Chamber Quantification
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
95 Terms
What views visualize the left atrium?
PLAX
PSAX
Apical 4, 5, 2, 3
SC 4C, SAX
TEE: transgastric long axis, 2Ch, lower/middle esophageal, upper esophageal
Why are TEE views not optimal for accurate dimension measurements of LA?
Because the entire LA frequency cannot be fit in the image sector
What phase are LA measurements taken?
End-systole = atria at biggest size, just before MV opens
How is LA diameter measured in M-mode?
in PLAX, perpendicular to Ao root and measured at level of the Ao sinuses from LE to LE
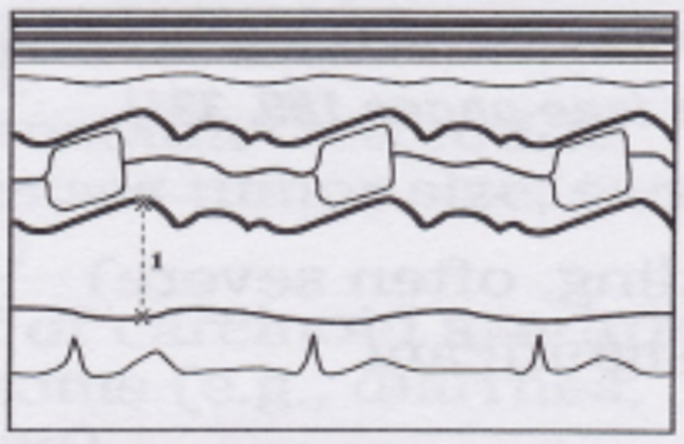
How is LA diameter measured in 2D?
in PLAX with perpendicular orientation to LA posterior wall

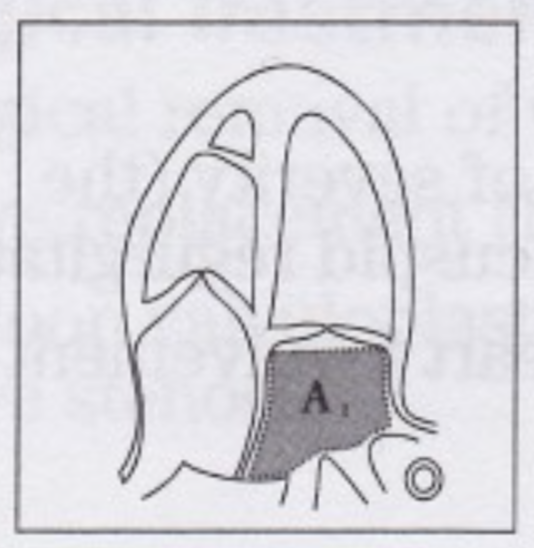
How is LA area measured?
Measured in AP4 at end-systole by tracing the LA inner border
excludes area under MV annulus and inlet of Pv
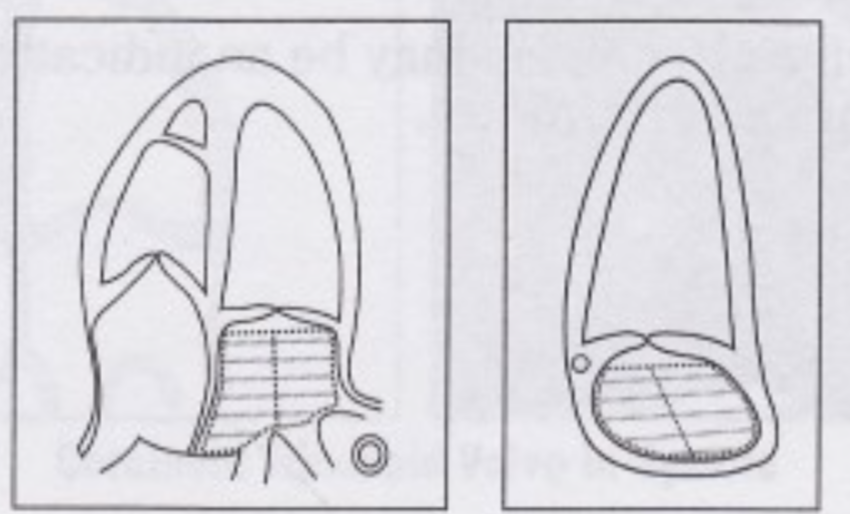
How is LA volume measured using the Biplane area-length technique?
1. tracing the LA area of blood-tissue interface on AP4 and AP2
2. Measure the LA length in AP4 and AP2
3. Calculate volume using formula

What is the volume formula for Biplane area-length technique?
LAvol = (0.85 x A1 x A2) ÷ L
How is the LA volume measured using the Simpson's biplane method of disks?
disk summation technique: adding the volume of a stack of cylinders of height and area calculated by orthogonal minor and major transverse axes, D1 and D2
What is the volume formula for Simpson's biplane method?
LAvol = (D1 x D2 x D3) x 0.523
What is the LA volume index (LAVI)?
LA volume ÷ BSA measured (ml/m2)
BSA
body surface area
What major physiologic roles does the LA fulfill?
Contractile pump that delivers 20-30% of LV filling (atrial kick)
Reservoir that collects Pv return during systole
Conduit for the passage of stored blood from LA to LV during early diastole
What is the purpose of M-mode and 2D echo in LA function assessment?
Assessing LA dimension and motion of anterior LA wall (posterior Ao wall)
What is the purpose of Doppler in LA assessment?
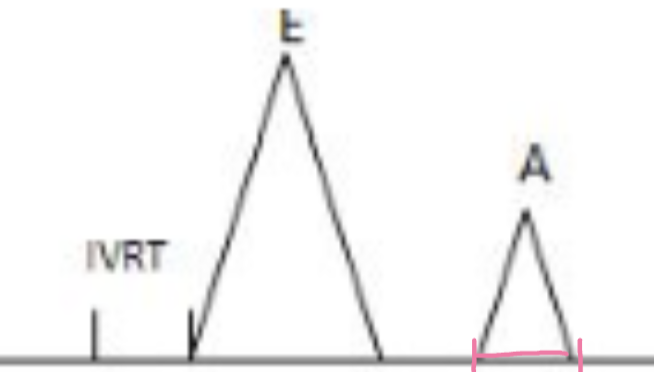
A-wave of MV inflow representing atrial systole
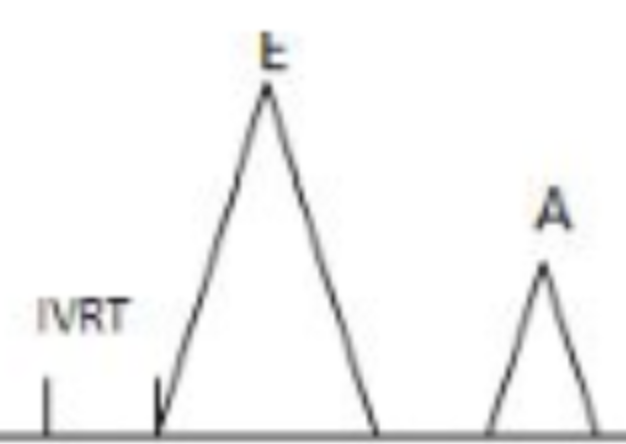
A max velocity (VTI)
LA contractility
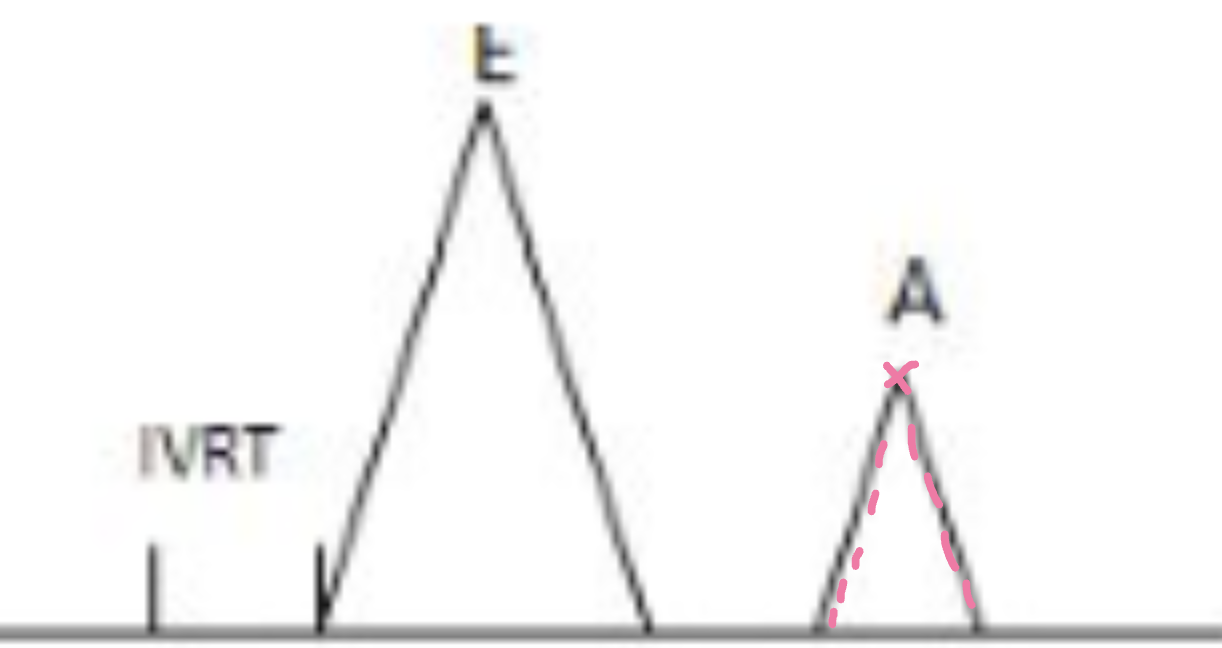
A-time/duration
Length of atria systole
What structures are relevant to the LA function?
LA appendage
Interatrial septum
Pulmonary veins (Pv)
What is the purpose of measuring max velocity at the mouth of LAA in TEE?
correlates with force of LA contraction/emptying
What views can visualize integrity abnormalities of the interatrial septum?
PSAX @Ao , AP4, SC 4Ch, LA TEE
What can help visualize shunts and pressure gradient calculations when such shunts exist?
Color doppler interrogation
What views are the pulmonary veins visualized?
AP4, SSN SAX and TEE
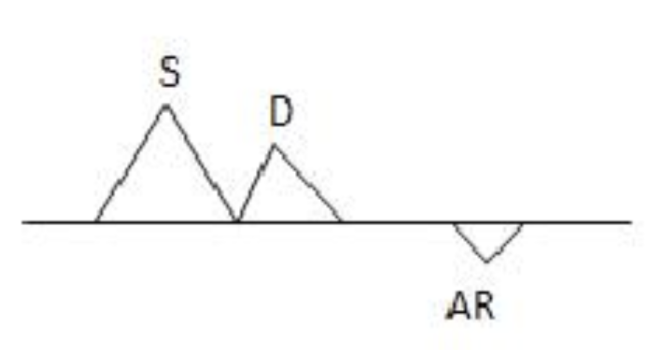
What is the purpose of doppler for Pv?
Assesses LA pressure, important evaluation of LV diastolic function
What would a higher AR wave of Pv doppler indicate?
High LA pressures, which suggests abnormal diastolic function
What is LAE a marker for?
Severity of diastolic dysfunction + magnitude of LA pressure elevation
What patients typically show LAE?
Patients with significant MV disease
atrial arrhythmias
LV systolic and diastolic dysfunction
LV pressure overload
congenital heart disease
cardiac transplantation
What is LAE associated with, and what is the consequence?
Thrombus formation in LA, can cause embolization in cerebral arteries → stroke
What does the bowing of the IAS towards the RA suggest?
LA dilation or increased LA pressure
What is the LA/Ao ratio?
LA can be compared to Ao with a 1:1 ratio
What can a dilated Pv and LAA suggest?
LA dilation + Increased LA pressure
What are common interatrial septal abnormalities?
ASD, aneurysm, PFO, lipomatous hypertrophy
What is an IAS aneurysm?
midportion of atrial septum billows
What is lipomatous hypertrophy?
Fatty infiltration of superior and inferior portions of IAS can create dumbbell-shaped LA
What is PFO?
Patent foramen ovale, allowing intermittent blood flow in bidirectional fashion between two atria
How can the PFO shunt be identified?
Color doppler in PSAX@Ao, AP4, SC4, TEE
Contrast echo with saline bubbles - enhanced with Valsalva maneuver
Quantification of shunting - accurate with TCD
What can dilation of the Pv suggest?
Increased LA pressure
What does abnormal Pv flow patterns suggest?
LA pressure changes associated with diastolic dysfunction, severe MV disease, constrictive pericarditis, restrictive cardiomyopathy
What are the views visualizing the RA?
AP4
SC 4ch
PSAX@Ao
TEE:
- Mid-esophageal basal 4-Chamber view
- Mid-esophageal turned 60-90 degree to patients' right to view RVOT+RVI
- Mid-esophageal Bicaval view at 80-110 degree
- Transgastric long axis of right ventricle 0 degree
Where are RA dimensions primarily taken?
2D at Apical 4Ch at end systole
Where is major dimension of RA measured?
Longitudinal measurement from TV annulus parallel to the IVS to superior right atrial wall
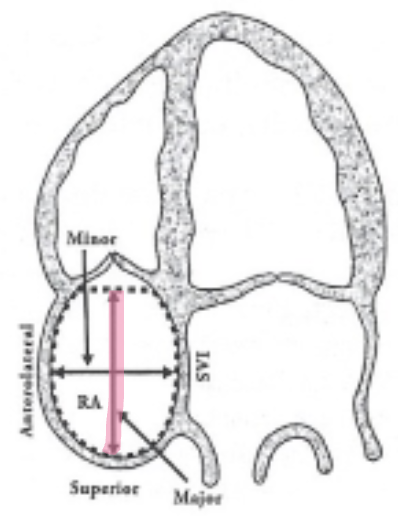
Where is minor dimension of RA measured?
Go perpendicular to long-axis, mid-level of right atria free wall to IAS
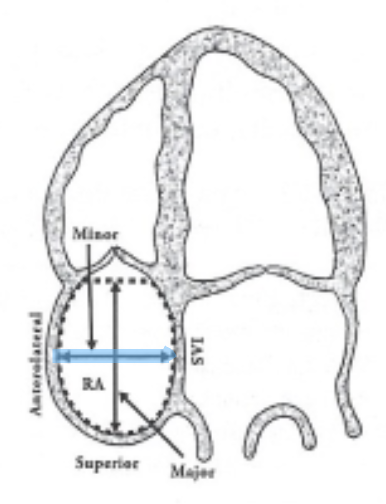
Where is the RA area measured?
Trace around RA across the TV annulus and exclude SVC and IVC and RAA

When should RA area be obtained ?
routinely in patients with known RV/LV dysfunction
when RA is visually larger than LA
How do you obtain RA volume in 2D?
Simpson biplane method by tracing RA wall at end-systole → RAv= (D1 xD2 xD3) x 0.523
What is RAVI?
RA volume index = RAvol ÷ BSA
How is RA pressure measured?
It is estimated by evaluating the IVC via sniff test.
Dilated IVC that does not collapse = 15-20 mmHg
Dilated IVC that collapses = 10-15 mmHg
Where can color doppler for RA be seen?
In AP4, PSAX, RVIT but are only used for qualitative data
What is a good indication of RAE?
If RA is larger than LA
What are right atrial functions?
Contractile pump that delivers blood to RV
Receives and stores deoxygenated blood from SVC, IVC, and coronary veins during ventricular systole
What is the purpose of 2D in RA function assessment?
Assess the RA dimensions, atrial septum motion and collapsibility of IVC
What is the purpose of Doppler in RA function assessment?
Assessment of RA filling done by viewing flow patterns of IVC or hepatic veins in SC 4Ch
What are the parts of the spectral wave form of IVC and Central Hepatic Vein?
Systolic = S
Diastolic = D
Atrial kick = a

When is there increased filling in the RA?
During inspiration (expansion of thoracic cavity= sucks in venous return)
What is the eustachian valve?
The fetal remnant of the valve of the IVC
What is the Chiari network?
Fetal remnant of the valve to the coronary sinus
What is the crista terminalis?
C-shaped ridge of tissue in the RA, ranging from SVC to IVC
What is a marker for RV systolic and diastolic function?
RAE
A deviated IAS toward the LA throughout the cardiac cycle may be a sign of...
Increased RA volume/pressure
RAE or dilation can be present in patients with the following:
Tricuspid valvular disease (TR, TS)
RV pressure overload (PHTN)
Atrial fibrillation
Congenital Heart Disease
Cardiac transplantation
Sleep Apnea
What does the bowing of the IAS toward the LA + distortion of the right heart with no movement suggest ?
compression by extracardiac structures within the liver or mediastinum.
What can the bowing of the IAS toward the LA with a mass in RA is suggestive of?
A cyst or tumor
When is a thrombus in the RA appendage commonly found?
In consequence of low flow, atrial arrhythmia, or Prescence of catheters and pacemakers
A multilobed, freely mobile, and wormlike thrombi is more likely formed in?
Lower extremities
What 10 views visualize the RV?
PLAX
RVIT
RVOT
PSAX @Ao
PSAX @MV
PSAX @PM
AP4
AP5
AP3
SC 4Ch
Structures of RV
TV
PV
RV free wall
IVS
Moderator band
Where is the RV free wall thickness measured?
at end-diastole using Subcostal 4Ch or PLAX
Using 2D or M-mode - measure at the tip of the anterior TV leaflet, assessing the RV dimensions and wall motions
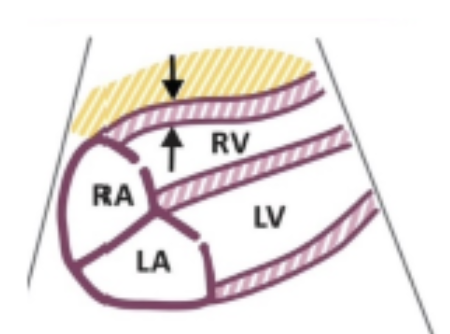
What is the normal free wall thickness?
≤ 0.5 cm
Where is 2D RV linear dimension measured?
In 2D at AP4 at end diastole
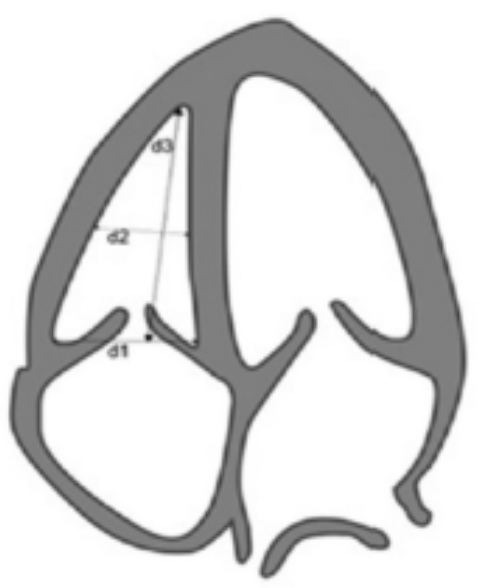
Where is d1 measured?
Basal diameter → base of chamber from corner to corner behind TV leaflets
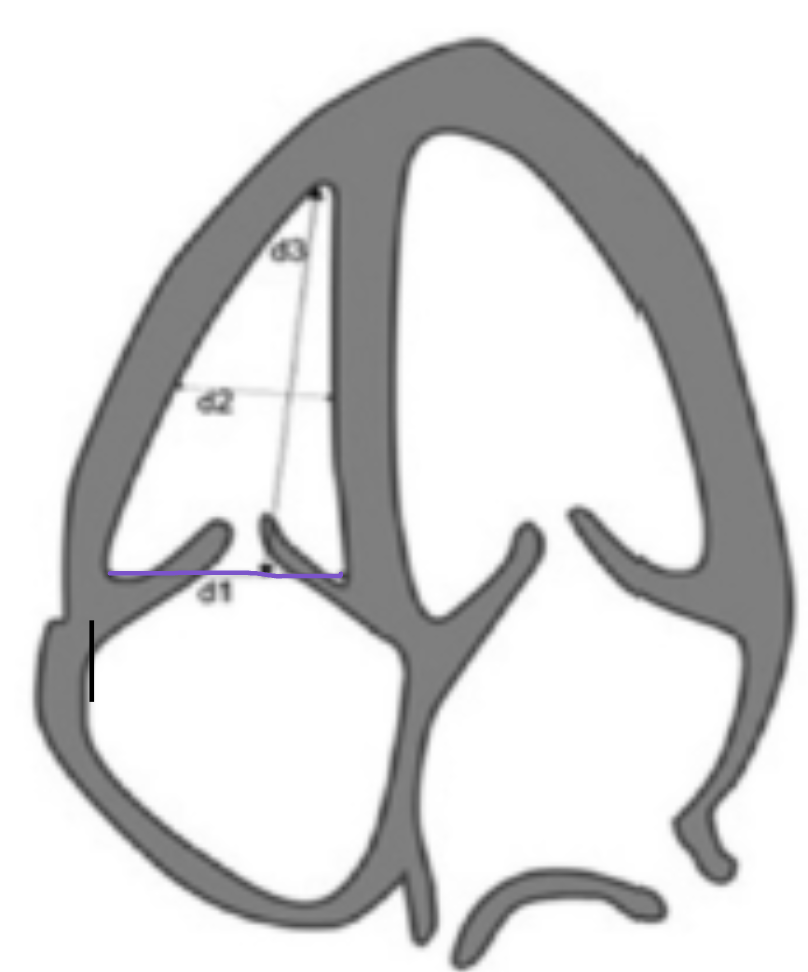
What is a normal d1?
≤ 4.2 cm
Where is d2 measured?
Mid-cavity dimension → measure at the middle third of RV at level of papillary muscles, stay under MB
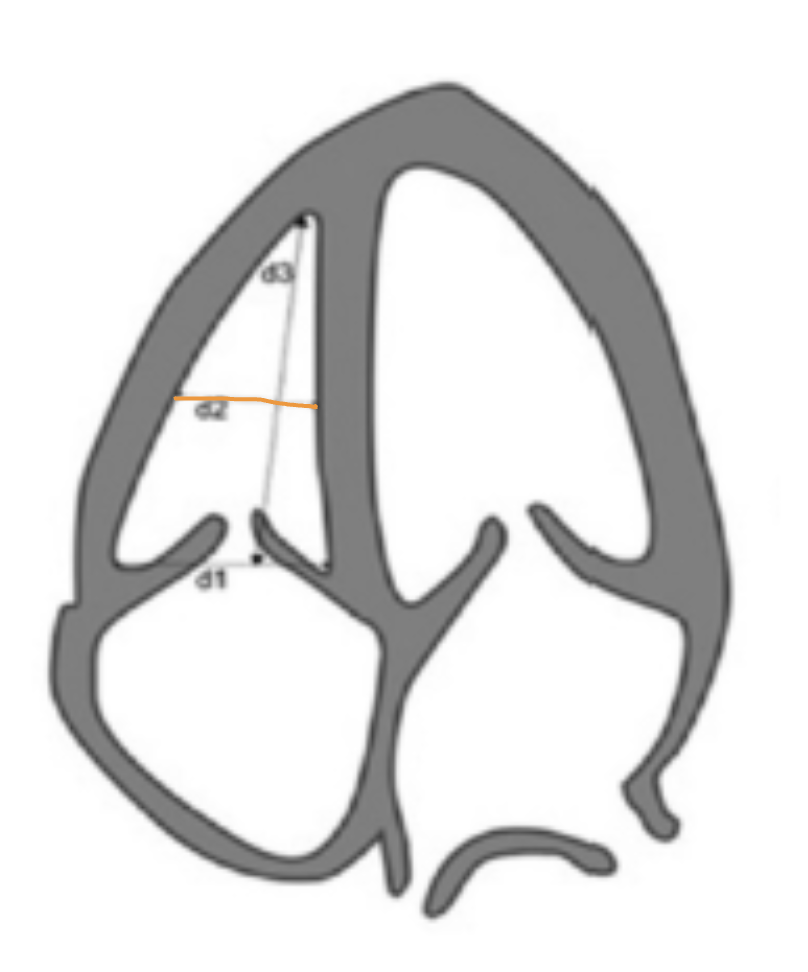
What is a normal d2?
≤ 3.5 cm
Where is d3 measured?
Longitudinal dimension → measure at mid plane of the TV annulus to RV apex

What is a normal d3?
≤ 8.6 cm
How is RVOT dimension measured?
In 2D at PSAX or subcostal at end-diastole
Where is RVOT proximal (RVOT2) measured?
Using PLAX or PSAX AO measure RVOT
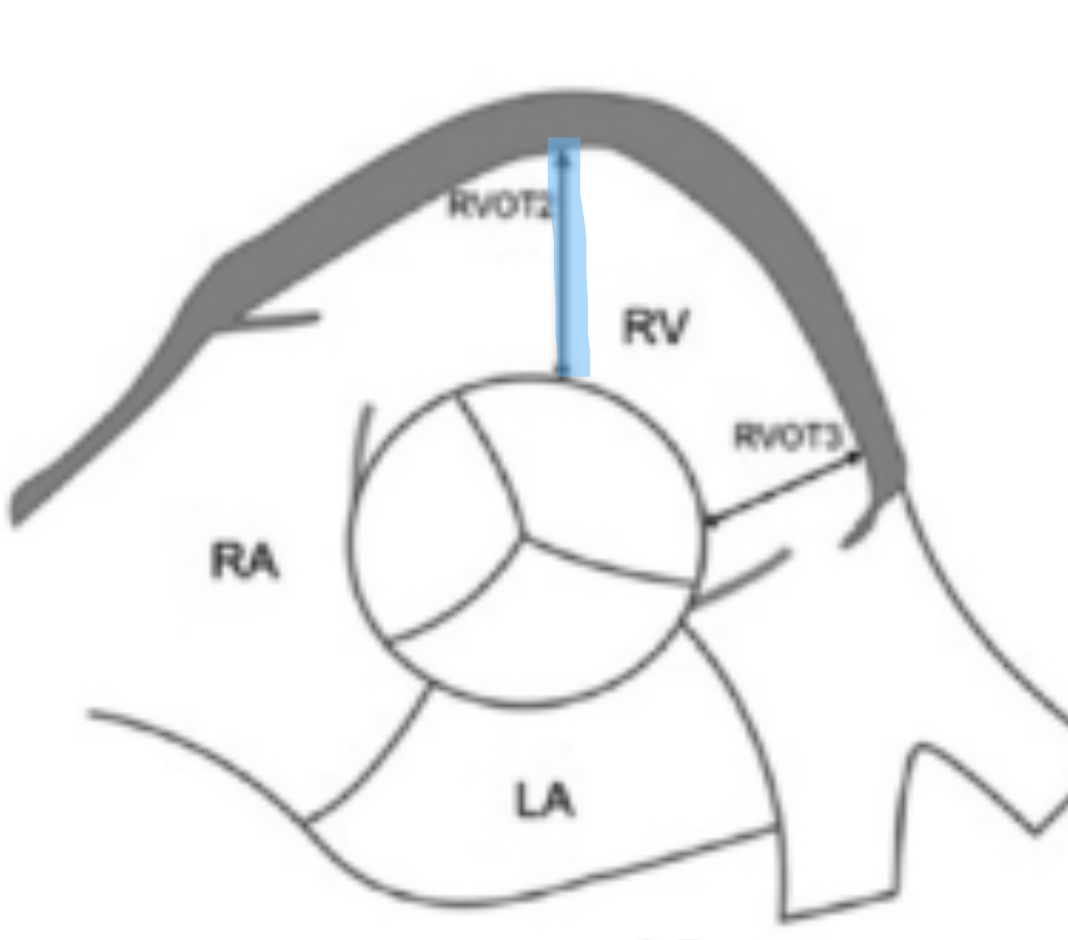
What is a normal RVOT proximal?
≤ 3.3 cm
Where is RVOT distal (RVOT3) measured?
Using PSAX Ao measure RVOT near the PV annulus
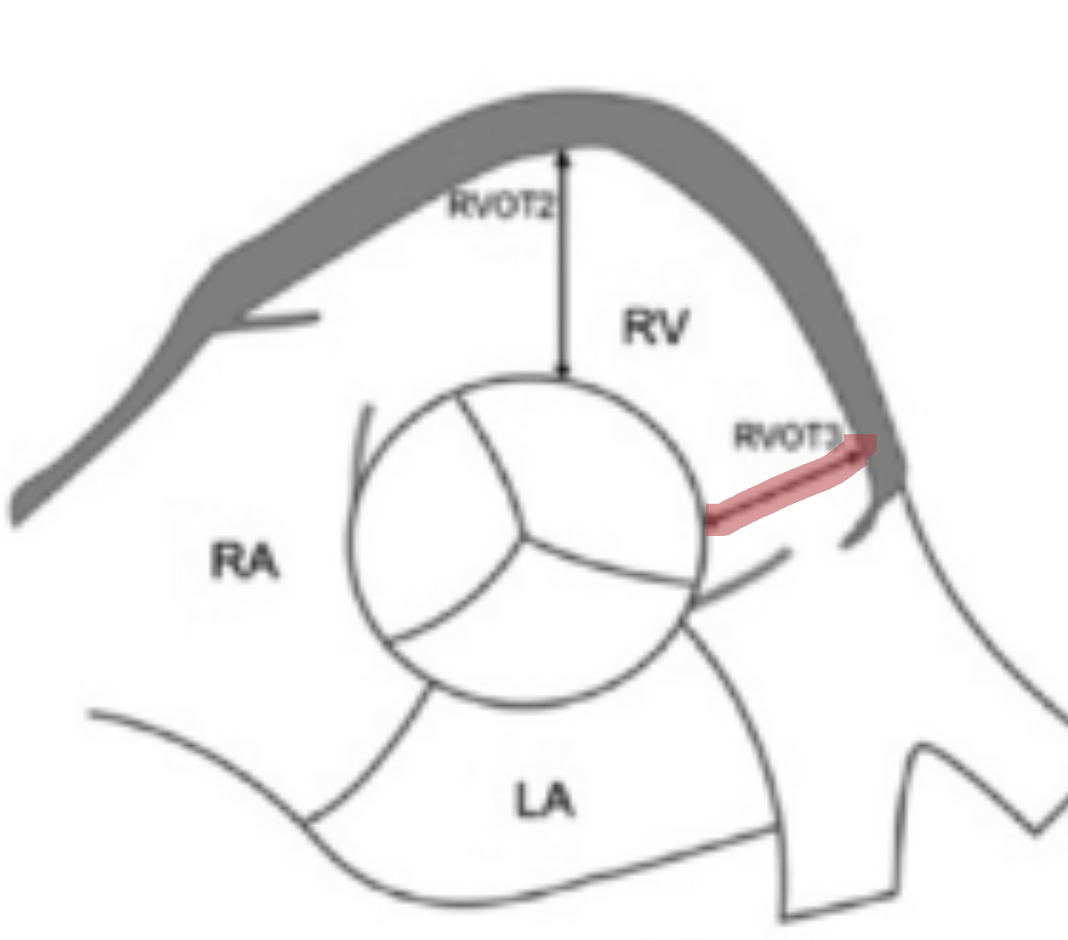
What is a normal RVOT distal?
≤ 2.7 cm
What is the function of the RV?
Contractile pump that delivers unoxygenated blood into pulmonary circulation
How do you measure RV area and Fractional Area Shortening?
Using 2D at AP4, trace at the TV annulus, along the wall to the apex, down the IVS, and back to the annulus
Perform this in end-diastole AND end-systole
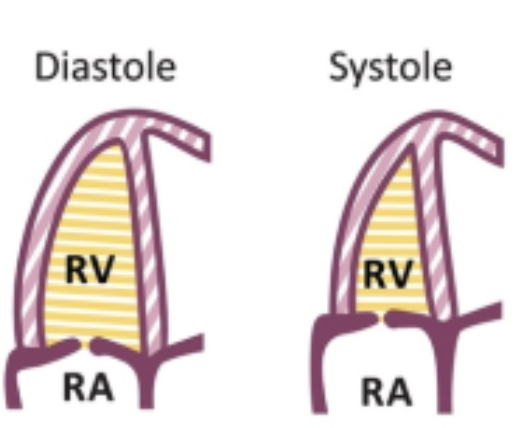
What is an abnormal FAC?
Less than 35%
What is TAPSE?
Tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion → Amplitude of the free wall up and down during peak systole
how do you measure TAPSE?
Using M-Mode at AP4, Place cursor through TV annulus and measure the longitudinal motion of TV anulus at peak systole
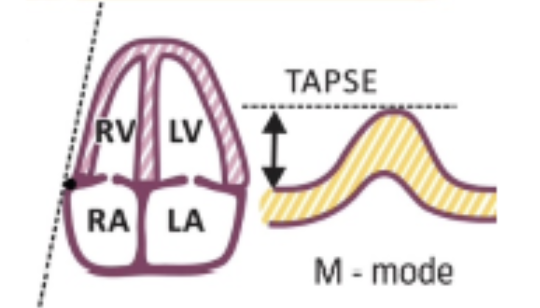
What is a normal TAPSE?
1.7 - 3.1 cm
Why do we use tissue doppler imaging at RV and how do you measure it?
Measuring the speed of the tissue moving up and down
In AP4, place gate at the TV annulus or in the middle of basal segment to measure peak systolic velocity
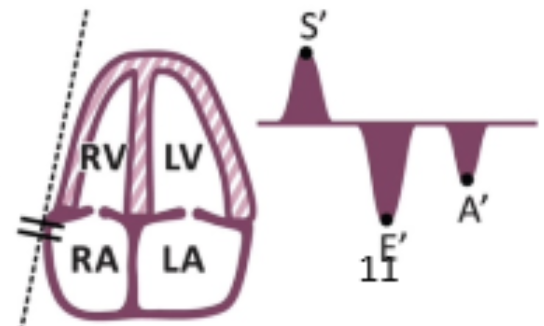
What is a normal S' ?
10-14 cm/s
How do you assess RV diastolic function?
RV diastolic function follows the pattern of the LV, so it is discussed with LV diastolic function
What is RV dysplasia?
The replacement of RV myocardium with adipose or collagen
What are common signs of RV dysplasia?
RV enlargement
focal RV wall motion abnormalities
localized aneurysms of free wall
How does RV dysplasia appear in ultrasound?
echogenic
What is ARVD and what does it cause?
Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia is a rare form of familial RV cardiomyopathy, may cause Vtach and sudden cardiac death
What happens in a hypercontractile RV?
Pulmonary hypertension, pulmonary embolism, long term sleep apnea
What causes RV volume or pressure overload?
Constrictive pericarditis and cardiac tamponade
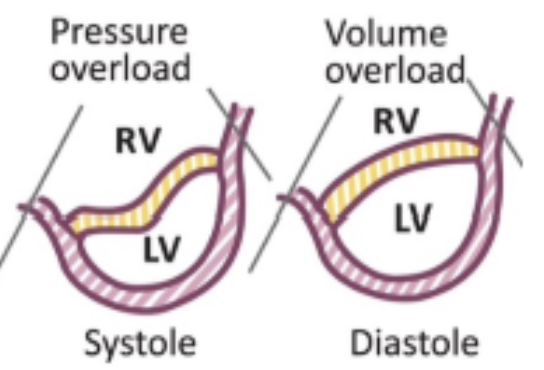
What is a result of RV volume or pressure overload?
Ventricular interdependence: Septal shift and D shaped LV