Engine Parts Identification
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms

What is this part and what does it do?
Camshaft: Shaft that holds all cam lobes. Driven by the crankshaft using a belt, chain, or gears.
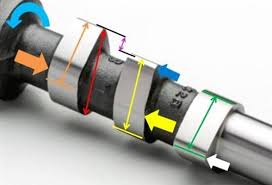
What is this part and what does it do?
Cam lobes: Determines how far and how long the valve will stay open. Far = Left, How long = Duration.
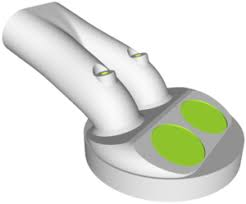
What is this part and what does it do?
Intake port: Passage for the air and fuel to enter the cylinder.

What is this part and what does it do?
Intake Valves: Opens and closes the port (larger diameter).
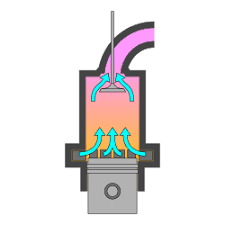
What is this part and what does it do?
Combustion Chamber: Area where fuel is burned.

What is this part and what does it do?
Engine Block: Foundation of all engine parts. (starting lego) (Bottom end of engine) (strong metal)

What is this part and what does it do?
Connecting Rod: Connects crankshaft to piston.

What is this part and what does it do?
Crankshaft: Changes up/down (reciprocating) motion of the piston into rotary movement. (up and down to circular motion)
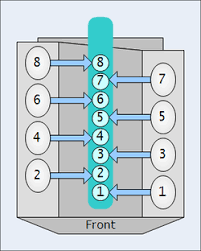
What is this part and what does it do?
Cylinder: Area where piston moves up and down. Bore = Diameter of cylinder. Stroke = Distance traveled by the piston.

What is this part and what does it do?
Piston Pin: Connects to the connecting rod and also allows piston to swivel. (wrist pin)

What is this part and what does it do?
Piston: Receives the force from the expanding gases as fuel is being burned. Slides up and down in the cylinder.
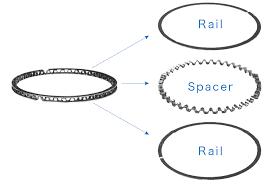
What is this part and what does it do?
oil control ring: Controls how much oil is left on the cylinder walls.

What is this part and what does it do?
Compression Ring: Seals the piston inside the cylinder.

What is this part and what does it do?
Cylinder Head: Seals off the top of the cylinder and forms part of the combustion chamber. House the valves, ports, springs, etc.

What is this part and what does it do?
Exhaust Port: Passage for the exhaust to leave the cylinder.

What is this part and what does it do? (smaller of the two)
Exhaust valve: Opens and closes the exhaust port. This way exhaust can leave the engine.

What is this part and what does it do?
Valve Spring: Closes the valve

What is this part and what does it do?
Spark Plug: Provides an air gap that allows the spark to ignite the fuel.

What is this part and what does it do?
Valve cover: Covers all valve-train parts so they may be lubricated and oil won’t leak.

What is this part and what does it do?
Crankcase: Open space around the crankshaft to let it spin. Oil and blow-by-gases are located in this area.

What is this part and what does it do?
Harmonic Balancer - An (also called a crankshaft or vibration damper) is a device attached to the front end of the crankshaft that reduces and controls torsional vibrations caused by the crankshaft twisting (torque) during engine operation.
Function:
The harmonic balancer absorbs and dampens the twisting forces (harmonics) created as each cylinder fires. This protects the crankshaft, bearings, and other engine components from stress and potential failure, while also helping keep engine operation smooth.

What is this part and what does it do?
The flywheel (in manual transmission vehicles) is a large, heavy, circular component that bolts to the rear of the crankshaft and serves several important purposes:
Flywheel (manual):
Provides rotating mass to keep the engine running smoothly between power strokes.
Has a friction surface for the clutch disk to engage and disengage power to the transmission.
Contains a ring gear around its edge that the starter motor engages to crank the engine.

What is this part and what does it do?
The flexplate (in automatic transmission vehicles) is a large, heavy, circular component that bolts to the rear of the crankshaft and serves several important purposes:
Flexplate (automatic):
Much lighter and thinner than a flywheel.
Connects the crankshaft to the torque converter in automatic transmission.
Also has a ring gear for the starter motor to crank the engine.

What is this part and what does it do?
A front or rear crankshaft seal: An oil seal located at each end of the crankshaft where it passes through the engine block.
Front crankshaft seal (timing cover seal): Keeps engine oil from leaking where the crankshaft extends through the front of the engine to drive the harmonic balancer and accessory belts.
Rear crankshaft seal (rear main seal): Prevents oil leaks where the crankshaft connects to the flywheel or flexplate at the back of the engine.

What is this part and what does it do?
The engine oil pan: a metal (sometimes plastic or composite) reservoir bolted to the bottom of the engine block.
Function:
Hold and stores the engine’s supply of oil when the engine is not running.
Collects oil as it drains back down from the engine’s moving parts.
Houses the oil drain plug (for oil changes).
In many cases, also contains the oil pickup tube screen location, which sends oil to the oil pump.

What is this part and what does it do?
Main bearings (split bearings):
Semi-circular metal bearings that support the crankshaft inside the engine block.
Allow the crankshaft to spin smoothy while reducing friction.
Carry the engine’s load and keep the crankshaft aligned.

What is this part and what does it do?
Main bearing caps:
Heavy-duty caps that bolt over the crankshaft main journals and bearings.
Hold the crankshaft securely in place in the engine block.
Work together with the engine block and main bearings to prevent crankshaft movement.

What is this part and what does it do?
The crankshaft thrust bearing: A type of engine bearing designed to control the axial movement (forward and backward motion) of the crankshaft inside the engine block.
Function:
It prevents the crankshaft from “walking” or shifting end-to-end due to forces from the clutch, transmission, or torque converter, ensuring that the crankshaft stays properly aligned with the connecting rods and main bearings.

What is this part and what does it do?
Connecting Rod bearing caps and bearings: The rod bearings are smooth, curved, inserts that sit between the connecting rod and the crankshaft, allowing the rod to move smoothly as the crankshaft turns. The rod bearing cap bolts to the bottom of the connecting rod to hold the bearing in place around the crankshaft journal. Together, they let the crankshaft and connecting rods move freely while reducing friction and carrying engine loads.

What is this part and what does it do?
The exhaust manifold: A component of the engine that collects exhaust gases from each cylinder and directs them into a single pipe toward the exhaust system.
Function:
It bolts to the cylinder head and ensures that the hot gases are funneled smoothly away from the engine, helping reduce back pressure and noise.

What is this part and what does it do?
Camshaft phaser: The camshaft phaser replaces the fixed chain or belt sprocket with a hydraulic camshaft timing sprocket, or cam actuator. Each camshaft phaser uses high-engine oil pressure to rotate the camshaft in relation to its drive sprocket.

What is this part and what does it do?
Crankshaft Sprockets: A crankshaft sprocket is keyed to the crankshaft snout. A larger camshaft sprocket, with either metal or plastic teeth, bolts to the camshaft. The timing chain transfers power from the crankshaft sprocket to the camshaft sprocket. Like timing gears, the chain sprockets have timing marks. The marks must line up to properly time the camshaft with the crankshaft.

What is this part and what does it do?
Timing chain: A timing chain and sprockets can also be used to turn the camshaft.

What is this part and what does it do?
Chain tensioner: A chain tensioner may be used to take up the slack in the chain as it and the sprockets wear. It is usually a spring-loaded plastic or fiber block. The spring pushes the block outward, keeping a constant tension on the chain. A chain-type camshaft drive for an OHC engine commonly uses guides and sometimes a tensioner.

What is this part and what does it do?
Chain guides: A chain guide may be needed to prevent chain slap. Chain slap occurs when the chain flaps back and forth because of excessive slack in the chain. The guides have a metal body with either a plastic or Teflon face. This allows the chain to slide on the guide with minimum friction and wear.

What is this part and what does it do?
Camshaft Sprockets: The timing belt sprockets are usually made of cast iron (steel) or aluminum. The crank sprocket is keyed to the crankshaft snout. The camshaft sprocket normally bolts to the front of the camshaft. A dowel pin may be used to position the camshaft sprocket correctly. Belt sprockets have timing marks, just like timing gears and chain sprockets. The timing marks must be aligned with specific points on the engine. This properly times the opening of the engine valves.
What is this part and what does it do?
What is this part and what does it do?
What is this part and what does it do?