Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
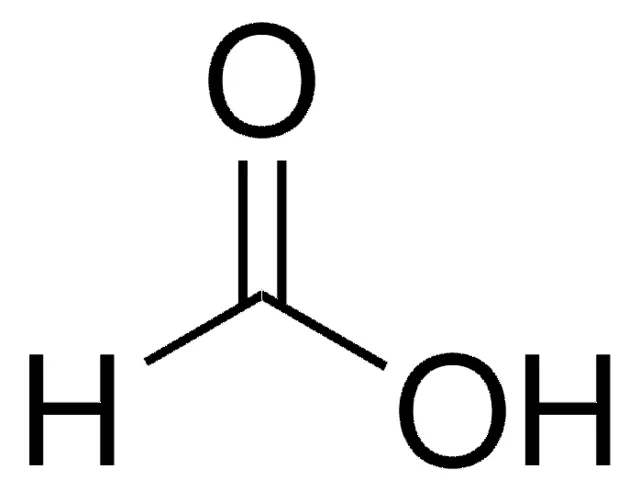
What is the name of the carboxylic acid shown?
Formic acid.
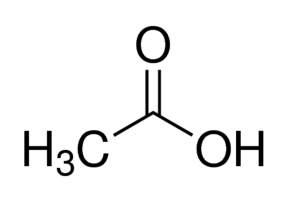
What is the name of the carboxylic acid shown?
Acetic acid.
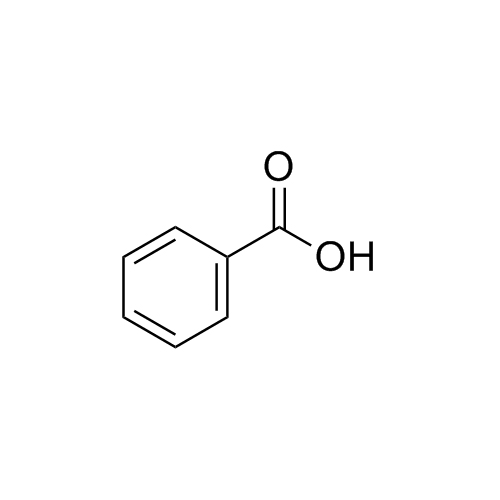
What is the name of the carboxylic acid shown?
Benzoic acid.
What are the IUPAC rules for naming a carboxylic acid?
Find the longest chain containing the carboxyl group, and change the corresponding alkane name to one containing the suffix -oic acid (ex. butane to butanoic acid).
Consider the carboxyl carbon to be position one for numbering purposes.
Name carboxylic acids where the carboxyl group is directly attached to a benzene ring as derivatives of benzoic acid.
True or False: Carboxylic acids have higher IUPAC naming priority than alcohols.
True. Carboxylic acids are considered higher naming priority than alcohols.
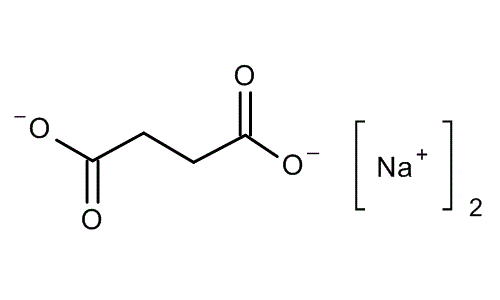
What is the name of the carboxylate salt shown?
Sodium succinate.
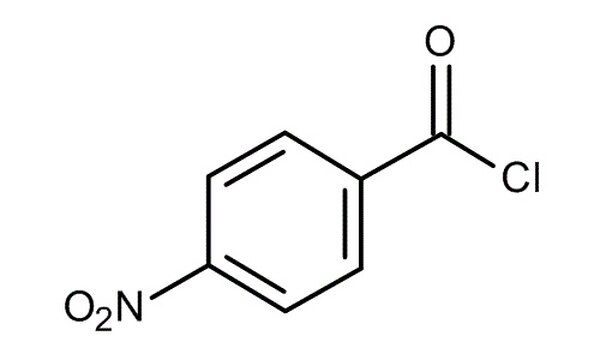
What is the name of the acid chloride shown? Provide reasoning for why the name is considered proper by IUPAC rules.
The acid chloride is p-nitrobenzoyl chloride.
The correct suffix for naming acid chlorides is -oyl chloride, and the substituent group is a nitro group located in the para position, denoted by the ‘p’ prefix.
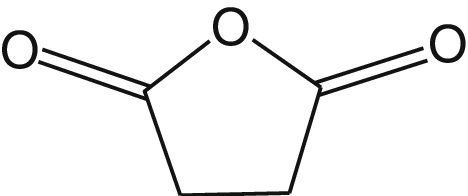
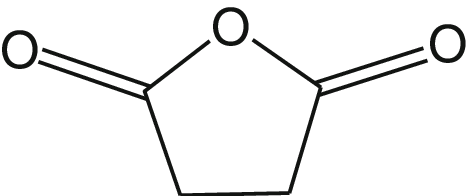
What is the name of the acid anhydride shown?
Succinic anhydride.
What are the IUPAC rules for naming esters?
Locate the part of the ester that used to belong to an alcohol, then name that section as an alkyl group.
Locate the part of the ester that used to be the carboxylic acid (with the double-bonded O), and name it with the suffix -ate.
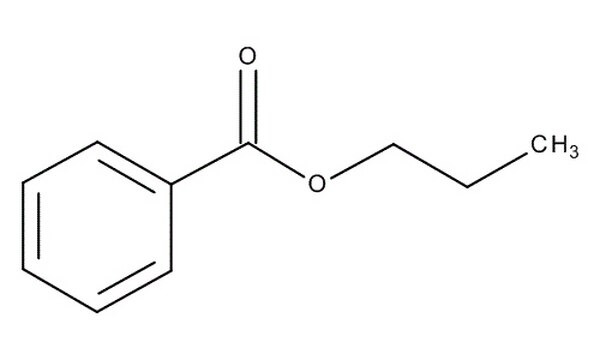
What is the name of the ester shown?
Propyl benzoate.
What are the IUPAC rules for naming amides?
Any substituent groups on the nitrogen atom are first given as alkyl or aryl groups with the prefix N.
The suffix used to denote the rest of the structure (named using the longest continuous carbon chain containing the nitrogen) is -amide.
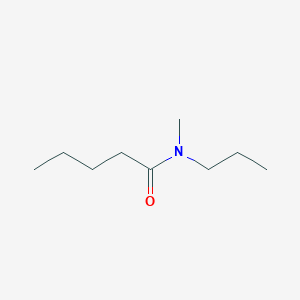
What is the name of the amide shown?
N-methyl-N-propylpentanamide.
What are the IUPAC rules for naming nitriles?
Find the longest chain containing the nitrile group, and name according to the corresponding alkane name.
Add the suffix -nitrile to the end.
True or False: Carboxylic acids have lower boiling points than esters.
False.
Carboxylic acids have higher boiling points than esters, due to their tendency to form dimers connected by strong hydrogen bonds, effectively doubling their molecular weight and increasing their boiling point.
Why do primary and secondary amides have higher boiling points than tertiary amides?
Because primary and secondary amides have hydrogens attached to their nitrogens, and thus have the ability to hydrogen bond in order to increase their intermolecular associations, while tertiary amides do not.
What reactants can be used to produce benzoic acid?
By using hot KMnO4 in basic conditions (NaOH), with a second step addition of H3O+, benzoic acid can be formed from any carbon-based substituent off of a benzene ring.
What method and set of reactants forms a carboxylic acid from a primary alcohol?
The Jones Oxidation, performed by using H2CrO4 and acetone.
How can nitriles be used to form a carboxylic acid?
Via hydrolysis, in which water is added to a nitrile under basic conditions to yield a partial hydrolysis to an amide, then water and heat are added under acidic condition to yield a carboxylic acid.
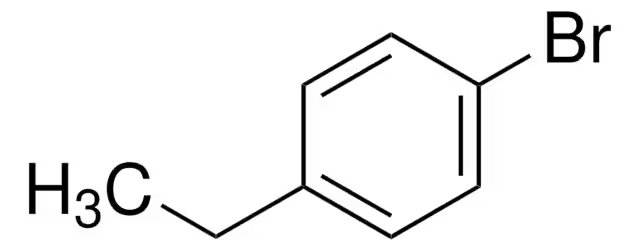
What reactants can be used to form a carboxylic acid from the structure shown? Explain the reasoning behind the reactants used.
1.) Magnesium metal.
2.) CO2
3.) H3O+
The use of magnesium metal converts the alkyl halide into a Grignard reagent. Then, the addition of CO2 allows the structure to be converted to a carboxylate ion. Finally, the addition of H3O+ protonates the oxygen to yield a carboxylic acid.
What reactants can be used to form an acid chloride?
SOCl3, PCl3, or PCl5. All can be used to form an acid chloride from a carboxylic acid, albeit with different byproducts.
How can an acid chloride be reverted to a carboxylic acid?
Through the addition of water in acidic conditions.
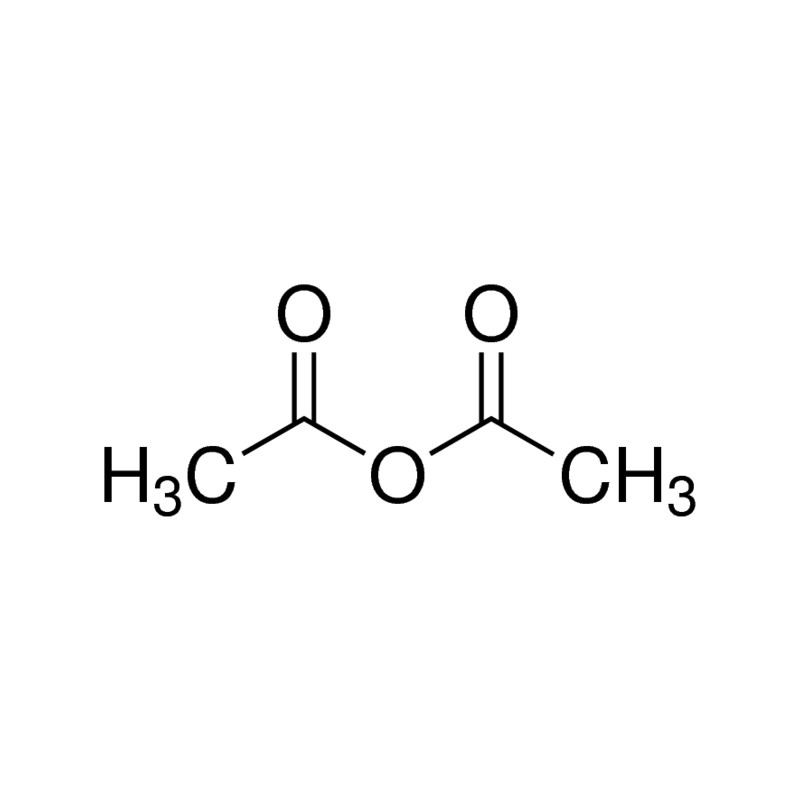
How is this structure formed?
Through the addition of acetyl chloride to acetic acid, in the presence of a weak base.
What reactants are used to form an ester from an acid chloride?
An alcohol in the presence of a weak base.
Can a tertiary amine be used to form an amide from an acid chloride?
No, since a tertiary amine cannot be deprotonated, as it has three ‘R’ group substituents attached to it.
How can a carboxylic acid be formed from an acid anhydride?
Through the addition of water.
True or False: Acid anhydrides have significantly different reactivity than acid chlorides.
False.
Acid anhydrides have very similar reactivity to acid chlorides, and in fact produce the same structures (esters and amides) as them when mixed with the same reactants.
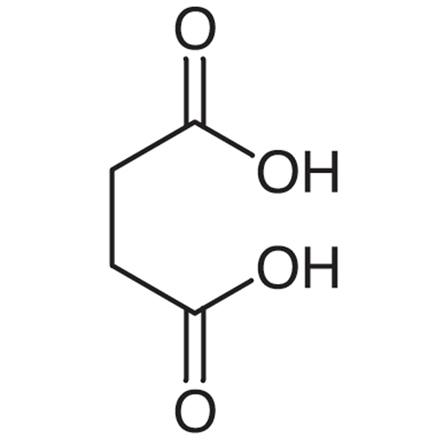
How can this structure be formed from a dicarboxylic acid? What is the main byproduct of this reaction?
Through the addition of heat, which drives off water from the structure of succinic acid.
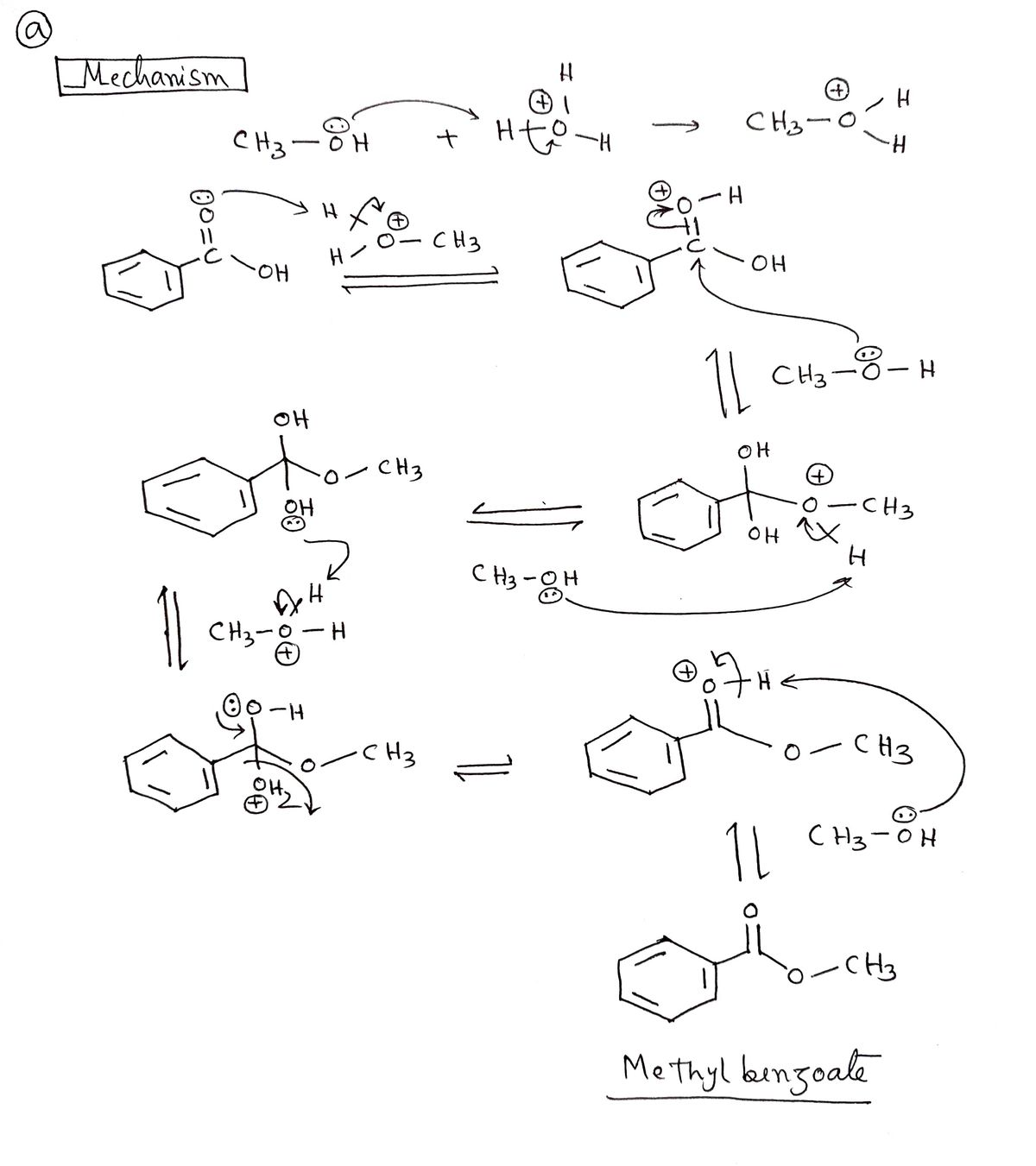
What is the name of the mechanism shown?
Fischer esterification.
What reactants are necessary for a Fischer esterification to take place?
A carboxylic acid combined with an alcohol, in the presence of a catalytic acid (HCl or H2SO4) with the addition of heat.
What is saponification?
The base-mediated cleavage of esters, in which NaOH is added to an ester to yield a carboxylate salt.
What reactants are required for a saponification reaction to take place?
1.) A strong acid (NaOH)
2.) H3O+
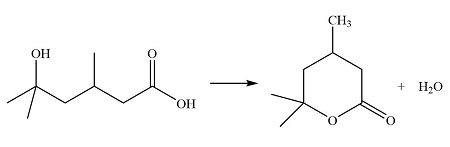
What is a lactone?
An ester formed from a compound that contains both an alcohol and a carboxylic acid in the same molecule, forming a cyclic ester.
Why are two equivalents of an amine used to form an amide via an acid chloride or acid anhydride?
One amine is used to form the bond to the central carbon, while the other acts as a base to accept the bonded amine’s lost proton.
Why is peptide synthesis not a commonly used method of amide formation?
Because it requires the use of DCC, a reactant that can cause severe allergic reactions.
True or False: Amides can be hydrolyzed under acidic or basic conditions.
True.
Amides can be hydrolyzed under acidic or basic conditions, though acidic conditions are typically more commonly applied.
What term is used to describe the cyclic counterparts of amides?
The cyclic counterparts of amides are known as lactams.