Neuroscience: Membrane Potential, RC Circuit Model, and Time Constants
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Membrane Potential
Difference in electric charge across the neuronal membrane.
Resting membrane potential
Typically ~ -70 mV in neurons.
RC circuit
A neuron can be represented as an RC circuit.
Resistance (R)
Due to membrane + channels.
Capacitance (C)
Due to lipid bilayer.
Battery
Provides a voltage (potential energy source) created by ion gradients (e.g., Na⁺, K⁺).
Capacitor
Stores electrical charge; cell membrane = capacitor.
Capacitance formula
ε = permittivity, A = area, d = thickness.
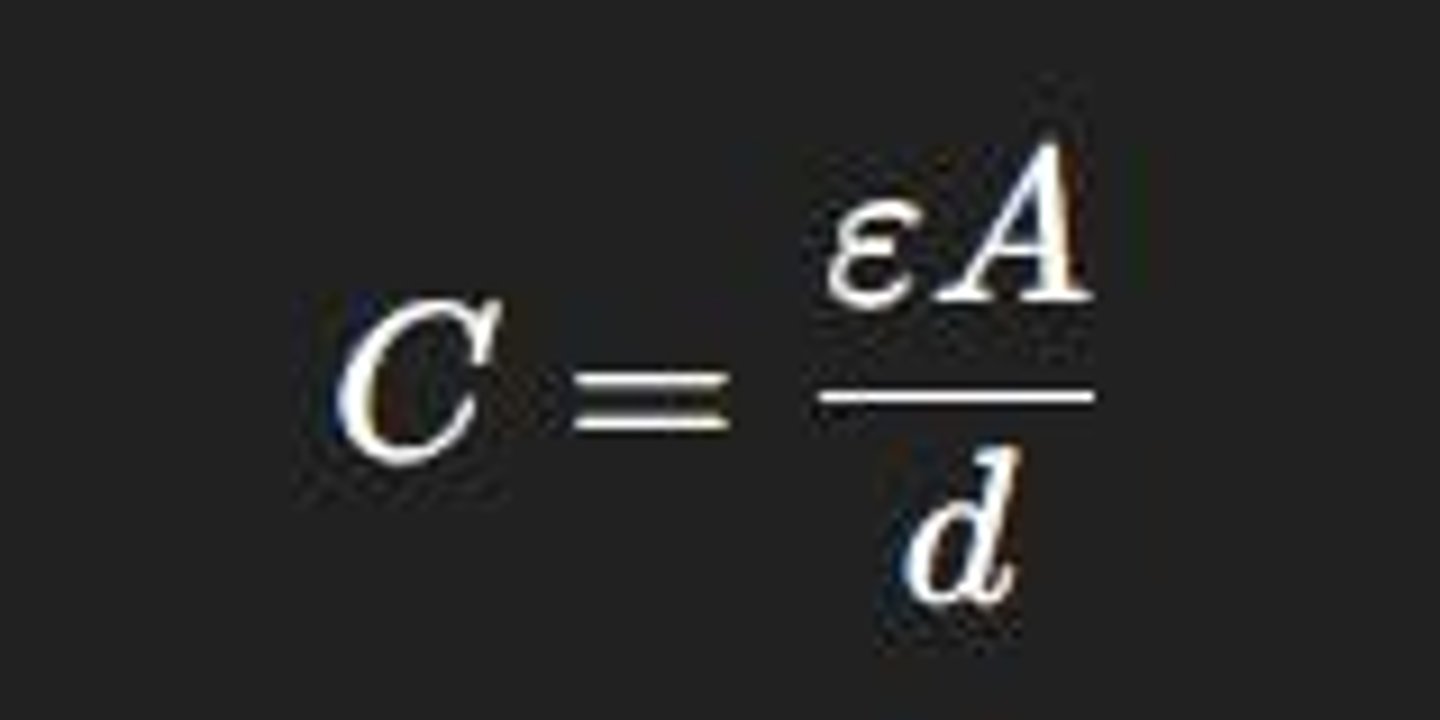
Resistor
Limits current flow; membrane proteins/channels = resistors.
Resistance formula
ρ = resistivity, l = length, A = cross-sectional area.
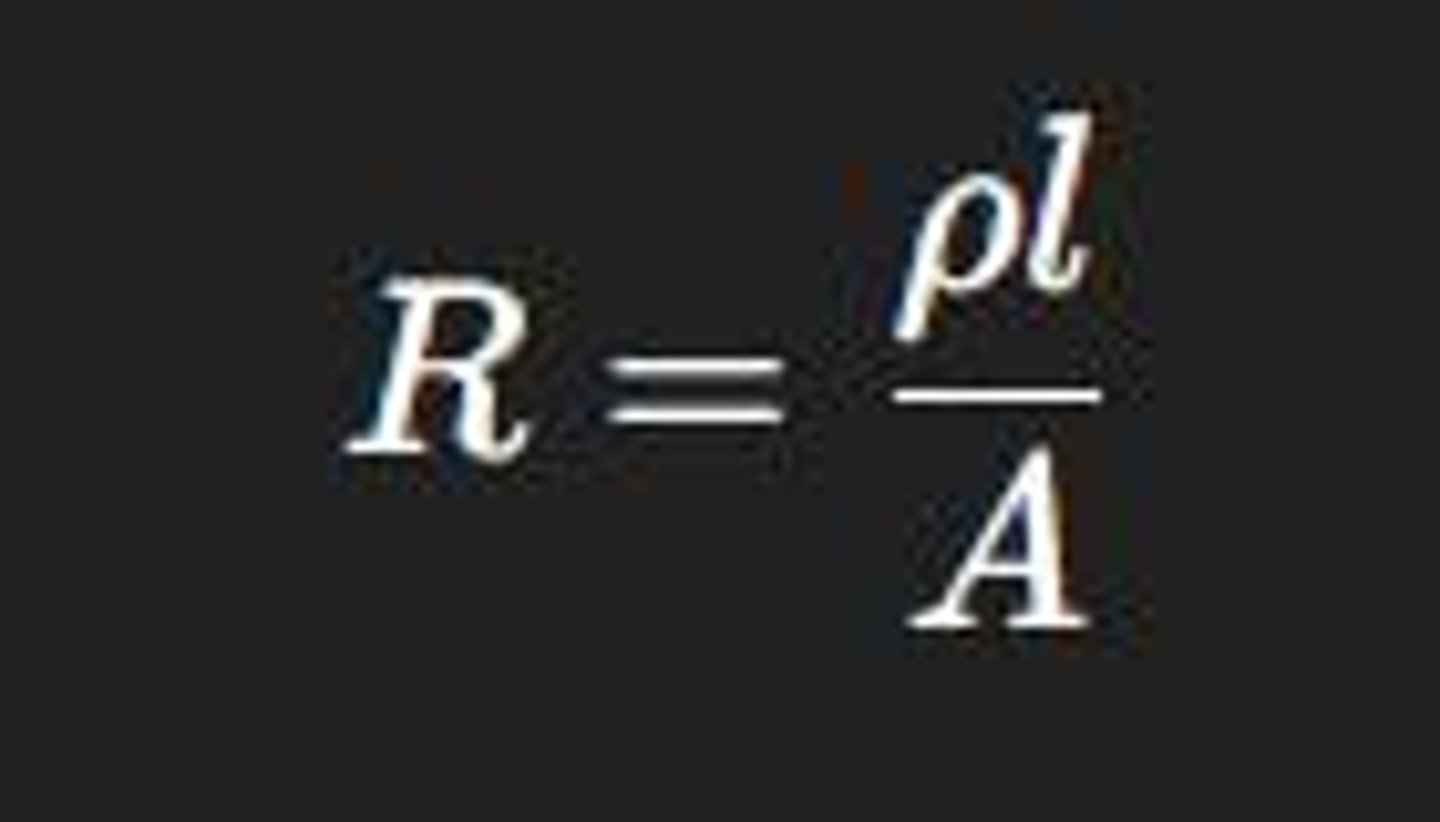
Membrane Resistance
Combined effect of R_lipid bilayer (high resistance) and R_channels (lower resistance).
Time Constant (τ)
Time required for voltage to reach 63% of its final value after a current is injected.
Voltage Change Over Time
Follows an exponential equation.
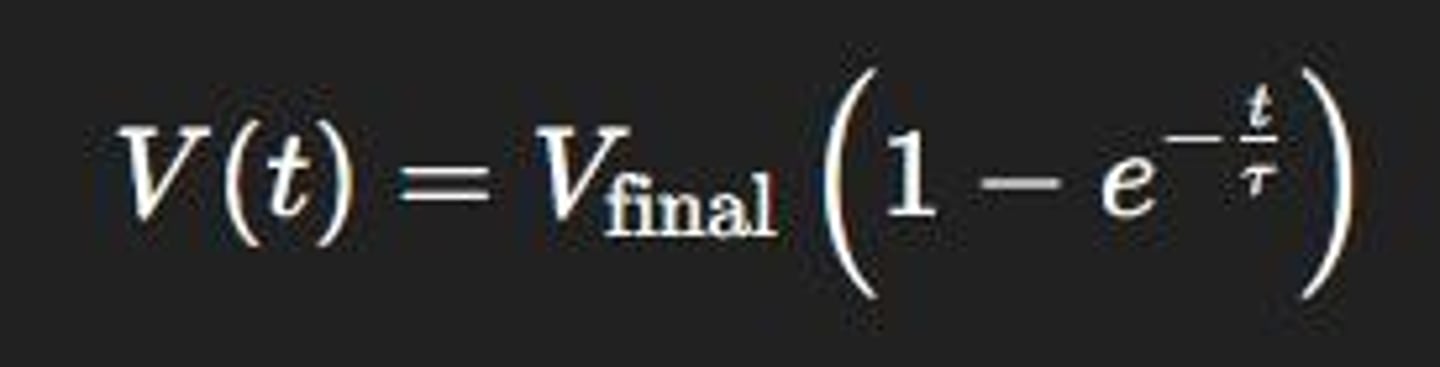
Time Constant Benchmarks
1τ = 63%, 2τ = 85%, 3τ = 95%, 4τ = 98%, 5τ = 99.3%, 6τ = 99.7%.
Smaller τ
Indicates faster response.
Larger τ
Indicates slower response.
Current Injection in Cells
Injecting current changes the voltage across the cell membrane.
Graph Shape
Starts at baseline (V₀), gradually rises to a new steady voltage (V_final).
Voltage Equivalence
V_inside - V_outside = voltage across membrane.
Key Terms to Know
Membrane potential, Capacitor, Resistor, Time constant (τ), Steady-state, RC circuit, Voltage response to current injection.