Oceanography Exam 2
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
masses of water in motion
Ocean Currents
driven by wind
Surface Currents
from high to low pressure
How does pressure move?
rises, less dense
hot air
more dense and sinks
cold air
dominant wind flow is vertical, also called doldrums
Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ)
The deflection of an objects path due to Earth's rotation
Coriolis effect
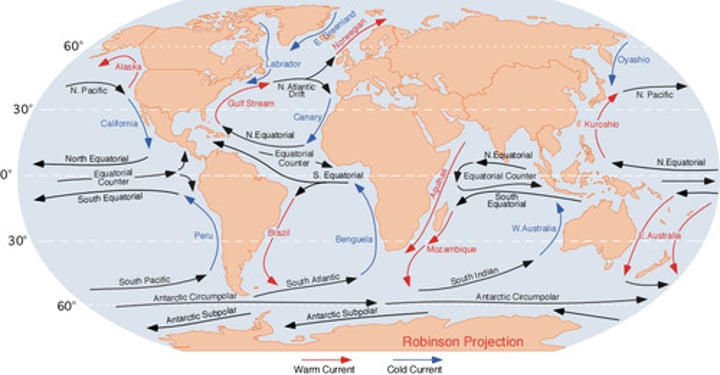
circulating ocean currents created by the Coriolis effect
ocean gyre
Indian, South and North Pacific, North and South Atlantic
What are the ocean gyres?
wind flow is deflected right as it is transported into surface water, makes a spiral shape
Ekman spiral
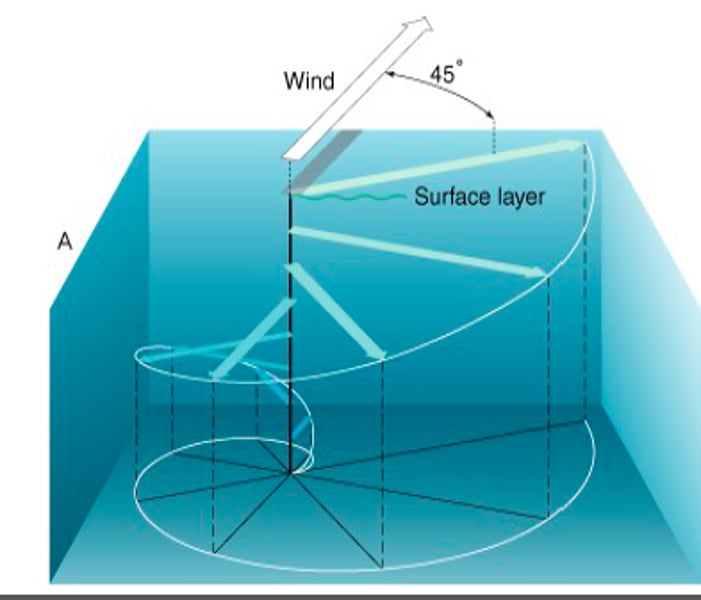
driven by gravity and modified by the Coriolis force that creates a build up of water in the middle of a gyre
Geostrophic flow
North Equatorial Current, Gulf Stream, North Atlantic Current, Canary Current
North Atlantic Gyre
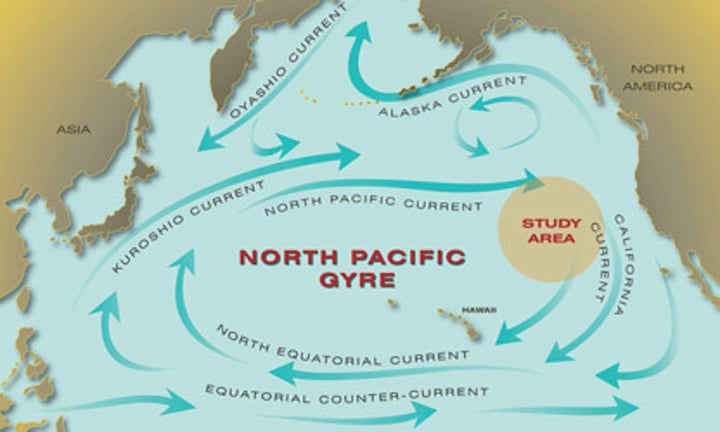
North Pacific Current, California Current, North Equatorial Current, Kuroshio Current
North Pacific Gyre
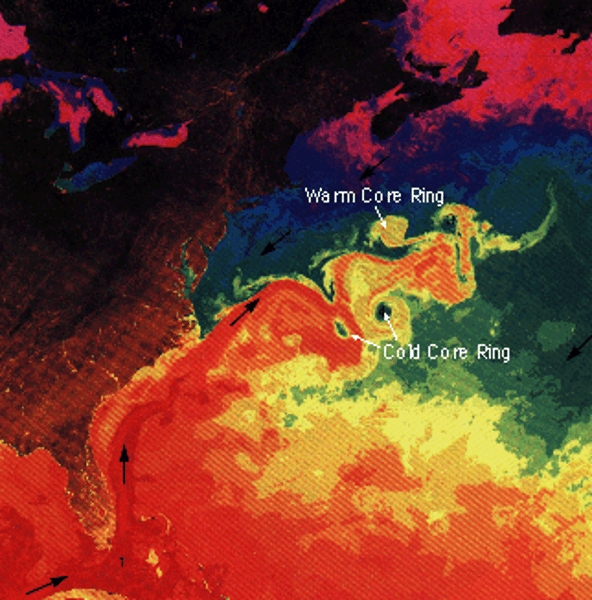
loops formed from currents that move independently from current
eddies
Driven by density differences in salinity and temperature
deep ocean currents
Processes by which rock, sand, and soil are broken down and carried away (i.e. weathering, glaciation)
Erosion
sediment accumulating in new locations.
Deposition
made of available elements bonding together, building blocks of sediments
Minerals
composed of various minerals, form rocks
Sediment
minerals --> sediments --> rocks
what makes up rocks?
The most abundant group of minerals in the earth's crust.
Feldspars
the chemical weathering of feldspar produces
clay minerals
mineral
Quartz
mineral
Calcite
rock that forms when magma cools and solidifies
igneous rock
rocks that change due to heat and pressure from magma
metaphormic rock
The type of rock that is made of hardened sediment.
sedimentary rock
derived from land, transported from mountains and hills to rivers by wind
lithogenous
mixed surface layer
a layer of water in which there is a rapid change of density with depth
Pycnocline
most of ocean, density increases but movement slows
Deep Layer
The densest ocean water
Antarctic Bottom Water
The movement of deep, cold, and nutrient-rich water to the surface
upwelling
The movement of water from the surface to greater depths.
downwelling
erosion from continental rise on the seabed
turbidity current
accumulated on continental shelf
Neritic
accumulated on ocean basins
Pelagic
formed from hard parts of dead organisms
Bigenous
common, microscopic shells from planktons
oozes
shell fragments
sands
cemented reefs, skeletons, etc
solid structures used in sediments
most common
Calcite (CaCO3)
zooplankton (they eat phytoplankton)
Foraminifera
Photosynthetic phytoplankton
Coccolithophores
depth at which carbonate begins to dissolve
Lysocline
essentially glass
Silica
dotted looking, photosynthesizing phytoplankton
Diatoms
zooplankton (eat phytoplankton: diatoms)
Radiolarians