human physiology exam 1 (chapters 1-6)
1/179
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
180 Terms
physiology
the study of functions of living things
homeostasis
maintaining a relatively stable internal environment
first step of scientific method
make observations
negative feedback loop
change in a human condition(variable) leads to a response which COUNTERACTS that change (ex. body gets too cold, so shiver to warm up)
positive feedback loop
change in a condition leads to a response which amplifies change (ex. giving birth(oxytocin), ovulation, blood clot)
dynamic constancy
variables always changing
intrinsic maintenance of homeostasis
cells within the organ sense a change and signal neighboring cells to respond appropriatly (self advocate)
extrinsic maintenance of homeostasis
outside of organ (something else is monitoring)
skeletal muscle
striated, multinucleated, voluntary
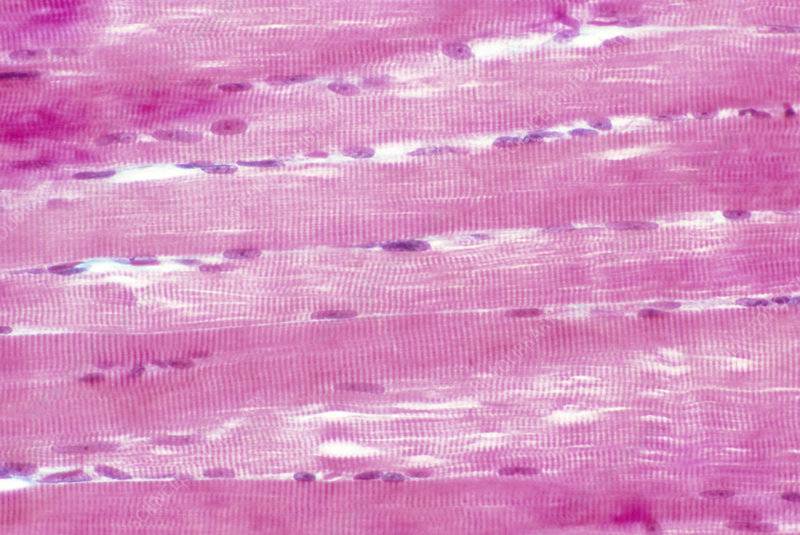
smooth muscle
no striations, involuntary (found in organs)
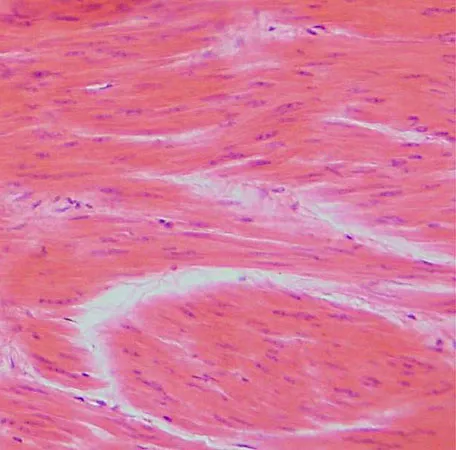
cardiac muscle
striated, involuntary, heart muscle
neurons
high speed communication via electrical signals
neuroglua
support of neurons (maintain environment)
epithelial tissue
cover body surfaces, lines organs and tracts
connective tissue
connection, structure, support, transportation
adipose tissue
large cells (adiposites) most of interior occupied by a droplet of triglycerides
cartilage
cells found in small cavities (lacunae) in the matrix
organ
two or more primary tissues that fuction together to perform fuction
totipotent stem cells
can become any cell or placenta
pluripotent
can become any cell but NOT placenta
multipotent
can only become organ it is specialized for
adult stem cells
undifferentiated cells found in some organs, maintain and repair tissue
intracellular fluid
area inside the cell
extracellular fluid
outside the cell, made up of plasma (blood) and interstisial (between cells)
covalent
SHARING electrons, strongest bond
nonpolar covalent bond
atoms share electrons EQUALLY
polar covalent bond
unequal shaeing of electrons, unequal charge bwteen regions
ionic bond
one atoms GIVES elecrons to another , have strong electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions
cations
positively charged ion
anions
negatively charged ion
hydrogen bond
weak attraction between polar molecules (opposites attract)
polar molecules (hydrophobic or hydrophilic)
hydrophilic (water soluble)
nonpolar molecules (hydrophobic or hydrophilic)
hydrophobic (water insoluble)
carbohydrates (sugars)
major source of energy in the body
monosaccharides
basic unit, one carbon ring
disaccharide
two monosaccharides joined by COVALENT bond
polysaccharides
many glucose molecules strung together, stored as glycogen, starch, fiber
triglycerides
3 fatty acids and a glycero backbone
saturated fatty acids
every carbon is fully bonded with hydrogrens
unsaturated
not all carbons fully bonded to hydrogens, some (c=c) double bonds
phospholipids
contain phosphate group instead of third fatty acid (ampipathic)
ampipathic
posses both polar (head) and nonpolar (tail) ends
cholesterol
needed to synthesize hormones, regulate cell membrane rigidity
corticsteroids
hormone produced by adrenal (above the kidneys) glands
sex steroids
hormones produced by gonads
prostaglandins
signaling, circulates to tell parts of the body what to do (inflammation, ovulation)
peptide bond
covalent bond linking carboxyl group of one AA to amino group of the next
polypeptide
molecule consisting of many joined amino acids
glycoprotein
protein + carbohydrate
lipoprotein
protein +lipid (carrier molecule in the blood)
HDL
"good" removed fat from blood
LDL
"bad" contributes to clogging arteries
enzymes
proteins that speed up reactions by lowering activation energy
peripheral proteins
"doorway" inside OR outside the cell, help get messages across if theyre polar
integral proteins
integrated into membrane, pathway to get THROUGH
selective barrier
nonpolar molecules can freely move in/out by themselves
endocytosis
invagination of plasma membrane to pull materials into the cell
phagocytosis
cell extends pseudopods to "pacman" eat a SPECIFIC pathogen
pinocytosis
a cell takes a RANDOM "gulp" of extracellular fluid
exocytosis
merging of vesicle with plasma membrane (get something OUT)
cilia
hair-like structures that "beat" into the extracellular fluid for movement
flagella
tail on sprem
microvilli
small finger-like projections that increase surface area for more absorbtion
cytoskeleton
framwork of cell, microtubules (railway) and microfilaments
lysosomes
break down large molecules, contain digestive enzymes
autophagy
self distruction of cell, (cancer if doesnt work)
genetic disorders
body doesnt make a specific protein
peroxisomes
oxidative reactions, contain hydrogen peroxide, breakdown of fatty acids
mitochondria
double membrane (electron transport train occurs on inner membrane), possess own dna
ribosomes
use mRNA to make amino acid chains
SMOOTH endoplamic reticulum (SER)
synthesis of steroids, storage of calcium in skeletal muscles
ROUGH endoplasmic reticulum (RER)
modifies proteins with the help of ribosomes (help with protein modification)
golgi complex
shipping, made of cisternae
first 30 amino acids
hydrophobic and attracted to membrane of rough er (later taken to the lysosome)
chromatin
state of chromosomes when not dividing, spaghetti, makes it easier to find instructions
genes
sequence of DNA containing info needed to make proteins, "snippets" encode for more than one protein
chromosome
tightly coiled DNA containing genes
genome
all the genes in the human body
proteome
all the proteins produced in the human body
transcription
using dna to make rna in the nucleus
translation
synthesize of proteins, occurs in cytoplasm
replication
making a copy of DNA (for new cell) in mitosis
promoter region
attracts molecules to site
rna polymerase
"unzips" DNA
splicing
slicing of mRNA so initil is not the same as final
introns
sections to take out in splicing
exons
sections that remain after splicing to be put back together
semi-conservative
in DNA synthesis, conserving old strand
interphase
growth, DNA replication, growth
prophase
DNA forms chromosomes
metaphase
spindle fibers line up
anaphase
pull apart of fibers
telophase/cytokinesis
divide
humans have __ pairs of chromosomes
23
autosomes
code for traits
homologous chromosomes
each chromosome in a pair have the same things on them, but not same DNA, one becomes dominant
meiosis
two times cell division, produces four "half" cells
necrosis
pathological cell death (shouldn't happen), damages adjacent cells
apoptosis
programed cell death (lysosome and perozisome bursts inside cell)
hyperplasia
increase in number of cells