Pre-clinical dental hygiene Exam 1 review
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
individual autonomy and respect for human beings
People have the right to be treated with respect. They have the right to informed consent prior to treatment, and they have the right to full disclosure of all relevant information so that they can make informed choices about their care.
confidentiality
respect the confidentiality of client information and relationships as a demonstration of the value we place on individual autonomy. We acknowledge our obligation to justify any violation of confidence
societal trust
We value client trust and understand that public trust in our profession is based on our actions and behavior.
non-maleficience
We accept our fundamental obligation to provide services in a manner that protects all clients and minimizes harm to them, and others involved in their treatment.
beneficence
We have a primary role in promoting the well-being of individuals and the public by engaging in health promotion/disease prevention activities.
justice and fairness
We value justice and support the fair and equitable distribution of health care resources. We believe all people should have access to high-quality, affordable oral healthcare.
veracity
We accept our obligation to tell the truth and expect that others will do the same. We value self-knowledge and seek truth and honesty in all relationships
standard precautions
protects DHCP dental health care professional and patients from transission agents such as
blood
saliva
all bodily fluids except sweat
nonintact skin
mucous membranes
Body fluids of ALL patients are
treated as if they were infectious.
● Exposure Control Plan
● Consistency between HCP’s to
prevent Cross-Contamination
universal precautions
most emphasis on bloodboorne pathogens
cross contamination
spread of microorganisms from one source to another
person to person
person to inatimate object and then to another person
factors that influence infection
number of organisms
virulence
immune status of the host
general physical health and nutritional stauts
classification of aerosols
small 3-5 microns
breathed into lings
cavitron
larger remain airborne a short time visible
greater than 50 microns
particle from cavity prep or daliva
tuberculosis
Transmission: Inhalation of tubercle bacilli
○ Mycobacterium tuberculosis
● Symptoms:
○ Low-grade fever
○ Loss of appetite
○ Weight loss
○ Tires easily
● May have reactivation tuberculosis
● Clinical examination: look for lymphadenopathy
hep a transmission
fecal oral
hep b transmission
All body fluids carry the virus
■ Blood, saliva, semen, and vaginal fluids are infectious
■ Percutaneous
● Needle sticks
■ Sexual exposure
■ Blood transfusions or blood products
hep c transmission
Percutaneous
○ Parenterally
○ Blood
○ Found in saliva
● 4 million infected in the US*
○ Upgraded from 3.2 million
● 80% develop chronic infection
● Baby Boomers!
○ Born 1946 - 1964
○ Sex, Drugs, Rock & Roll
hep b prevention
Immunizations
■ 95% effective
■ After 15 year check status
○ Safe use of disposable syringes and needles
The vaccine for Hepatitis B protects
against?
Hepatitis D
human herpesviruses
Highly infectious
● Produce latent, recurrent tendencies
● Immunosuppressed patients are at risk - opportunistic
HPV
Over 200 Types
○ 40 can infect genital and oral areas
● Types 16 & 18
○ 80% of cervical cancer
○ Type 16 is most likely oncogenic HPV to
progress to cancer and is attributed to
95% of head and neck cancers
● Vaccination
○ 3 Step
○ Children 11-12 years
○ Up to age 26
HIV Infection
HIV-1 is the virus
● HIV attacks the immune system
● CD4 T Lymphocytes
● Unable to fight off
● infection, disease, cancer
● Opportunistic infections – AIDS
● Antiretroviral Therapy
● Strict ART regimen can achieve viral suppression.
● Preexposure Propholaxis - PrEP
● Prevents HIV infection in high-risk indivisuals
MRSA
Found on healthy human skin
● Causes serious infection when
enters the bloodstream or
subcutaneous tissues
● Transmitted by direct and indirect
contant
● Resistant to antibiotic therapies
reccomended vaccines
Hep. B, Influenza, Measles, Mumps, Rubella, Varicella, COVID-19
critical items
instruments anything the comes in contact with blood or tissues
semi critical items
items that go in the mouth but no blood
mirror impression xcp
noncritical items
items that are contact with the the pt but not the mouth ]
bp cuff and dental chair
modified pen grasp index and thumb
on the instrument handle
holds instrument
modified pen grasp middle finger
rest lightly against the shank
helps guide working end
feels vibrations transmitted from working end to shank
modified pen grasp ring finger
on oral structure often tooth
advances ahead of the other fingers in the grasp
stabilizes and supports the hand for control and strength
modified pen grasp pinky
near ring finger held in a naural relaxed manner
has no function in the grasp
work related ergonomic risk factors
Repetitive motion
● Frequent resisted hand/finger motion
● Use of vibrating instruments
● Forceful pinching & gripping of small
diameter instruments
● Static posture
workplace related risk factors ergonomics
Patient & operator's chair
● Placement & design of delivery unit
● Scheduling
● # of patients
● Work hours
worker related risk factors ergonomics
Work style
● Stress level
● Posture
● Attitude
● Fitness
what is ergonomics
Science of fitting physical & psychosocial work and work environment
to the individual
● Term coined in 1950
● Greek
○ "Ergon" – work
○ "Nomos" – natural laws
WMD
work-related musculoskeltal disorder
CTD
Cumulatative trauma disorder
RSI
repetitive Strain Injury
neutral posture
Appendages are neither away nor
toward the body's midline
● Shoulders are not abducted,
overextended, hunched
● Trunk is not flexed forward or
extended backwards, twisted or
laterally bent
● When seated – buttocks, thighs, legs
are evenly supported; arches behind
knees are open for free circulation;
lumbar region is supported
risk reduction
Instrument handle design
● Use only enough force to get job done
● Alternate using hand and vibratory instruments
(power scalers, handpieces)
● Wear proper fitting gloves
● Avoid excessive finger motion
● USE A MIRROR FOR INDIRECT VISION
Integrate stretches into daily routine
Stretch regularly - 3 minutes every hour
masticatory mucosa
Masticatory mucosa
Surrounds the necks of the teeth
Free
Interdental
Attached
alveaolar mucosa
Mucogingival Junction
Alveolar mucosa,
Frenum
the three Cs
-color
contour
consistency
color
Usually pink
Color will vary depending on
Thickness of tissue
Keratinization
Pigmentation
Vascularity
Presence of disease
contour
Flat and knife-like
Snugly adapted to the tooth
consistency
Texture/ smooth
Density: firm and resilient
Col
Central depression or concave area that is non-keratinized
Between buccal & lingual papillae
Conforming to interproximal bone
Inflammation starts here
looks like sagging tent
attached gingiva
Continuous with the free gingiva
Keratinized Stratified squamous epithelium
gingival fiber groups
Bundles of Gingival Fibers connect the gingiva to the bone and/or the tooth to provide support during chewing
alveolar mucosa
Thin,
Non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
Movable
Loosely attached to bone
Continuous
Different from the free & attached gingiva
the color is redder and highly vascular
indefinite contour smooth and shiny texture
soft and thin
uses of the perio probe
Assess the Periodontal Status for Preparation of a Treatment Plan
Determine Clinical Attachment
Conduct Mucogingival Examination
Make Other Gingival Determinations
Guide Treatment
Evaluate Success and Completeness of Treatment
Evaluation at Continuing Care and Periodontal Maintenance Appointments
Measure Oral Lesions for Clinical Documentation
gingival sulcus or crevice
crevice or groove between the free gingiva and the tooth
1-3mm in health
gingival pocket or pseudopocket
formed by gingival enlargement without apical migration of the junctional epithelium
>3mm
periodontal pocket
pockets form from disease or degeneration
causing apical migration of junctional epithelium/epithelial attachment
>3mm
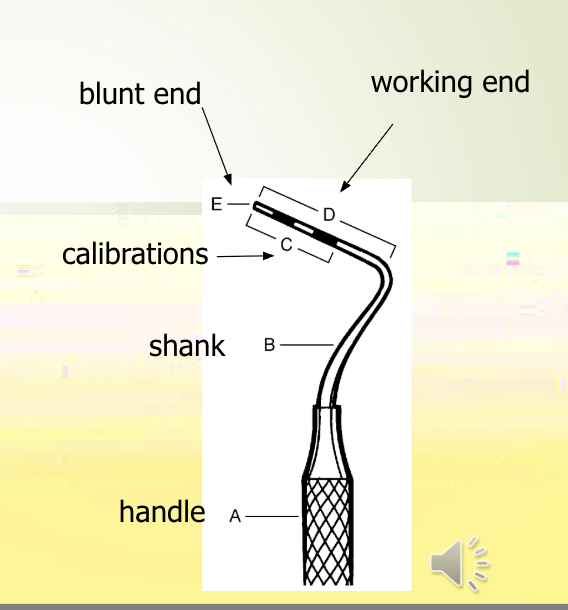
parts of the probe
Handle
Angled shank
Working end
Blunt end
Calibrations
marquis
round; color-coded; calibrations at 3, 6, 9, 12 mm
williams
round or flat; calibrations at 1, 2, 3, 5, 7, 8, 9, 10 mm
who
round; ball tip; calibrations at 3.5, 5.5 mm
nabors
round; curved, color-coded; calibrations at 3, 6, 9, 12
unc 15
round – calibrations at 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10, 11,12,14, 15
working end of probe
Slender, rod-like working ends
Cross-sections
Round
easy to adapt
may puncture epithelial attachment
Oval
Flat
less likely to puncture
difficult to adapt interproximally
probe selection criteria
Adaptability
Should adapt to the circumference of tooth
Markings
Easy to read
Length
Healthy mouth v. disease
assess the periodontal status
Preparation of treatment plan
perform a sulcus
perform a sulcus an pocket survey
Shape,
Topography
Dimensions
Measure depths
perform a muco gingval exam
Determine width of attached gingiva
Mucogingival involvement
make other gingival determinations
Bleeding upon probing – indicates disease
Recession
Plaque control
Any measurement : crown length, diastema, pathology, overbite, overjet, lesions, etc)
guide to treatment
Detect anatomical configurations (roots)
Detect submarginal deposits
Determine depth of pocket & instrument selection
Evaluate success of treatment
pocket characteristics
depth vries on each area of very tooth
location of margin
location of attachment
pockets tend to be deepest in the col area
anatomical features of the tooth influences prob direction (crown and root shape)
Dental Hygiene Process of care
ADPIED
Asses, Dagnose Plan Implement Evaluate Document
Diagnose
Problem Identification
Plan
selection of interventions
implement
activating the plan
evaluate
feedback on effectivness
document
comprehensive record-keeping
assess
data colection