Cardiovascular and respiratory system
1/145
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Anatomy & Physiology 12
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
146 Terms
Pulmonary circulation
Circulation regulated by the right side of the heart to the lungs with oxygen poor blood
Systemic circulation
Circulation regulated by the left side of the heart where blood from heart goes to the body
Inner layer of the arteries and veins
Layer of artery/vein with endothelium and connective tissue
Middle layer of the arteries and veins
Thickest layer of artery/vein where smooth muscle contract to regulate blood flow and bp. Elastic fibres for expansion but less elastic for veins.
Outer layer of arteries and veins
Layer of artery/vein where there is fibrous connective tissue and becomes loose connective tissue eventually
Arterioles
Smaller arteries that contains endothelium and elastic tissue with smooth muscle with fibres. When contracted, smaller diameter of vasoconstriction and larger diameter for vasodilation.
Vasoconstriction
When arterioles is contracted with increased blood pressure, decreased flow, and decreased heat loss.
Vasodilation
When arterioles is expanded with decreased blood pressure, increased flow, and increased heat loss.
Capillaries
Blood vessel that joins arterioles and venules where there’s thin walls composed only of a single layer of endothelium with a basement membrane. Has spincters.
Veins
Largest are superior vena cava and inferior vena cava. Has valves and carries deoxygenated blood other than pulmonary ____.
Venules
Small veins that drain blood from capillary beds with valves to prevent backflow of blood, akso with 3 layers.
Coronary arteries and veins
Supplies the heart with blood and removes wastes, branch off from the aorta. When blocked, blood cannot reach region of heart tissue and tissue with die.
Artery
Contains 3 layers and is a blood vessel. Largest is the aorta.
Hepatic vein
Vein that drains blood from the liver
Hepatic portain vein
Blood vessel that carries blood from the digestive tract/pancreas to the liver
Renal veins/arteries
Artery/veins of the kidneys
iliac veins/arteries
Arteries/veins for the lower body
Mesenteric arteries/veins
Arteries/veins for the large and small intestine
Carotid artery
Artery on each side of the neck that brings blood to the brain
Jugular vein
Vein that drains blood from the head
Pulse
Expanding and recoiling of an arterial wall that can be felt in any artery, when aorta expands and recoils with ventricular contraction, there are pressure waves in arteries
Blood pressure
Pressure of the blood against wall of a vessel, created by heart pumping. Lower reduces capacity to transport blood, and higher lead to artery weakening & rupturing.
Baroreceptors
Blood pressire receptors in the aorta and carotid arteries sensitive to high blood pressure. SEnds nerve impulse to brain to suppress sympathetic nerve and stimulate parasympathetic nerve. Slows down blood into the arteries.
Sympathetic nerve
Fight or flight nerve that increases nodes activity
Parasympathetic nerve
Nerve that decreases SA & AV node active, extrinsic way to manage heartbeat.
ECG diagram
A graph of voltage versus time graph of the heart. P when atria about to contract, QRS when ventricles about to contract, T when ventrucular muscles recover.
Sphygmanometer
Instrument that measures blood pressure of systolic bp and diastolic bp.
Skeletal muscle contractions
Contractions of the flow of blood in venules and veins
Hypotension
Low bp
Hypertension
High bp associated with cardiovascular dieases caused by diet, stress, and kidney involvement
Atherosclerosis
Plaque buildup due to saturated fats & cholesterol, making arteries narrower. Occurs in coronary arteries, carotid arteries, aorta, and leg arteries. Experience chest pain, stroke, and claudication (limb pain)
Beta-blockers
Treatment for atherosclerosis that prevents stimulation of the autonomic nervous system
Vasodilators
Prevents arteries contricting, treats atherosclerosis
Diuretics
Causes kidney to excrete excess salts and fluids, treats atherosclerosis
Arteriosclerosis
Natural hardening throughout the artery system due to aging
Stroke
When a portion of the brain dies due to lack of oxygen when arteriole bursts (aneurysm) or blocked by an embolism (blockage-clot, fat, air bubble). Causes death or paralysis. Feeds numbness in hands/faces, difficulty in speaking, temporary blindness in one eye. Women has nausea and general weakness.
Heart attack
When heart dies due to lack of oxygen, victim has angina pectoris (pain in the left arm), and death may result. There is chest discomfort, upper body discomfort, shortness of breath, sweating, nausea, and light-headedness. For women, no chest pressure.
Erythropoietin
Hormone that speeds up maturation of RBC in bone marrow
Thrombus
Stationary clot attached to the arterial wall
Embolus
When thrombus becomes dislodged and moves along the blood, get stuck in narrow vessel and block flow of blood
Phlebitis
Inflammation of a vein, blood may clot. If embolism winds up in a pulmonary arteriole, blocking lungs, pulmonary embolism (can kill)
Varicose veins
Abnormal and irregular dilations in superficial veins in lower legs, vales weak and ineffective due to backward pressure. In rectum are called hemorrhoids
Plasma
Liquid portion of blood (55%), contains nutruents, saltsm repiratory gases, wastes, hormones, blood proteins
Cellular components
Component of blood that is not plasma, containing erythrocytes, leukocytes, and platelets
Erythrocytes
Red blood cells that carries oxygen, main component is hemoglobin. Made from stem cells in bone marrow that lost nuclei and organelles. Makes energy using anaerobic glycolysis which breaks down glucose without oxygen.
Macrophages
A type of white blood cell that surrounds and kills microorganisms, removes dead cells, and stimulates the action of other immune system cells. Eats erythrocytes through phagocytosis
Anemia
Insufficient number of RBC and causes kidneys to release hormone erythropoietin
Leukocytes
WBC that are made from stem cells in bone marrow, larger than RBC, and increase when fighting infection. Has three types.
Granular leukocyte
A type of WBC that plays a key role in inflammation, allergic reaction, pus, and destruct bacteria and parasites.
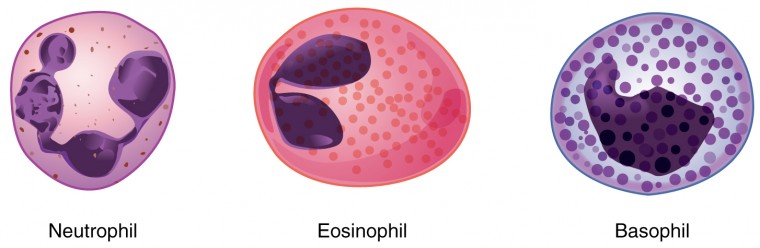
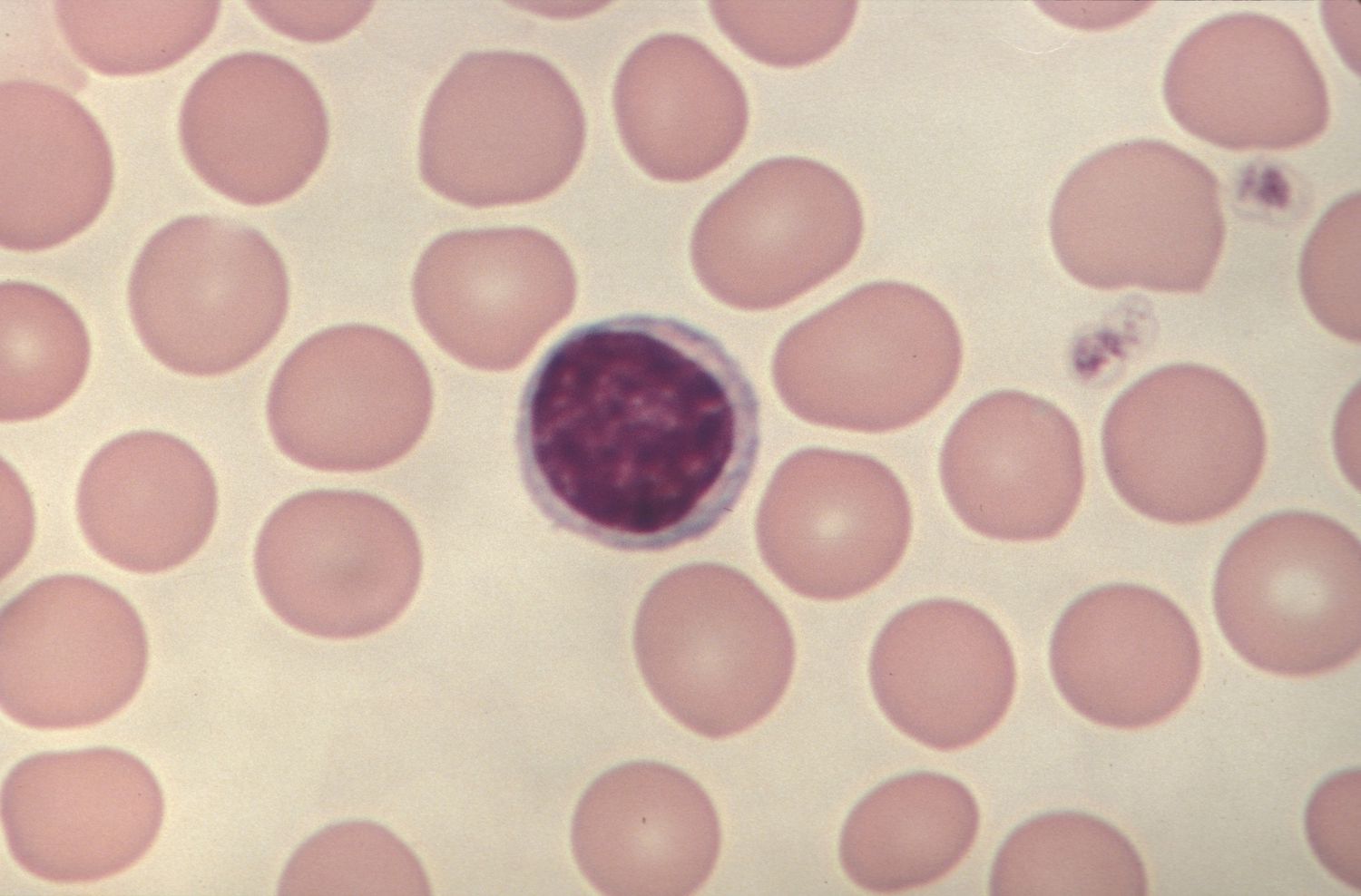
Neutrophils
A type of granular leukocyte that is the most abundant and uses phagocytosis
Basophils
A type of granular leukocyte that releases histamine
Eosinophils
A type of granular leukocyte that fihts parasitic worms
Lymphocytes
A type of leukocyte that contains B cell & T cell in immune response, made in lymph nodes, tonsils, spleen, etc. Produces antibodies, a type of agranular leukocyte.
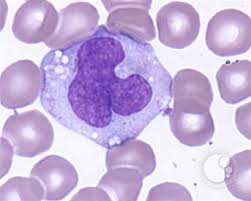
Monocytes
A type of leukocyte that mature into macrophages in body tissues, phagocytize foreign matter and organisms such as bacteria
Thrombocytes
Platelets which are cell fragments formed in bone marrow of fragmentation of large cells megakaryocytes. LAck nucleu and function in clot formation to stop bleeding.
Blood typing
Type of blood based on polysaccharides on the membrane of the erythrocyte. Attached to proteins and lipids in the membrane to trigger antigens. Extract antibody in blood and mix. Extract antobodies in blood and mix with anti-A / anti-B antibodies. If anti-A antibody clump, type A. Neither, O. If anti-D clump, positive.
Antigens
On ethryrocytes to help identify the type
Antibody
Found in plasma, not the antigen type and attacks those that foreign to the bodu. It is produced by white blood cell and bind to foreign antigens.
Agglutination
The clumping of particles, often cells or microorganisms, due to a specific interaction like an antibody binding to an antigen
RH system
A system to determine if someone has this antigen (positive) or not (negative).
Erythroblastosis fetalis
When erythrocytes of fetus is attacked by immune system of mom due to her having RH - and the body having RH + (2nd child)
Rhogam
A vaccine to prevent anti-RH antibody produced by the mother, contains anti-Rh antibody that attacks RH antigen. Given close to birth.
Arterial water exchange
As blood pressure is higher than osmotic pressure, water will leave the bloodstream through the capillaries
Venous water exchange
As blood pressure is lower than osmotic pressure, water will enter the bloodstream through the capillaries
Blood to cell at capillaries
Includes oxygen, glucose, amino acid, and nutrients
Cell to blood at capillaries
Includes carbon dioxide, urea, and waste
Lymphatic capillaries
Something that absorbs excess tissue fluid when some plasma don’t enter the veins again
Blood clotting/coagulation
Occurs when injury happens to maintain homeostasis. When blood changes from a liquid to a gel.
Prothrombin
Globulins manufactured and deposited in the blood by the liver where vitamin K is necessary and is necessary for clotting.
Fibrinogen
Globulins manufactured and deposited in the blood by the liver, necessary for clotting
Thromboplastin
Enzyme released by damaged cells that react with thrombocytes to form active plasma thromboplastin
active plasma thromboplastin
Prothrombin activator that reacts with prothrombin to form enzyme thrombin, requires calcium ions
Thrombin
Enzyme that severs two short amino acid chains from fibrinogen molecule
Fibrin
When fibrinogen molecule gets severed by thrombin
Fibrin fragments
Multiple fibrin joined together to form a fibre network for blood clot
Plasmin
When blood vessel repair initiates and this enzyme destroys the fibrin network and restores the fluidity of the plasma
Hemophilia
A blood clotting disorder that bleeds joints
Inflammatory reaction
Something that happens when skin is broken due to a minor injury, characterized by swelling and reddening at site of injury
Mast cell
A type of white blood cell found in connective tissue that plays a role in immune and allergic reaction
Bradykinins
A peptide that plays a key role in inflammation, blood pressure regulation, and pain perception
Pus
When neutrophils die when overcoming infection along with dead tissue, cells, bacteria, and white living cells
Breathing
Movement of air in and out of lungs
Respiration
All the processes involved in the exchange of gases between environment and cells of the body
Internal respiration
oxygen and carbon dioxide between blood and tissue fluid
Cellular respiration
When cells produce ATP in mitochondria that requires oxygen gas and releases carbon dioxide
Cilia
Traps dust and debris in nose cavities. In trachea, bent upward to move up mucus or other bad things inhaled. Some cells on top of nasal cavities are scent receptors
Glottis
The opening to the larynx is open
Vocal cords
Elastic ligaments that stretch from the back to the front of the larynx just at side of glottis, protected by cartilage (Adam’s apple). Vibrate when exposed to air and produces sound
Pitch
Depends on the length, thickness, and degree of elasticity and tension for sound
Trachea
Held open by cartilaginous rings and lined with ciliated mucous membranes
Epithelial tissue
Encloses the alveolar sac for easuer gas exchange
Lipoprotein
A film to prevent alveoli from collapsing and sticking together
Thoracic cavity
The space within the chest that houses vital organs and structures, including the heart, lungs, esophagus, trachea, thymus, and major blood vessels. It is enclosed by the ribcage, spine, and diaphragm.
Diaphragm
A thick dome shaped muscle that powers breathing
Pleural membranes
Encloses the lungs where one lines the chest and one lines the lung. In between has fluid for an air-tight seal.
Negative pressure
Power breathing as oxygen and carbon dioxide move from high pressure to low pressure
Pleural pressure
Pressure inside the lungs
Atmospheric pressure
Pressure outside in the environment
External intercostal muscles
When diaphragm contracts and move down, it contracts too by pulling ribs up and out to increase space in thoracic cavity when breathing in. Relaxes when breathing in.
Internal intercostal muscle
Does not move unless strenuous exercise that pulls rib cage down. Beneath the external intercostal muscle.