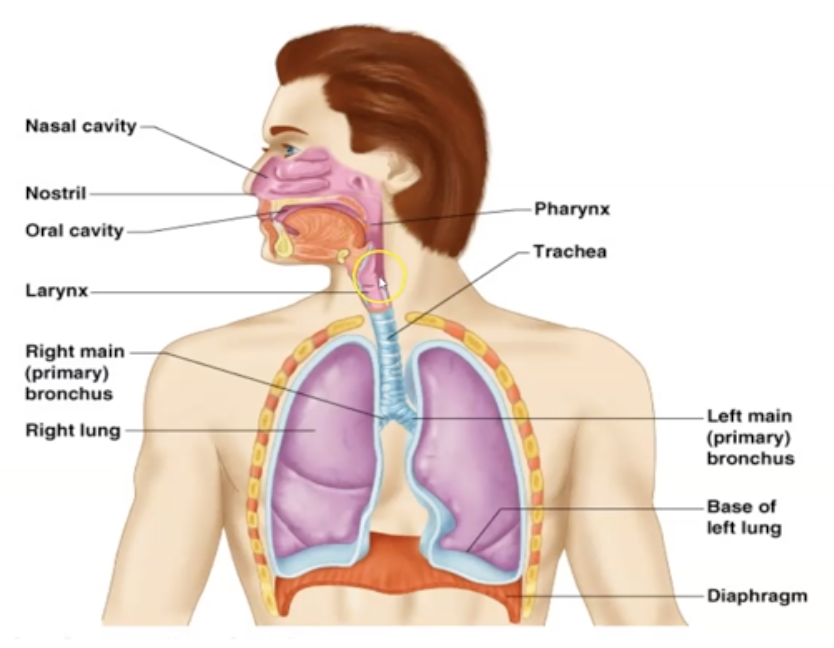
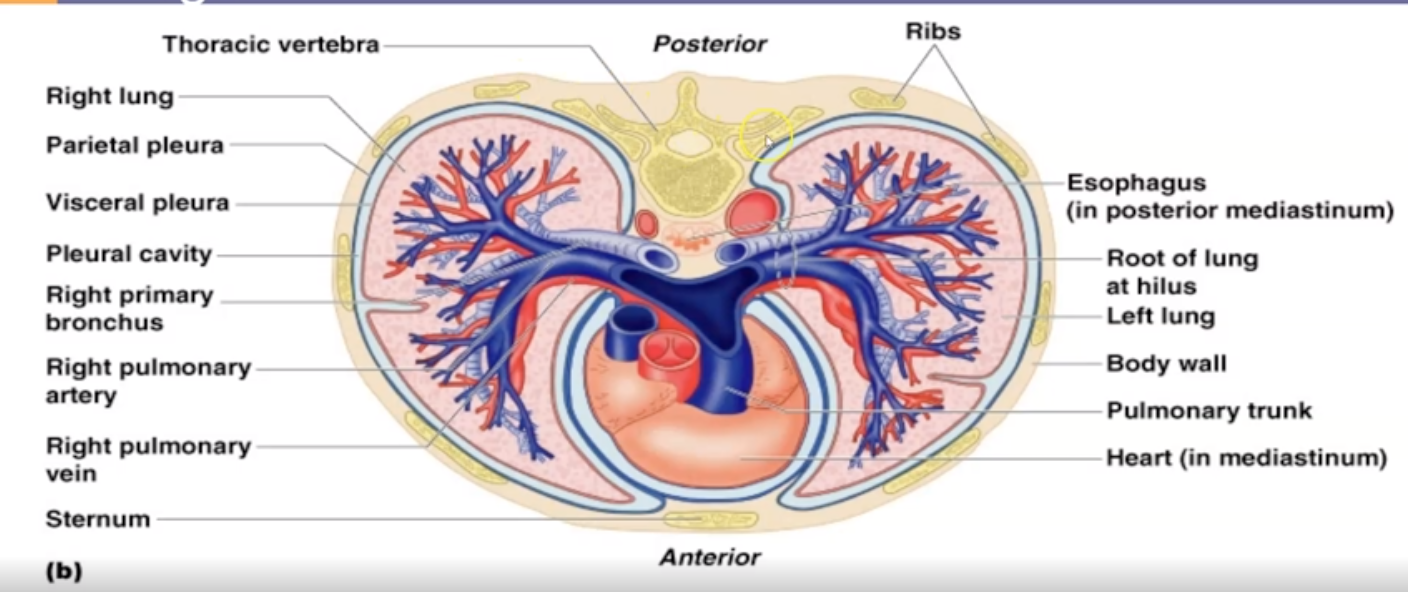
Summarize the Upper Respiratory Tract and Lower Respiratory Tract
Check the image
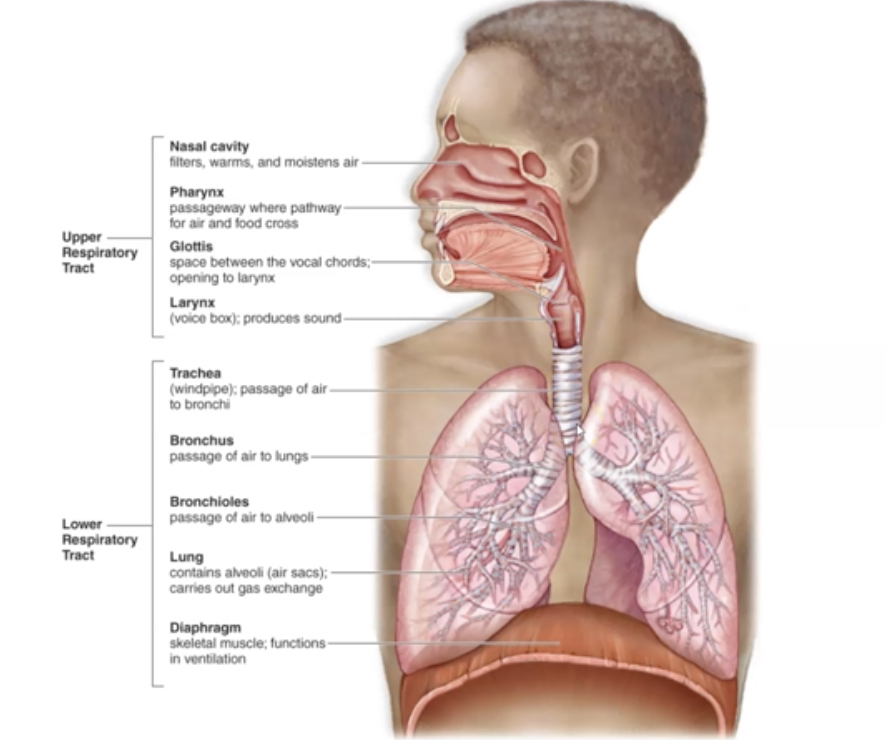
17
New cards
Name the first part of Lower Respiratory Tract
Trachea (windpipe). It connects Larynx with Bronchi
18
New cards
Explain Trachea
* Lined with ciliated mucosa
* Beat continuously in the opposite direction of incoming air.
* Expel mucus loaded with dust and other debris away from lungs.
* Walls are reinforced with C-shaped hyaline cartilage.
\
* Beat continuously in the opposite direction of incoming air.
* Expel mucus loaded with dust and other debris away from lungs.
* Walls are reinforced with C-shaped hyaline cartilage.
\
19
New cards
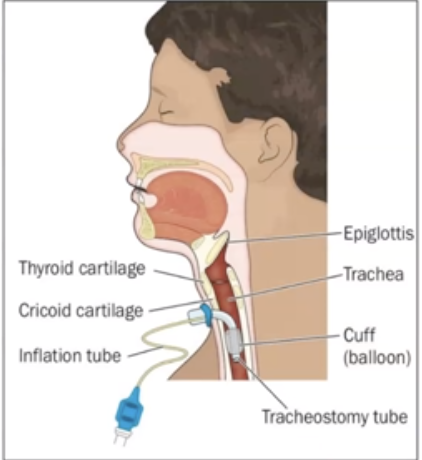
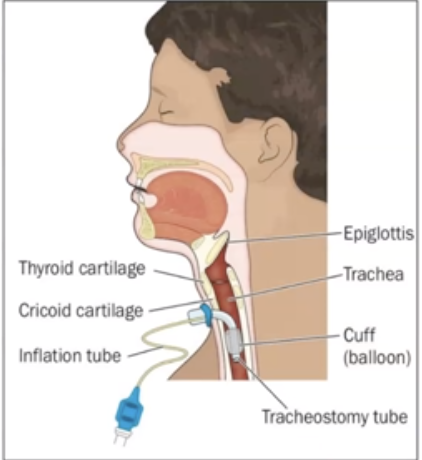
What is Tracheostomy?
incision made below the cricoid cartilage, and a tracheal tube is inserted to create an emergency air passageway
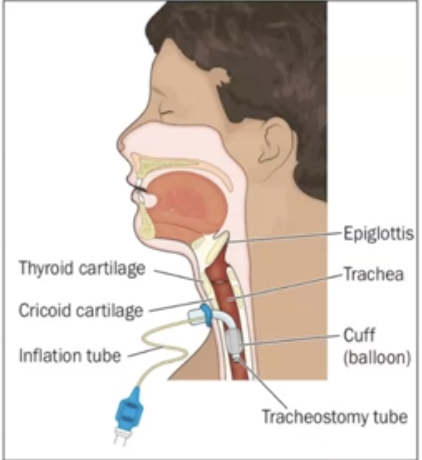
20
New cards
Name and Explain where air goes after Trachea?
Bronchi and Bronchioles. They are tubes that carry air from the trachea into the left and right lungs. (check image)
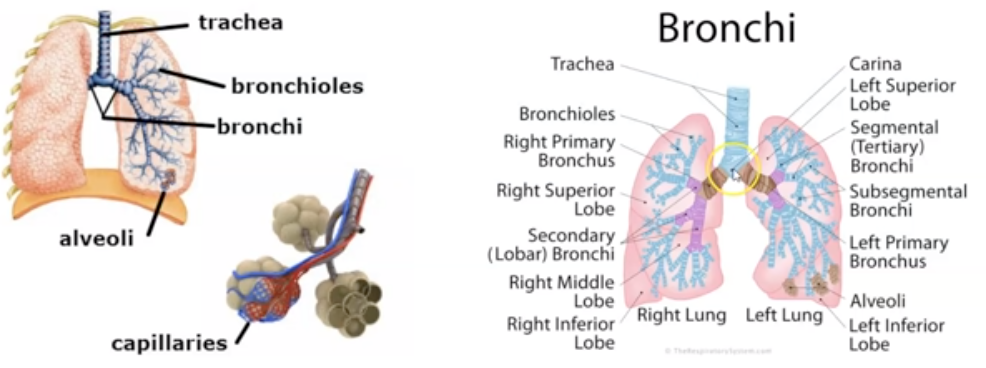
21
New cards
Explain the pathway air goes through Bronchi and Bronchioles
Trachea —> Primary bronchi —> secondary bronchi —> tertiary bronchi —> bronchioles —> terminal bronchioles —> alveoli
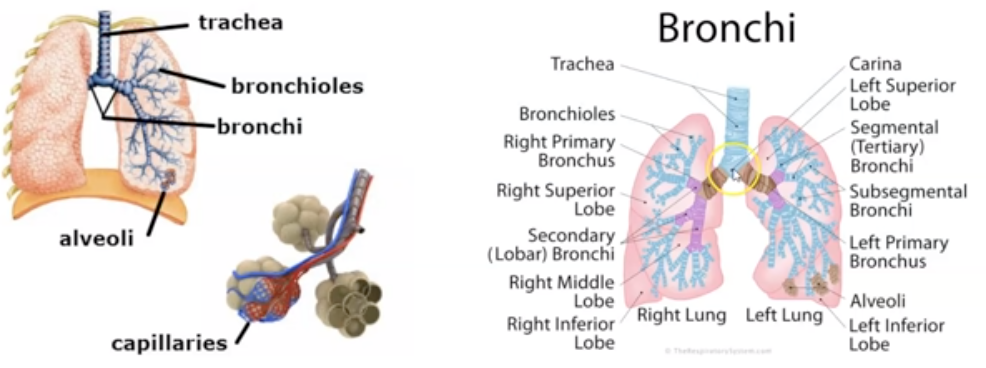
22
New cards
Where does air goes after Bronchi and Bronchioles?
Lungs. It occupies most of the thoracic activity and it major organ of respiratory system
23
New cards
Explain the parts of Lungs.
Vertical:
1. Apex: Near the Clavicle (Superior Portion)
2. Base: rests on diaphragm (inferior portion)
Horizontal:
1. Left Lung: Two lobes (because of heart tilted towards left, one lobe is not present)
2. Right Lung: three lobes
\
1. Apex: Near the Clavicle (Superior Portion)
2. Base: rests on diaphragm (inferior portion)
Horizontal:
1. Left Lung: Two lobes (because of heart tilted towards left, one lobe is not present)
2. Right Lung: three lobes
\
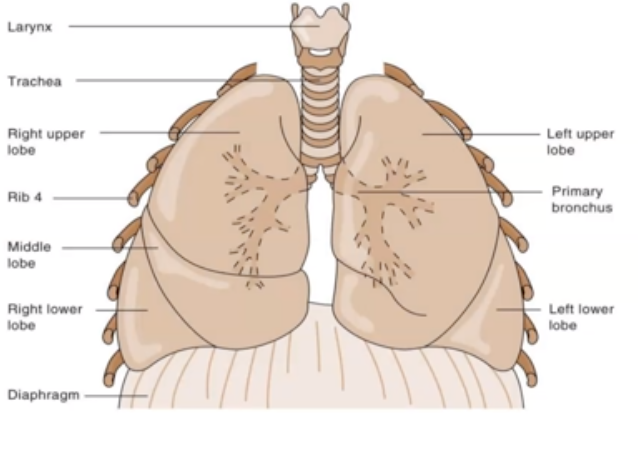
24
New cards
Name and Explain where the air goes after the Lungs?
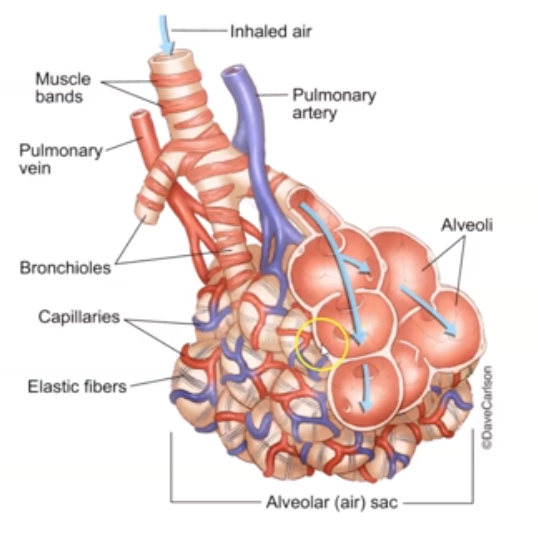
Alveoli. They are Air saces made out of simple squamous tissue that conduct gas exchange.
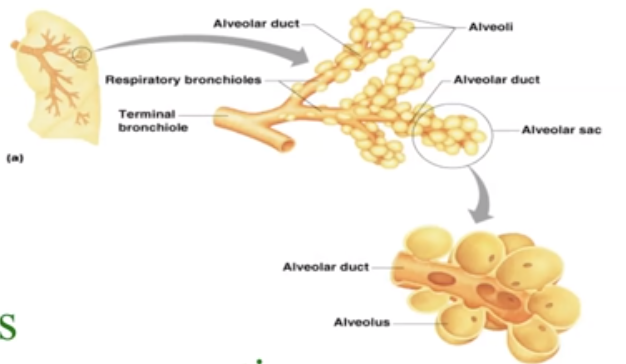
25
New cards
What are the parts of Alveoli?
Not really parts but:
1. ==Pulmonary Capillaries:== cover the external surface of the alveoli.
2. ==Surfactant:== coats the side to prevent closing.
1. ==Pulmonary Capillaries:== cover the external surface of the alveoli.
2. ==Surfactant:== coats the side to prevent closing.