Grade 11 Biology - Evolution
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
Evolution
changes in DNA of a species over time
Natural Selection
The environment selects which individuals produce the most.
Artificial Selection
When humans decide which individuals will breed
Adaptation
A change in protein synthesis giving an advantage to an organism but not a change in DNA
vestigial structures
A structure in an organism that has lost all or most of its original function.
Gene pool
The total collection of alleles in a population
Convergent Evolution
the evolution of similar traits in distantly related species eg. whales and sharks
Divergent Evolution
evolution of one or more closely related species into different species; resulting from adaptations to different environmental conditions.
Coevolution
process in which two or more species evolve in response to changes in each other
Eg. agouti and brazil nut
Lamarck
inheritance of acquired characteristics- proved incorrect
Galapagos Islands
Islands where Darwin notice adaptive radiation
Cuvier
a palaeontologist who proposed the theory of catastrophism
Lyell
a geologist who proposed the theory of uniformism
Macroevolution
large scale evolutionary changes including the formation of new species
Microevolution
Small changes in gene frequencies within one generation of a population/species.
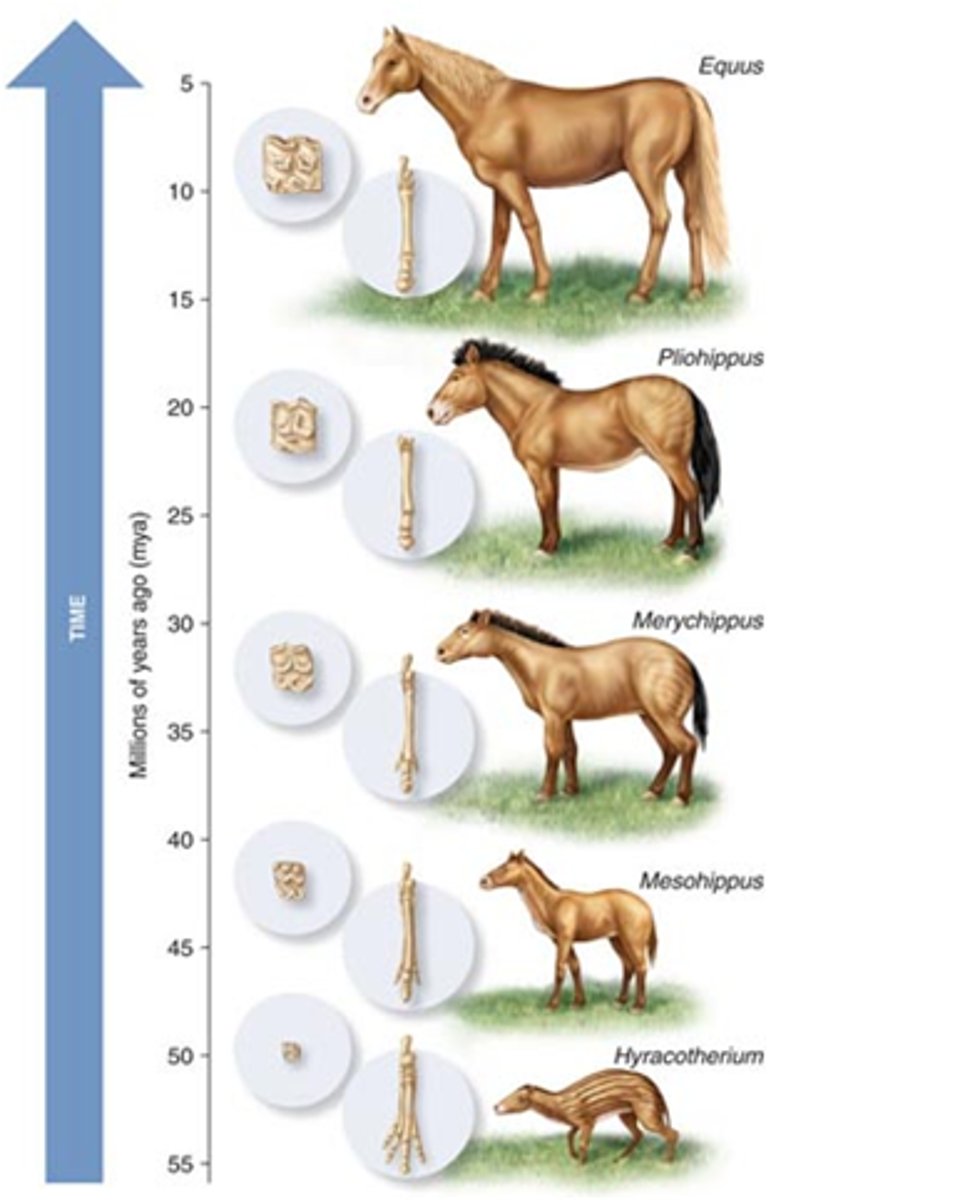
Allopatric Speciation
Occurs when the population is divided by a physical barrier into two subpopulations
Genetic Drift
changes to an allele's frequency as a result of chance; such changes are more pronounced in small populations
Gene Pool
All of the alleles in all the individuals that make up a population
Alleles
a specific form of a gene
Mutation
A change in DNA
homologous structures
Similar anatomical structures with different functions
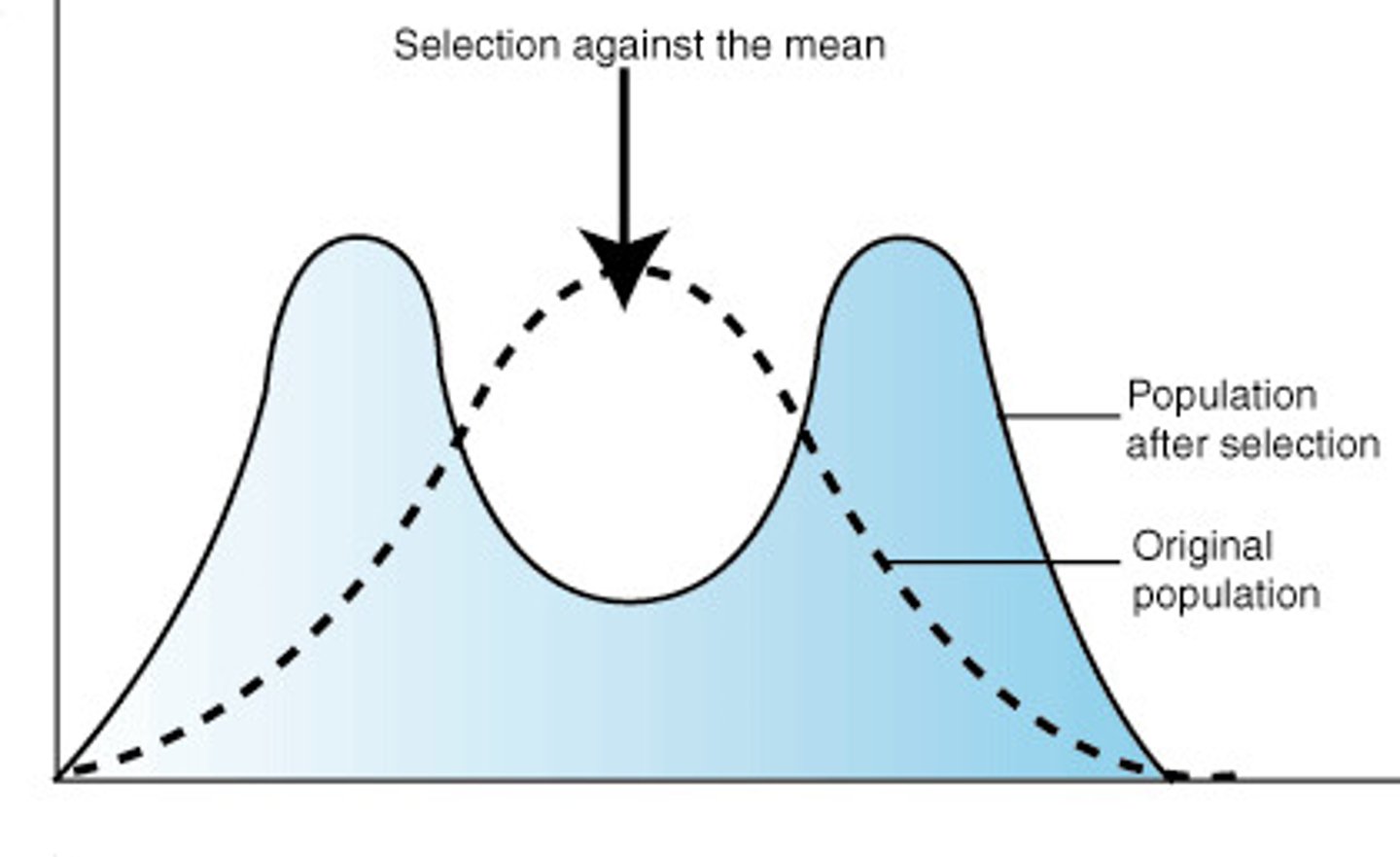
Disruptive Selection
a type of natural selection in which two extreme forms of a trait are selected
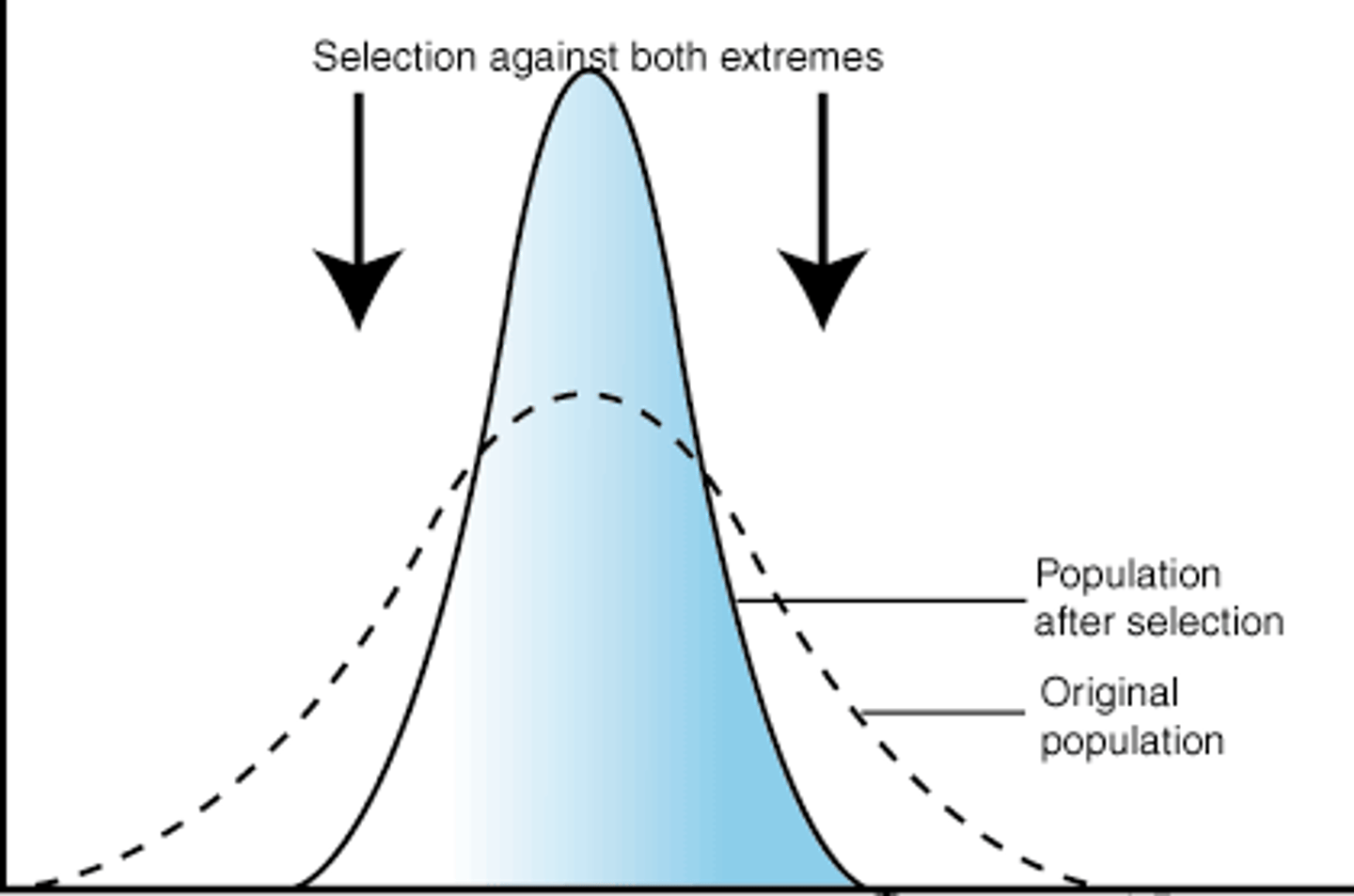
Stabilizing Selection
Natural selection that favours average individuals in a population
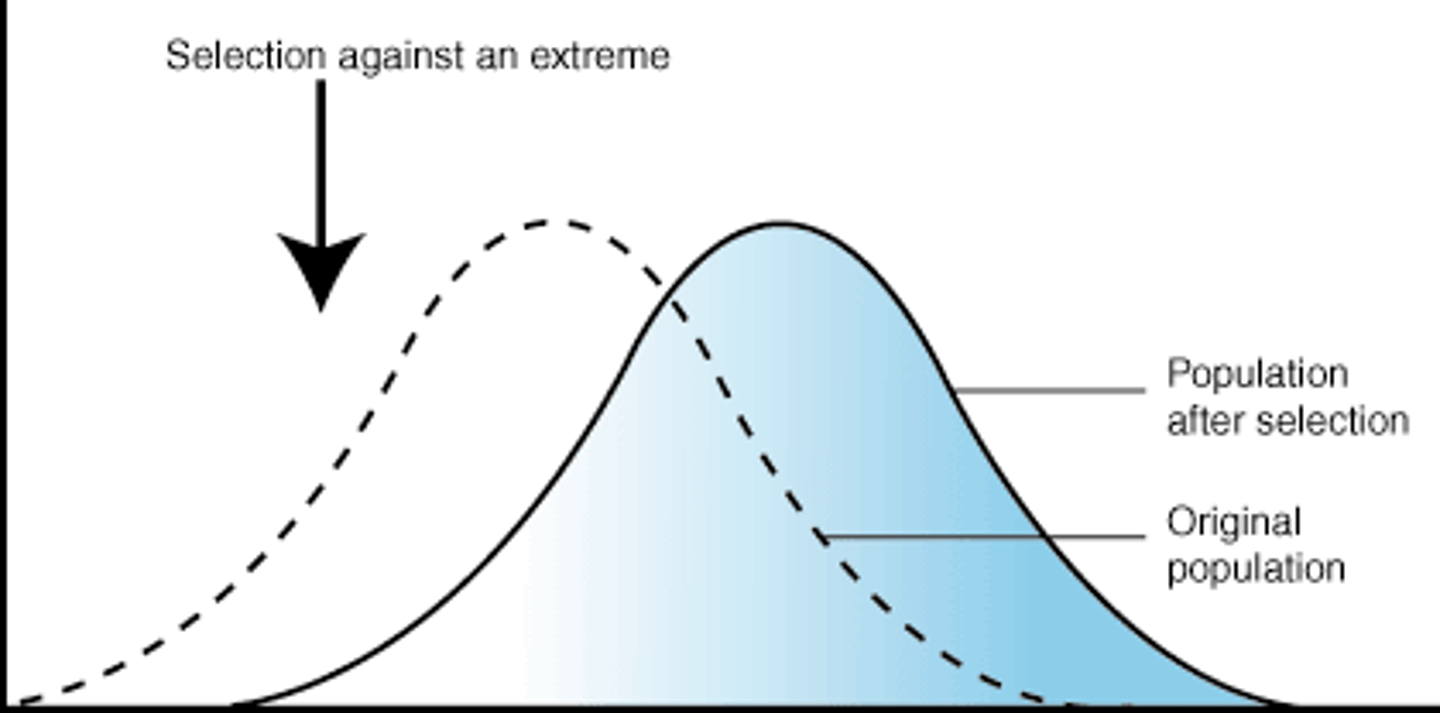
Directional Selection
occurs when natural selection favours one of the extreme variations of a trait
Adaptive Radiation
Evolution from a common ancestor that results in many diverse species adapted to different environments
Cladistics
a method of determining evolutionary relationships based on the presence or absence of recently evolved traits
Analogous structures
Similar functions with different anatomical structures
terestrial
Living on land
punctuated equilibrium
The theory that species evolve during short periods of rapid change
adaptive radiation
An evolutionary pattern in which many species evolve from a single ancestral species
Fossils
Traces of organisms that existed in the past
Embryology
The branch of zoology studying the early development of living things.
founder effect
When a portion of an original population breaks off and forms a new population
bottleneck effect
a population is reduced drastically from an event
gradualism
species evolve by the accumulation of many small changes over a long time period
punctuated equilibrium
The theory that species evolve during short periods of rapid change
behavioral adaptation
A change in the way an animal acts and responds to its environment.
Pre-zygotic
before fertilization
Post-zygotic
after fertilization
Behavioural
Two species have different courtship behaviours. eg. Songbirds
temporal
mating at different times. eg.frogs
Habitat
Species occupy different environments
gametic isolation
When sperm can't fertilize the eggs.
Zygotic Mortality
Fertilization, but no zygote
hybrid inviability
fertilized egg cannot progress past an early embryo
hybrid infertility
hybrid offspring are sterile or have low fertility