Week 4 Food Composition and Function
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
What sort of solvent dissolves lipids?
most are dissolved organic solvents like hexane, petroleum ether, chloroform, isopropanol and/ or pressure. There are some exceptions like monoglycerides
What are lipids generally?
nonpolar and hydrophobic with only small affinity to water and contain oxygen hydrocarbons
What are the rare polar lipids used for?
emulsifications (monoglycerides)
What are lipids classified as?
macronutrients but some are micronutrients (cholesterol)
What are lipids not?
easily digested in our digestive system (slow)
What are the biological functions of lipids?
long term energy storage, insulating, key components in hormone precursors (cholesterol) and components of cell membranes (triglycerides)
What are the food related functions of lipids?
solidification, aeration, color, flavor, texture, mouthfeel, tenderization, heat transfer
What are some examples of animal and plant lipids?
animal: milk fat, lard, marine fat-fish oil
plant: olive oil, soybean oil, coconut oil, avocado oil
What are some examples of visible lipids and invisible lipids?
Visible: butter, fat on outside of meat
invisible: almonds, avocado, tuna
The most common classes of lipids are?
fatty acid esters of glycerol, terpenes, steroids
What are the some types of fatty acid esters of glycerol?
triglycerides, diglycerides, monoglycerides, phospholipids
What can fatty acids be?
saturated or unsaturated with an even number of C atoms (exceptions microorganisms and dairy products)
What does saponifiable mean?
lipid reacts with NaOH ie. esters and triglycerides
What does non-saponifiable mean?
doesn’t react with NaOH
What is a triglyceride made of ?
glycerol backbone with 3 fatty acid tails
What are triglycerides?
predominate form of fat in foods and major form of fat in the body
What is an oil?
liquids at room temperature and used by plants for long term energy storage
What is a fat?
solid in room temperature and used by animals for long term energy storage
What can hydroxides (NaOH and KOH) do?
hydrolyze the esters in triglycerides to that you get glycerol and three FA- way to clean a surface from oil
What are important characteristics of fatty acids?
chain length is usually 16-24 atoms of C; degree of unsaturation 1 db= monounsaturated fatty acid, 2 or more db= poly unsaturated fatty acid; stereochemistry
What are the most common fatty acids in foods?
steric acid, palmitic acid, oleic acid, linoleic acid, linolenic acid, eicosatetraenoic acid, docosahexaenoic acid
What are the types of double bonds in fatty acids?
cis and trans- trans stacks easier = more solid
How does the IUPAC system for naming fatty acids work?
based on the number of carbons and double bonds; oleic acid = octadec-9-enoic acid where 9 is the position of the double bond
What is important about position of fatty acids in glycerol backbone?
it determines functional properties (melting, behavior, crystal structure, etc) and biological functions
How are some common names work for fatty acids?
often based on source but ex. Oleic acid (C18:1, n-9) 1 is the number of double bonds and n is the position
How does the omega system work for naming lipids?
counts from the methyl end and was adopted because it reflects biological relevance (enzymes and metabolism often act from the methyl end) ex. C18:1 n-9 where double bond is 9 carbons from the methyl end
What is the suffix for saturated fatty acids?
-anoic ex. octadecanoic acid = stearic acid
What is the suffix for unsaturated fatty acids?
-enoic ex octadecenoic acid = oleic acid
When there are multiple double bonds in a fatty acid what do you have to do?
indicate to positions ex octadeca-9,12-dienoic acid = linoleic acid
What are double bonds found most commonly?
in natural unsaturated fatty acids double bonds are usually cis and separated by 3 carbons (methylene-interupeted)
What factors affect melting point of fatty acids and how?
chain length: longer chain = higher melting point because more van der walls interactions means more energy needed to melt. Saturation: more saturated = higher melting point because no double bonds means tighter packing of molecules. Cis Vs Trans: trans = higher melting point because trans are more linear and pack better than cis.
What types of fatty acids crystalize more?
long, saturated, linear (trans)
What type of fatty acids are harder to crystalize?
ones with structural kinks that reduce packing efficiency (cis), unsaturated
How does hydrogenation of fatty acids work?
add H2 gas under heat (200C)
What are the positives of hydrogenation of fatty acids?
makes fat more solid, increases melting point, increases shelf life (no db = less oxidation)
Why does partial hydrogenation lead to?
leads to the production of trans FA, these can be bad for health
What is rancidity?
related to oil oxidation and associated to the development of unpleasant smalls (also changes in texture and appearance) of food, often effects the shelf life of a product
How does hydrolytic rancidity work?
the oil is broken down to FA and glycerol
How does oxidative rancidity work?
unsaturated FA are oxidized, epically prevalent in PUFA
What does rancidity depend on?
FA composition, temperature, water activity, metal ions, oxygen, light
What are some ways to prevent/ slow down rancidity
packaging: colored glass bottles, N2 to minimize exposure to O2. Storage: low temp, dark, low humidity. Additives: sugar, salt, antibacterial, antioxidants
What about trans fatty acids are unique?
they resist rancidity which is why they were put in many products; this stopped because they are related to health issues (brain, liver)
What are characteristics of hydrolytic rancidity?
accelerated by heat and water, catalyzed by enzyme lipase, FA cause the bad smell
What are characteristics of oxidative rancidity?
accelerated by light and metals, PUFA are more sensitive, be prevented using antioxidants
What are phospholipids used for in food and our body ?
emulsifiers because of their polarity
What are phospholipids in foods?
organ mean, egg yolk, milk, soybeans, wheat germ, peanuts
What is the basic steroid structure?
6 membered ring connected to 6 member ring connected to 6 membered ring to a 5 membered ring
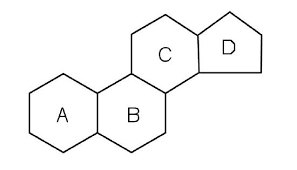
What is an example of a steroid?
cholesterol
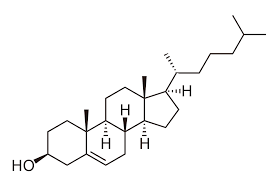
What is important about cholestrol?
it is the precursor for the synthesis of other important steroids (vitamin D)
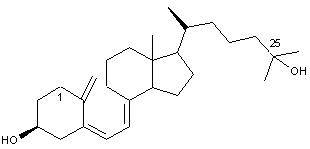
What are phytosterols?
natural components found in unsaponifiable matter of almost all edible oils
What is special about phytosterols?
they are plant based cholesterol fighters and may have anit-inflamatory and anticancer properties (further research needed)
How do phytosterols work?
they compete with cholesterol for absorption because of their similar structures reducing LDL cholesterol in blood
Where are phytosterols found?
vegetable oils, nuts and seed
What is the chemical structure of waxes?
mono-esters formed form long-chain fatty acids and long chain alcohols giving them unique protective and hydrophobic properties
How are waxes used in the food industry?
wax coating on fruits and vegetables to retain moisture, improve appearance and extend shelf life. They also enhance texture, gloss and stability in gum, candies and baked goods.
What are the functional benefits of waxes in food science?
act as emulsifiers and stabilizers, improving ingredient distribution and product consistency
What are terpenes used for?
nonpolar aroma components in foods (can be dissolved in oil based foods)
What are common terpenes?
limonene (lemon), thymol (oregano), eugenol (cloves), farnesene (apples)
How are terpenes used in food preservation?
natural oils from thyme, oregano, clove have antimicrobial properties to extend shelf life
What are the antioxidant and health benefits to terpenes?
exhibit antioxidant and bioactive affects, supporting functional foods and nutraceutical development
What are the edible coating and packaging benefits to terpenes?
used in edible coating and biodegradable packaging to enhance food preservation and sustainability