History of architecture test
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Pannonia architectural behaviour
Defenece focus on Danube frontier
strict Roman grid (Cardo-Decumanus)
clear rectangular stone forts with towers and gates
civil towwns grow beside the camps (vicus, municipium, colonia)
Pannonia building types
Catrum, Castellum, Burgus, Quadriburgium
Public: baths, forum, ampitheatre, granary
Inside forts: principia, barracks, hospital, workshops
Pannonia examples
Aquicum fortress: Roman military engineers
Savaria early christian chambers: Roman provisional engineers
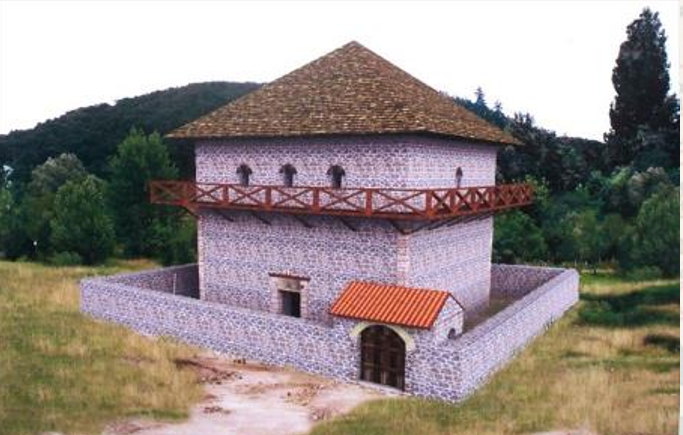

Pannonia Lepence
L: Lepence Burgus is a small 371AD watchtower
E: engineers of roman army built it under valentinian
P: part of the Danube frontier defence line
E: Exact square 18.3mx18.3m
N: no complex rooms, just a single tower
C: clear, simple geometry for border control
E: exterior is plain stone walls, small openings

Romanesque architectural behaviour
rise of stone churches
thick walls, small windows, round apses
monastic influence
early byzantine touches in some chapels
Romanesque building types
Basilicas
Parish churches
Rotundas
Monateries
Romanesque examples
Panohalma abbey: founded by prince geza
Tihany abbey: founded by king andrew I
Veszprem cathedral: kings and bishops
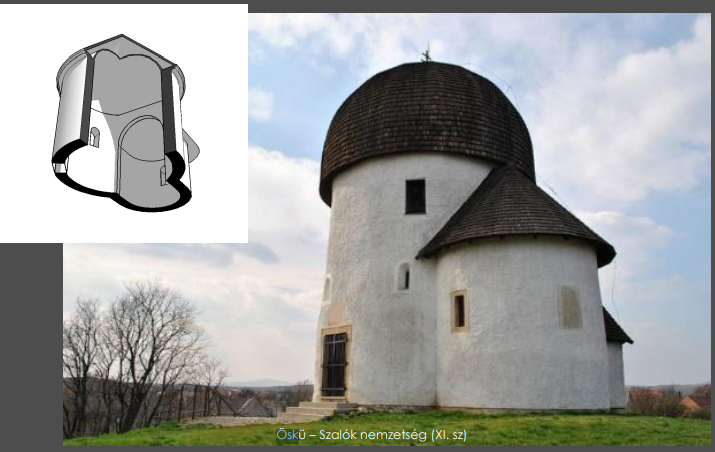
Romanesque öskü
Öskü founded by szalok clan
Ö: Öskü rotunda is an 11th century round church in Hungary
S: simple circular nave
K: Kept with thick stone walls
Ü: upper facade is plain stone walls, small windows, simple romanesque look, with unornamented medieveal structure

Gothic architectural behaviour
arrives via royal court and monasteries
pointed arches, ribbed vaults, tall towers
french and cisterian influence
after tartar invasion many stone castles
Gothic building types
castles,
cathedrals,
parish churches,
royal palace works
Gothic examples
Buda, our lady church by royal workshop
Kassa cathedral by parler workshop
Kolozsar st micheal by Local medieval masons
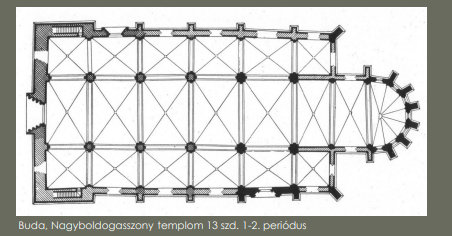
Gothic our lady church
Buda, our lady church by royal workshop begins in 1270s
B: budas main medieval church grew through the 13th-15th century as royal spiritual center
U: under french influence from lyon and local zsambek masters
D: divided into long naves, side aisles, one tower on the west
A: adopts french gothic pointed arches, rib vaults, simple stone facade with tall tower
Renaissance architectural behaviour
arrives with king matthias and italian masters
symmetry, logias, arcades, classical details
strong palace culture
after 1541 regional variation occurs
Renaissance building types
Royal palaces
villas
chapels
courtyard logia castles
Renaissance examples
Buda royal palace by king matthias and italian masters
Visegrad summer palace by king matthias, italian builders
Bakocz chapel by italian workshop
Renaissance Bakocz
Esztergom st adalbert cathedral by Loannes Florentinus, Andrea Ferrucci
B: built for cardinal bakocz, hungarys first complete renaissance interior
A: arranged around central plan
K: known for red marble walls
O: ordered classical proportions, round arches, clean proportions
C: connected italian models like florenc santo spirito sacristy
Z: zen like facade, smooth stone, simple ornament, elegant door frame

Baroque architectural behaviour
Jesuit led counter reformation architecture
2 tower facade, rich interiors
II Gesu model influences hungarian churches
aristocratic palace building
Baroque building types
Jesuit churches
cathedrals
castles/palaces
urban churches
Baroque examples
Nagy szombat university church by antonio/pietro spazzo
Győr carmelite by Martin Witter
Vac cathedral by Franz anton pilgrim and isidore canevale
Baroque Vác
V: vac cathedral planned by pilgrim built by canevale
Á: all in centrelizing plan, wide nave, strong axis, rome inspired space
C: clean facade: 2 tall towers, smooth walls, classical columns, big central pediment
Neoclassicism and Romanticism architectural behaviour
return to classical order (columns, pediments)
19th century reform era growth
Romanticism: medieval and national themes
large urban public projects
Neoclassicism and Romanticism building types
cathedrals
castles
tenement houses
synagogues
Neoclassicism and Romanticism examples
esztergom cathedral by Kuhnel, packh, hild, lippert
national museum by mihaly pollack
eger cathedral jozsef hild
Neoclassicism and Romanticism national museum
National museum mihaly pollack 1837-44
M: made in the reform era, became national symbol of hungarys identity
U: uses classical front, big step, tall columns, clean symmetry
S: simple rectangular plan
E: elegant facade pediment, collonade, smooth walls
U: unified interior rhythm
M: minimal exterior ornament
Historicism and turn of the century architectural behaviour
revival styles: neo gothic, neo renaissance, neo baroque
influence: vienna, munich, berline, zurich
budapest becomes grand capital during this era
turn of the century, szecesszio/ art nouveau
Historicism and turn of the century building types
palaces,
churches,
Public institutions,
art nouveau museums
Historicism and turn of the century examples
opera house by miklos ybl
parliament by imre steindl
museum of applied arts by ödön lechner
Historicism and turn of the century museum of applied arts
museum by ödön lechner 1893-96
L lechner created it to introduce new national hungarian style
E emerging szecesszio colourful tiles, folk inspired pattern
C curved roof
H hungarian motif
N new national style blending folk inspiration and modern structure
E exterior bright zsolnay ceramics
R recognizable icon of budapests turn of the century architecture
Modernism and socialist realism architectural behaviour
strong modern influence
clear geometric functional modernism
modern sacred architecture simplified forms and modern material
public buildings showing monumental but clean modern character
afetr wwii early socialist realism more classical and rigid in form
Modernism and socialist realism Building types
urban planning projects,
modern churches,
government buildings,
residential building,
industrial and infrastructural
housing estates
Modernism and socialist realism examples
szeged domter, rerrich bela
budapest varosmajori church arkay aladar, arkay bertalan
budaors airport bierbauer virgil and kralik laszlo
Modernism and socialist realism church
varosmajori church 1932-34 arkay alader and arkay bertalan
V varosmajori church hungarys earliest modern church
A arkay alader began arkay bertalan completed
R rectangular volums form the body of the church
O open modern compositions without historic decor
S simple tower besides main hall
M modern sacred architecture clear geometry
A all surfaces clean light and functional
J joined interior spaces create calm modern atmosphere
O orderly proportion gives church modern identity
R recognized landmark of early hunagrian modernism
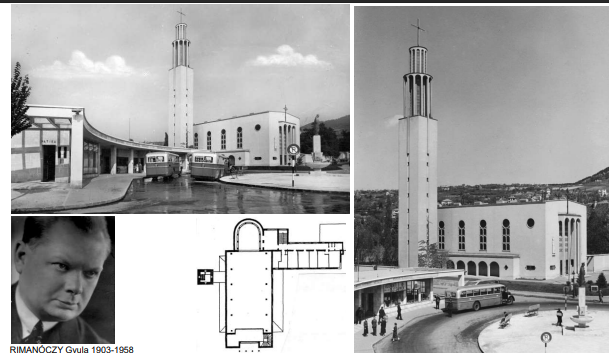
Late modern and contemporary tendencies architectural behaviour
move from social realism after 1954 debate to modern architecture
focus on function simple forms glass and concrete
industrialized building prefabrication
architects look for freedom new technology modern design
clean geometry efficient buildings no ornament
Late modern and contemporary tendencies building types
housing blocks
offices
hotels
hospitals
factories
airports
reconstrcution of historic street
Late modern and contemporary tendencies examples
chemolimpex office by gulyas zoltan
toth arpad setany apartments by janossy gyorgy
anabella hotel balaton fured by pazmandi margit
Late modern and contemporary tendencies office
chemolimpex office by gulyas zoltan 1963
C clear modern office block
H handeled by gulyas zoltan
E emphasis on function and clean planning
M modern materials concrete frame and glass facade
O ordered rectangular mass with no ornaments
L light horizontal windows dominate
I integrated into 1960 budapest development
M marks shift to post 1954 modernism
P pure box shape
E express industrialzed design ideas
X exterior stays transparent and minimal
