BIOL 233: Cardiovascular and Blood
1/397
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
398 Terms
a good way to describe the cardiovascular system is
"pressure is distance"
the heart is ______ anchored to anything
NOT
an average HR is ~
72 bpm
an athlete's HR is typically
an example is ~40 bpm
much lower
Heart rate is NOT ______; instead, it is _____
static; dynamic
Heart sounds come from
valves closing
when the heart is challenged, it meets that by
changing (ex. shape)
the heart is _______ in the body
midline
the heart's apex points towards
the left hip
the heart is encased in the
pericardium
How much pericardial fluid is normal?
~2-3 tsp
Pericardium is:
fixed, so it can't expand
the problem with the pericardium being fixed, is that ___________; what is that condition called
when fluid surrounds the heart, the sac can't expand; pericarditis
how many layers of the heart is there
3
What is the outtermost layer of the heart wall
epicardium
what is the middle layer of the heat wall
myocardium
What is the innermost layer of the heart?
endocardium
heart muscle looks like its being
rung like a sponge from the bottom up
the right ventricle can be
pretty thin
What is the BP in the right ventricle?
25/8
Which ventricle is thicker?
left ventricle
Why is the left ventricle thicker than the right?
because it is opposed by more force
What is the BP in the left ventricle?
120/80
the left ventricle only gets bigger if you
work it
muscle is NOT
unilateral
what is the purpose of heart valves
prevent back flow of blood
Heart valves open and close in response to __________.
pressure
AV valves are _____ between beat
open
AV valves are loose leaflets of _________ (they have no __________)
connective tissue; structure
semilunar valves are ________ between beats
closed
What are the 2 AV valves?
tricuspid and bicuspid (mitral)
the left AV valve is called
bicuspid or mitral valve
the right AV valve is called
tricuspid valve
What are the 2 semilunar valves?
pulmonary and aortic
the left semilunar valve is called
aortic valve
the right semilunar valve is called
pulmonary valve
AV valves have a ring of ___________ to anchor them
connective tissue
tendinous cords
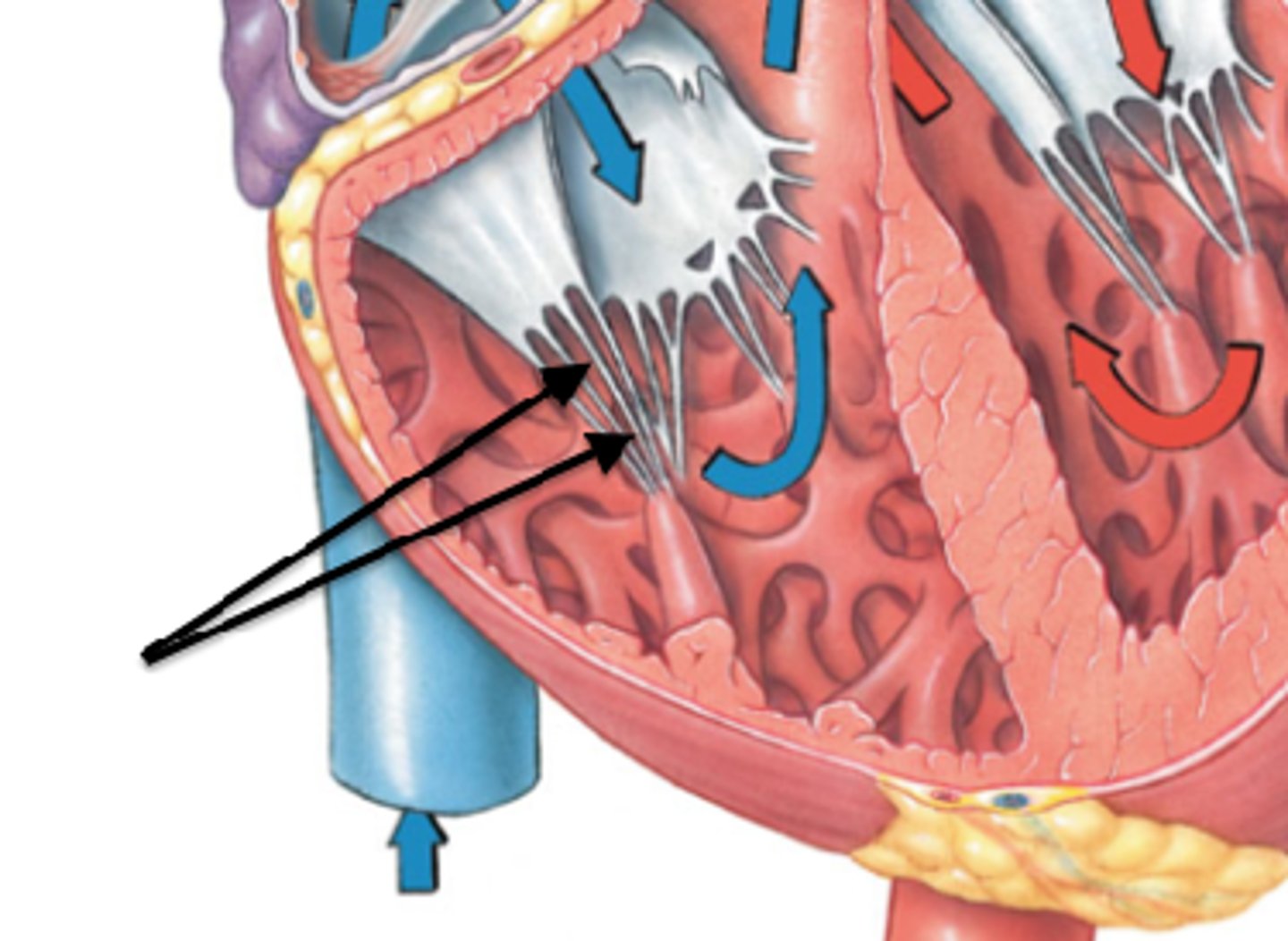
what is the purpose of tendinous cords
keeps the valves from going back
papillary muscles
papillary muscle contracts the same time as the
walls
Why don't semilunar valves have chordae tendineae?
because they're closed until pressure builds
What are the two circuits of the heart?
pulmonary circuit and systemic circuit
which circuit of the cardiovascular system needs more pressure
systemic
Where does the pulmonary circuit go?
heart--->lungs--->heart
where does the systemic circuit go?
heart--->body--->heart
coronary circulation is it's own
circuit
the coronary arteries come right off the
aorta
how many heartbeats per lifetime
2 1/2 billion
cardio muscle is NOT ________; it is more "_________" together
unidirectional; woven
What do intercalated discs do?
provides additional structure and keeps the heart from ripping itself apart
What do intercalated discs contain?
desmosomes and gap junctions
What are gap junctions?
channels that allow exchange of material
what is the reason for the heart being able to beat so much
mitochondria
why do mitochondria keep the heart beating so much?
keeps it in an aerobic state
What is aerobic?
requires oxygen
What are cardiomyocytes?
cardiac muscle cells
cardiomyocytes
what is the trigger for muscle contraction
binding of calcium to troponin
you need to have calcium on the outside of the cell in order to __________; what is this called?
release other calcium; calcium-induced calcium release (CICR)
Depolarization
contraction happens
what is the charge inside of the cell during depolarization
positive
what makes it positive during depolarization
Na+ (sodium)
what allows for repolarization
K+ (potassium)
Repolarization
relaxation
what is the charge inside the cell during repolarization
more negative
How does repolarization occur?
via the opening of V-gated K+ channels
what is the first step of an action potential in cardiomyocytes
voltage gated Na+ channels open
what is the second step of an action potential in cardiomyocytes
Na+ inflow depolarizes the membrane and triggers the opening of still more Na+ channels, creating a positive feedback cycle and a rapidly rising membrane voltage
what is the third step of an action potential in cardiomyocytes
Na+ channels close when the cell depolarizes, and the voltage peaks at nearly +30 mV
what is the fourth step of an action potential in cardiomyocytes
Ca2+ entering through slow Ca2+ channels prolongs depolarization of membrane, creating a plateau. Plateau falls slightly because of some K+ leakage, but most K+ channels remain closed until end of plateau
what is the fifth step of an action potential in cardiomyocytes
Ca2+ channels close and Ca2+ is transported out of cell. K+ channels open, and rapid K+ outflow returns membrane to its resting potential
look at the __________ to determine contraction length
plateau
why do some contractions last longer?
because Ca2+ is around longer
When the AV valves are open
the semilunar (pulmonary and aortic) valves are shut
what occurs during phase 1 of the cardiac cycle
ventricular filling/passive filling between beats and atrial contraction
during passive filling, what is the percentage of blood volume in the left ventricle
80%
during atrial contraction, what is the percentage of blood volume
20%
what is the name of the total of volume in phase 1
End diastolic volume (EDV)
What does end diastolic volume mean? What does it equal?
EDV: AMOUNT OF BLOOD IN VENTRICLES AT THE END OF FILLING; Venous Return aka PRELOAD
What is preload?
volume of blood in ventricles at end of diastole
what happens during phase 2a of the cardiac cycle
isovolumetric contraction phase
what occurs during isovolumetric contraction?
all four valves are closed
isovolumetric contraction makes up the
first heart sound (S1)
What is afterload?
resistance left ventricle must overcome to circulate blood
what must happen in isovolumetric contraction
afterload
what happens during phase 2b of the cardiac cycle
ventricular (rapid) ejection
what is open during ventricular ejection
aortic valve
what happens during phase 3 of the cardiac cycle
isovolumetric relaxation
what occurs during isovolumetric relaxation
all 4 valves are closed
isovolumetric relaxation makes up what
second heart sound (S2)
what is the name of the total volume during isovolumetric relaxation
End Systolic Volume
What is end systolic volume (ESV)?
volume of blood remaining in each ventricle after contraction
what happens after isovolumetric relaxation
the cardiac cycle goes back to the "beginning" with ventricular filling
how do you measure cardiac output (CO)?
CO= Stroke Volume (SV) x Heart Rate (HR)
What is stroke volume?
how much blood is ejected and how much is left
how do you calculate SV?
End Diastolic Volume (EDV) - End Systolic Volume (ESV)
how can you regulate stroke volume
contractility, afterload, and preload
the main thing to focus on with contractility, is the concentration of
calcium
more calcium =
can bind to more troponin