VETM*4490: Derm Path
1/186
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
187 Terms
3 general components of 'skin'
• epidermis
• dermis
• adnexa
cells of the epidermis = ...?
keratinocytes
(basal, spinous, granular, squamous types)
type of keratinocytes in the stratum corneum
squamous (corneocytes)
type of keratinocytes in the stratum granulosum
granular
type of keratinocytes in the stratum spinosum
spinous
type of keratinocytes in the stratum basale
basal cells
structures that hold spinosal keratinocytes in the stratum spinosum together
desmosomes
structures that anchor basal cells in the stratum basale to the dermis
hemisdesmosomes
"desmo-" in desmosome means...?
ligament
difference between cornification vs. keratinization
same thing
granular keratinocytes in the stratum granulosum have ____________ granules
keratohyaline
general term for thickening of the stratum corneum
hyperkeratosis
what are the 3 histologically recognized layers of the stratum corneum
• basket weave layer
• compact keratin layer
• nucleated cells
significance of finding basket weave hyperkeratosis on histology
means it was stimulated to thicken but no trauma (wasn't scratched off)
significance of finding compact hyperkeratosis on histology
means the basket weave layer was either removed or did not develop (most commonly scratching b/c pruritis)
term for incr. nucleated corneocytes in the stratum corneum
parakeratosis
(a.k.a. parakeratotic hyperkeratosis)
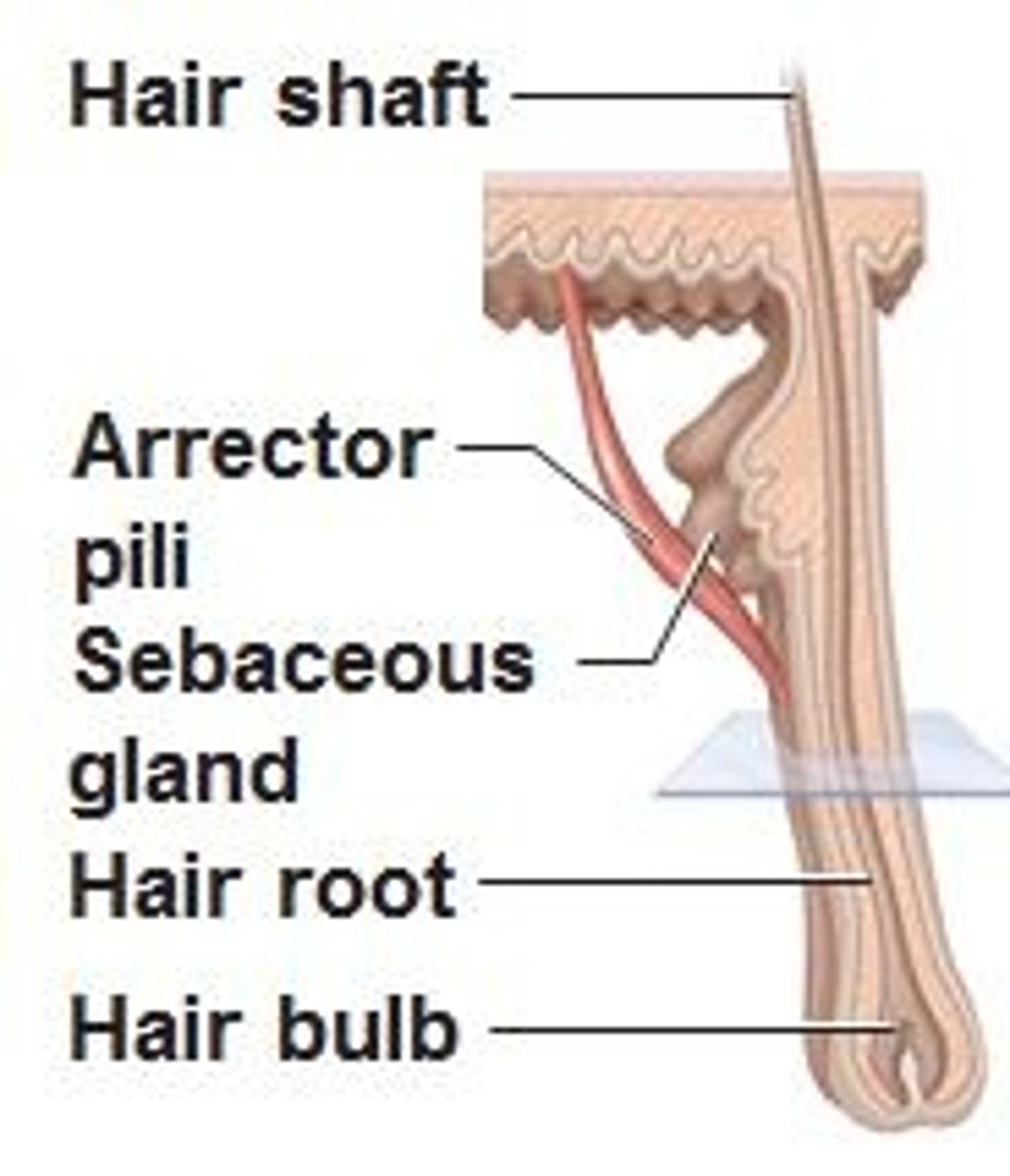
where does the arrector pili muscle insert on the hair follicle
isthmus; deeper than the sebaceous gland
the stratum corneum is generally how many cell layers
20
general response of epidermis to injury
hyperplasia
term for hyperplasia of the stratum granulosum
hypergranulosis
term for hyperplasia of the stratum spinosum
acanthosis
term for hyperplasia of the stratum basale
basal cell hyperplasia
product of the sebaceous gland & its function
sebum -> contributes to lipid barrier
the isthmus of a hair follicle extends from __________ to __________ histologically
sebaceous gland to arrector pili muscle attachment site
components of the dermis
• CT (collagen, elastin)
• blood vessels
• nerves
• lymphatics
non-neoplastic skin masses
• cysts
• hamartomas
• misc
definition of a cyst
cavity lined by epithelium
definition of a hamartoma
excessive normal tissue in a location where it is normally found (usually fibroadnexal)
types of cysts
• follicular (infundibular, isthmus, panfollicular)
• glandular (sebaceous duct, sweat glands)
epidermal neoplasms that can arise from spinous keratinocytes
• acanthoma
• squamous cell carcinoma in situ
• squamous cell carcinoma (SCC)
epithelial neoplasms that can arise from basal keratinocytes
• basal cell tumour
• basal cell carcinoma
the prefix "acantho-" means...?
spiny
epithelial neoplasms that arise from a combination of epidermal cell types
• papilloma
• basosquamous tumour
• basosquamous carcinoma
the prefix "kerato-" means...?
keratin-producing
the suffix "-blastoma" means...?
adult stem cell tumour
how common are trichoepitheliomas? Are they benign or malignant?
very common, benign
list 3 general tumour types of the sebaceous gland
• adenoma
• epithelioma
• carcinoma
list 2 general tumour types of sweat glands
• adenoma
• carcinoma
prefixes that refer to the dermis & subcutaneous CT?
fibro-
myxo-
the prefix "rhabdomyo-" refers to...?
skeletal muscle
mesenchymal (stromal) tumours of skin are usually:
a) benign
b) infiltrative w/o metastasizing
c) infiltrative w/ mets
d) highly variable
a) benign
b) infiltrative w/o metastasizing
c) infiltrative w/ mets
d) highly variable
round cell tumours [5]
• histiocytic
• mast cell tumour
• plasmacytoma
• lymphoma
• TVT
the _____________ are referred to as "hepatoid glands"
perianal
3 general tumour types of perianal glands
• adenoma
• epithelioma
• carcinoma
is the metastatic rate of apocrine adenocarcinomas of the apocrine gland of the anal sac high or low
high
differentials for nailbed mass
• inclusion cyst
• keratoacanthoma
• SCC
• osteosarcoma
• malignant melanoma
how many biopsies should you take when doing skin biopsies
6 = good
3 = minimum
(taken from multiple sites from a range of lesions)
how to prep a skin site for biopsy
• don't surgically prep the biopsy site
• include scale and crust
• don't clip the hair completely off (they section along the hair)
instruments to use for skin biopsy
1. Baker skin punch:
6mm usually
3mm for delicate sites
2. Scalpel -> wedge/ excisional biopsy for large lesions
where to take skin biopsies for the following lesions:
a) pruritis or scales
b) crusts
c) nodules
d) ulceration
e) alopecia
a) pruritis or scales: range of affected areas
b) crusts: pustules, vesicles, new lesions, crusts
c) nodules: incisional biospy
d) ulceration: edge of lesion, vesicles
e) alopecia: severe & less severely affected areas
when are derm cases good candidates for biopsy?
• clinical work-up unsuccessful
• clinical features of immune-mediated disease or other diseases where biopsy confirmation is necessary
• no response to apparently appropriate therapy
• anything really unusual or serious (ex. hyphomycosis, pustular demodicosis)
information to include when sending skin biopsies to derm pathologist
• full signalment -breed, age, sex
• history - duration, major clinical issues, previous workup & response, other test results
• description of lesions - correct terminology, distribution, pruritus scale, pictures
• attempted treatments & results - esp. Abx, parasite Tx, steroids
• your DDx - preferably ranked
3 parts of a derm path report
• description of microscopic lesions
• diagnosis
• comment
name of the C fibre nerves that extend into the epidermis and transmit 'itch signals'
intraepidermal nerve fibres (IENF)
how are intraepidermal nerve fibres (IENF) stimulated
• directly (ex. traumatic neuroma, nerve sheath tumour, dry skin, intradermal lymphocytes)
• chemical mediators
• keratinocyte products (cytokines)
how can superficial pyoderma result from pruritus
itchy -> scratch off stratum corneum -> reduced barrier function -> superficial infection
deepest layers of epidermis removed in 'hot spot' (superficial spreading pyoderma)
stratum basale & spinosum
how can pruritus cause alopecia
scratching, chewing, etc. -> hair breakage
examples of chemical mediators that stimulate IENF (-> pruritus)
• insect bite (venom = vasoactive amines - histamine & serotonin)
• mast cell degranulation (d/t scratching, IgE mediated -> type I hypersensitivity)
how can histamine result in:
a) erythema
b) wheals
a) erythema: vasodilation -> hyperemia
b) wheals: incr permeability -> edema
most common & least specific derm pattern
perivascular dermatitis
"acral" refers to...?
peripheral
what are 'actinic' effects
effects from sun rays
how does low humidity result in pruritus
dry skin -> direct stimulation of IENFs
how does epitheliotrophic lymphoma cause pruritus
the neoplasic intraepidermal lymphocytes directly stimulate the IENF
why do insect bites cause pruritus
the venom = vasoactive amines (histamine, serotonin) -> chemical mediators, stimulation of IENF
Medical treatments for pruritus that target chemical mediators
• antihistamines
• corticosteroids
• cyclosporine
• oclacitinib (Apoquel)
• caninized monoclonal Ab against IL-31 (Cytopoint)
histo term for erythema (reddening of skin)
vascular dilation
(often with endothelial hypertrophy)
define hives
a.k.a. wheals
= transient sharply circumscribed raised lesions resulting from dermal edema
histo term for wheal
dermal edema
outcomes/ sequelae of pruritus
• self trauma & reduced barrier function -> scaling, ulceration, alopecia, actinic effects, pyoderma
• perivascular dermatitis (PVD)
histo patterns seen with perivascular dermatitis
epidermis:
• compact hyperkeratosis
• hypergranulosis
• acanthosis
dermis:
• vascular dilation
• edema
• endothelial hypertrophy
cell type expected in perivascular dermatitis (PVD) due to cutaneous adverse food reaction (CAFR; food allergy)?
a) cell-poor
b) eosinophilic
c) neutrophlic
d) lymphocytic
e) histiocytic
a) cell-poor
b) eosinophilic
c) neutrophlic
d) lymphocytic
e) histiocytic
cell type expected in perivascular dermatitis due to xerosis (dry skin)?
a) cell-poor
b) eosinophilic
c) neutrophlic
d) lymphocytic
e) histiocytic
a) cell-poor
b) eosinophilic
c) neutrophlic
d) lymphocytic
e) histiocytic
cell type expected in perivascular dermatitis (PVD) due to leishmania?
a) cell-poor
b) eosinophilic
c) neutrophlic
d) lymphocytic
e) histiocytic
a) cell-poor
b) eosinophilic
c) neutrophlic
d) lymphocytic
e) histiocytic
cell type expected in perivascular dermatitis (PVD) due to superficial pyoderma?
a) cell-poor
b) eosinophilic
c) neutrophlic
d) lymphocytic
e) histiocytic
a) cell-poor
b) eosinophilic
c) neutrophlic
d) lymphocytic
e) histiocytic
cell type expected in perivascular dermatitis (PVD) due to chronic antigenic stimulation ex. chronic pyoderma?
a) cell-poor
b) eosinophilic
c) neutrophlic
d) lymphocytic
e) histiocytic
a) cell-poor
b) eosinophilic
c) neutrophlic
d) lymphocytic-plasmacytic
e) histiocytic
cell type expected in perivascular dermatitis (PVD) due to flea allergy dermatitis (FAD)?
a) cell-poor
b) eosinophilic
c) neutrophlic
d) lymphocytic
e) histiocytic
a) cell-poor
b) eosinophilic
c) neutrophlic
d) lymphocytic
e) histiocytic
cell type expected in perivascular dermatitis (PVD) due to canine atopic dermatitis (CAD)?
a) cell-poor
b) eosinophilic
c) neutrophlic
d) lymphocytic
e) histiocytic
a) cell-poor
b) eosinophilic
c) neutrophlic
d) lymphocytic
e) histiocytic
^could be cell poor or eosinophilic
cell type expected in perivascular dermatitis (PVD) due to canine allergic dermatitis?
a) cell-poor
b) eosinophilic
c) neutrophlic
d) lymphocytic
e) histiocytic
a) cell-poor
b) eosinophilic
c) neutrophlic
d) lymphocytic
e) histiocytic
histo term for scales
• thickened stratum corneum
• hyperkeratosis
• parakeratosis
derm term for an accumulation of loose fragments of keratin (stratum corneum)
scale
a scale is a ____________ (process) defect
cornification
difference between a primary vs. secondary cornification disorder
primary = failure to release corneocytes
secondary = reactive hyperplasia
3 examples of primary cornification disorders (failure to release corneocytes)
• nasodigital hyperkeratosis
• nasal hyperkeratosis of Labs
• ichthyosis
secondary cornification disorders (reactive hyperplasia) occurs d/t...? [3]
basic response of epidermis to injury:
• trauma, scratching
• infection
• altered barrier function
clinical correlate of hyperkeratosis
scaling
term for retention of nuclei in the stratum corneum
parakeratosis
3 causes of parakeratosis
• Zn responsive dermatosis
• vitamin A responsive dermatosis
• superficial necrolytic dermatitis (hepatocutaneous syndrome)
clinical correlate of parakeratosis
scaling
clinical correlate of hypergranulosis (hyperplasia of stratum granulosum)
no clinical correlate
clinical correlate of acanthosis (hyperplasia of stratum spinosum)
no clinical correlate
histological term for a skin plaque
same: plaque
which part of the hair follicle is identical to the epidermis?
infundibulum
histological term for excessive keratin forming in infundibulum of hair follicle
follicular keratosis & follicular parakeratosis
clinical term for excessive keratin forming in infundibulum of hair follicle
follicular casts;
comedones
what are comedones
follicles plugged with keratin (blackheads, whiteheads)
histo term for comedones
follicular dilatation and keratosis
what is a 'crust'
dried inflammatory exudate on surface of skin
ex. dark crust usually = hemorrhagic;
yellow-green crust typical of pyoderma
histo term for crusts
serocellular crust