NUTR 400 4.3 Fat Soluble Vitamins
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Properties of Fat Soluble Vitamins
Vitamins A, D, E, and K
small amounts are needed for good health
Dissolves in lipid
stored in adipose tissue and the liver
can be toxic in high amounts
in the “fatty” potion of foods
leaves the SI via chylomicrons
absorbed in the small intestine
deficiencies take longer (compared to water soluble) to appear because we have so much storage space
Primary functions of Fat-soluble vitamins?
Vit A: vision and cell differentiation; functions as a hormone
Vit D: Bone growth/maintenance, cell development/immunity'; functions as a hormone
Vit E: Antioxidant
Vit K: Blood Clotting and bone formation
Vitamin A: A group of fat-soluble compounds
Retinoids:
the active form of vit A (preformed)
Retinol (The only one in our diet)
Retinal
Retinoic Acid
Carotenoids
Has vitamin activity after conversion to active form in the body (provitamins)
Beta-carotene – primary carotenoid in our diet
Carotenoids
Fat soluble plant pigments
SOME can be converted to Vit A (pro vit A)
Most common ones:
Provitamin A carotenoids:
β-carotene (most abundant vitamin A provitamin)
α-carotene
β-cryptoxanthin
lutein, zeaxanthin, lycopene
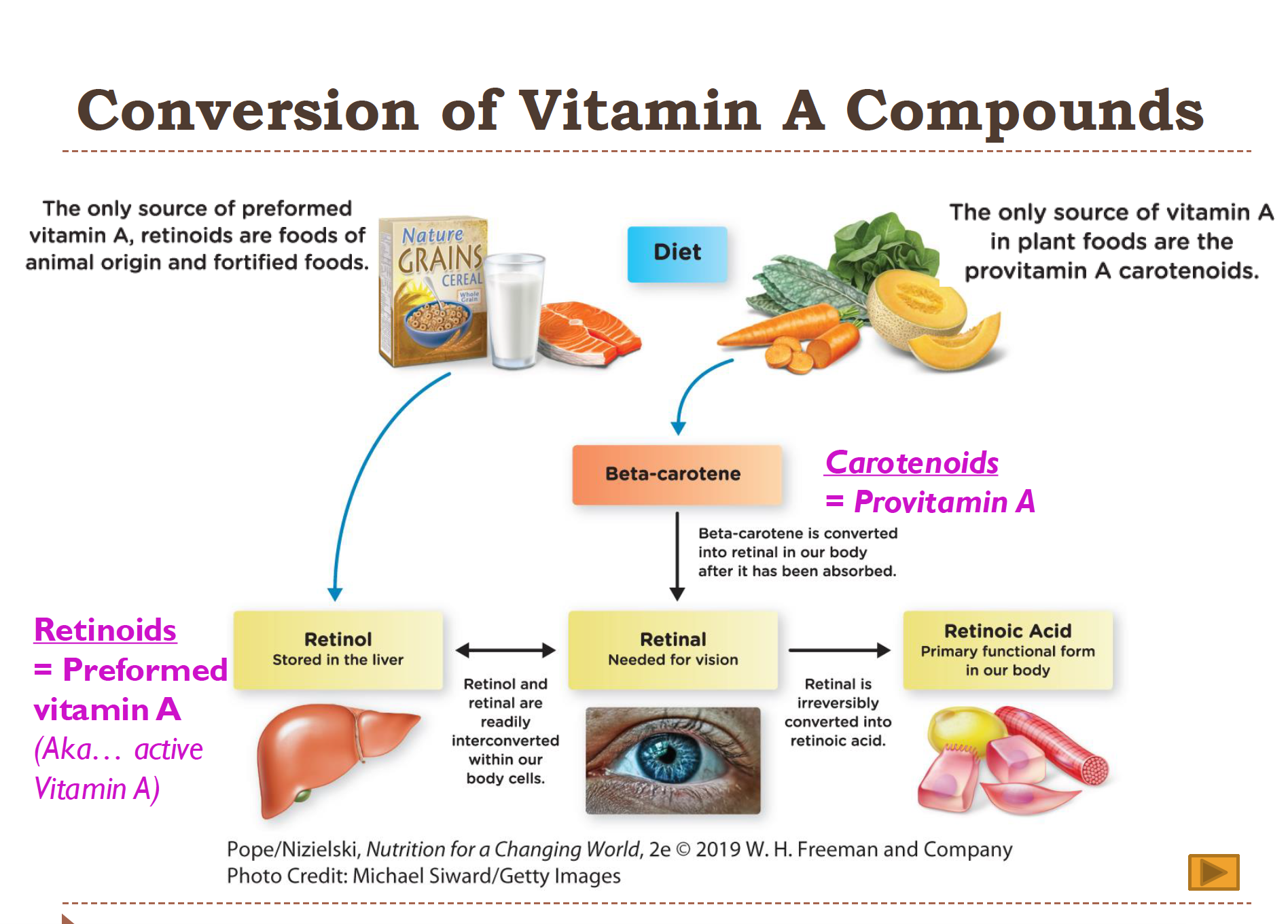
Conversion of Vitamin A Compounds
Carotenoids (provitamin A) → converted in intestine → Retinol (active, storage form) → Retinal (vision) → Retinoic Acid (gene regulation).
Provitamin A: plant-based (beta-carotene)
Preformed vitamin A: animal-based (retinol)
Retinol = storage + transport
Retinal = vision use
Retinoic acid = gene expression (cannot go backward!)
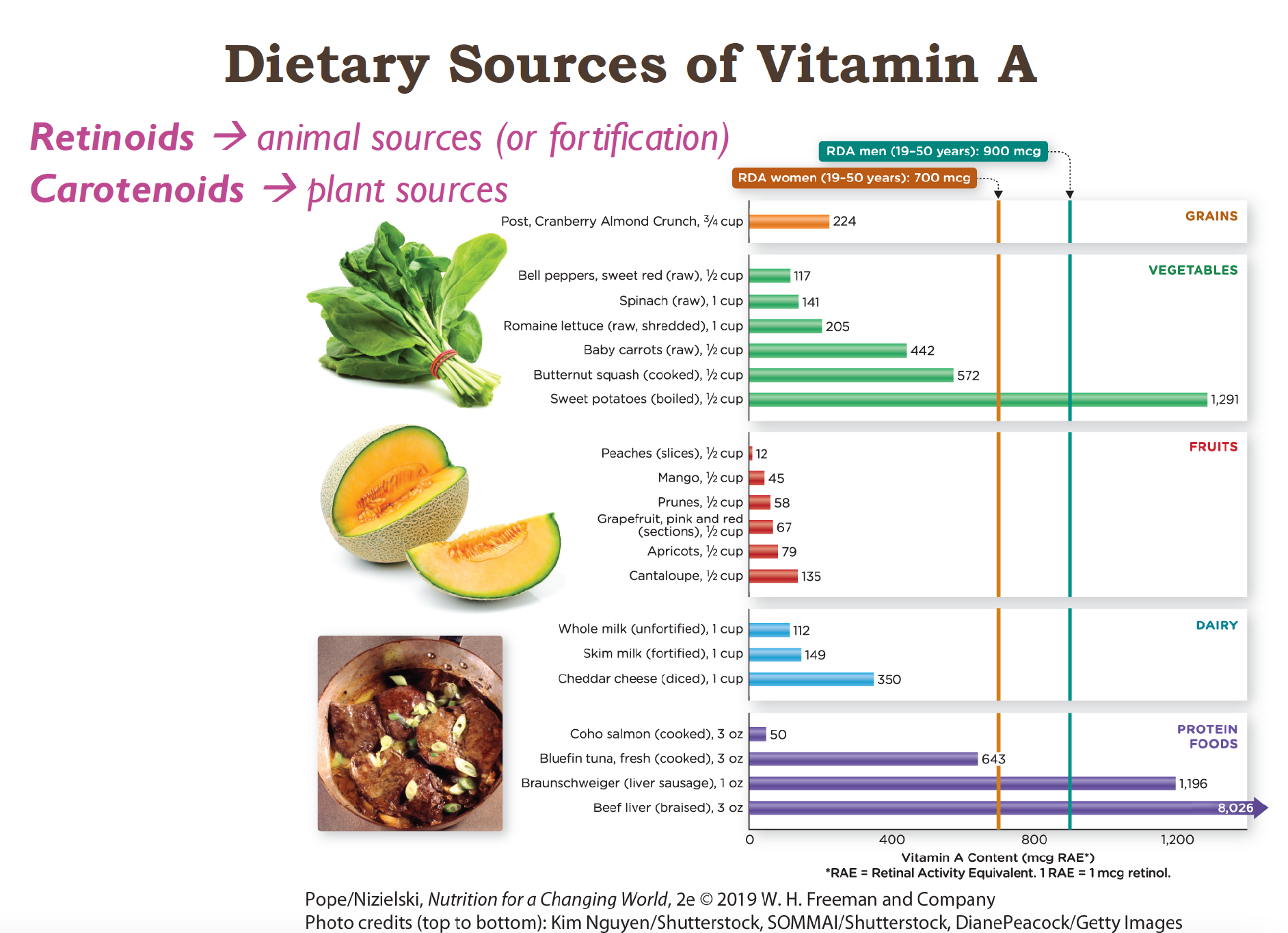
Dietary Sources of Vit A
40% of the US consume under the RDA
2/3 of Vit A is consumed as preformed vitamins (Retinol aka already active Vit A)
Preformed: Highest in livers! So animal products like:
Liver
Eggs
Dairy (milk, cheese, butter)
Fish (especially oily fish)
Provitamins:
plants! (yellow/orange/red veggies and fruit)
dark leafy greens
**CAROTENOIDS ARE LESS BIOAVAILABLE THEN RETINOIDS
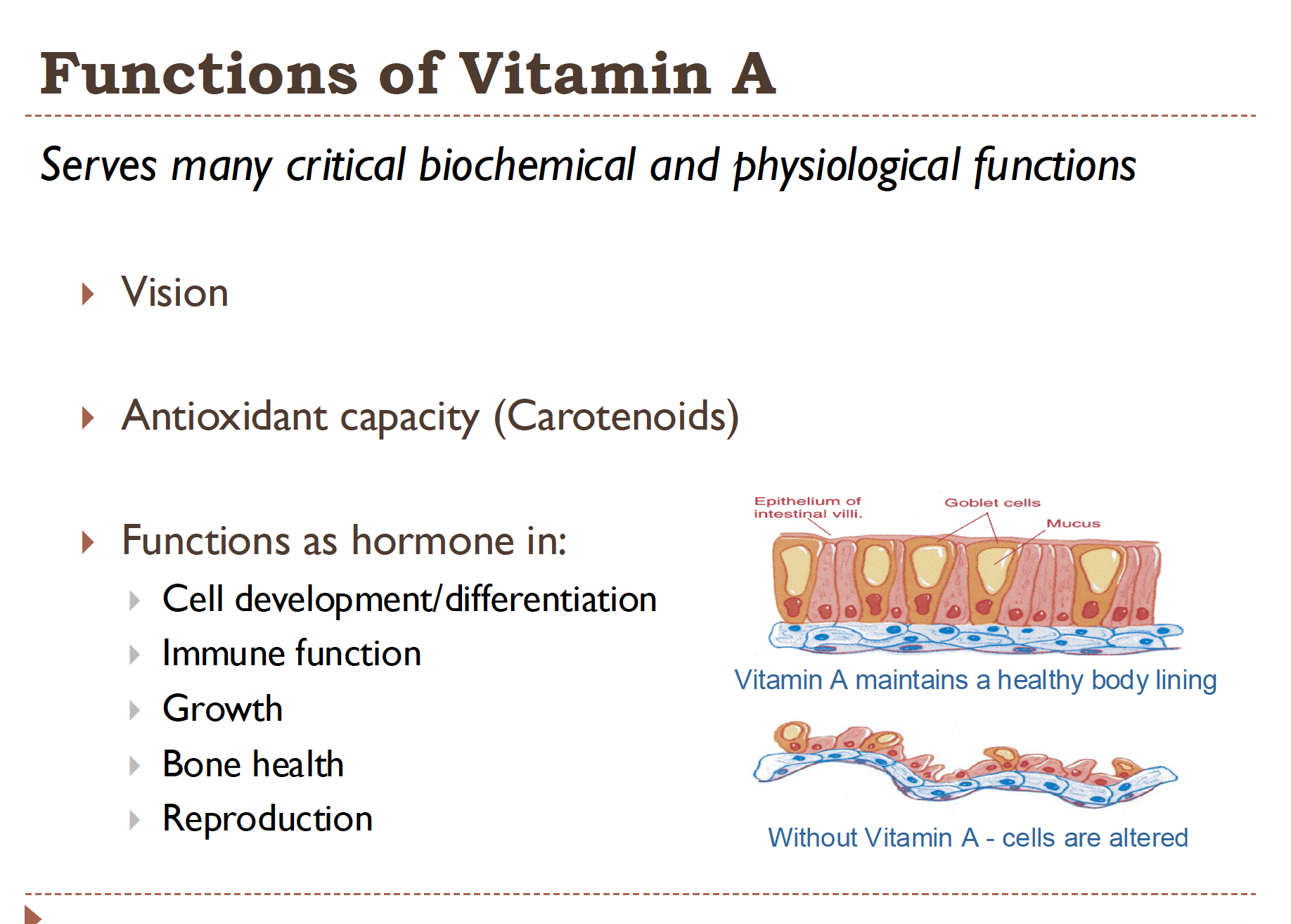
Functions of Vitamin A
Vision
antioxidant capacity (Carotenoids)
functions as a hormone in:
Cell development
immune function
growth
bone health
reproduction
Helps to maintain a healthy body lining (epithelial cells) without Vit A these cells would remain immature and wouldn’t form a solid barrier for the body
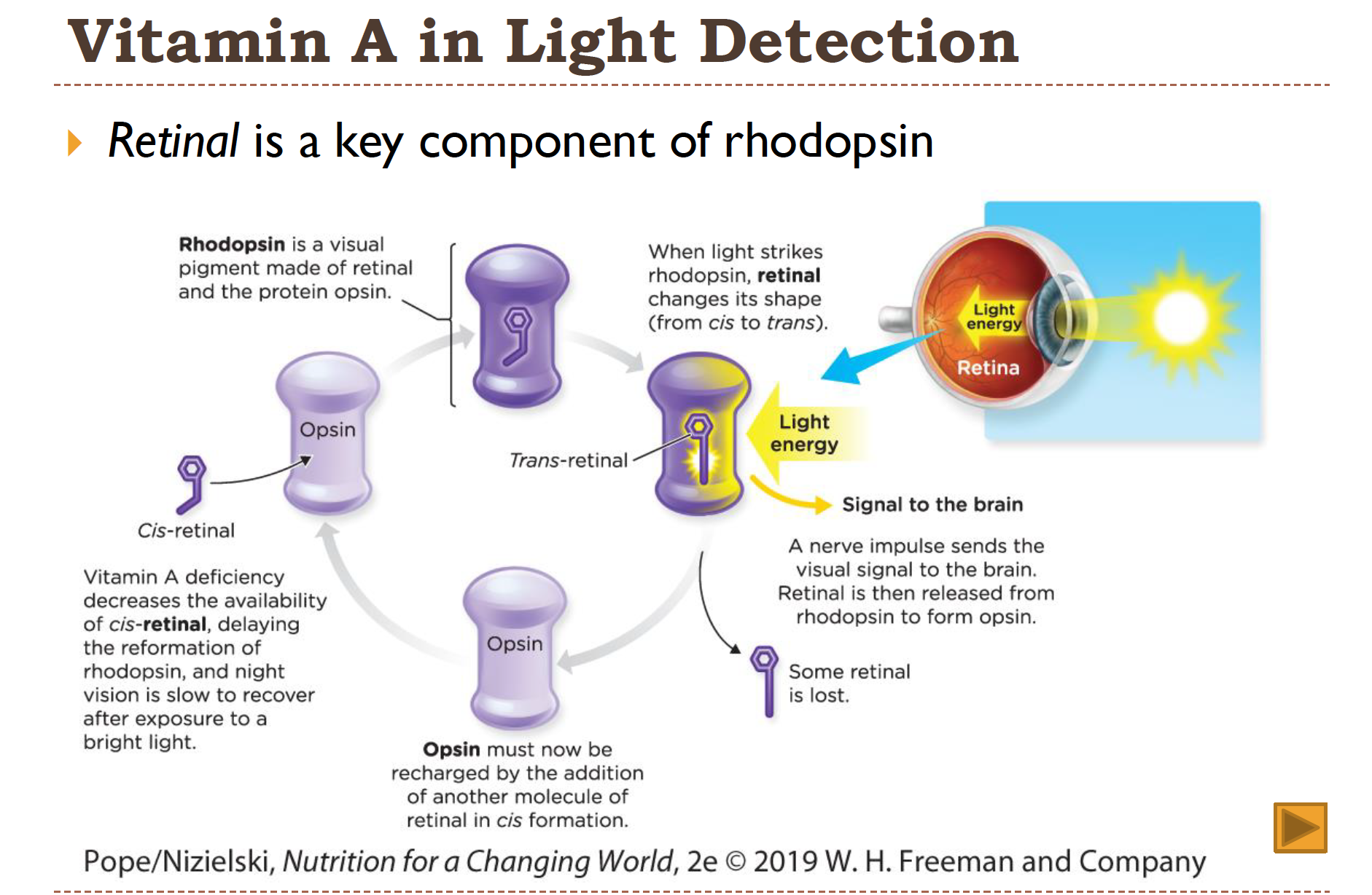
Vitamin A in light detection (Vision)
retinal is a key component of rhodopsin!
Rhodopsin-
Detects the light in our eyes
The visual pigment that is formed when cis-retinal binds to Opsin (a protien)
Vit A helps convert the light into nerve impulses, which tell the brain what we’re seeing!
The rods in our retina allow us to see in low light
Vitamin A Deficiency: Night Blindness
in a dark room, you can make out shapes. Then a flash of bright light blinds you, as the pigment in the retina is bleached! Your eyes adjust! Without Vit A, this process takes much longer
After this- the production of mucus in our tears will DEC, drying the cornea of our eyes! This can cause blindness
The leading cause of blindness in kids world wide!

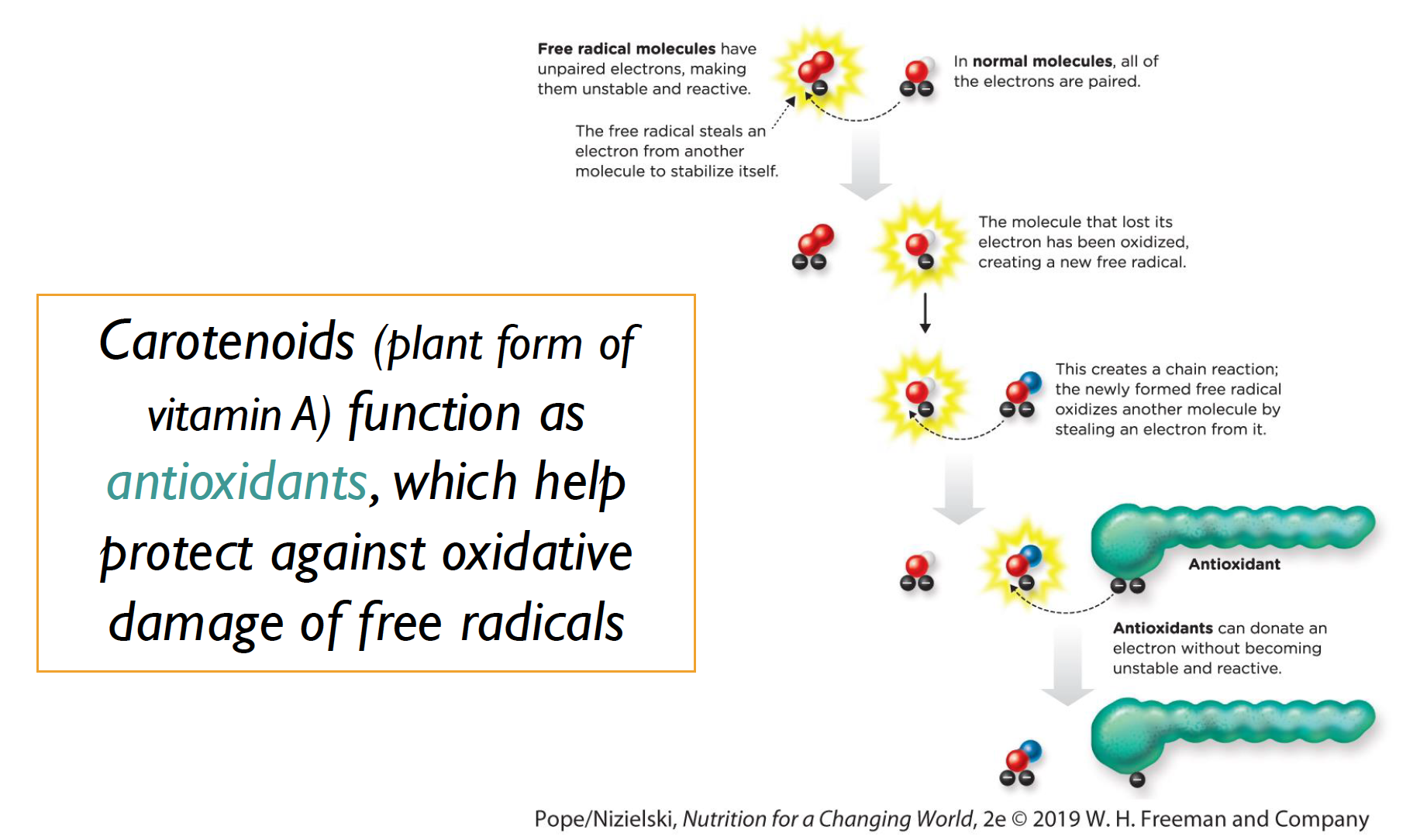
Do Carotenoids act as antioxidants?
YES! they help to protect from free radicals!
Vitamin A Deficiency: Hypovitaminosis A
when you have little preformed Vit A!
Night blindness
Permanent blindness
Impaired immunity
Rough, dry, or scaly skin (from the lack of mucus)
Keratinization (our epithelial cells cannot form properly, and are full of keratin!)
Vitamin A Toxicity!
When a large dose of preformed Vit A is consumed!
Complications:
Blurred vision
liver abnormalities
reduced bone strength
birth defects
Increased risk for lung cancer in smokers
*UL = 3,000μg RAE/day
Carotenoids
NOT toxic
supplements are not recommended
only thing that can happen is
Carotenemia (Orange skin)
Vitamin D
“Sunshine vitamin”- With UV light exposure, can be produced from cholesterol in the skin
Limited sun exposure → essential to consume Vitamin D in the diet
Must be activated in the liver and kidneys to fulfil its biological function!
Vitamin D Functions
Acts as a hormone
helps bone growth/maintenance
regulates calcium metabolism
Blood levels, absorption, excretion
regulates protein synthesis
possibly regulates cardiovascular function?
Dietary sources of Vitamin D
fatty fish, cheese, eggs, and a few others are the few with vit D naturally
fortified foods (such as milk) are good sources
Vitamin D2 = Ergocalciferol (from plant sources)
Vitamin D3 = Cholecalciferol (from animal sources) (ALSO the form our body makes)
RDA = 15 mcg/day (at the age of 70 it INC to 20 to help with bone loss)
Sunlight exposure
Interferes with one’s ability to make Vitamin D:
Living far away from the equator
Wearing sunscreen
Staying indoors
Having darker skin (they need 3x more)
aging
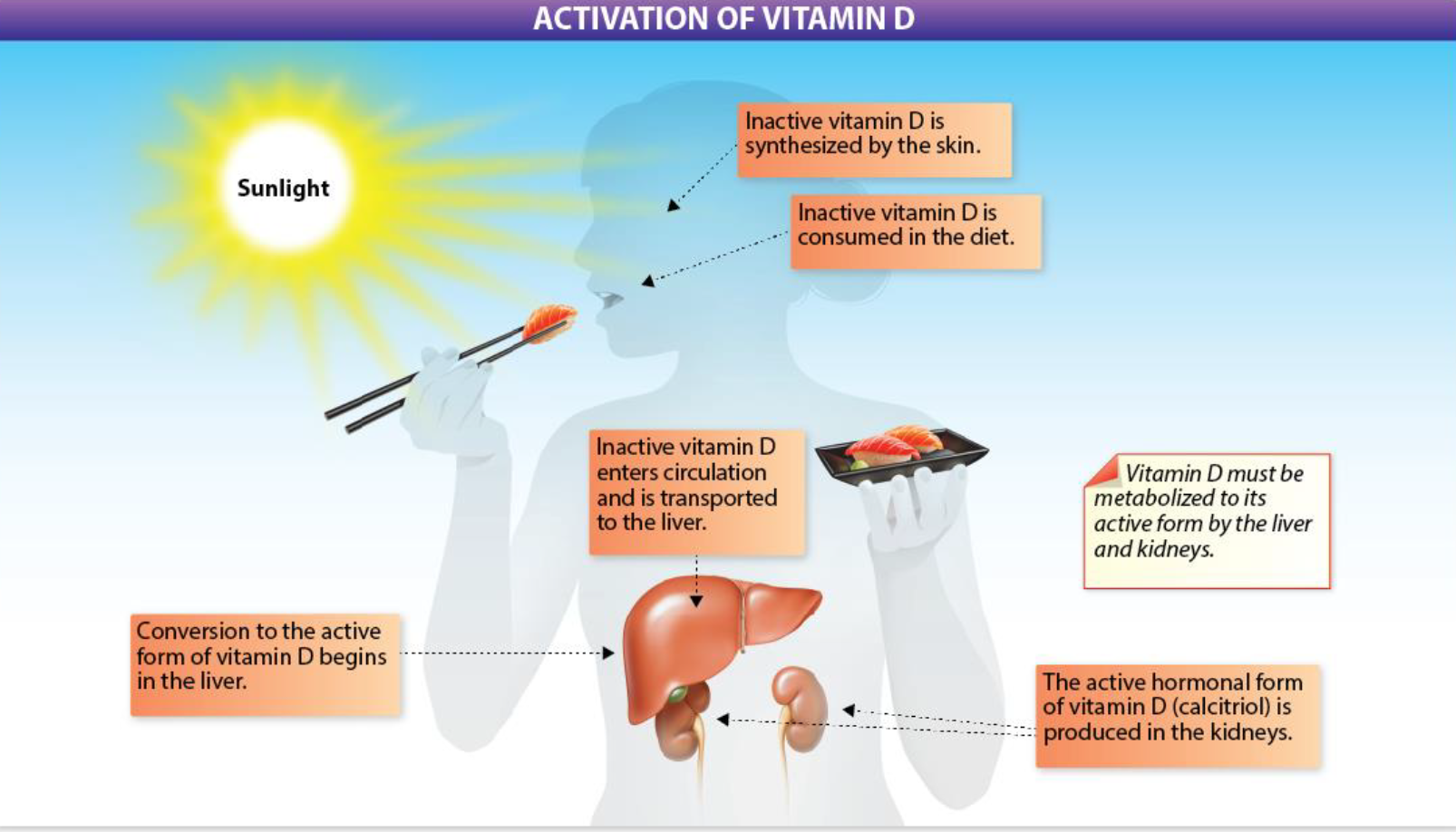
Vitamin D Activation
synthesis by the skin or consumed by the diet
enters circulation and is transported to the liver
conversion to active begins in the liver, anf is finished in the kidneys
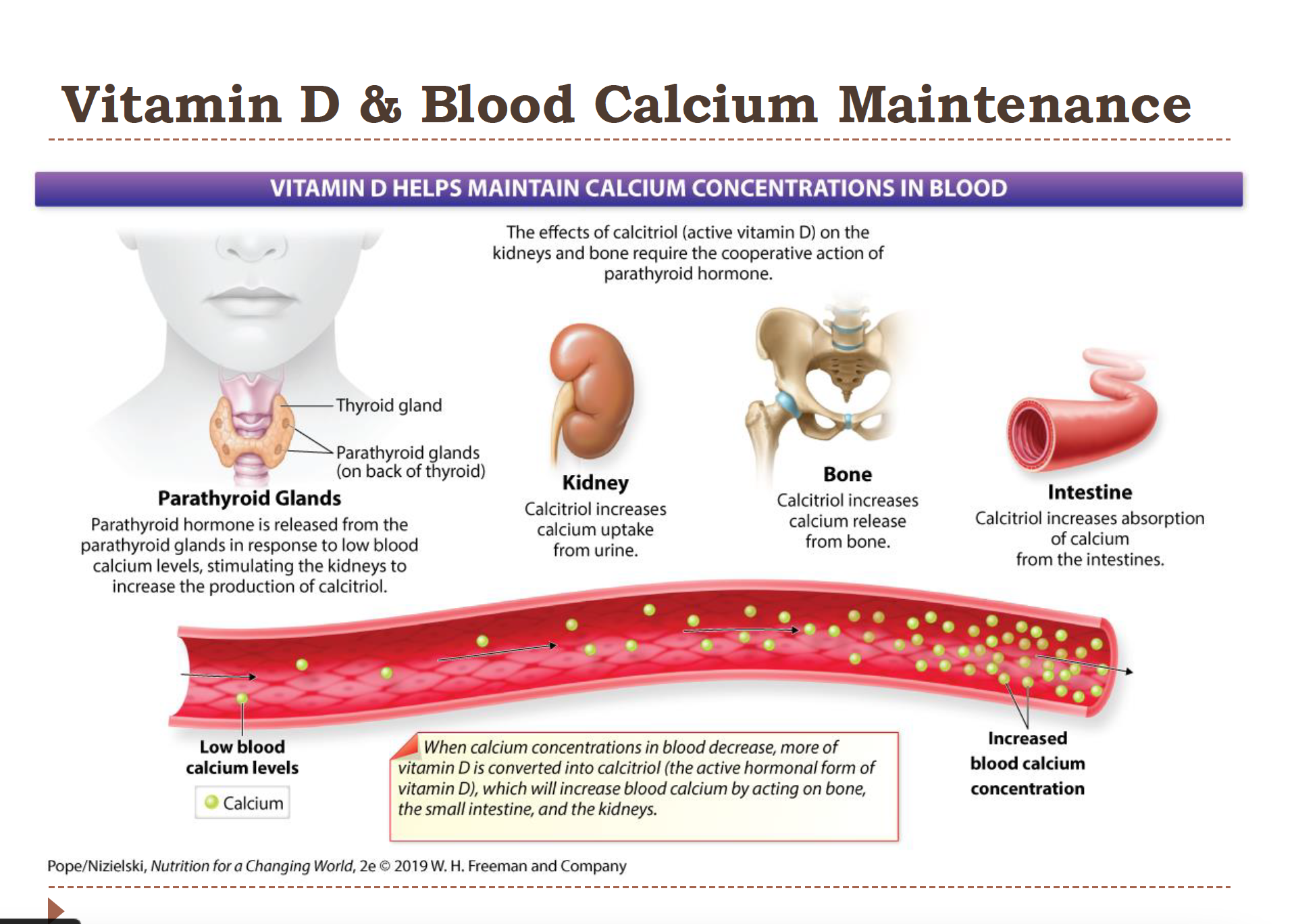
Vitamin D and Blood Calcium Maintenance
most calcium is stored in the bones; less than 1% circulates the blood. It is very important!
1. Parathyroid glands- the parathyroid hormone is released from here in response to low blood calcium levels
2. Kidney – Calcitriol increases calcium reabsorption in the kidneys
(So less calcium is lost in urine.)
3. Bone- calcitriol increases calcium release from bone
4. Intestine – Calcitriol increases the absorption of calcium from the intestine
**Calcitriol is what Vit D is converted to!
Vitamin D Deficiency
Rickets- bowed legs and knocked knees (in children)
Osteopenia- soft/weakened bones! painful (in adults)
Other chronic diseases:
cancer
Autoimmune disease
Kidney disease
Type 2 diabetes
Cardiovascular disease
Vitamin D toxicity
Hypervitaminosis D
from too may supplements
Excessive calcitriol (active Vitamin D)
Leads to hypercalcemia (too much calcium in the blood)
Symptoms may include:
Loss of appetite
Weight loss
Irregular heartbeat
Frequent urination
Leads to the calcification of soft tissues and damage to the heart and blood vessels, as well as the formation of kidney stones
**UL = 100 mcg/day (4,000 IUD)
Vitamin E
encompass a group of fat soluble compounds called tocopherols
Most active form = α-tocopherol
functions as an antioxidant!
incorporated into cell membranes
in LDL’s (that would otherwise increase plaque forming potential)
In white blood cells that mainine immune function
DIetary sources of Vitamin E
Best sources- Nuts/seeds/some oils/dark leafy greens
easily destroyed in food prep/storage (so low/no heat and airtight containers help
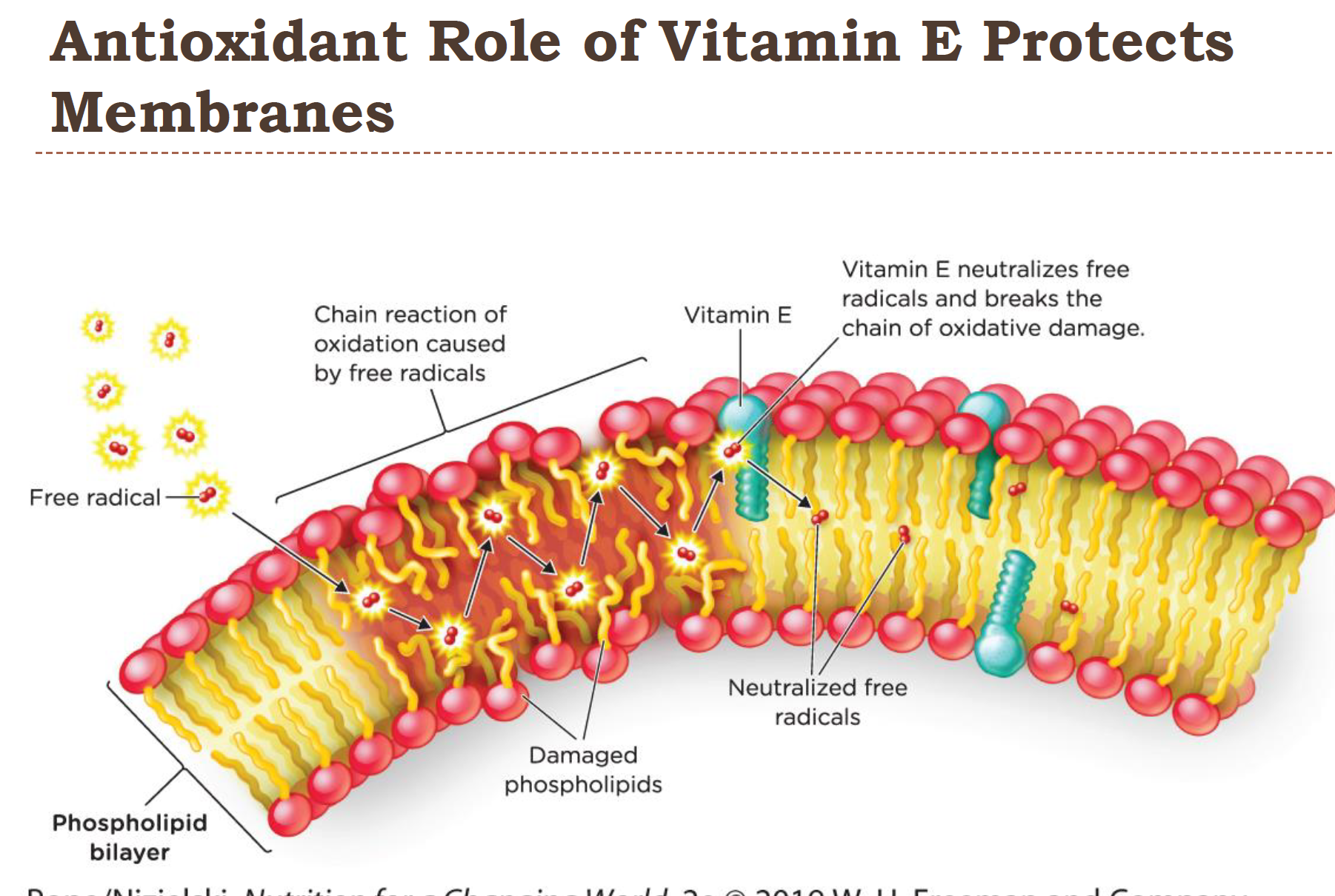
Vitamin E and protects cell membranes
since it’s fat soluble vitamin E is great at stopping oxidation in membranes and LDL’s
role in reducing plaque formation in blood vessels and protects white blood cells from oxidation
other antioxidants help make each other more active and effective! (like Vit C)
Vitamin E protects from chronic disease
cancer-
Antioxidant nutrients protect DNA
Diets ↑ Vitamin E associated with ↓ cancer risk
cardiovascular disease-
May ↓ plaque formation
Supplementation NOT encouraged
cataracts-
Related to free radical damage
Antioxidants may delay or prevent
Vitamin E Deficiency and Toxicity
Deficiencies
RARE!
Neuromuscular problems
Hemolytic anemia
*infant formula now fortified with vitamin E
Toxicity-
Less likely to be toxic tha Vit A or D
UL = 1000 mcg/day (1500 UL) which is 60x the RDA
only observed with high supplement intake!
INC the tendency to bleed, which can have real bad effects
such as hemorrhagic stroke!
Vitamin K
Functions:
needed for protien synthesis
needed for blood clotting
deficiencies can cause uncontrolled bleeding! since the blood clotting is what typically stops the bleeding
bone metabolism
modifies bone proteins- which allows them to bind calcsum and regulate bone function
The Three Forms of Vitamin K
Vitamin K1 – plant (aka the food we eat)
Vitamin K2 - bacteria
Vitamin K3 - synthetic (Commercially produced)
Dietary Sources of Vitamin K
Best source- leafy greens!
some cheese, fruit, veggies, and veg oils are also pretty good
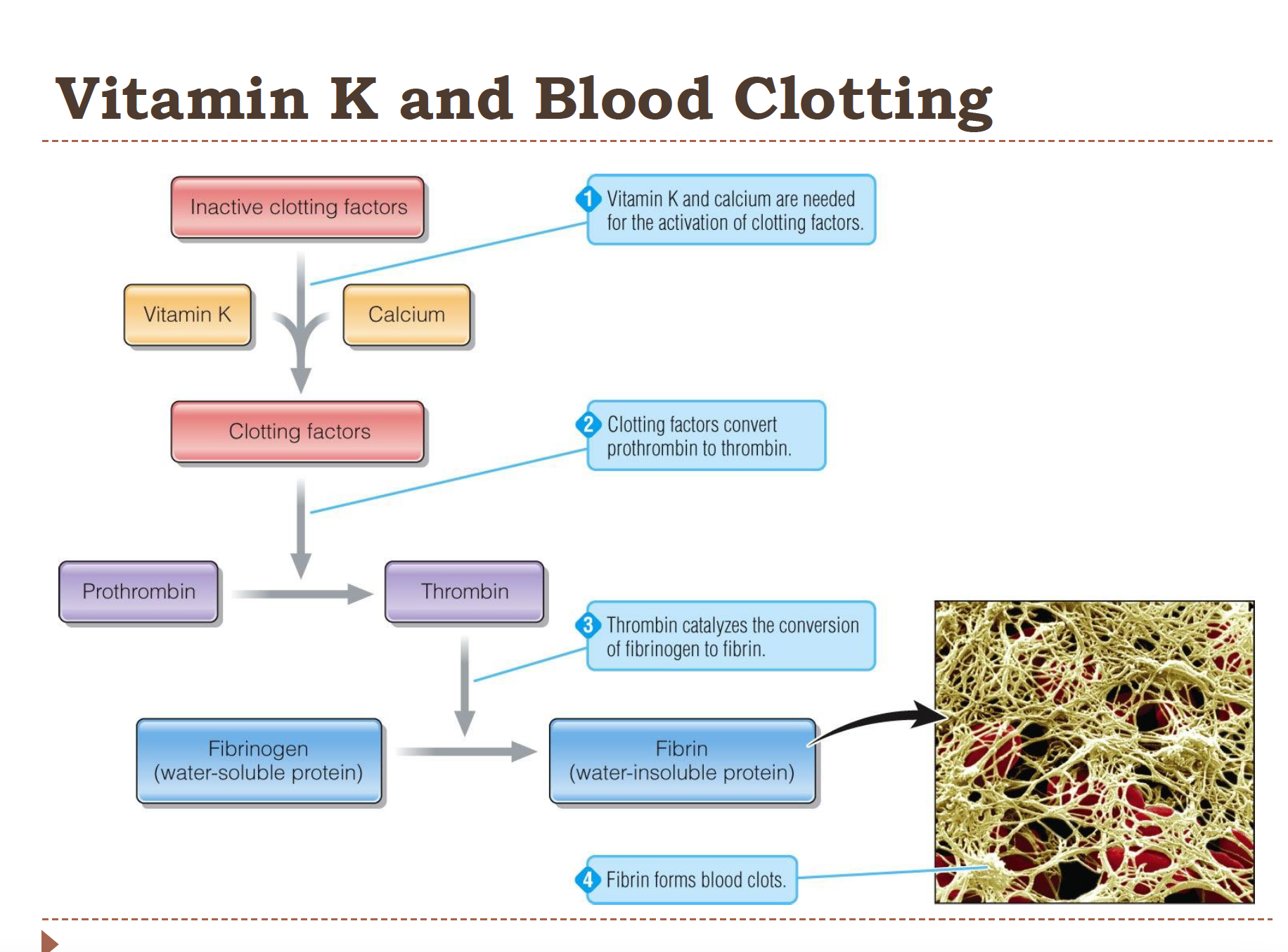
Vitamin K and blood clotting
Vitamin K + calcium activate clotting factors
Activated clotting factors convert prothrombin → thrombin
Thrombin converts fibrinogen → fibrin
Fibrin forms the blood clot
Vitamin K Deficiency and Toxicity
Deficiency
Rare
potential causes:
Fat malabsorption
medications
Consequences
hemorrhaging (excessive or uncontrolled bleeding)
fractures
Toxicity
No evidence of toxicity at any level, so there is no UL
Vitamin K is given at birth
since the early 1960’s at birth infants have been given vit K
Reduces hemorrhage risk because they have limited liver stores (vit K is stored in the liver) and vitamin K is low in breast milk
Intestinal bacteria not yet producing vitamin K