AP human Geography unit 1.1
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
My notes
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Maps
Tools that depict spatial patterns.
Spatial patterns
How and where different geographic features occur on the earth’s surface.
Absolute distance
Specific distance that can be measured in feet or miles
Relative distance
Measures social, cultural, or political differences or similarities between two locations.
Absolute direction
cardinal directions(north,south,east, and west)
Relative direction
Describes one location in reference to another.
Clustering and dispersal
Show how different phenomena are organized across an area.
Clustering
ex-buildings in new york
Dispersal
ex-farms in the midwest
Elevations
Measures the height of geographic features relative to sea level.
Map scale
Tells you how the distance on the map relates to distance in the real world.
Direction
Represented on map by a compass rose.
Compass Rose
Indicates the cardinal directions:north,south,east, and west.Can sometimes give intermediate directions.
Scales
Tells how much of the world we’re seeing on the map(not distance like map scale)
Reference maps
Display specific geographic locations.
Thematic maps
Specialize in displaying geographic information.
Chloropleth map
Visualizes data from a specific geographic region in different colors.
Cartogram
Distorts the size of geographic shapes to display differences in data.
Graduated symbol
Also known as a “proportional map”
Dot distribution
Uses dots to visualize the location of certain data points.
Isoline map
Use lines to depict changes in data.
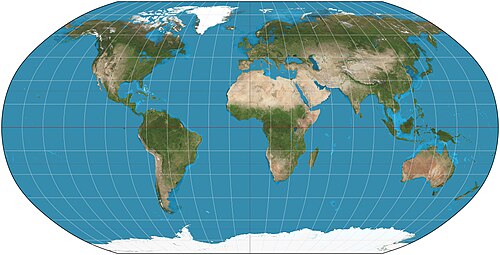
Mercator projection
A map whose latitude and longitude lines meet at right angles(square), a really good map for determining direction, distortion increases further from the equator.
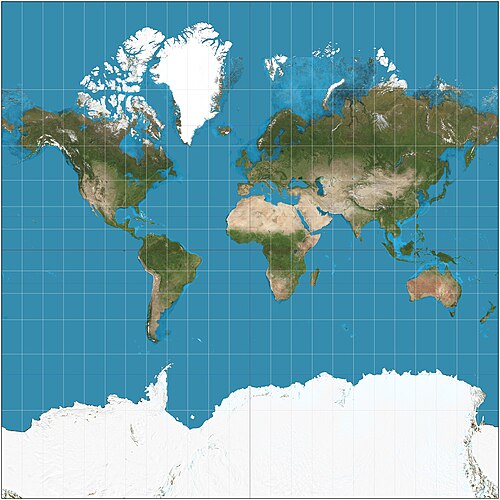
Peters Projection
Depicts continents according to the true size of their landmass, the shapes are inaccurate though.
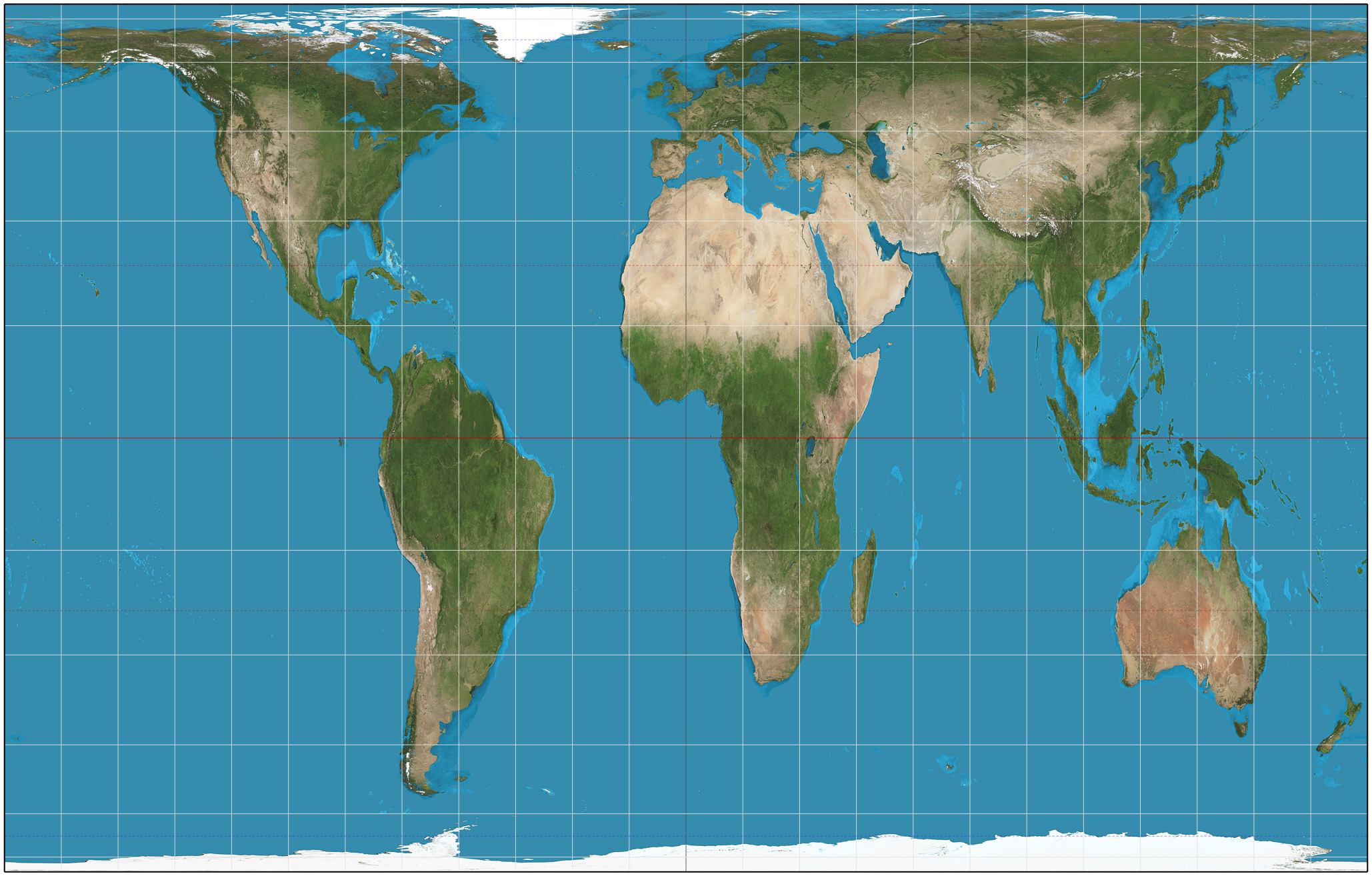
Goode Homosoline projection
Accurately represents the shapes of the land masses but has to break up the oceans to do so.
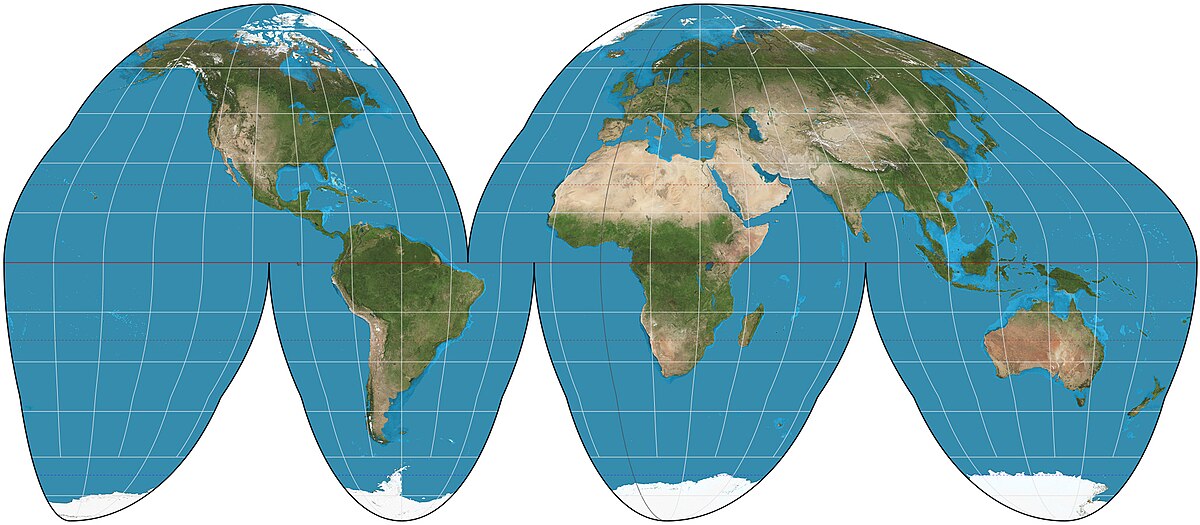
Polar projection
Views the world from the north or south pole, directions are true and the land shapes are accurate near the middle but distort farther from the center.
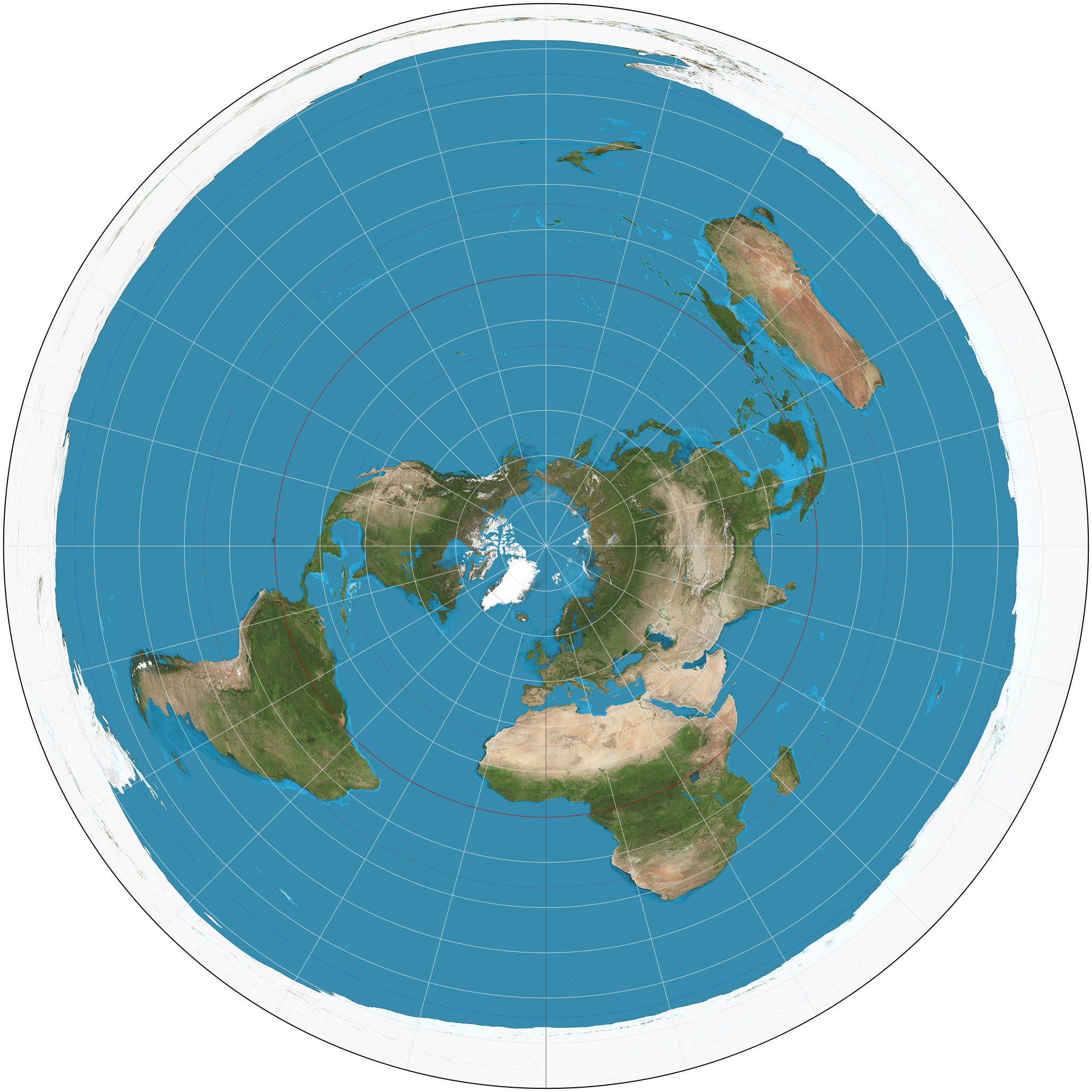
Robinson projection
Distributes all kinds of distortion to all parts of the map(compromise between mercator and peters)