AP Macro Unit 4
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
Money
Is something that used to purchase goods and services, therefore it has intrinsic value that’s set by the number of goods and services
What is considered Money?
1.) Intrinsic value
2.) U.S Dollars as Fiat Money
Unit Account
People commonly accept money as a way to set prices
Bank Assets
This is when bank loans out money and earn interests
Bank Liabilities
When the bank owes you money that they have to pay back
Fractional Reserve banking system
when a banking system has a non-zero reserve requirement or anything higher than 0. This is where the rest of demand deposits may be loaned out to individuals or customers.(This doesn’t apply when it’s 0)
The banking system
this is made up by many different banks, including comerical banks and investment
Commercial Banks
they store your money and pay you interest. They also loan out money and earn interest
Reserve requirements
The central bank sets the percentage of customer demand deposits that a bank MUST hold in reserves(not loan out)
How is money created through an economy?
With the Fractional Reserve Banking system, where money is loaned out to customers or businesses
Bank Balance sheets
They show the amounts of bank assets and bank liabilities each individual bank has, and both sides are equal to each other
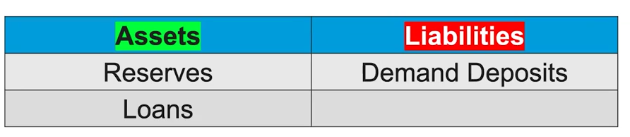
How do Banks keep track of the change in reserves?
changes in demand deposits affect the size of the bank’s required and excess reserves
Required Reserves
the percentage of demand deposits the banks must hold in reserves
Excess Reserves
the percentage of demand deposits banks choose to hold on to. These can be loaned out to individuals and businesses if there’s no excess reserves.
Excess Reserves equation
Total demand deposits - (Required Reserves + Loans)
Required Reserves equation
Demand deposits x required reserves ratio
What happens when there is no excess reserves?
The rest of the money is loaned out
What happens to the excess reserves and loans, when the required reserves goes up?
The excess reserves and loans goes up by the same amount
Maximum increase money supply equation
Excess reserves x money multiplier(1/rrr)
Does buying bonds(securities) expand or contract the economy(money supply)?
Expand
Does selling bonds(securities) expand or contract the economy(Money supply)?
contract
The money multiplier(definition)
used to determine maximum changes to the banking system when deposits or withdrawals from demand deposits. This only happens when the banking system has a non-zero reserve requirement.
Money Multiplier equation
1/rrr
Customer Withdrawals
When customers withdraw money, it’s withdrawn from a bank’s reserves(bank’s assets), and it’s subtracted from a bank’s demand deposits(a bank’s liabilities).
Required Reserve Ratio
the percentage of customer deposits that the bank must hold in reserve and cannot lend out
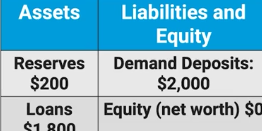
Assume that the required reserve ratio is 10%
What is the dollar value of new loans that first superior bank can make
0 because they’ve already loaned out their maximum excess reserves
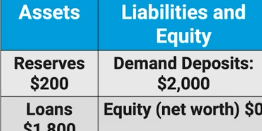
Assume that the Required Reserve Ratio is 10%
Mr. Smith deposits $100 of cash in a demand deposit account at the first superior bank. Calculate the maximum amount of new loans that the first superior bank can now make?
$90 because $10 is the required reserve and there’s $90 left to loan out
Maximum change over time for Loans
The increase in loans x money supply(1/rrr)
Maximum change over time for Demand Deposits
The increase in Loans x Money supply(1/rrr)
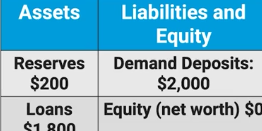
Assume that the Required Reserve Ratio is 10%
As a result of Mr. Smith’s $100 cash deposit, calculate the maximum changes over time for:
1.) Loans
2.) Demand Deposits
1.) $90(excess reserves) x 10= $900
2.) $100 × 10 = $1,000
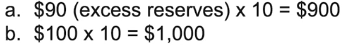
M1
good being supplied and demanded
Transactions Motives
a term that shows that people want to hold money in hopes of something beneficial
Money demand
People choosing to hold their wealth as money with two components of assets demand for money with interest bearing assets or through cash
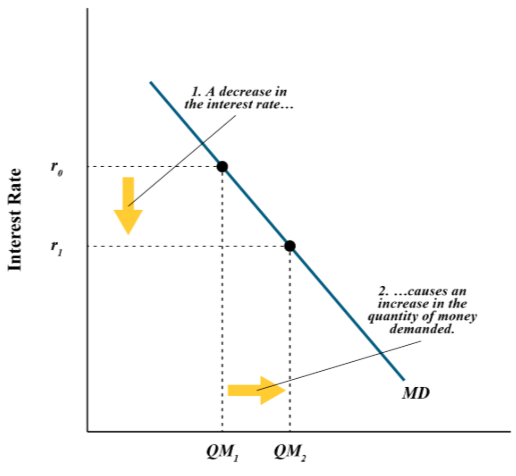
Money demand graph
x-axis: Quantity of money
y-axis: Nominal Interest rate(opportunity costs for holding money)
What happens when you hold your money in cash?
You're not earning the interest you could’ve earned when holding your cash in a certificate of deposit or some other interest bearing assets
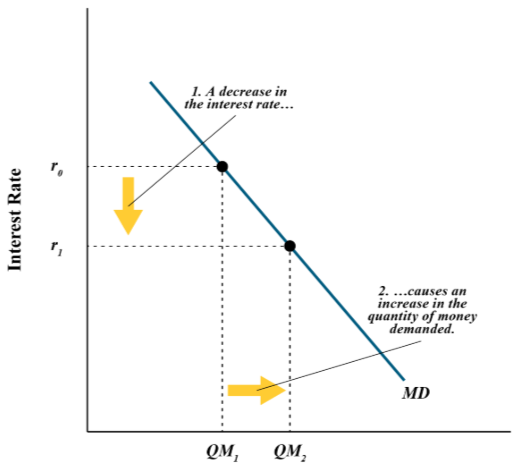
When there’s low nominal interest rates the people hold __ money?
More
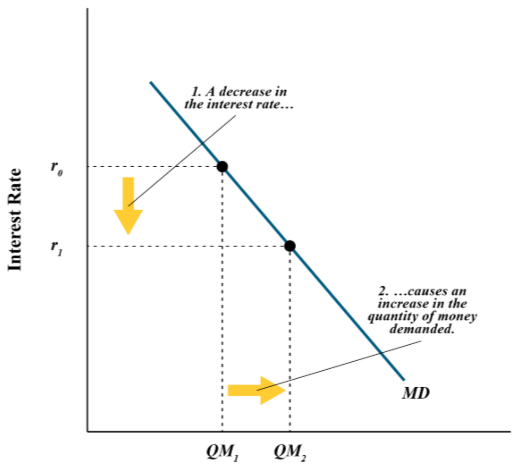
When there’s high nominal interest rates the people hold __ money?
Less
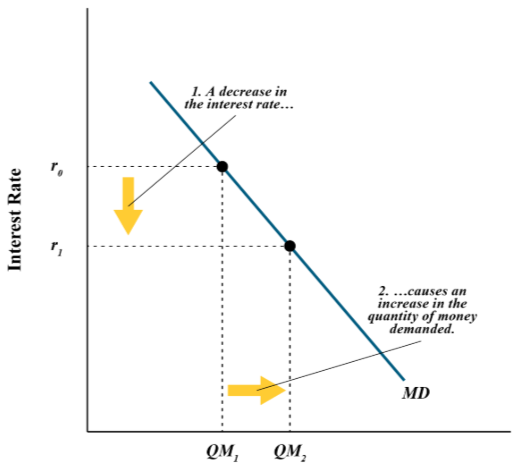
Transaction demand for money
Money needed to process the transactions in the economy through the Real GDP equation = C + I + G + X(which is Exports - Imports)
What causes an increase in the Money Demand?
An Increase in C + I + G + X
An Increase in Price Level
An Increase in Inflation Expectations
An Increase in Desire to hold wealth as money
What causes an decrease in the Money Demand?
A decrease in C + I + G + X
A decrease in Price Level
A decrease in Inflation Expectations
A decrease in Desire to hold wealth as money
Money Supply
It’s determined by actions of the central Bank when there are scarce reserves and changes in banks lending. It shows how much it has available to loan out
What causes an increase in the Money supply(Rightward shift)?
Increased lending
Expansionary monetary policies
What causes a decrease in the Money Supply(Leftward Shift)?
Decreased Lending
Contraction Monetary policy
Effects of Lower interest
More Gross Investment → More Physical Capital stocks → More Growth
Impacts of Higher interest
Less Gross Investment → Less Physical Capital stocks → Less Growth
The Shifters of Money Demand
1.) Price Level
2.) Incomes
3.) Technology
Scarce Reverses
Central banks target their policy rate(the amount banks charge each other, it’s called a federal funds rate in the U.S.) through changes the Money supply.
1.) discount rate
2.) Reserve Requirement
3.) Open Market Operations
An increase in the Policy rate, Discount rate, and selling bonds, causes the Money Supply to __?
Decrease
Ample Reserves
The Banks get paid this rate by the central bank on their reserve balances
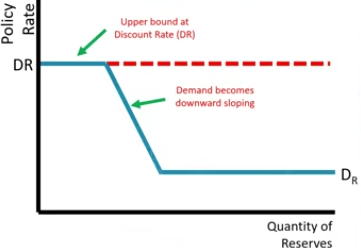
Where can you find the policy rate on the Reserves Market graph?
At the Equilibrium
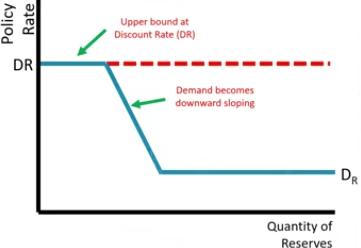
Where is the Discount rate on the Reserves Market graph?
At the upper bound
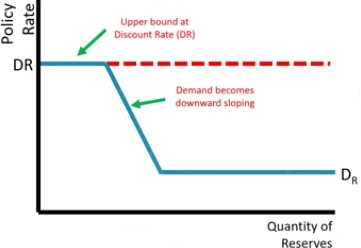
Where can you find the demand on the Reserves Market graph?
Downward sloping line
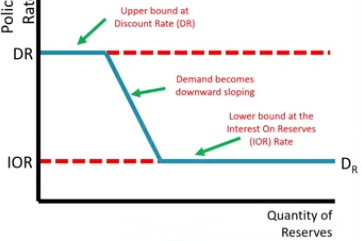
Where can you find the Interest on Reserves Rates?
Lower bound
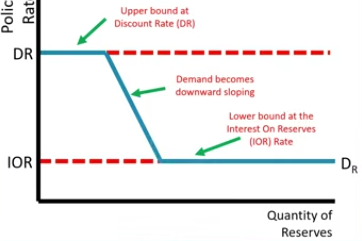
Supply of Reserves
It’s controlled by the central bank(also called the federal Funds rate in the U.S.), therefore it won’t be impacted by the policy rate which makes it vertical
Open Market purchases/buying bonds shift the Supply of Reserves __?
Right
Open Market Sales/selling of bonds shift the Supply of Reserves __?
Left
Where can you find the Scarce Reserves on the Ample Reserve graph?
Downward Slope region
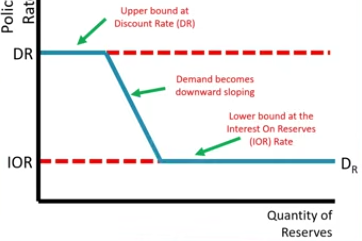
Open Market Operations can only effect the Supply of reserves on the downward sloping region of Ample Reserves graph?
Yes
Decrease in Discount Rate will only move the upper bound on the Ample Reserves graph __?
Down
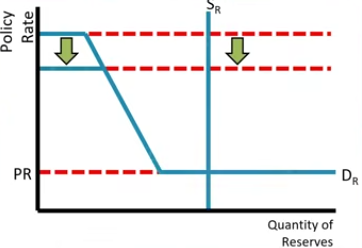
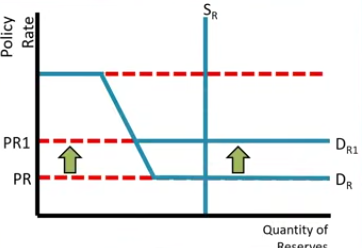
Changes in the Interest on Reserves Rate will only effect the policy rate or the discount rate?
Policy rate
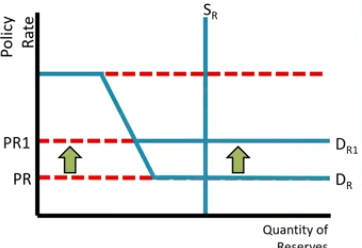
Increase on the Interest on Reserves only moves the lower bound __?
Up
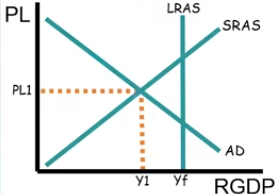
What does this reveal about this economy?
It’s in a recession
Expansionary Monetary Policy and Contractionary Monetary Policy only Shifts Aggregate Demand, Long-Run Aggregate Supply, or Short-Run Aggregate Supply?
Aggregate Demand
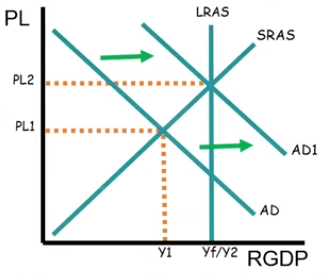
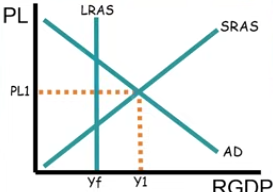
What does this reveal about this economy?
Inflationary period
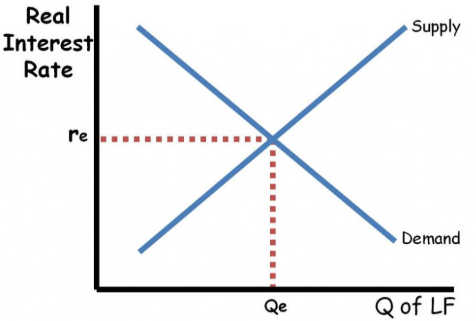
Loan-able Funds Market
The amount of money available to be loaned out in a relationship between the Borrowers(representing the Demand curve) and the Lenders(representing the Supply curve)
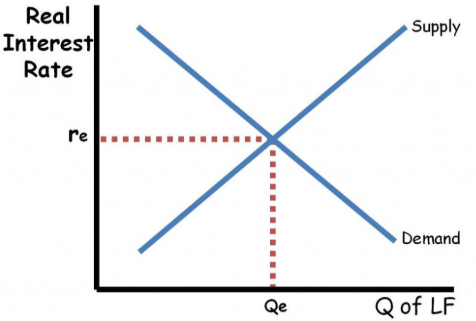
If the price of the loan is high, borrowers will borrow __?
Much
Supply to Loan-able funds
Savings that money deposits are available to loan out
When the real interest rate is low, the savings is going to be __ therefore the quantity of loan fund is _?
1.) Small
2.) Small
Holding Cash would __ Supply of Loanable funds
Decrease
What is the Supply to Loanable funds made up of?
Made up of private and public savings
Deficit Spending
When the government does more borrowing than spending?
When the government is borrowing money it will __ the Demand while it _ the supply because there is less money being saved
1.) Increase
2.) Decreases
Crowding Out
when the government deficit spending doesn’t help the economy because it increases Real interest rates and decreases investment/Growth