MD 6. Carbonyl-carbonyl Condensation Reactions
1/4
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
5 Terms
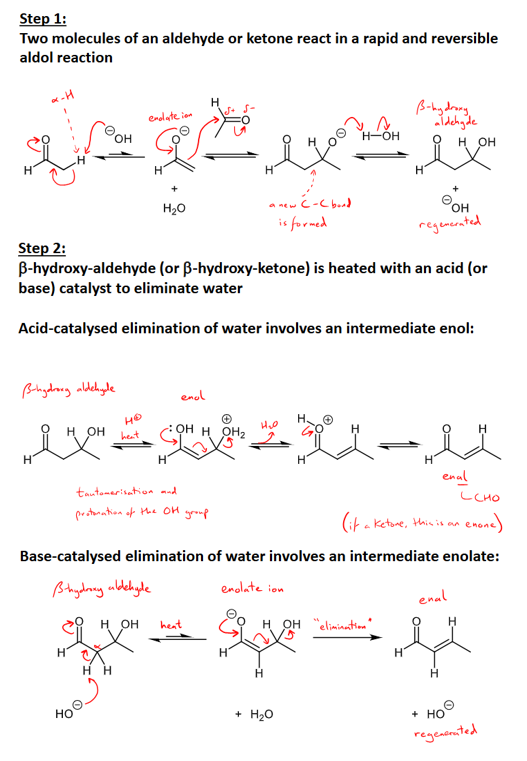
What is the Aldol condensation and mechanism?
a base catalysed dimerization reaction for all aldehydes and ketones with alpha-hydrogen atoms
step 1 - two aldehydes or ketones react in a rapid reversible aldol reaction
step 2 - beta-hydroxy-aldehyde (or -ketone) is heated with an acid or base catalyst to eliminate water and form an enal
acid-catalysed elimination of water involves an intermediate enol and the base catalysed elimination of water involves an intermediate enolate ion
What is a crossed aldol reaction? What are the number of products and the disadvantage of this?
It is the reaction of two different aldehydes or ketones
There are four possible products formed from this: A + B = AA + AB + BA + BB
if the aldehydes and ketones can form enolate ions equally well and can both act as electrophiles in nucleophilic additions the four products will be made
However, as the maximum yield of a single product is low this is rarely used in synthesis
What three things can cause a crossed aldol reaction give a single product in high yield?
A single product in high yield can be made if:
one of the carbonyls is unable to form and enolate as it has no alpha-hydrogens
the carbonyl compound unable to form the enolate ion is more reactive to nucleophilic addition than the carbonyl that CAN form an enolate ion
The carbonyl able to form the enolate ion is added to the mixture slowly
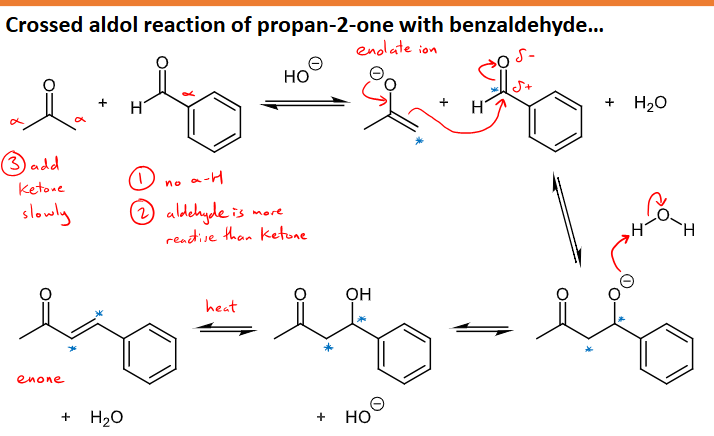
What is an example reaction/mechanism for a crossed aldol with a high yield of one product?
reaction of propan-2-one with benzaldehyde
Benzaldehyde is more reactive but has no alpha hydrogens so it ticks off the first two requirements for the high yield of a single product
And propan-2-one is added to the mixture slowly to fulfil the final requirement
Forms an enone with a water molecule by-product
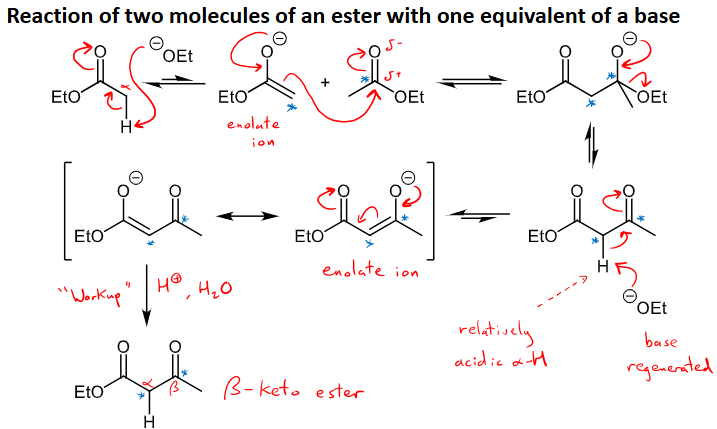
What is the Claisen condensation and what type of reaction is it?
Condensation of esters: reaction of two molecules of ester with one equivalent of a base
Forms a beta-keto ester