Genetic Basis of Human Disease - Gene Therapy
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
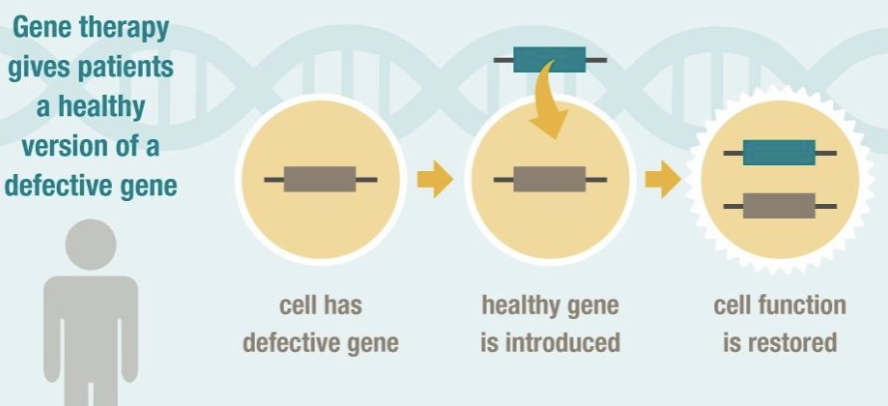
______ ______ is a novel therapeutic branch of modern medicine for correcting a defective disease-causing gene
gene therapy
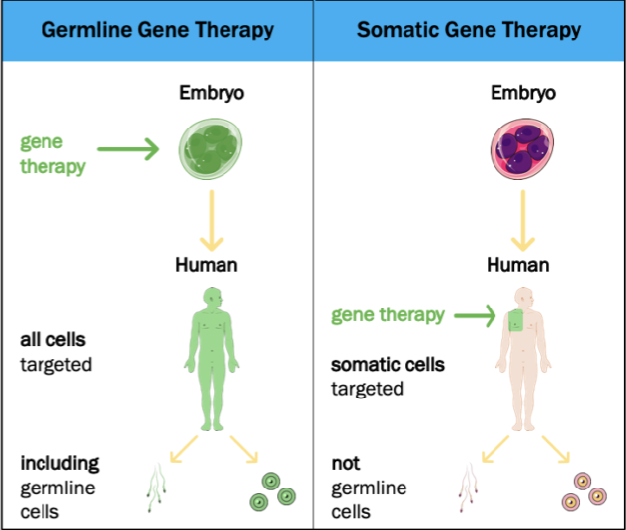
Types of Gene Therapy → Cell Types
______ gene therapy: therapeutic gene —> somatic cells —> NOT inherited
______ gene therapy: therapeutic gene —> germ cells —> inherited to later generations
somatic
germline
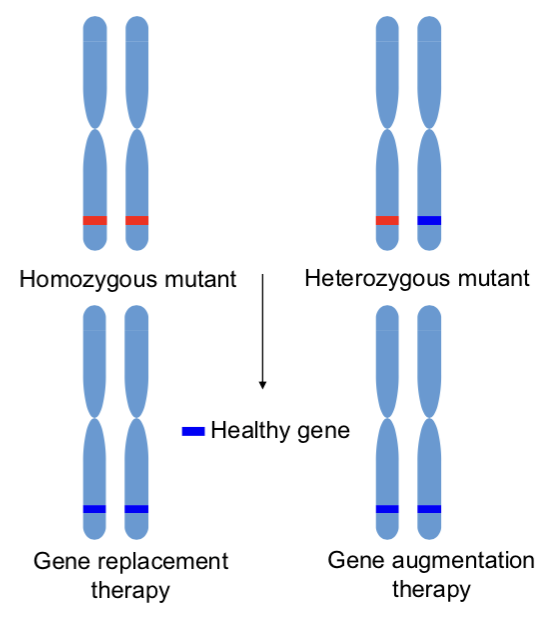
Types of Gene Therapy → # of Defective Copies
______ ______ therapy: replacement of homozygous mutant gene
______ ______ therapy: correction of heterozygous mutant gene
gene replacement
gene augmentation
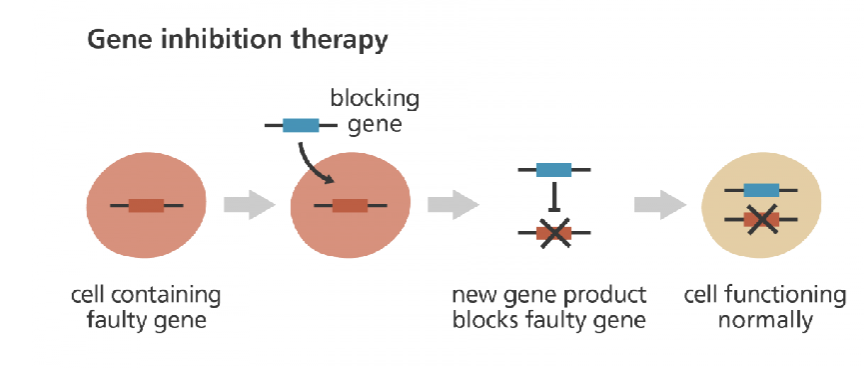
______ ______ ______: a blocking gene is introduced to eliminate the activity of a gene that promotes the growth of disease-related cells (e.g., cancer causing genes, for example activation of an oncogene)
gene inhibition therapy
Gene therapy to kill specific cells can be achieved in one of two ways:
Introduction of “______” gene.
Introduction of “______” gene.
suicide
marker
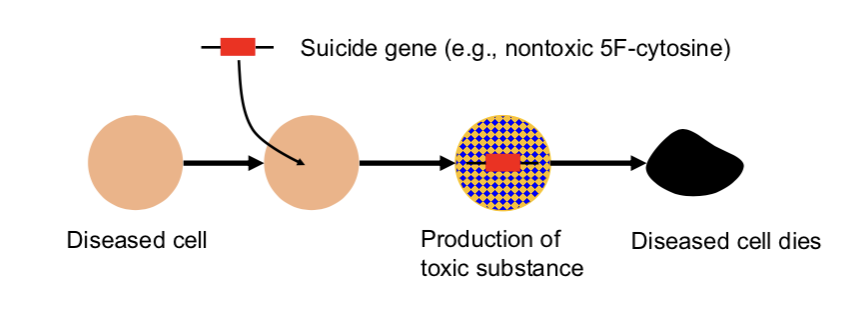
______ gene therapy: introducing viral or bacterial genes to tumor cells —> allows conversion of a non-toxic compound (converts the pro-drug ______ to ______) to a lethal medication.
suicide, 5-fluorocytosine (5-FC), 5-fluorouracil (5-FU)
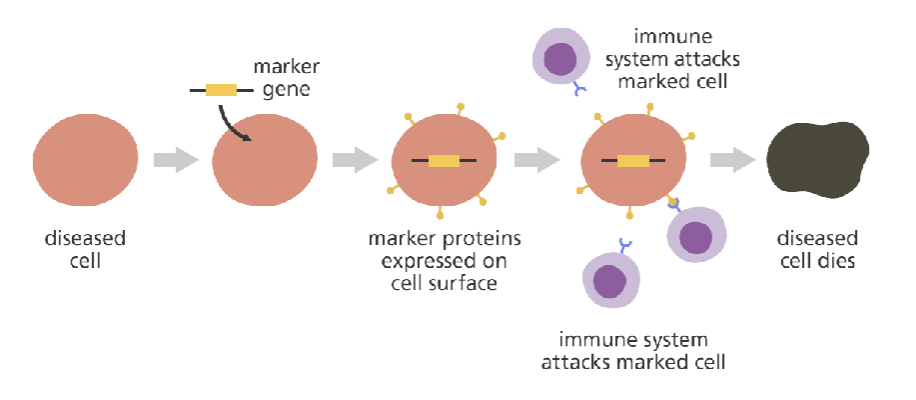
______ gene therapy: causes expression of a protein that marks the cells so that the diseased cells are attacked by the body’s natural immune system.
marker
Steps in Gene Therapy (5)
Defective gene identification
Cloning the identical healthy gene (therapeutic gene)
Loading the vector with the therapeutic gene
Gene delivery to the target cell
Functional activity (augmentation, suppression or repair)
Step 2: Cloning
DNA cloning is the process of making multiple, ______ copies of a particular piece of DNA.
______ ______ cut open the plasmid and “paste” the therapeutic gene via ______ ______.
the plasmid is introduced into bacteria (or other cell types) via a process called ______
bacteria with the ______ (correct/incorrect) plasmid are used to make more plasmid DNA
identical
restriction enzymes, DNA ligase
transformation
correct
Step 3: Loading the Therapeutic Gene in Vectors for Gene Delivery
The ______ acts as a vehicle to carry the therapeutic DNA into the cells of a patient with a genetic disease.
Types of Vectors:
______ vectors —> (e.g., retrovirus, adeno virus, etc.)
______ vectors —> (e.g., naked DNA, liposome, etc.)
vector
viral
non-viral
______ ______ gene therapy or direct therapy: direct delivery of a therapeutic gene into the cells of a particular organ in the body via viral or non-viral vector.
______ ______ gene therapy or cell-based delivery: transfer of therapeutic gene into cultured cells and then introduction of genetically modified cells into the body.
in vivo
ex vivo
Advantages of non-viral vectors > viral vectors (4)
Have lower risk for immune reaction and cytotoxicity
Have the potential to deliver larger genetic payloads
Are cost effective and easier to synthesize
Have no risk of insertional mutagenesis
Disadvantages of non-viral vectors > viral vectors (2)
Have lower efficiency of transfecting host cells
Have higher risk of degradation by nucleases
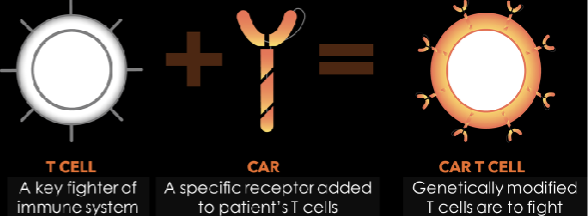
Targeted Gene Therapy to Treat Cancer: ______ ______
a new receptor is added to a patient’s ______ ______
CAR = ______ ______ ______
once the T cell has the CAR —> ______ ______
in 2017, FDA approved CAR T cell therapy for ______ ______ ______ and ______ ______
CAR-T cell
T cells
chimeric antigen receptor
CAR-T cell
acute lymphoblastic leukemia, advanced lymphomas
Gene Therapy to Cure LCA
about 2,000 individuals in the U.S. have ______ ______ ______
retina degenerates due to mutation in ______ gene
Spark Therapeutics clinical trial results demonstrated 93% Phase III subjects (27 out of 29 patients) responded ______ (positively/negatively) —> EXPENSIVE —> $425,000 PER EYE.
Leber’s Congenital Amaurosis
RPE65
positively
Gene Therapy to Treat AIDS
HIV needs ______ to enter CD4 cells, so gene therapy blocks or removes it to stop the virus from infecting T cells.
ZFN gene therapy —> ______ ______ —> cuts out the CCR5 gene from the surface of CD4 T cells, making them resistant to HIV, and then these modified T cells are returned to the patient.
CCR5
ZFN overexpression
Challenges of Gene Therapy (4)
Delivering the therapeutic gene to the right place and switching it on are major challenges
Therapeutic gene can induce an immune response in the patient
There is a risk that the therapeutic gene may disrupt the activity of a normal gene
Gene therapy is expensive
______ ______ ______ —> a procedure in which a patient receives healthy stem cells to replace damaged stem cells
Stem cells have the ability to ______ into a large number of cell types
Stem cells can be used for ______ ______
stem cell transplation
differentiate
gene therapy
Types of Stem Cell Transplantation
______ → the donor is an identical twin of the patient
______ → the patient’s own marrow or peripheral blood is used
______ → an allogeneic donor is one other than the patient
______ → donor is a different species
syngeneic
autologous
allogenic
xenotransplant
stem cells have the capacity to:
______ ______ → produce unaltered daughter cells
differentiate into specialized tissue cell types (potency)
______ → can generate all cell types
______ → can generate a limited number of cell types
______ → can generate only one cell type
self-renew
pluripotent
multipotent
unipotent
Types of Stem Cells
______ stem cells → high capacity of self-renewal and pluripotent
______/______ stem cells → multipotent; hematopoietic or intestinal stem cells
______ ______ stem cells → pluripotent stem cell derived from adult
somatic cells by overexpressing Oct4/Sox2/Klf4/c-Myc or Oct4/Sox2/Nanog/LIN28
embryonic
adult/somatic
induced pluripotent