Phosphate bond energy
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
ATP
- adenosine triphosphate
- adenine, ribose + phosphate group
- discovered in 1929 by Karl Lohmann
- energy released when the phosphate bonds are broken
- only compound that transfers chemical energy to energy requiring processes
- involved in the energy receiver - energy donor cycle (harnesses energy from macronutrient breakdown & transfers energy for biological work)
Energy currency
ATP is likened to being an energy currency - it simplifies the coupling of energy producing reactions to energy requiring reactions.
However:
ATP cannot be accumulated or transferred (from cell to cell)
Once the 'currency' has been used, no more can be generated & the cell dies.
Cells possess mechanisms to stop this from happening:
Fatigue in muscle arrests ATP utilisation during physical activity
Maintenance of the ATP / ADP concentration ratio in cells usually takes precedence over all cell function 50 : 1 ATP:ADP ratio preferred
Reactions involving ATP
- Hydrolysis: ATP --> ADP + P
- exergonic reaction - energy is released when phosphates are cleaved from ATP
- catalysed by adenosine triphosphatase (ATPase)
- a further phosphate group can be cleaved: enzyme is adenosine diphosphatase (ADPase)
- leaves a single phosphate attached to adenosine (adenosine monophosphate [AMP] )
- ATP resynthesis: ADP + P --> ATP
Adenylate kinase
involved in ATP regeneration from ADP
most important at the onset of exercise
2 ADP ------> ATP + AMP
ATP storage
stored in small amounts until needed
-only 3 oz in body
-limited capacity for energy production
-ATP synthesis must occur during exercise
limited storage of ATP means that rapid resynthesis is essential to allow normal functioning, let alone maximal exercise
ATP replenishment
our body has to replenish ATP we burn before we can keep going
- there is a high demand for ATP replenishment in the body
- there are metabolic processes that allow for this
- replenishment sites can happen in the mitochondrion and the cytosol
- glycolysis + phosphocreatine system
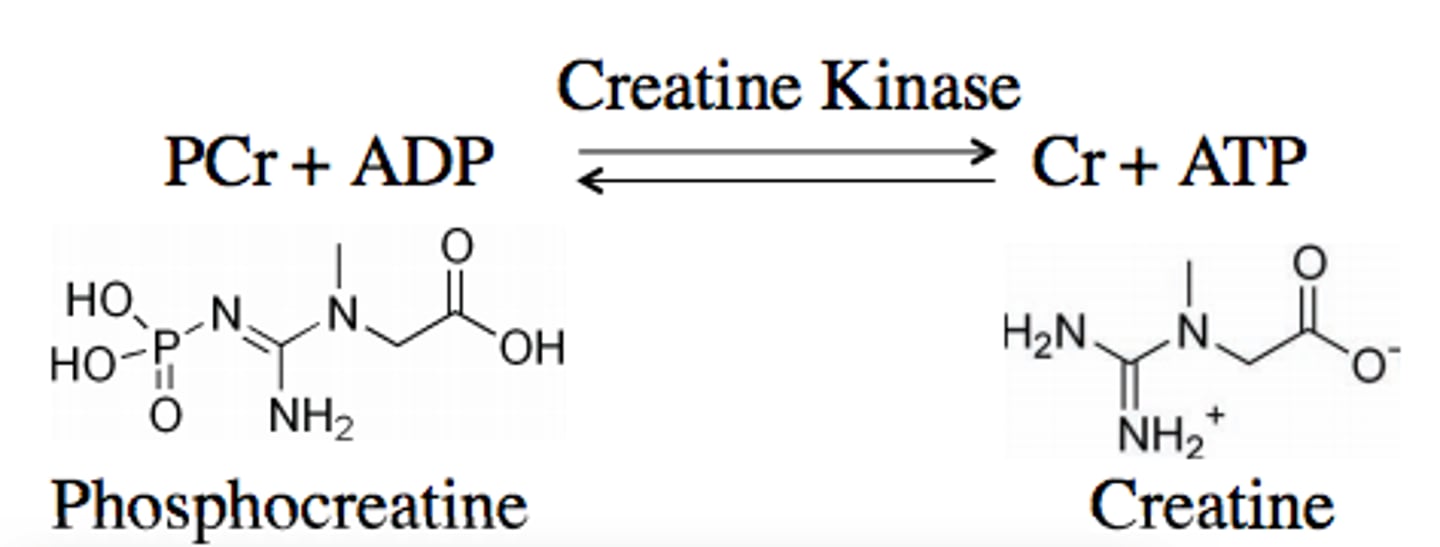
phosphocreatine system
instant replenishment of ATP is achieved by high energy phosphate phosphocreatine (PCr)
- mediated by the enzyme creatine kinase (found in abundance at locations of ATP hydrolysis and regeneration)
- stimulus for CK activity is an increase in ADP conc (thus lots of ATP hydrolysis has been happening)