ACC 220 Chapter 4 Homework
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
Activity-based costing (ABC)
A two-stage costing method in which overhead costs are assigned to products on the basis of the activities they require.
ABC differs from traditional cost accounting in three ways
1. Non-manufacturing as well as manufacturing costs may be assigned to products, but only on a cause-and-effect basis
2. Some manufacturing costs may be excluded from product costs.
3. ABC uses more cost pools
Activity
an event that vcauses the consumption of overhead resources
Activity Cost Pool
A “bucket” in which costs are accumulated that relate to a single activity measure in an activity-based costing system.
Activity Measure
An allocation base in an activity-based costing system; ideally, a measure of whatever causes the costs in an activity cost pool.
Two common types of activity measures
Transaction Driver
Duration Driver
Transaction Driver
simple count of the number of times an activity occurs
Duration Driver
a measure of the amount of times needed for an activity
Five Levels of Activity: Unit Level
Activities performed for each unit of production
Five Levels of Activity: Batch Level
Activities performed for each batch of products
Five Levels of Activity: Product Level
Activities performed for and identifiable with an entire product line
ex. changing product (color, model, etc)
Five Levels of Activity: Customer Level
Activities that relate to specific customers
Five Levels of Activity: Organization Sustaining
Activities required to support or sustain an entire production process and not dependent on number of products, batches or units produced
Level of Activity: Various individuals manage the parts inventories
Product Level
Level of Activity: A clerk in the factory issues purchase orders for a job
Batch Level
Level of Activity: The personnel department trains new production workers
Organization Sustaining Level
Level of Activity: The factory's general manager uses her office in the factory building
Organization Sustaining Level
Level of Activity: Direct labor workers assemble products
Unit Level
Level of Activity: Engineers design new products
Product Level
Level of Activity: The materials storekeeper issues raw materials to be used in jobs
Batch Level
Level of Activity: The maintenance department performs periodic preventative maintenance on general-use equipment
Organization Sustaining Level
Designing an ABC System
Step 1 - Define activities, activity cost pools, and activity measures
Step 2 - Assign overhead costs to activity cost pools
Step 3 - Calculate activity rates
Step 4 - Assign overhead costs to cost objects using activity rates and activity measures
Step 5 - Prepare mangement reports
ABC Limitations
-Substantial resources required to implement and maintain
-Resistance to unfamiliar numbers and reports
-Desire to fully allocate all costs to products
-Potential misinterpretation of unfamiliar numbers
-Does not conform to GAAP. Two costing systems may be needed.
Activity rate
An overhead rate in activity-based costing. Each activity cost pool has its own activity rate, which is used to assign overhead to products and services.
Unit Level Measures
Machine Hours, DL Hours, and Units Produced
Batch Level Measures
Purchase Orders Processed, Production Orders Processed, Number of setups, Setup Hours, Pounds of Materials Handled/Moved
Product Level Measures
Hours of Testing Time, Number of Part Types, Hours of Design time
Facility Level Measures
DL Hours
Predetermined Overhead Rate
Estimated Total Manufacturing Overhead/Estimated Total Amount of the Allocation Base
Activity-based management
A management approach that focuses on managing activities as a way of eliminating waste and reducing delays and defects.
Benchmarking
A systematic approach to identifying the activities with the greatest room for improvement. It is based on comparing the performance in an organization with the performance of other, similar organizations known for their outstanding performance.
What are the 3 common approaches to assigning overhead cost to products?
Plantwide overhead rates, departmental overhead rates, and activity-based costing.
Parts administration is an example of
Product Level Activity
Production order processing is an example of a
Batch Level Activity
Purchase Order Processing is an example of a
Batch Level Activity
Which of the following activities would be classified as a batch-level activity?
a)Setting up equipment
b)Designing a new product
c)Training employees
d)Milling a part required for the final product
Setting up Equipment
T/F. Departmental overhead rates applied on the basis of a single activity measure will eliminate any distortions in unit costs due to product diversity
False
T/F. In activity-based costing, departmental overhead rates are used to apply overhead to products.
False
In activity-based costing, unit product costs computed for external financial reports includes
Direct Materials, Direct Labor, and MO
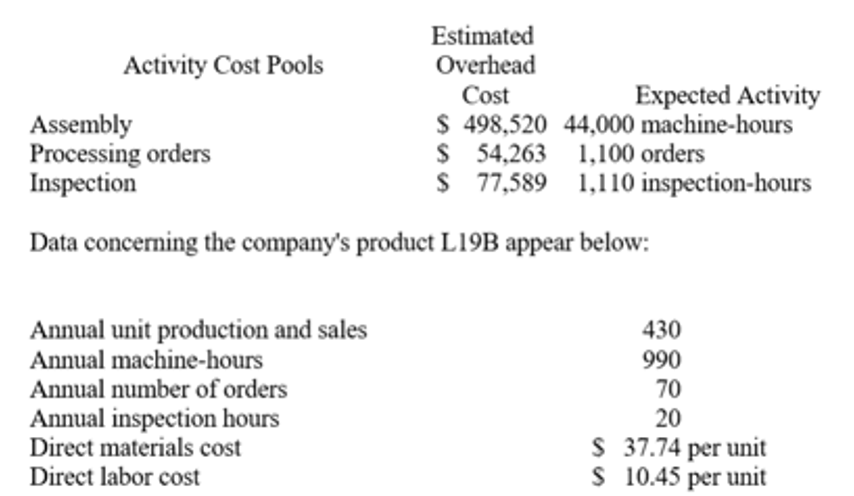
According to the activity-based costing system, the unit product cost of product L19B is closest to: (Round your intermediate calculations to 2 decimal places.)
$85.56 per unit
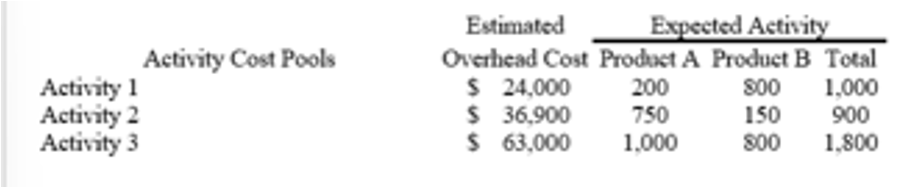
Lindsey Company uses activity-based costing. The company has two products: A and B. The annual production and sales of Product A is 5,000 units and of Product B is 2,000 units. There are three activity cost pools, with estimated total cost and expected activity as follows:
$14.11
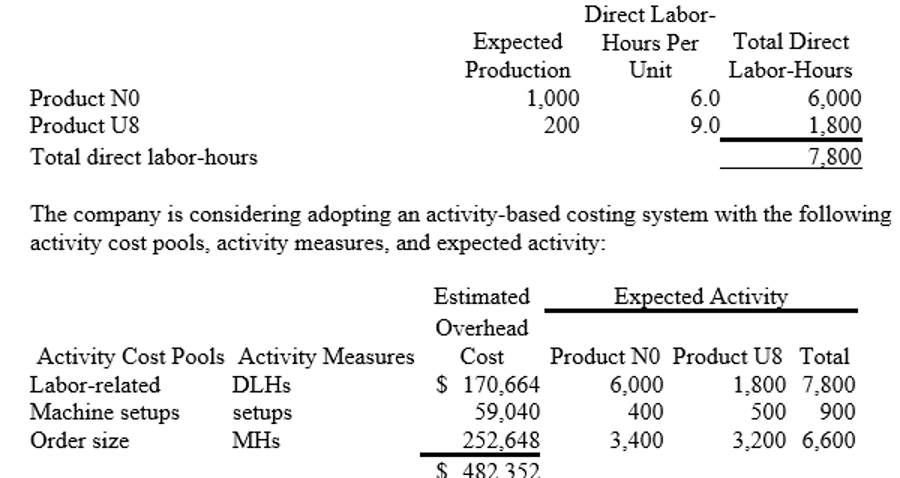
Foisy, Inc., manufactures and sells two products: Product N0 and Product U8. Data concerning the expected production of each product and the expected total direct labor-hours (DLHs) required to produce that output appear below:
The total overhead applied to Product U8 under activity-based costing is closest to: (Round your intermediate calculations to 2 decimal places.)
194,680
Preventive maintenance is performed on general-purpose production equipment.
Facility-level
Products are assembled by hand.
Unit-level
A security guard patrols the company grounds after normal working hours.
Facility-level
Purchase orders are issued for materials to be used in production.
Batch-level
Modifications are made to product designs.
Product-level
New employees are hired by the personnel office.
Facility-level
Machine settings are changed between batches of different products.
Batch-level
Parts inventories are maintained in the storeroom. (Each product requires its own unique parts.)
Product-level
Insurance costs are incurred on the company’s facilities.
Facility-level
Which of the following statements about processing costing is false?
Process costing accumulates costs by department.
Process costing assigns departmental costs uniformly to all identical units that pass through the department during a period.
Process costing systems compute unit costs by department.
Process costing is used when a company produces a continuous flow of units that are distinguishable from one another
Process costing is used when a company produces a continuous flow of units that are distinguishable from one another.
Which of the following statements about companies that use processing costing is false?
A processing department is an organizational unit where work is performed on a product and where materials, labor, or overhead costs are added to the product.
Costs are accumulated by department.
Raw material costs are added only to the first processing department.
A separate Work in Process account is maintained for each processing department.
Raw material costs are added only to the first processing department.