Digestion
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
What are the four stages of food processing?
ingestion
digestion
absorption
elimination
What are the three types of ingestion?
filter feeding
fluid feeding
bulk feeding
What type of ingestion do humans do?
bulk feeding
What are the two ways in which digestion is carried out?
mechanical
chemical
mechanical digestion
taking big pieces of food and breaking them down into small pieces of food
ex: chewing
chemical digestion
molecules are being broken down
ex: enzymes that carry out hydrolysis
What are the two possible locations of digestion?
intracellular or extracellular
Unicellular, porifera, and cnidaria organisms undergo (intra/extra)cellular digestion.
intracellular digestion
Bilateria organisms undergo (intra/extra)cellular digestion.
extracellular digestion
What are the two main parts of the digestive system?
alimentary canal
accessory organs
alimentary canal
one-way tube with 2 openings (mouth & anus);
continuous with the outside;
has compartments
sphincters
smooth muscle valves between one compartment and another
What are the accessory organs of the digestive system?
tongue
salivary glands (3 major pairs)
pancreas
liver
gallbladder
peristalsis
waves of smooth muscle contraction & relaxation that moves food
make the digestion of nutrients graphic organizer
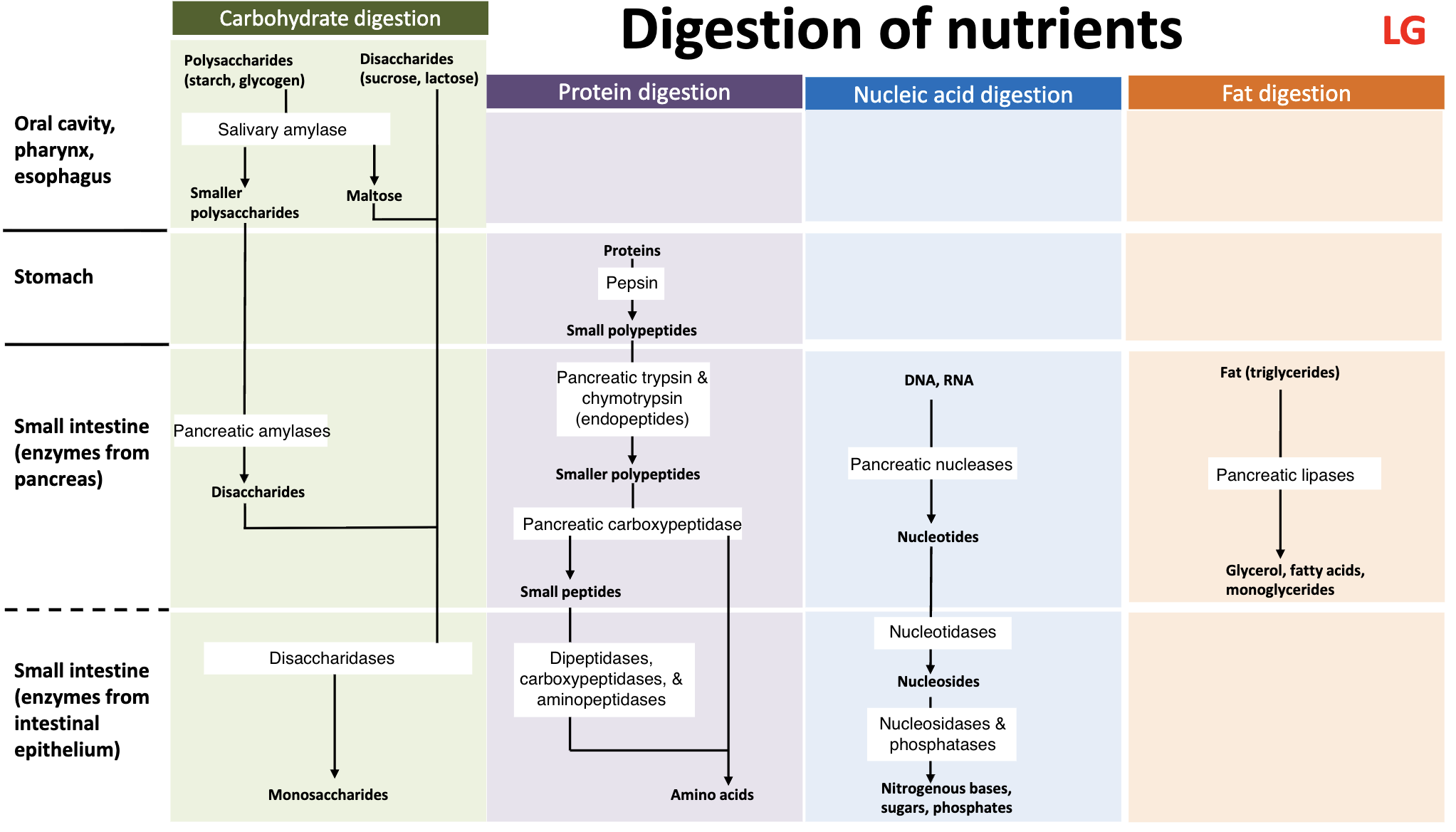
In what way is the nervous system triggered before ingestion?
salivary secretion
The tongue forms a ____, or mass of food, and moves it for swallowing.
bolus
What is the path of a bolus?
oral cavity →
pharynx →
esophageal sphincter →
esophagus →
cardiac sphincter →
stomach
stomach wall
elastic & has folds
Gastric glands secrete…
gastric juice
What are the three cells that make up the gastric glands?
chief cells
parietal cells
mucous cells
What do chief cells produce?
pepsinogen
What do parietal cells produce?
HCl (pH ~ 2)
What do mucous cells produce?
mucus
What is the mechanical function of the stomach?
churning
What is the chemical function of the stomach?
HCl converts pepsinogen into pepsin
What is the main digestive enzyme of the stomach?
pepsin (an endopeptidase)
What breaks specific internal peptide bonds into smaller polypeptides (not amino acids)?
pepsin
The chyme that leaves the stomach is a mixture of…
partially digested carbohydrates
smaller polypeptides
undigested material
What is the pH of chyme?
2
Chyme leaves the stomach through the…
pyloric sphincter
How long is the small intestine?
~ 6 meters long
Why is the small intestine called the “small” intestine?
small diameter
What are the 3 divisions of the small intestine?
duodenum
jejunum
ileum
Villi & microvilli increase…
surface area
villi and microvilli
projections of tissue;
exchange surface
What are the functions of the small intestine?
mechanical digestion of fats
chemical digestion
absorption of nutrients & water
Fats are hydrophobic or hydrophilic?
hydrophobic
Why don’t the enzymes work on fats?
because the enzymes are hydrophilic
Where is bile produced?
liver
Where is bile stored?
gallbladder
Bile is released through the…
bile duct
After bile is released through the bile duct, where does it go?
into the duodenum of the small intestine
What do bile salts do?
emulsify fats;
large masses of fats → smaller droplets of fat
The emulsion of fats increases…
surface area
Why is the use of bile in digestion mechanical and not chemical?
bile does not use enzymes (chemical) to break down the fat molecules into their chemical building blocks, it physically (mechanical) divides them into smaller physical pieces
How does the small intestine mechanically digest fats?
bile
How does the small intestine chemically digest foods?
pancreatic juice
intestinal epithelium
Pancreatic juice moves through a duct into the…
duodenum of the small intestine
What is in pancreatic juice?
bicarbonates
several enzymes
aminopeptidases
enzymes that cleave single amino acids at the amino end
carboxypeptidases
enzymes that cleave single amino acids at the carboxyl end
What does the intestinal epithelium have in it?
enzymes
dipeptidases
hydrolyze dipeptides
Where does nutrient absorption occur in the small intestine?
intestinal villi
Why are intestinal villi an exchange surface?
nutrients use it to go from intestinal lumen to the bloodstream
What three processes are involved in the absorption of water and nutrients in the small intestine?
simple diffusion
facilitated diffusion
active transport
SEQ & draw the breakdown and absorption of lipids
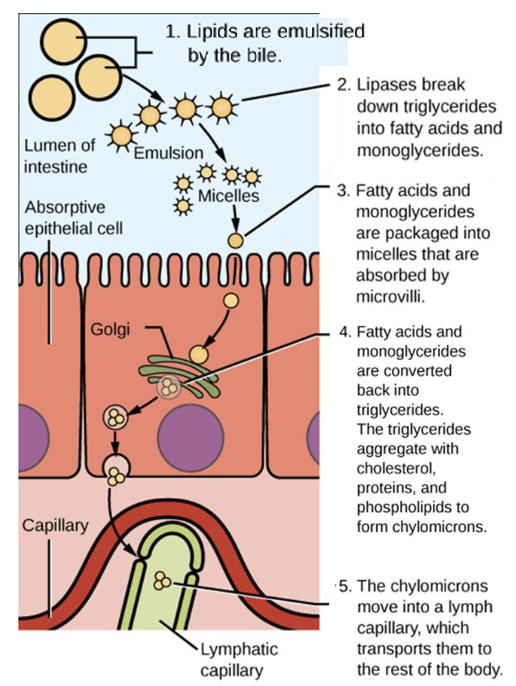
What organ gets first access to nutrients from the small intestine?
liver
Through what structure does the liver get first access to nutrients from the small intestine?
hepatic portal vein
What are the three main functions of the liver?
convert glucose → glycogen
synthesize protein
inactivate toxins
At the end of the small intestine, most nutrients are…
absorbed
What is left at the end of digestion in the small intestine?
undigested material
indigestible material
dead cells & bacteria
bile salts
Why is the large intestine called the “large” intestine?
large diameter
What are the 4 divisions of the large intestine?
ascending colon
transverse colon
descending colon
sigmoid colon
What are the functions of the large intestine?
water absorption
host bacteria that produce vitamin K, B1, B2, B12
elimination of digestive waste as feces