Stroke & bleeding risk assessment in AF
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
what are the two types of ischaemic stroke
thrombotic → clot forms in brain
embolic → clot forms elsewhere and travels to the brain to cause a blockage
a stroke with AF is called a cardio-embolic stroke
what is the link between AF and strokes
irregular heartbeat of AF → chambers of heart don’t empty fully when heart contracts → pooling of blood in chambers of heart → clot, which can leave heart and reach blood vessel in brain → cardio embolic stroke (type of ischaemic stroke)
AF is a leading cause of ischaemic strokes
Stroke is often the first presentation of AF
AF is associated with more severe strokes and ‘longer’ TIAs
what are risk factors for embolic stroke
atrial fibrillation is a potent, independent risk factor but actual risk is dependent on other risk factors such as
age
gender
co-morbidities
what is the prevalence of AF
3% in adults
prevalence increases with age and with co-morbidities
what are the most effective pharmacological intervention to prevent the risk of stroke in patients with AF
anticoagulation
vitamin K antagonists like warfarin
DOACs
(antiplatelets are no longer recommended)
why is the risk with anticoagulant therapy
anticoagulants are high risk drugs that increase the risk of major bleeds
we needs to balance the benefits against the increased risk of bleeding using
CHA2DS2-Vasc stroke risk score
ORBIT bleeding risk score
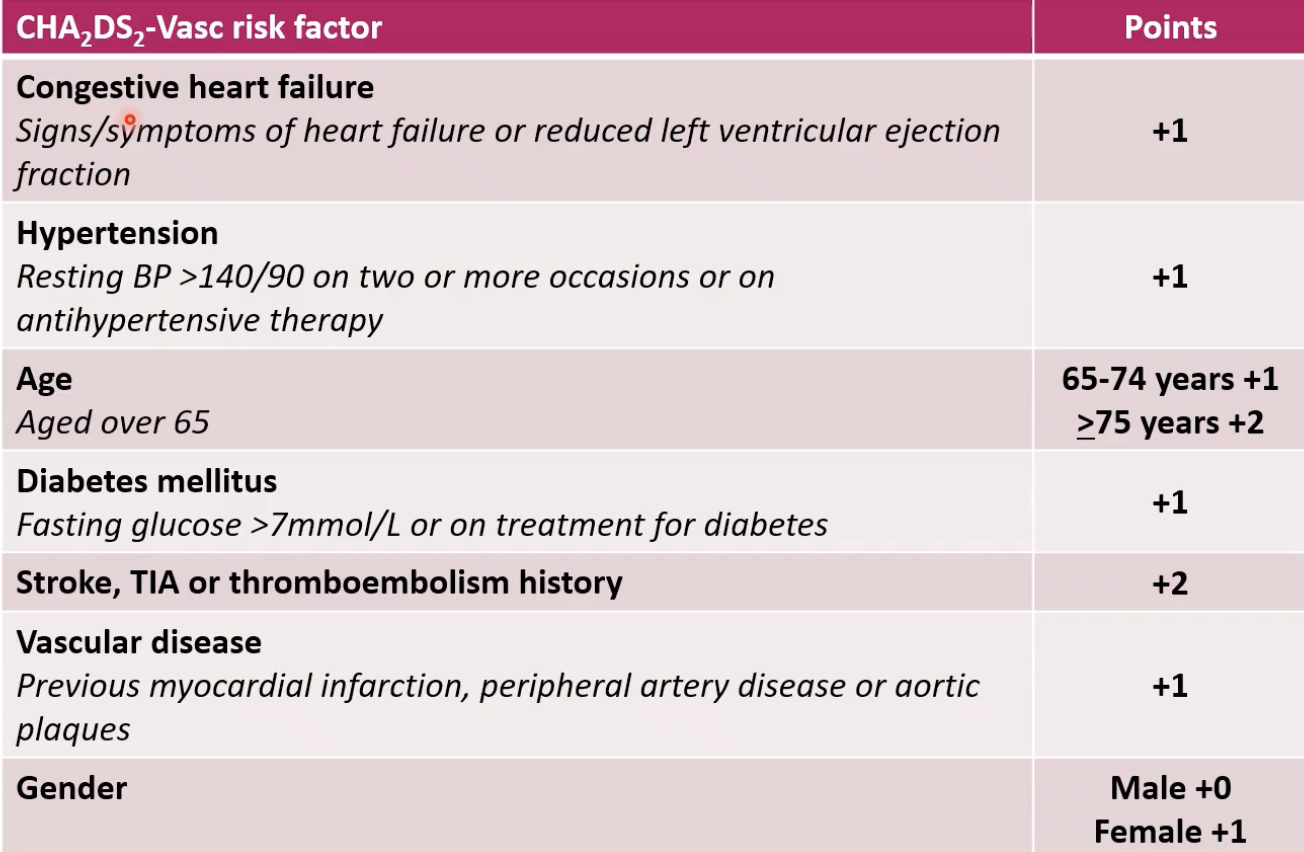
what is the CHA2DS2-Vasc score
a risk assessment tool that estimates the likelihood that any given with with AF will suffer stroke in the next 12 months
used to support clinical decision-making, regarding suitability for anticoagulant therapy
each letter of the acronym represents an independent risk factor, which contribute 1 or 2 points to the final score
higher score → greater risk of the patient suffering a stroke
calculating CHA2DS2-Vasc score: what are the different risk factors
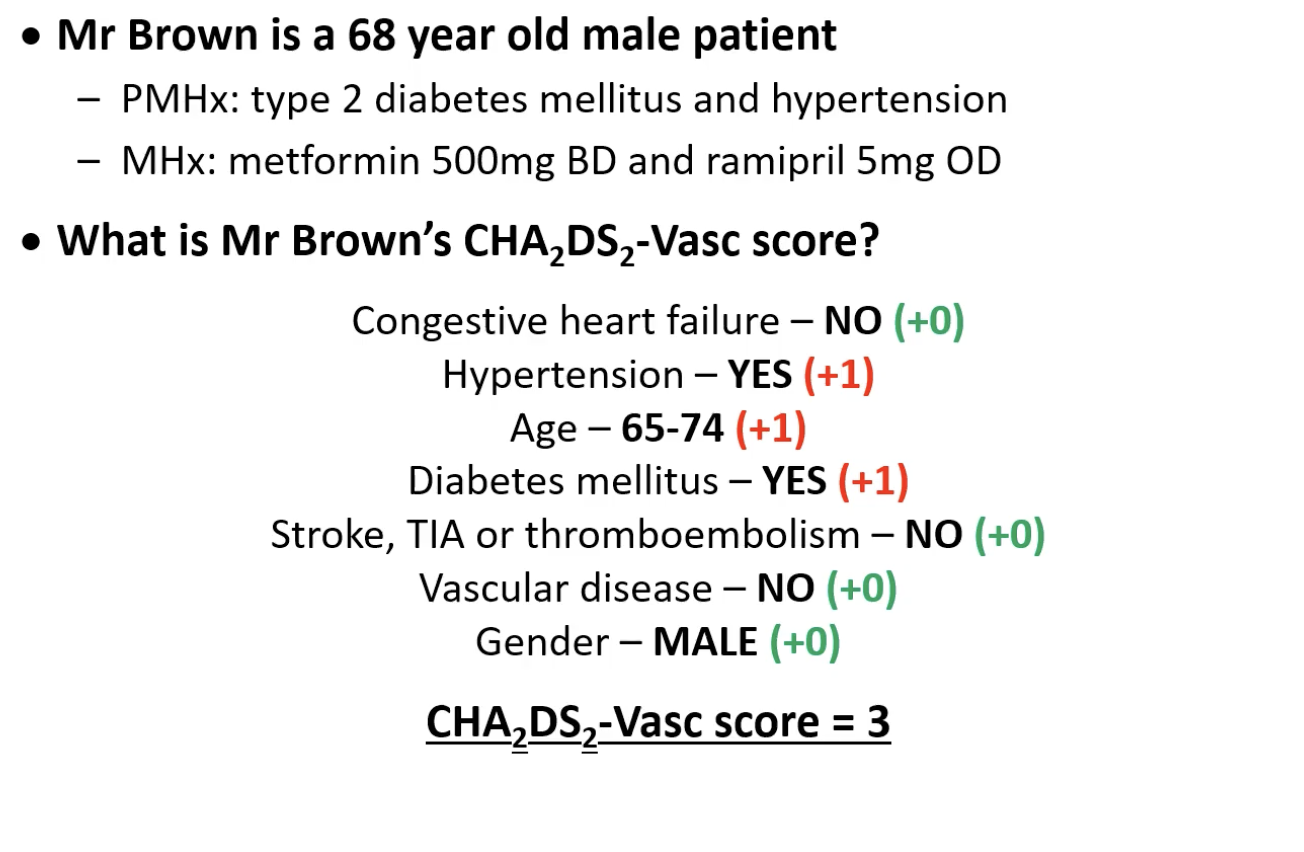
CHA2DS2-Vasc score: example patient
what are the clinical effects of the CHA2DS2-Vasc score
the score correlates to an estimated risk of having a stroke over the following 12 months
higher score → the greater the risk of having a stroke + the greater the benefit of anticoagulation
NICE have recommendations to prevent stroke
don’t offer stroke prevention to people under 65 with AF and no risk factors under than their gender
consider anticoagulation for men (but not women) with a score of 1
offer anticoagulation to people with a score of 2 or above
regardless of their score, take account of the patient’s bleeding risk
how do you explain stroke risk to patients
regardless of the CHA2DS2-Vasc score, it is the patient’s decision whether they accept or reject anticoagulation
we have the responsibility to explain the risk, in order to support patients to make informed decisions
what is the ORBIT score
a risk assessment tool that estimates the likelihood that a patient with AF, who is on oral anticoagulation, will suffer a major bleed in the coming 12 months
used to support clinical decision-making, regarding suitability for anticoagulant therapy
each letter of the acronym represents a risk factor, or factors that contribute to the final score
higher score → greater risk of suffering a major bleed
some risk factors are modifiable
calculating ORBIT score: what are the different risk factors

what are the limitations of the ORBIT score
there are many bleeding risk factors that are not considered in the ORBIT score, but are part of other risk assessment tools such as HAS-BLED
hypertension
liver disease
ischaemic stroke history
Labile INRs (unstable, fluctuating International Normalized Ratio in patients taking anticoagulant medications, typically warfarin.)
medications other than antiplatelets e.g. SSRIs, NSAIDs
alcohol intake (>8 units/week)
need to fully investigate modifiable risk factors anyway, regardless of the tool used
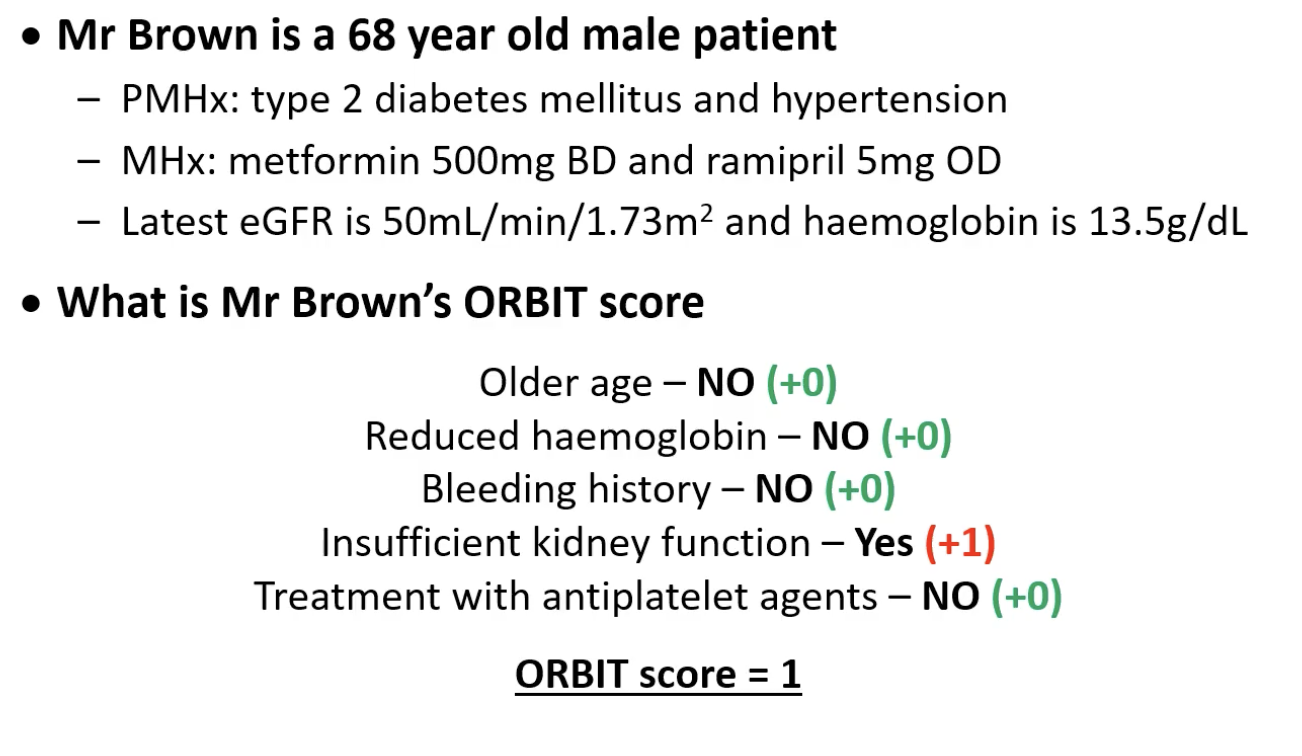
ORBIT SCORE score: example patient
what are the clinical effects of the ORBIT score
the score correlates to an estimated risk of the patient suffering a major bleed in the next 12 months
higher risk → greater risk of having a major bleed: low (0-2) = 2.4%, medium (3) = 4.7%, high (>4) = 8.1%
some risk factors are modifiable
NICE have recommendations for assessing bleeding risk and modification/monitoring of risk factors
unlike CHA2DS2-Vasc score, there are no definite threshold over which treatment should not be offered
for many people, the benefits of anticoagulation outweighs the risks
don’t withhold anticoagulation solely due to age or falls risk