elasticity - econ chapt 4
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
elasticity
a measure of how much consumers and producers will respond to a change in market conditions
what can elasticity be applied to
both supply and demand
what does elastciity meausre
responses to a change in the price of a good, c ahnge in the price of a related good, or a chnage income
elasticity allows for people to anticipate what
how OTHERS WILL RESPOND to chanages in market conditions
price elasticityc of demand/supply
how much the quantity demanded/supplied changes when the price of a good changes
cross price elasticity of demand
how much the demand curve shifts when the price of another good changes
income elasticity of demand
how much the demand curve shifts when consumers incomes change
price elasticity of demand
the size of the change in the quantity demanded of a good or service when its price changes
quantity demanded generally decreases when…
price increases
when is something more elastic
when consumers buying decisions are highly influenced by price
small change in price → large change in quantity demanded
when is something more inelastic
when consumers are not very sensitive to price changes
price elasticity is the percentage change of what
percent change in the quantity of a good that is demanded in response to a given percentage change in price
price elasticity of demand eq
% change in Q demanded/ % change in P
mid-point method
method that measures percentage change in quantity demanded (or quantity supplied) relative to a point midway between two points on a curve; used to estimate elasticity
percent change in quantity demanded formula
q2-q1/avg of q = q2-q1/(q2+q1/2)
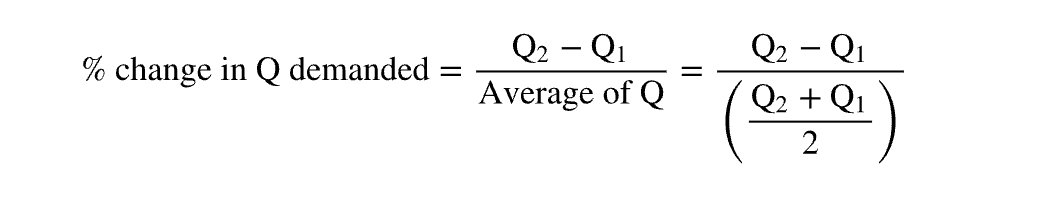
percent change in price formula
same as quanity demanded but with p1 and p2
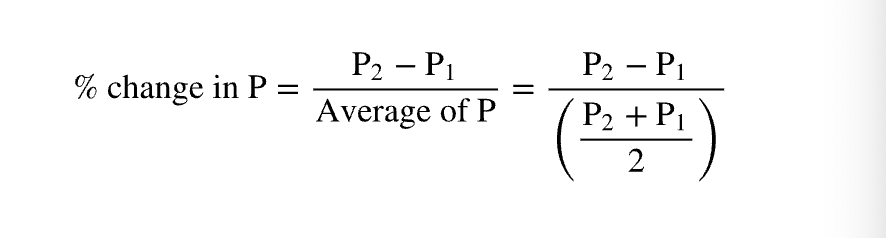
price elasticity of demand
put both percent change in price and quantity demanded together
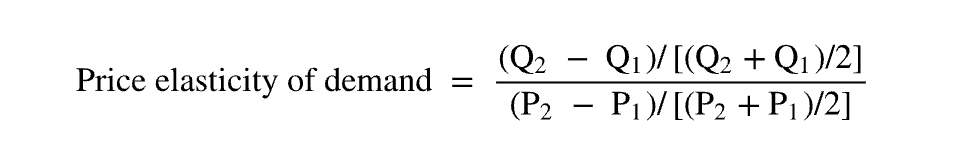
-1.38 price elasticitty of demand means?
1 percent increase in the price → 1.38 percent DECREASE in the quanitity of the product demanded
the price elasticity of demand will ALWAYS BE A ____ NUMBER
NEGATIVE
positive change in price will cause..
negative change in the quanitity demanded
negative change in price will cause…
posiutive change in the quanitity demanded
some economists drop the negative sign of elasiticity of demand
yes. do not be fooled, price elasiticty of demand is ALWASY nagtive, whether or not its printed.
think of it in ABSOLUTE VALUE
determinants of price elasticity of demand
availability of subsitutes
relative need and relative cost
the time needed to adjust to price changes
availability of subsitutes
if close subs are available for a goo then the demand for that good with be MORE ELASTIC than if only distant subs are available
availability of subsitutes example
price elasticity of demand for cranberry juice = relativiely elastic
if price is too high, consumers may switch to grape juice
degree of necessity
when a good is a bsic necessity, people will buy it even if its price rises
demand for socks/home heating during winter is not very elastic
people want to maintain that level of comfort
demand for luxuries is likely to be more or less elastic?
more
more ppl can eaisly do w out these when their prices rise
heavily demands on circumstances
cost relative to income..
if consumers spend a very small share of their incomes on a good, theur demand for the good will be less elastic than otherwirse
if a good costs a very large proportion of a persons income, the demand for the good will be more elastic
goods often have much more elastic demand over….
the long run than over the short run
adjusting to price changes takes some time
scope of the market
how someone defines the market changes how the ealsticity of demand changes
we dont always need to estimate elasticity precisiely to know that consumers will react differently to price changes for products
true - you can get a general idea from the shape of the demand curve
perfectly elastic demand
demand for which any increase in price will cause quantity demanded to drop to zero; represented by a perfectly horizontal line
perfectly inelastic demand
demand for which quantity demanded remains the same regardless of price; represented by a perfectly vertical line
graph for perfectly elastic/inelastic
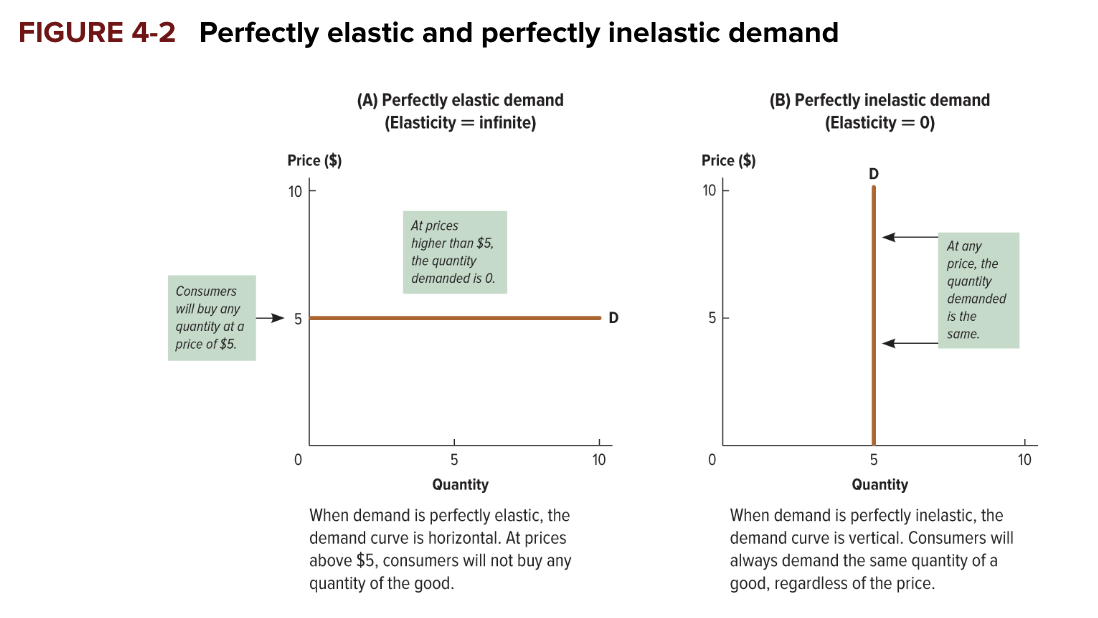
elastic
demand that has an absolute value of elasticity greater than 1
a given percentage change in the price ofa. good will causes an even LARGER PERCENTAGE CHANGE IN THE QUANITITY DEMANDED
inelastic
demand that has an absolute value of elasticity less than 1
a given percentage change in price will cause a SMALLER percentage change in the quantity demanded
unit-elastic
demand that has an absolute value of elasticity exactly equal to 1
percentage change in prices = percent change in quantity demanded
elastic, inelastic and unit-elastic graph
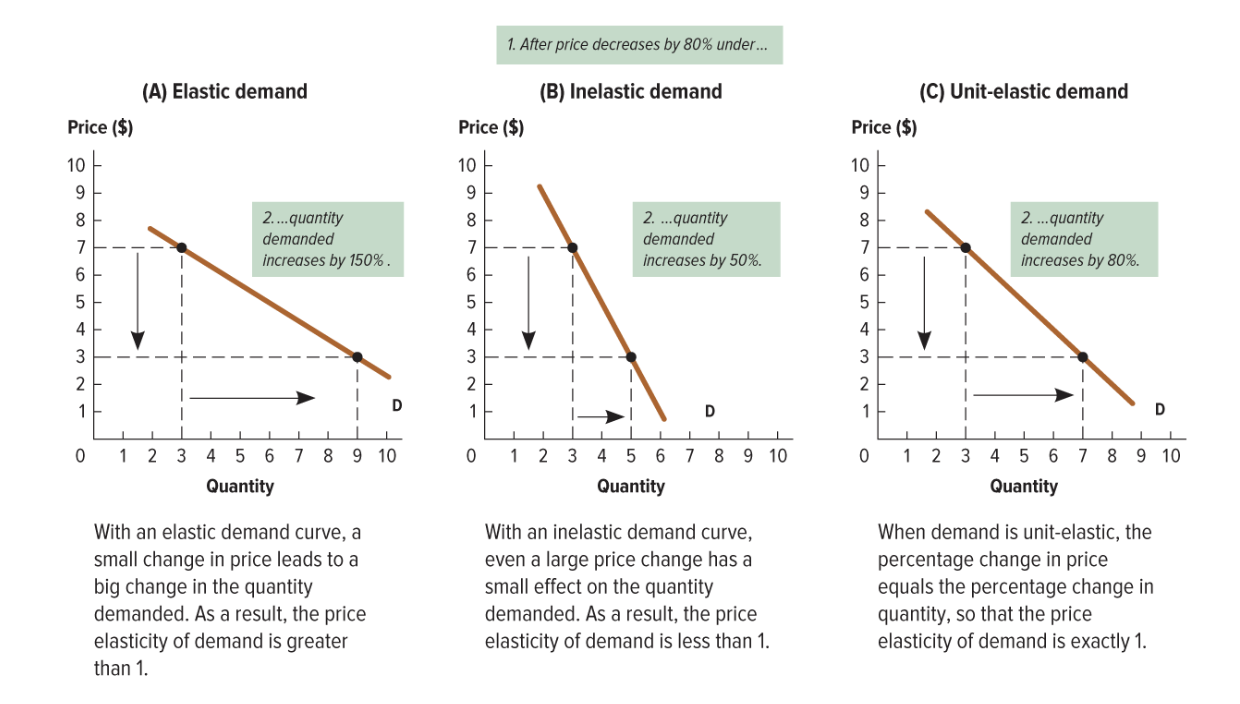
what will elasticity tell a manager
determins whether price increase will causes total revenue to rise or fall
total revenue
the amount that a firm receives from the sale of goods and services; calculated as the quantity sold multiplied by the price paid for each unit
how does an increase in price affect total revenue
quantity effect - decrease in total revenue that results from selling fewer units
price effect - increase in total revenue that results from recieving a higher price for each unit sold
what happens when quantity effect outwieghs the price effect
a price increase will cause a drop in total revenue
what happens when price effect outweighs the quantity effect
a price increase will raise total revenue
when demand is elastic, a price increase causes a…
proportionally larger decrease in the quantity demanded, and the total revenue falls
when demand is inelastics, what happens with percentage change in price/quanitity demanded
the percnt change in price is LARGER than the percent change in quanitity demanded - price effect outweighs the quantity effect, and total revenue increases
what happens when price rises with inelastic demand
consumers will purchase less of a good when its prie rises, but the change in the quantity demanded will be proportionally less than the change in price
elasticity varies along the demand curve
TRUE. soooo it changes as you move along the curve, and it refers to one place at a timeon the curve
general rule of demand and elasticity
demand tends to be MORE ELASTIC WHEN PRICE IS HIGH
more INELASTIC when price is LOW
the ealsticity is different at different points along a linear demand curve
yes!!!
going from 45 to 40 dollars is a much smaller difference in percnetage terms than ging from 10 to 5 dollars, even if the slope of the curve is the same between both sets of points
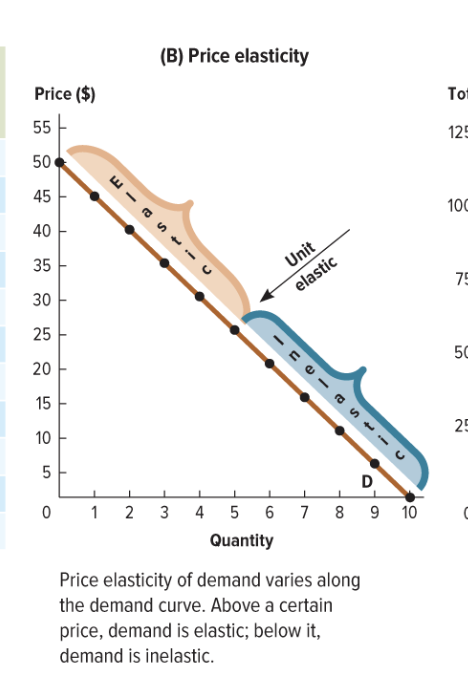
where does the maximum revenue occur
where the demand is unit-elastic
on a linear demand curve, what happens with revenue and price
revenue first increases as the rpice increases, and then decreases with higher prices
price elasticity of supply
the size of the change in the quantity supplied of a good or service when its price changes
what does price elasticity of supply measure
producers responsiveness to a change in price, just as the price elasticity of demand measures consumers responsiveness to a change in price
tells us how much quantity supplied changes as w emove along the supply curve
price elasticity of supply
% change in quantity supplied/ % change in price
price elasticity of supply
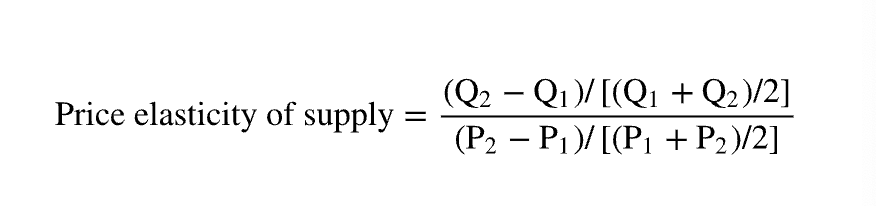
supply is perfectly elastic if…
teh quantity supplied could be anything at a given price, and is zerio at any othe rprice
supply if perfelctly inealstic if…
the quantitity supplied is the same, regardless of the price
three factors that are detemrinants of a supplies ability to expand production
availbility of inputs
flexbility of the production process
time needed to adjust to changes in price (same w the elasticity of demand)
avalilibity of inputs
elasticity of supply depnds on the elasticity of the supply of inputs
higher and higher prices will be needed to convince the producer to go to the extra expense
flexibility of the production process
easiest way for producers to adjust the quantity supplies = draw production capacity away from other goods when its price rises / to reassign capacity to other goods when its price falls
adjustment time
supply is more elastic over long perods than over short periods
prodcuers can make more adjustments in the long run than in the short run
two other types of demand elasticities
cross price elasticity of demand
the income elasticity of demand
cross-price elasticity of demand
a measure of how the demand for one good changes when the price of a different good changes
cross price elasticity of demand between A and B
% change in quantity of A demanded / % change in price of B
nonprice determinant of cross-price elasticity
the price of a subsititue or a complement - entire demand curve shifts
measure this by obsvering the change in quantity demanded
cross price elasticity of demand for substitutes
positive - an increase in the price of one will cause and increase in the quantity demanded of the other
corss price elasticity of super close substitutes
very close - a change in the price of one will cause a large change in the quantityu demanded of the other, so that cross price elasiticity will be HIGH
cross price elasticity is neagtive when…
two goods are complements (consumer togetehr)
the realtive size of elastciityc tells us how strongly the two goods are…
linked! strong complements = CP elasticity is a large NEG number
two goods r loosley linked = CP elasticity will be negative
income elasticity of demand
a measure of how much the demand for a good changes in response to a change in consumers’ incomes
income elasticity of demand formual
percent change in quantity demanded / percent change in income
necessities and luxuries are normal good, but…
the sizes of their income elasticityes are VARIED
if the good is a necessity, income ealsiticty of demand will be…
positive and less than 1
if the good is a luxury, income ealsiticty of demand will be…
greater than 1
when is income ealsicity of demand negative
for inferiro goods - bc quantity demanded decreases as incomes increase
FOUR MEASURES OF ELASTICITY
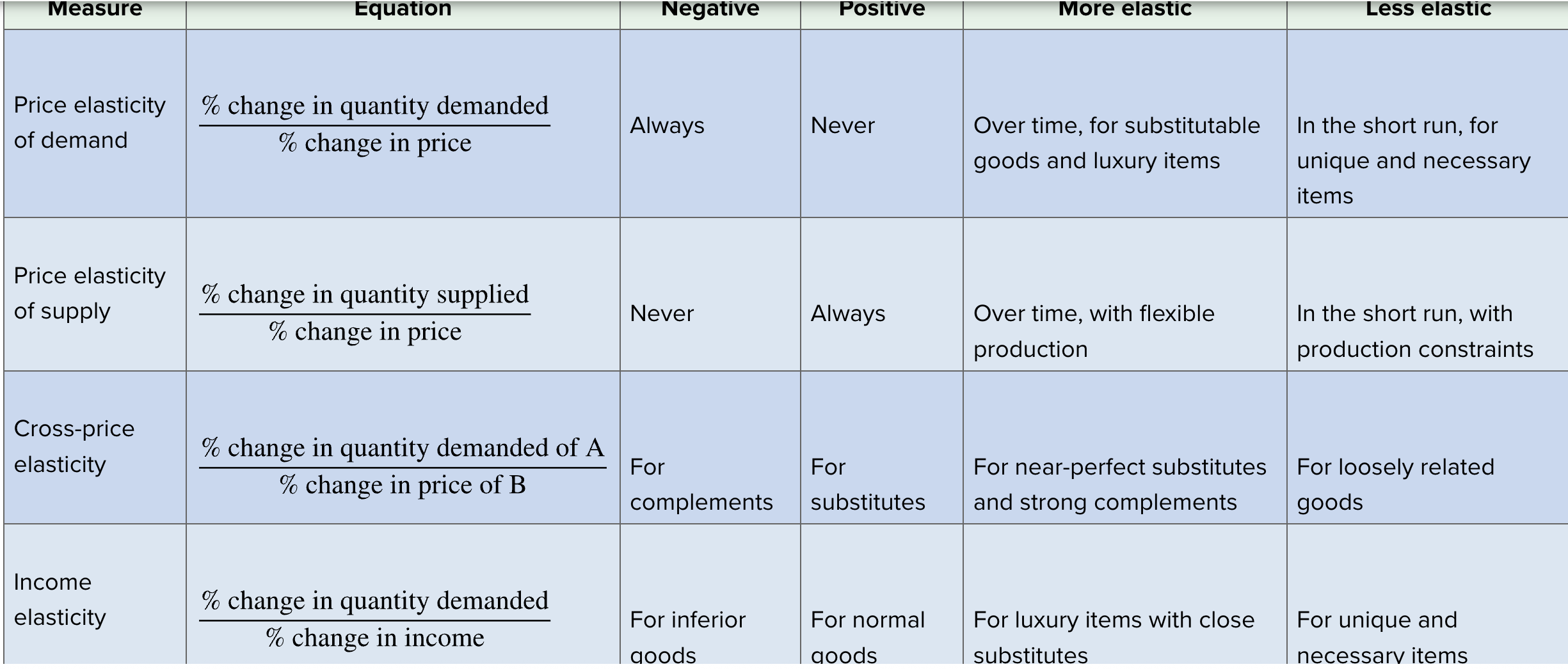
When demand is elastic and the price changes,
the quantity effect outweighs the price effect.
When demand is inelastic, a rise in price results in a smaller percentage decrease in quantity demanded.
Here, the price effect dominates, leading to increased total revenue. This occurs because consumers continue purchasing despite higher prices, often due to a lack of substitutes or the necessity of the good.
When demand is elastic,
decrease in price will increase total revenue.
The general formula for the price elasticity of supply is
% change in Q supplied/ % change in P.
When demand is inelastic and the price changes, the
price effect outweighs the quantity effect.
If a good is a necessity, income elasticity of demand will be
positive but less than 1
why use the midpoint method
because it doesnt depend on the direction of change!!
price-elastic supply
if the price changes, so does the producer willingness to provide more/less. so if the price of a good increases, the producer is able/willing to provide MORE of it to the consumers because producers will profit off of it more.
positive vs negative cross-price elasticity
POSITIVE = the goods involved r SUBSTITUTES
when price increases of one, demand increases of other
negative = complements
when price of one increases, demand decreases of other
NEGATIVE income elasticity of demand
when you buy less of something as your income increases
like hotdogs!
main deterinant of supply elasticity
how quickly PER UNIT costs increase with an increase in prodiction
if increased production requires much higher costs, then the supply curve will be…
inelastic
if increased production requires much normal/constant costs, then the supply curve will be…
elastic