Chapter 5 The Solow Growth Model
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
TERMINOLOGY ONLY
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
what is the principle of Transition Dynamics?
This principle states that the growth rate depends on the distance from the steady state!
For example, if a county is far below its steady state then it will grow faster
if it is closer to the steady state it will grow at a slower rate
in other words, capital accumulation is faster when the gap is large and slows as the economy approaches steady state.
Why do, on average, rich and poor countries grow at similar rates in the real world??
the reason being is that many counties be they rich or poor are already in their steady states
some countries are poor because of low steady state level usually caused by low investment rates and productivity
What are the strengths of the solow model?
the solows model explains what determines a countries long term steady state income (NOT LONG TERM GOWTH)
Using transition dynamics, this concept can help us explain the differences in growth rates
ie: countries further from the steady state grows faster
What are 4 weaknesses of the solows model?
this model focuses on capital, leaving total factor productivity(TFP) unexplained
It doesn’t explain cross country differences in investment or productivity
it assumes that investment rates are fixed, not determined within the model
Like i said within the pros of this model, it DOES LACKS A THEORY OF STSTAINED LONG TERM GROWTH.
What is the solow growth model?
the solows growth model is an extension of the production function with a feature that allows accumulation of capital overtime
(1/5) rewrite solows production function
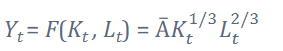
(2/5) rewrite resource constraint

(3/5) rewrite capital accumulation

(4/5) rewrite labor
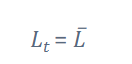
(5/5) rewrite investment and consumption formula