App 10 - innervation of tongue, teeth, and face
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
orange
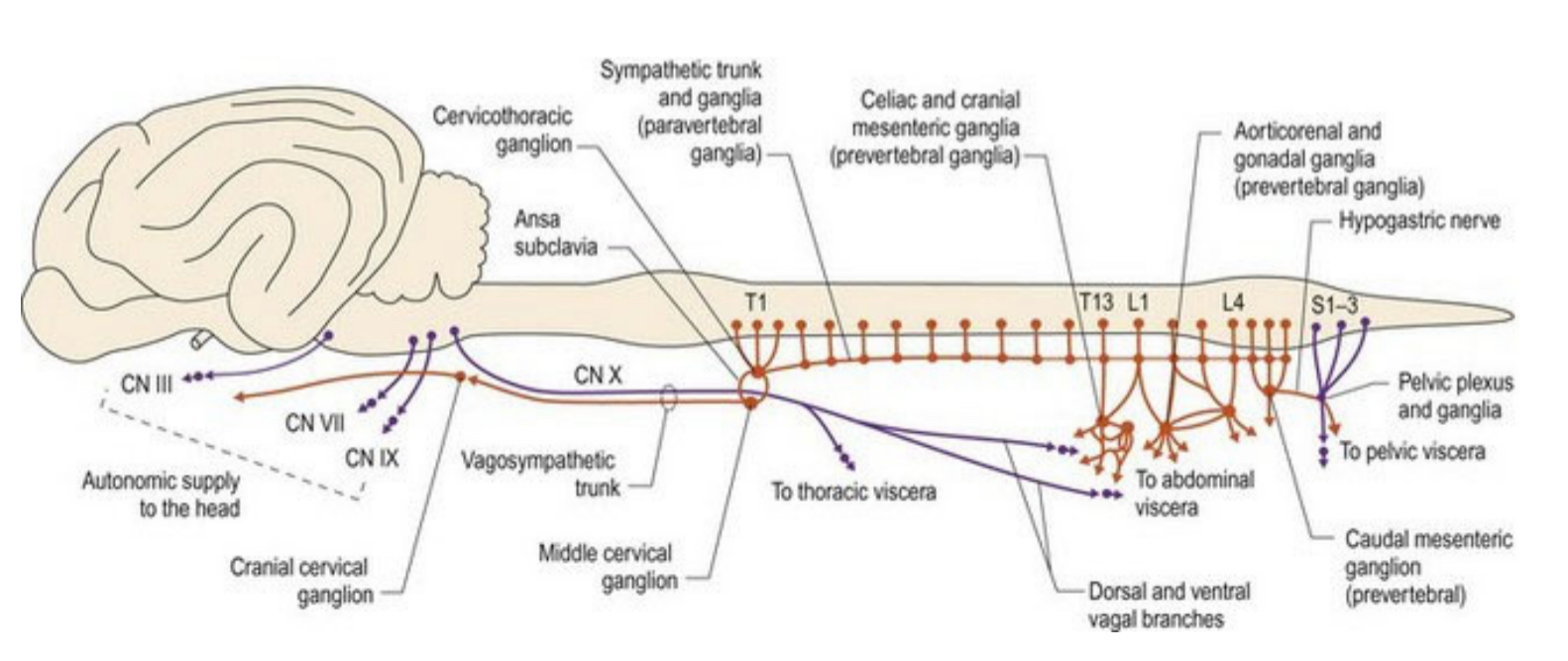
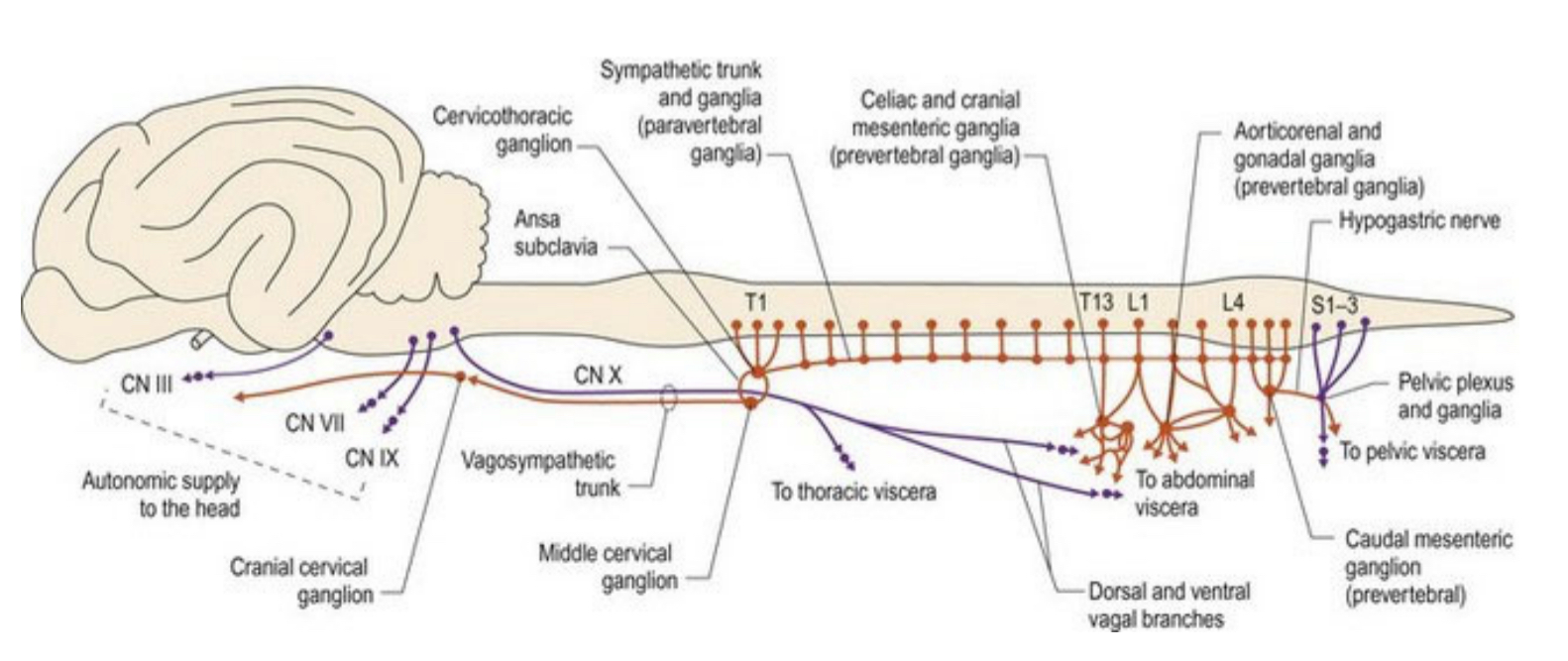
sympathetic nervous system
purple
parasympathetic nervous system
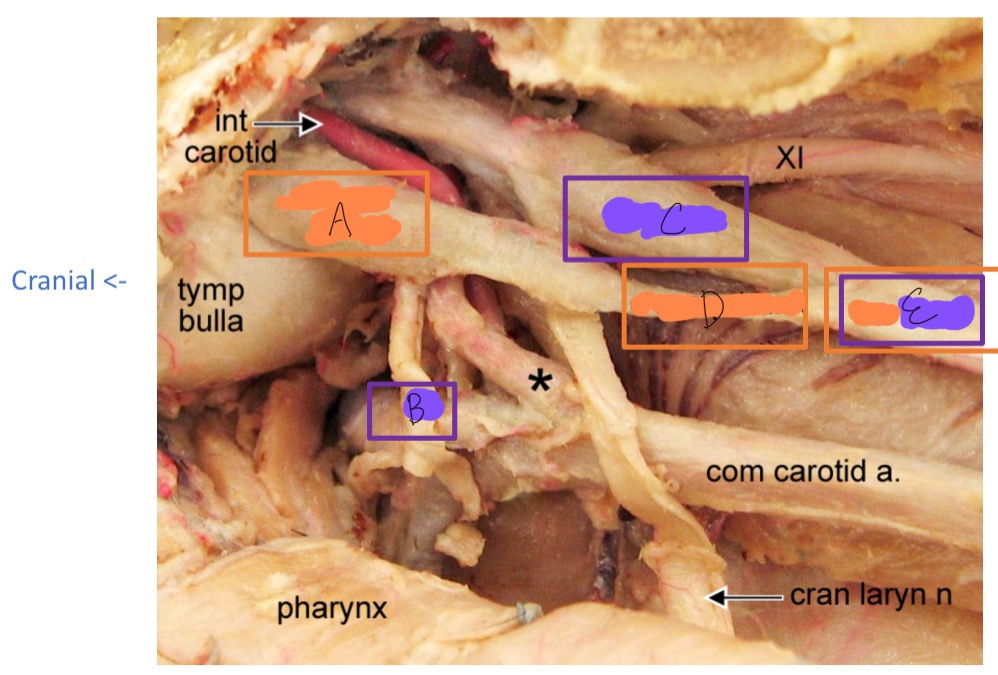
A
cranial cervical ganglion
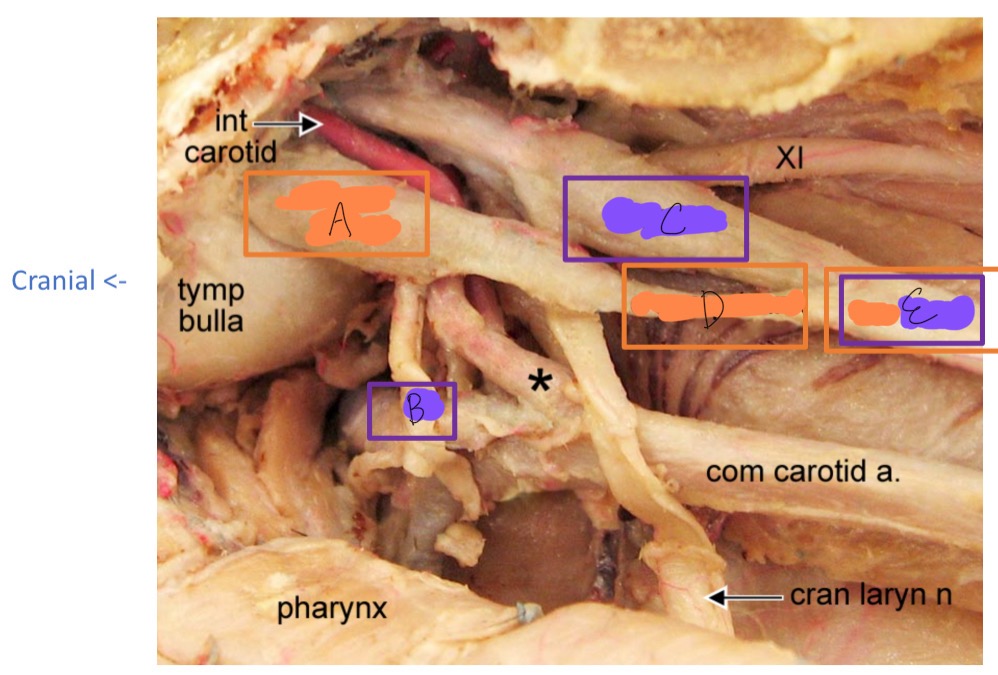
B
cranial nerve IX
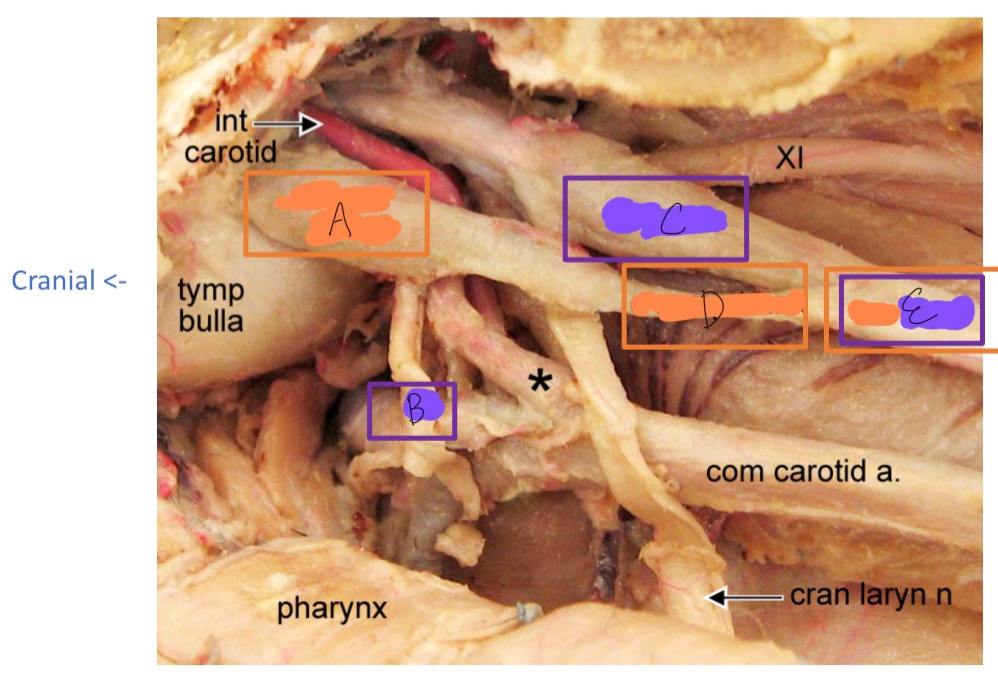
C
vagus N
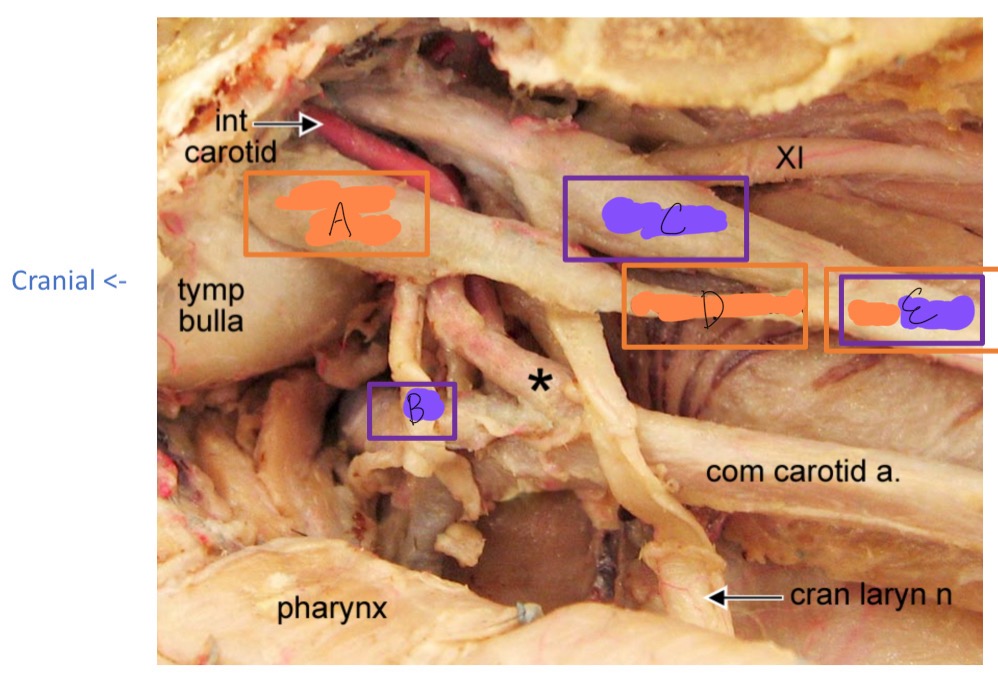
D
cervical sympathetic trunk
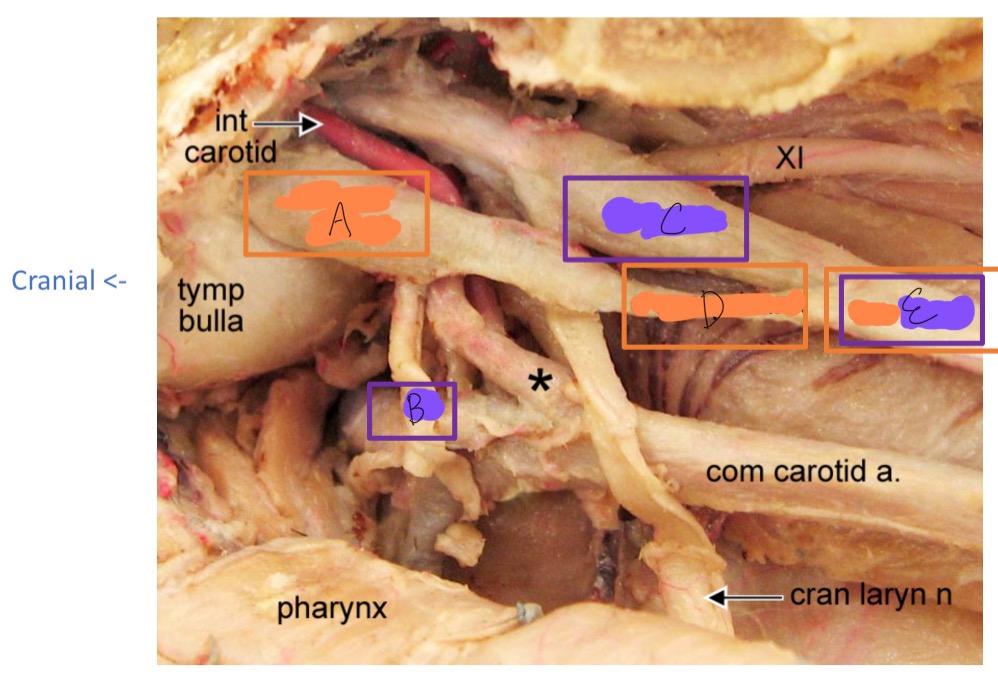
E
vagosympathetic trunk
which cranial nerves carry parasympathetic nerve fibers
III, VII, IX, and X
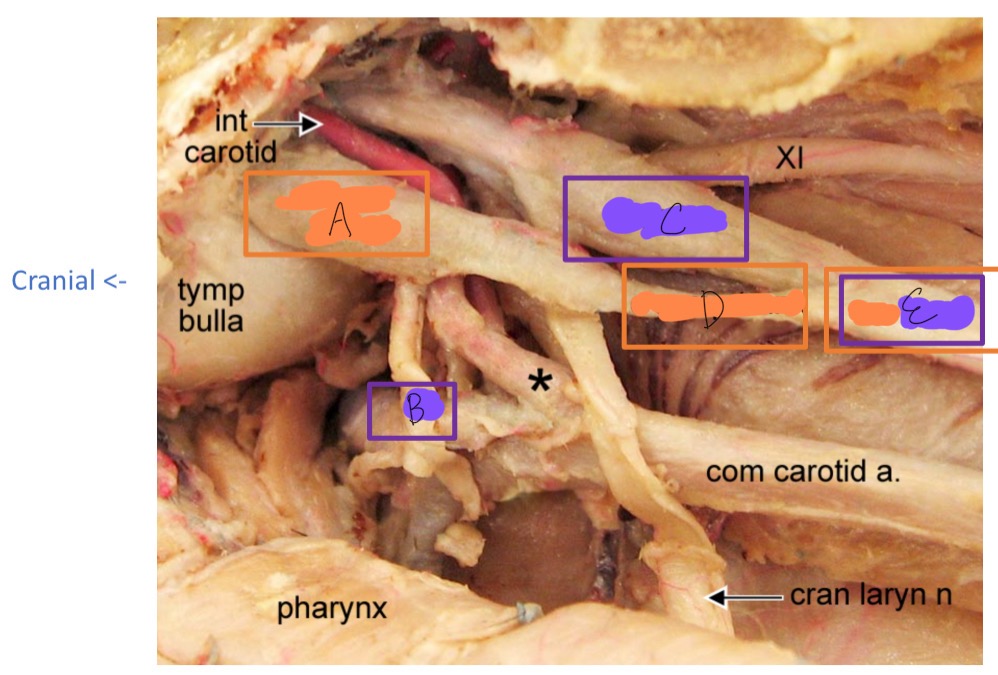
*
carotid sinus
the lingual n. supplies sensory or motor innervation
sensory
the hypoglossal n. supplies sensory or motor innervation
motor
What do CN IX and X contribute to?
sensation to root of tongue
what does CN VII (via chorda tympani branch) contribute to
taste ('“special” sensation)
CN V (trigeminal) branches into what nerve, with lingual following after
mandibular n.
What is the role of CN XII (hypoglossal n.)
motor to all extrinsic and intrinsic tongue muscles
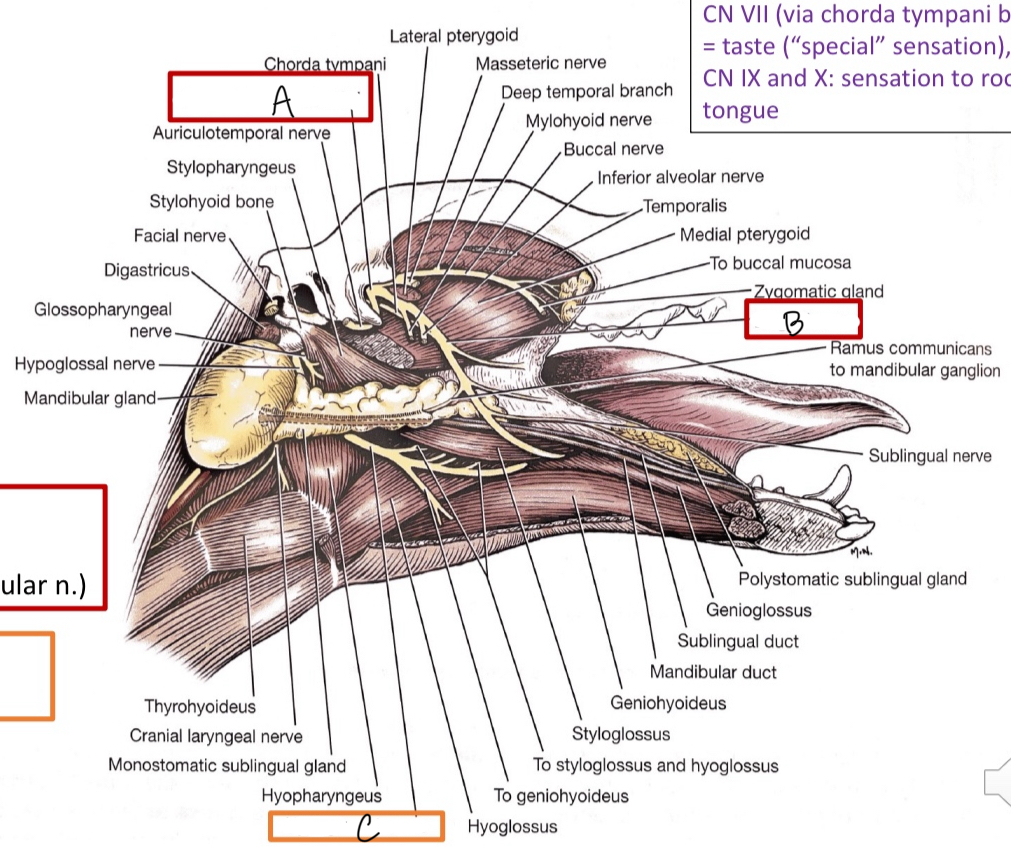
A
mandibular branch of V
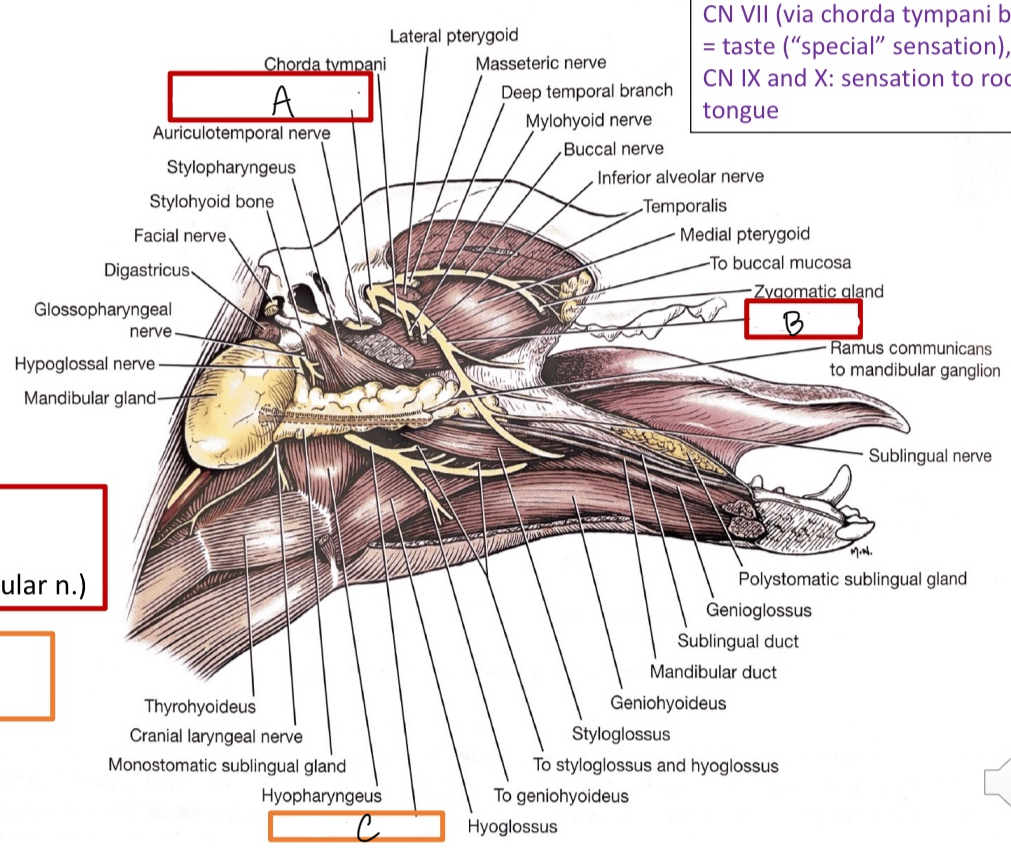
B
lingual n.
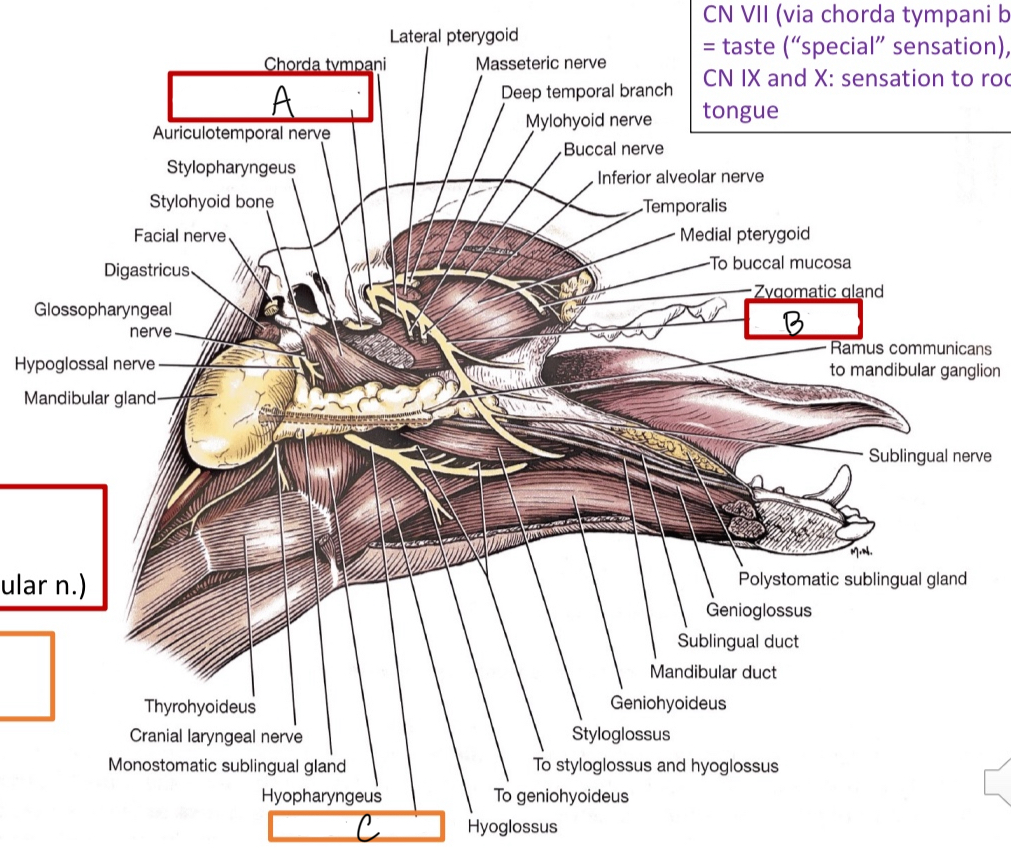
C
hypoglossal n.
most trigeminal n. branches lie fairly
deep
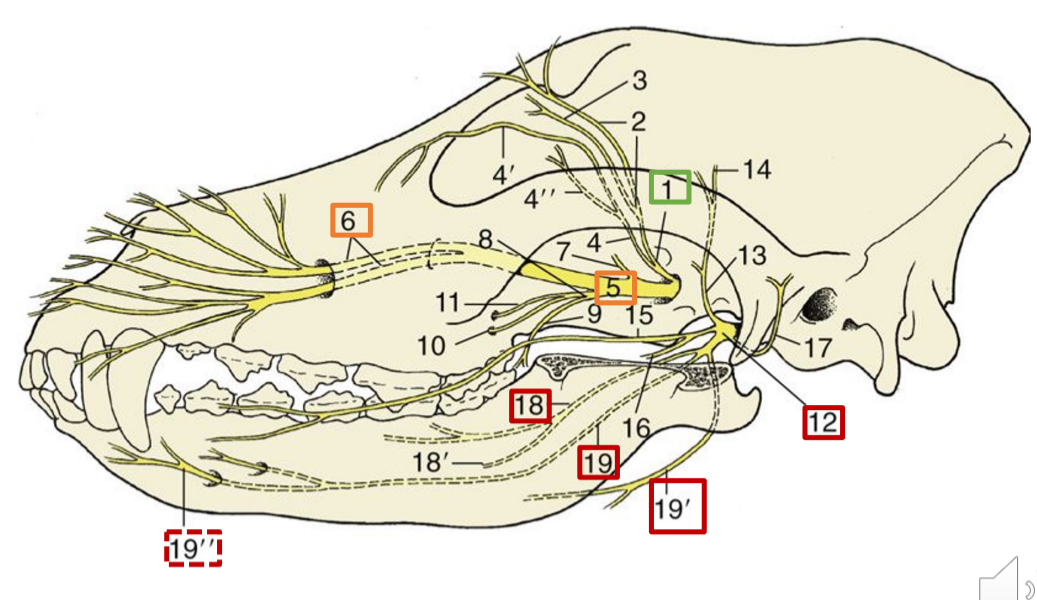
1
opthalmic n.
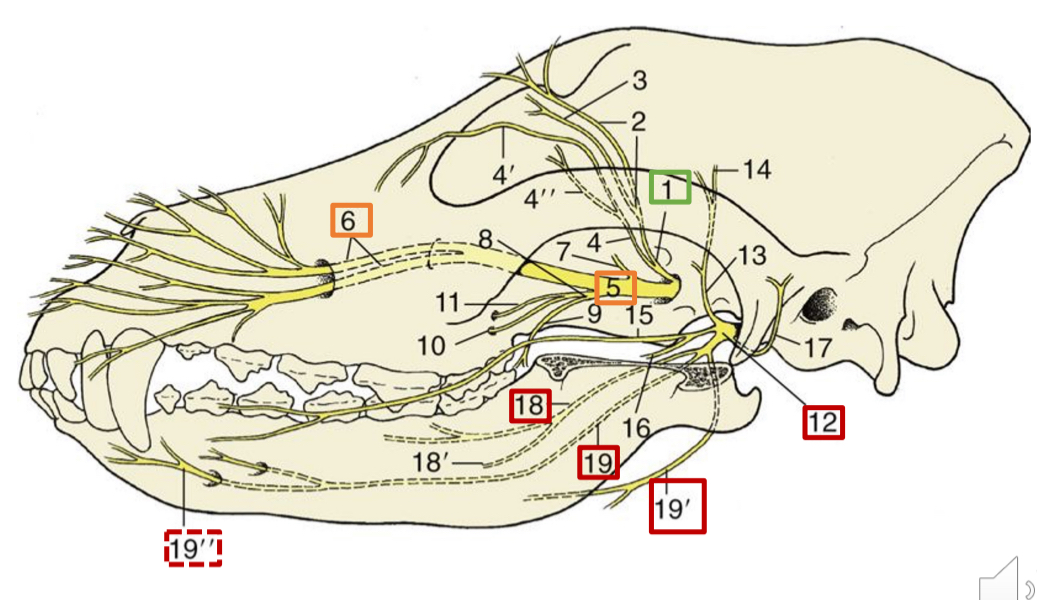
5
maxillary n.
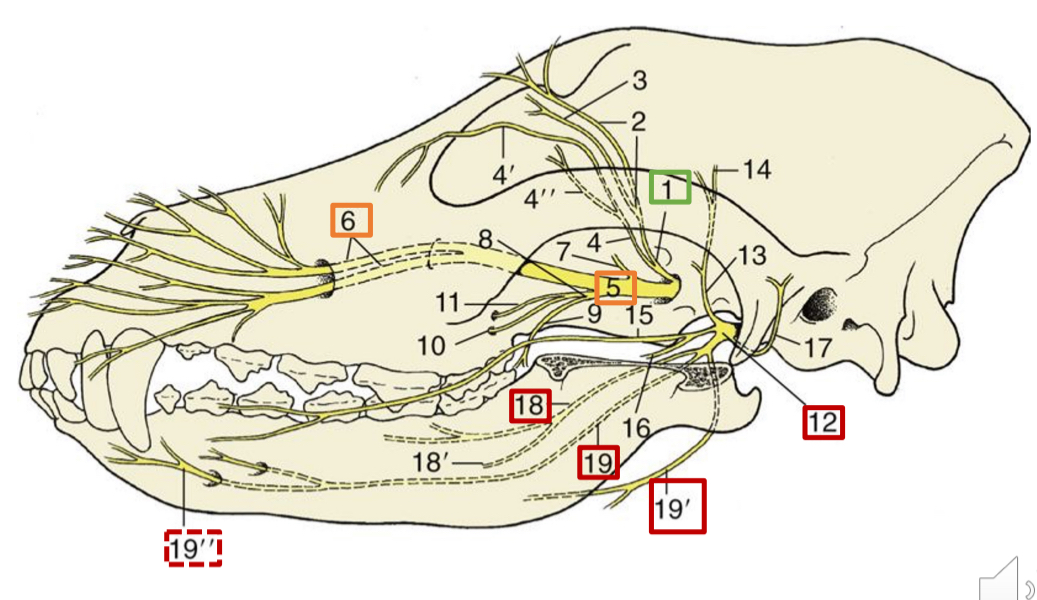
6
infraorbital n.

12
mandibular n.
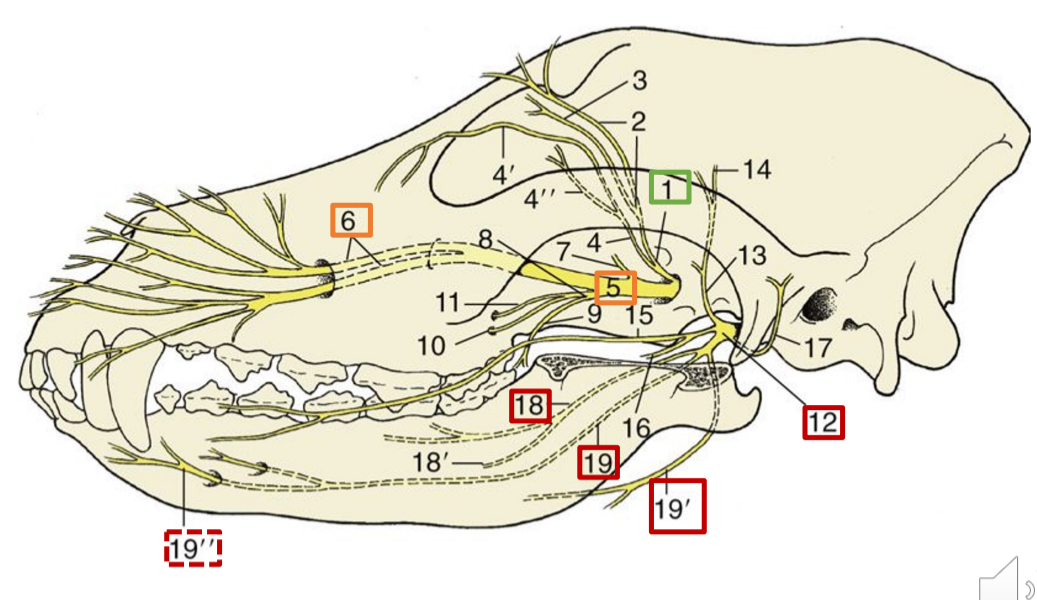
18
lingual n. (skeleton dog)
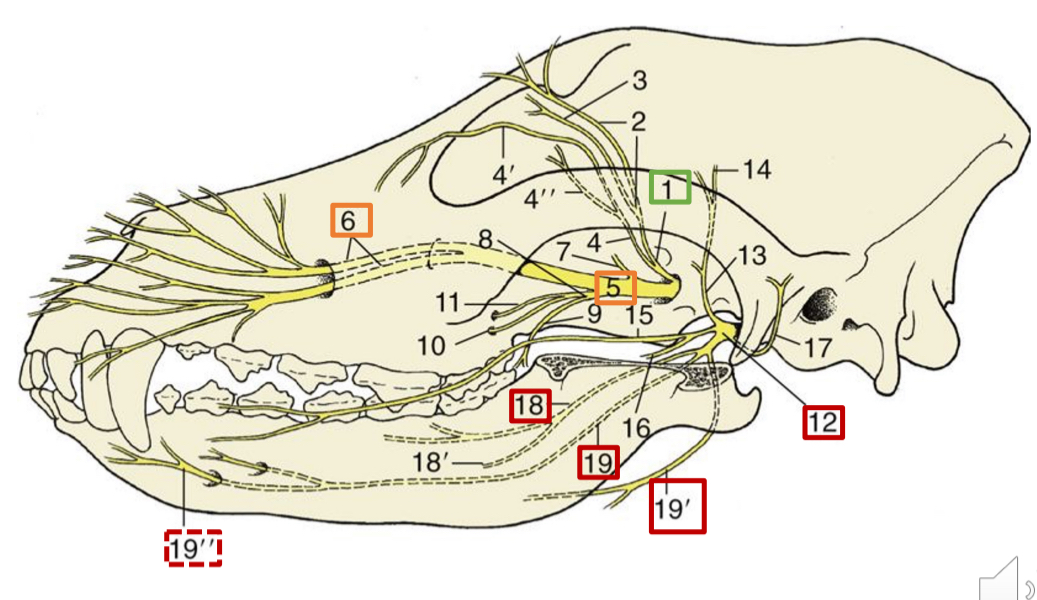
19
inferior alveolar n.
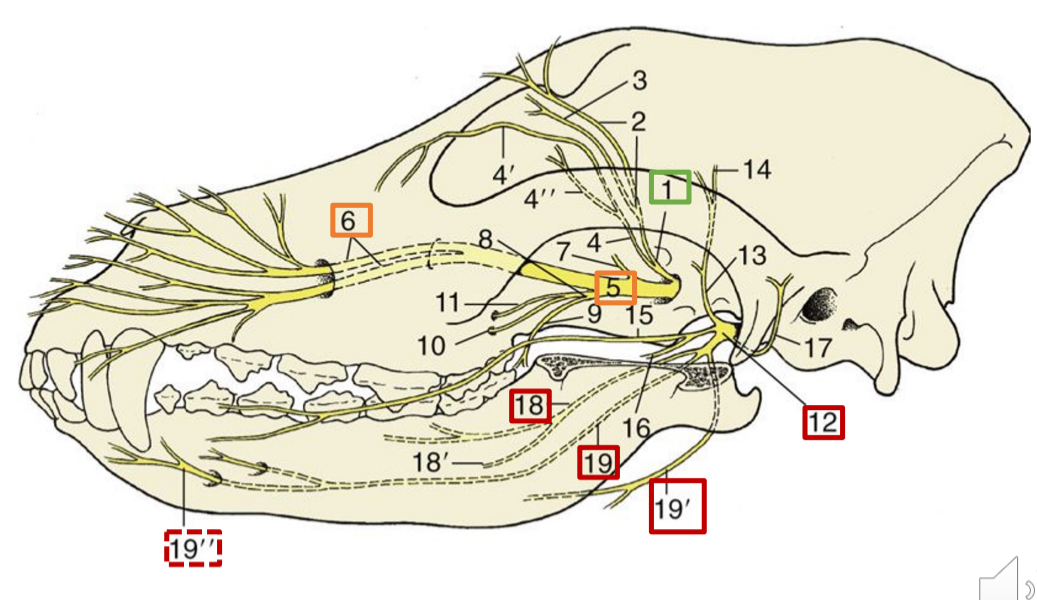
19”
mental n.
19’
mylohyoid n.
Dental Blocks improve
analgesia and decrease general anesthesia requirements
which block would you use for infraorbital n./infraorbital foramen
rostral maxillary regional block
which block would you use for maxillary n./maxillary foramen
caudal maxillary regional block
which block would you use for middle mental n. /mental foramen
rostral mandibular regional block
which block would you use for inferior alveolar n/mandibular foramen
caudal mandibular regional block
the Rostral maxillary regional block provides regional analgesia to…
Incisors, canine, 1st 3 premolar teeth of the
corresponding side. The adjacent maxillary bone and
surrounding soft tissue are also affected.
the caudal maxillary regional block provides regional analgesia to
Bones, teeth, soft tissues of the upper jaw, including
the hard palate and the soft and hard palatal mucosa
on the corresponding side
the rostral mandibular regional block provides regional analgesia to
Incisors and canine tooth of the corresponding side
along with the adjacent bone. *Note: soft tissues are
better blocked with the caudal mandibular regional
block
the caudal mandibular regional block provides regional analgesia to
All mandibular teeth, mandibular bone, and soft
tissue on the corresponding side rostral to the
injection site
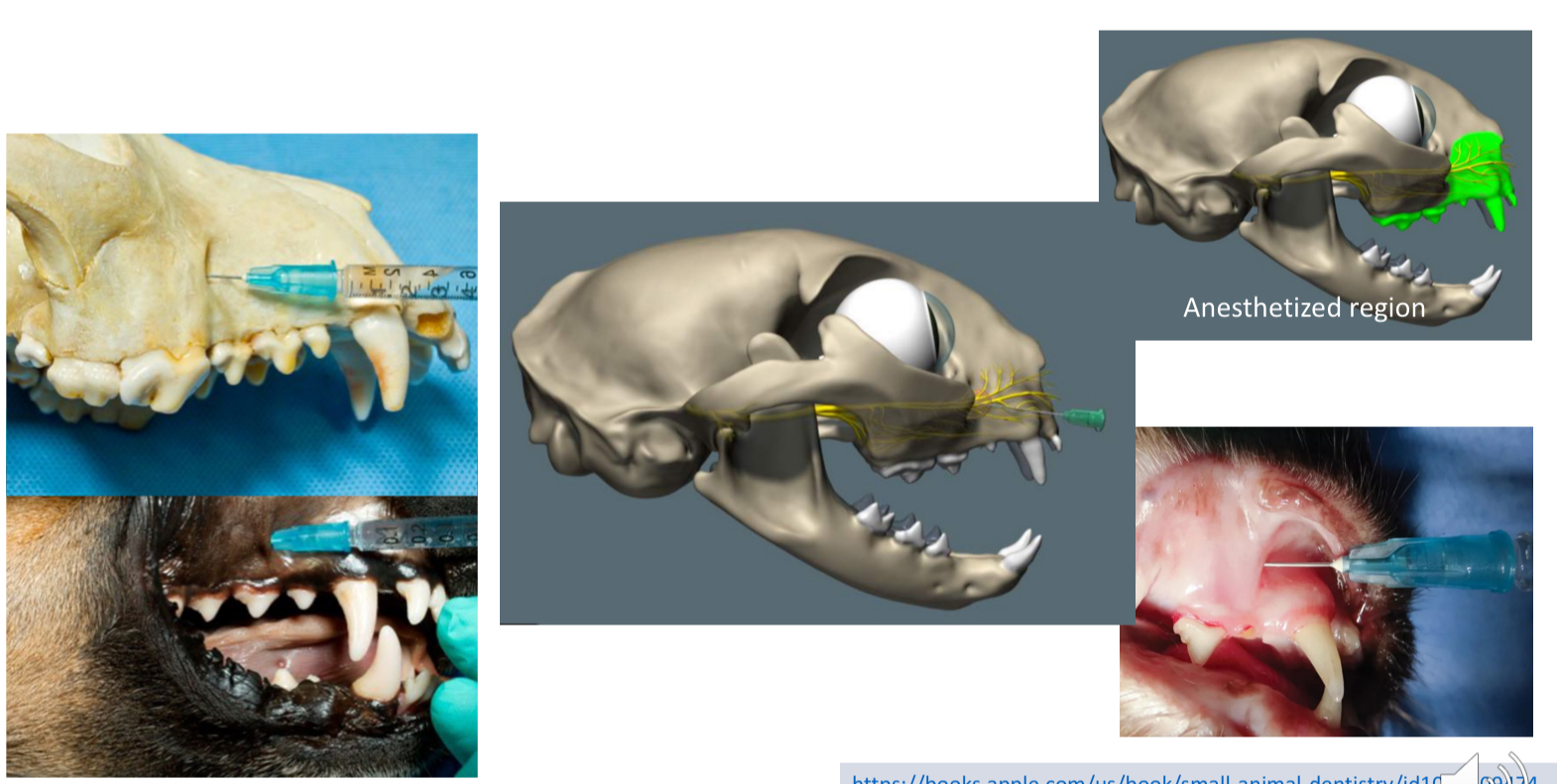
which nerve block is thsi
rostral maxillary block (infraorbital n.)
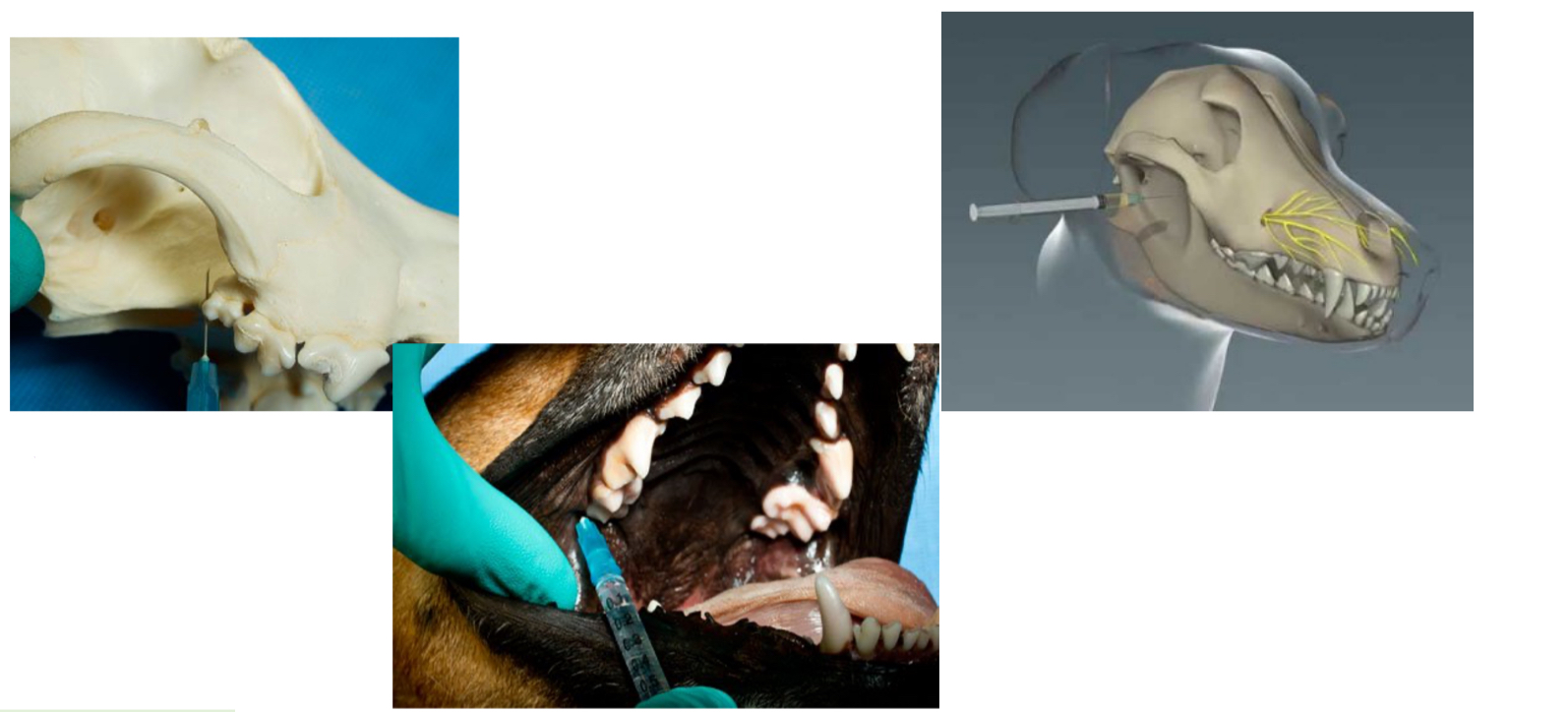
which nerve block is this
caudal maxillary block (maxillary n.)
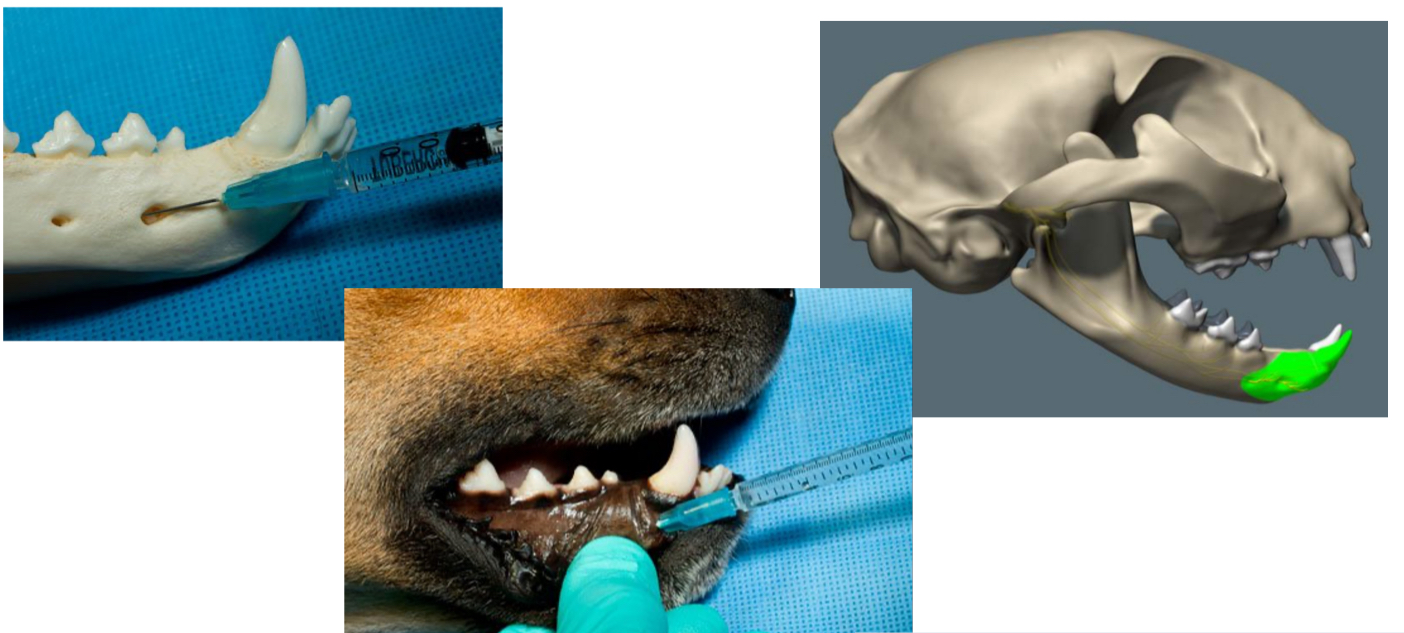
which nerve block is this
rostral mandibular block (middle mental n.)
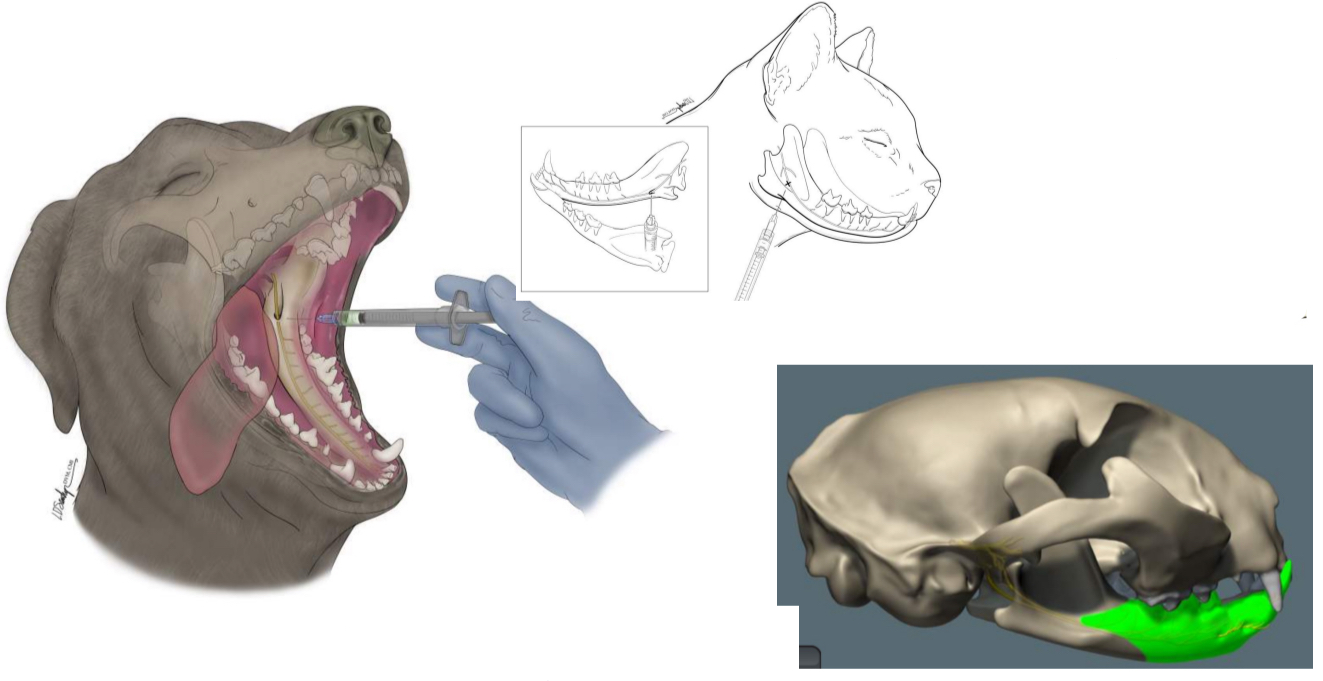
which nerve block is this
caudal mandibular block (inferior alveolar n.)
what should you be careful of with the caudal mandibular block (inferior alveolar n.)
may also cause lingual n. to be blocked, so absent tongue sensation until it wears off
the trigeminal nerve supplies both
sensory innervation and motor innervation
to where does the trigeminal nerve supply sensory innervation
face
jaw
oral tissue
to where does the trigeminal nerve supply motor innervation
muscles of mastication
what is trigeminal neuritis
absent/decreased sensation
dropped jaw
difficulty eating and drinking
most facial n. (CN VII) branches lie fairly
superficial
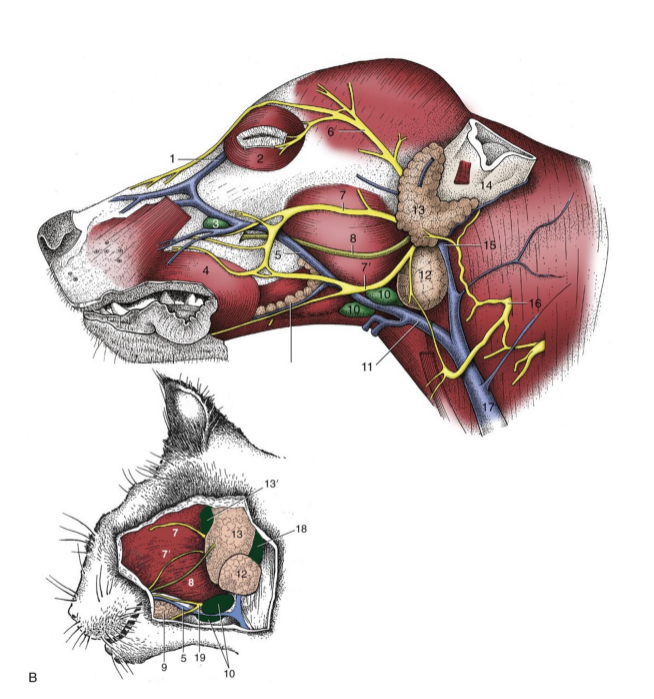
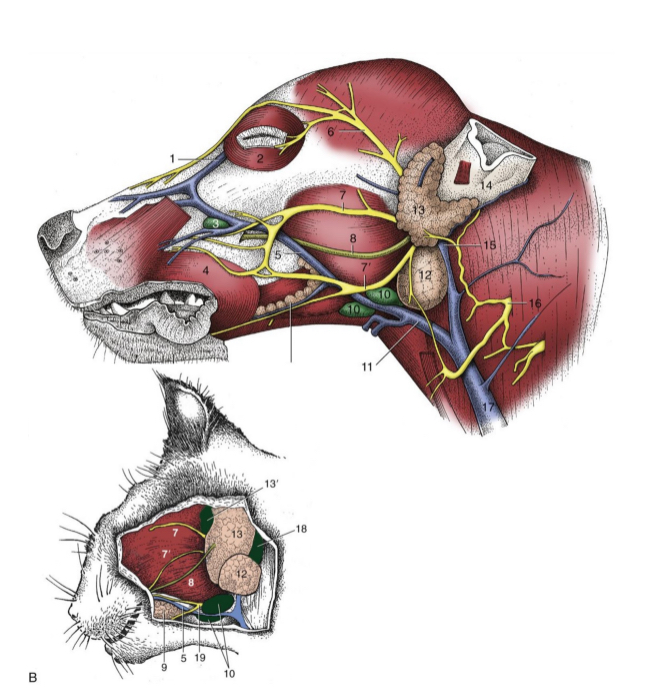
5
facial n. (cat and dog)
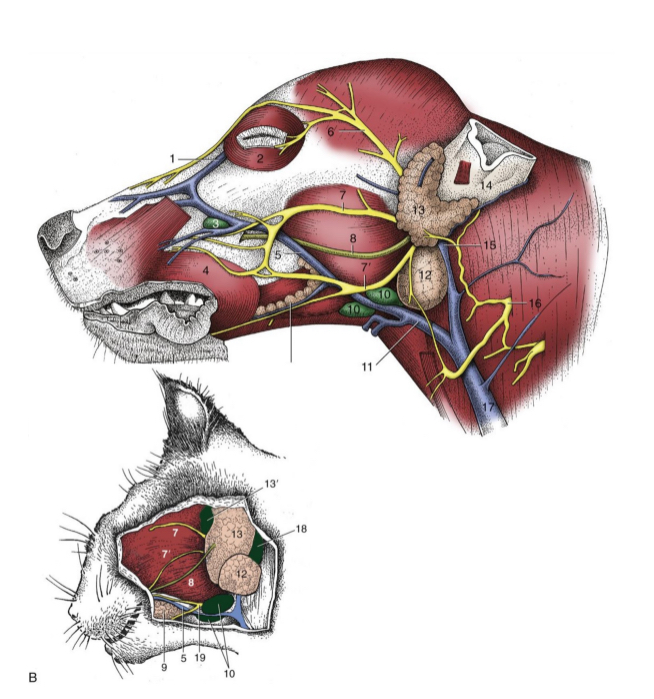
6
auriculopalpebral n. (cat and dog)
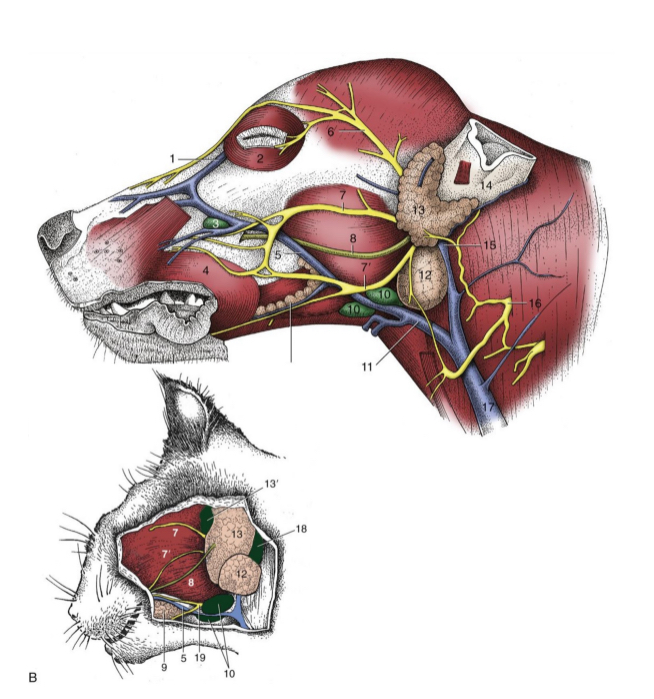
7 and 7’
dorsal and ventral buccal n. (cat and dog)
8
parotid duct (cat and dog)
10
mandibular lymph nodes (cat and dog)

11
linguofacial vein (cat and dog)
12
mandibular gland (cat and dog)
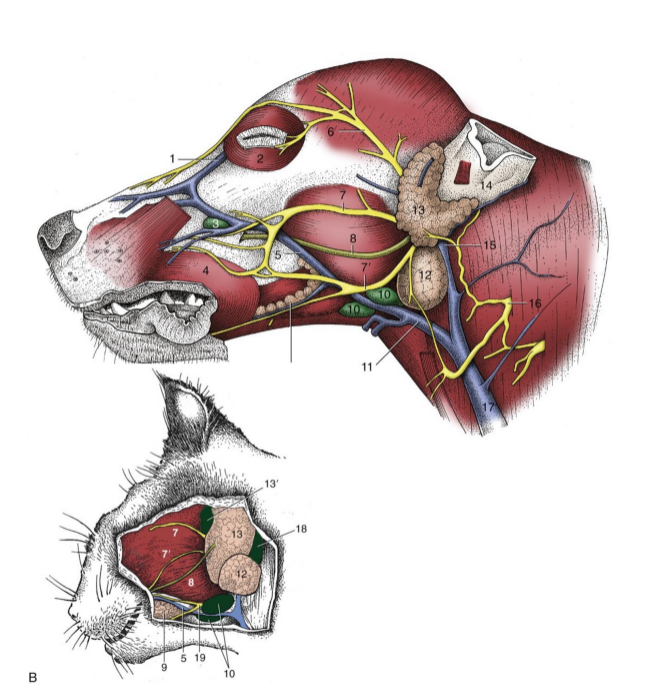
13
parotid gland (cat and dog)
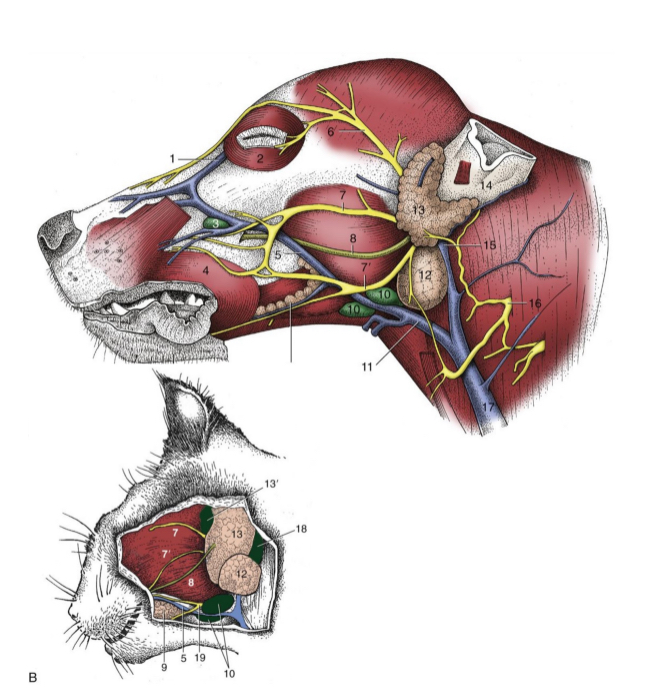
14
base of ear(cat and dog)
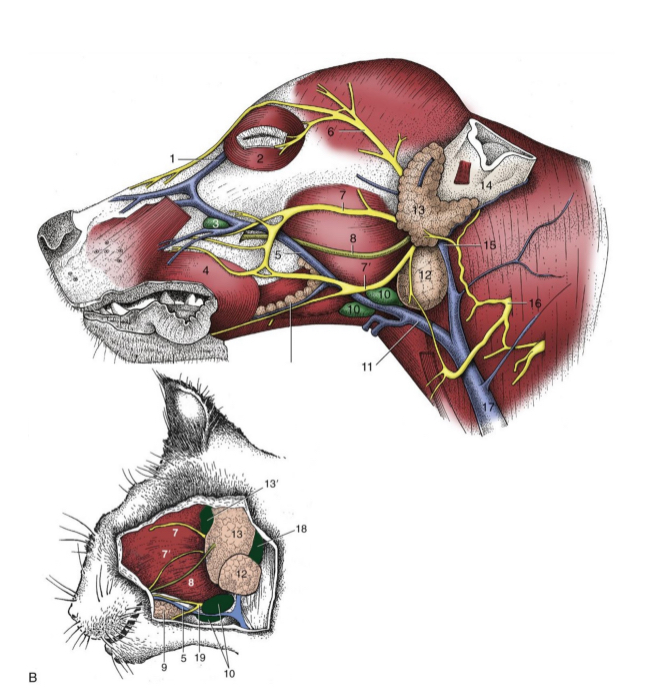
15
maxillary vein(cat and dog)
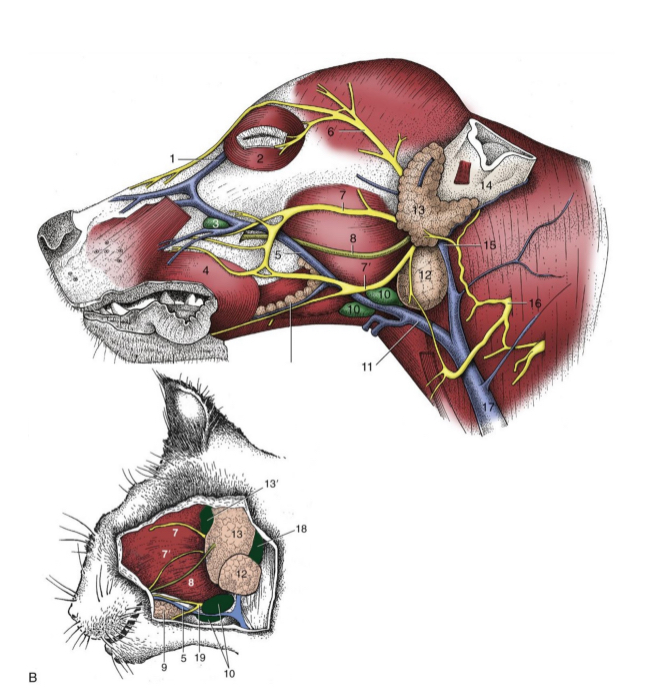
17
external jugular vein(cat and dog)
19
facial nerve, ventral branch (cat and dog)
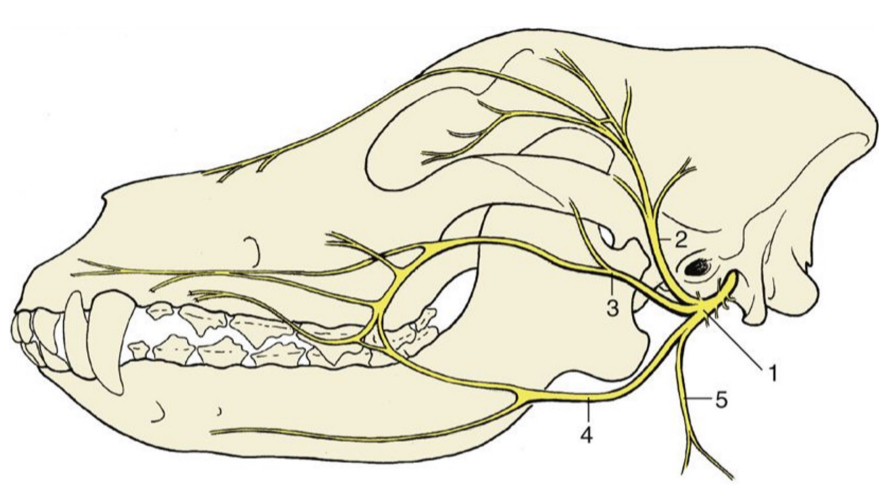
1
facial nerve (skeleton)
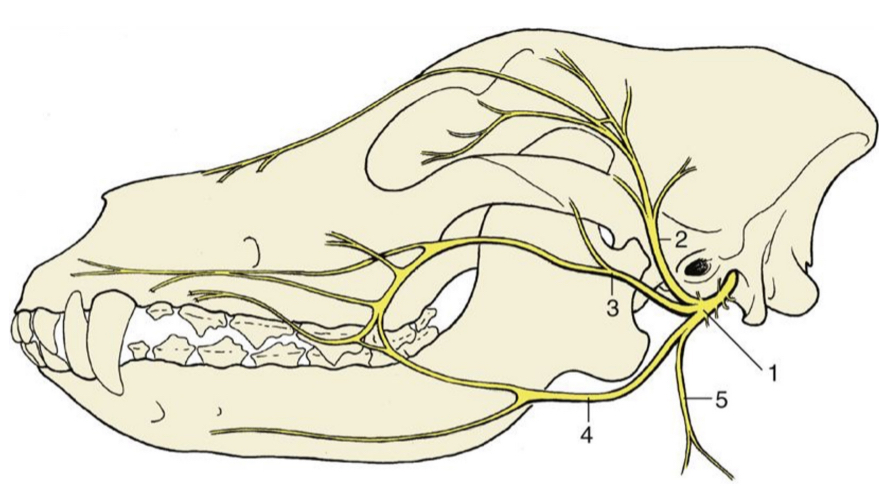
2
auriculopalpebral n. (skeleton)
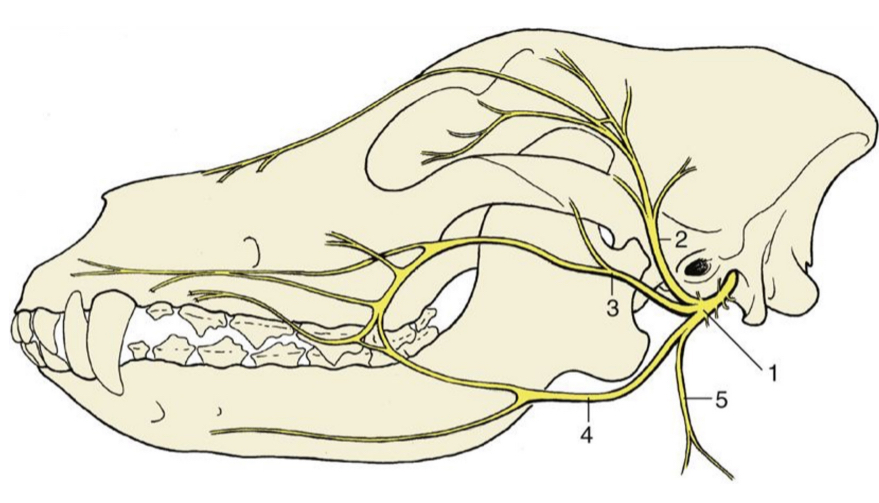
3
dorsal buccal n. (skeleton)
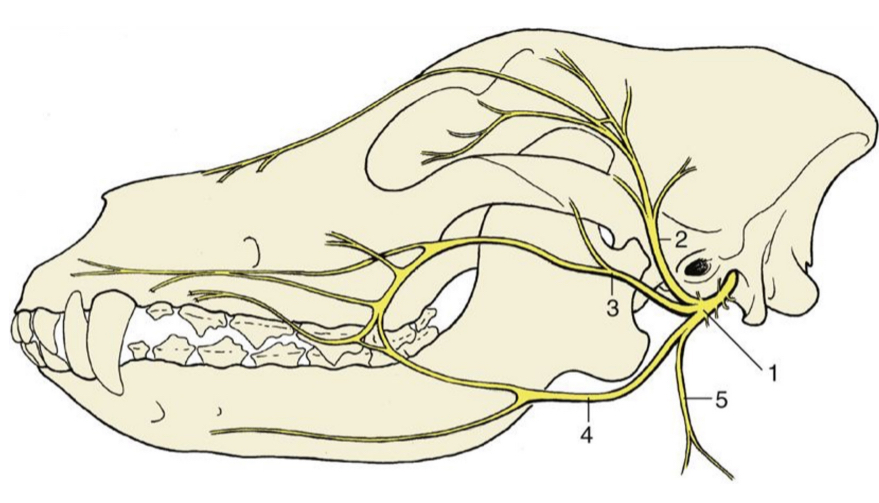
4
ventral buccal n. (skeleton)
what does the facial nerve innervate
muscles of facial expression
what is facial nerve paralysis
muscle laxity on affected side
in addition, the facial nerve carries parasympathetic fibers innervating glands: __________, ______, ______,_____ and innervates the ____ ____
nasal
lacrimal
mandibular
sublingual salivary
taste buds