2.5 Fluid Mechanics
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What is an" “incompressible” fluid ?
A liquid
In a liquid, molecules are weakly bonded, such that they can move around each other while staying close together. It has a surface when it is in a container.
What is a “compressible” fluid ?
A gas
No bonds link its molecules ; they move freely in space without natural interactions. So it gas occupies the entire volume of its container
What is the formula for the density ?

What is Pressure ?
Scalar quantity measuring the magnitude of the pushing force applied by this substance on a unit area of contact with a container

How can Liquid develops pressure ?
Liquids develop pressure from “gravitational contribution” because the gravity field attracts the liquid downward, thus pushing on the bottom of the container. Being able to flow but blocked by the walls, the liquid pushes similarly on the walls.
So the pressure of a liquid increases with the depth of the liquid column. At a given depth level, the pressure of the fluid is identical at every point and in all directions.
What is the pressure of a column of liquid ?
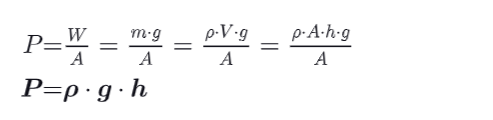
Does Gravity impact gases ?
It’s negligible, but thermal contribution that develops pressure; increasing the temperature leads to an increase in molecular motion and, thus, more interactions with the walls of the container
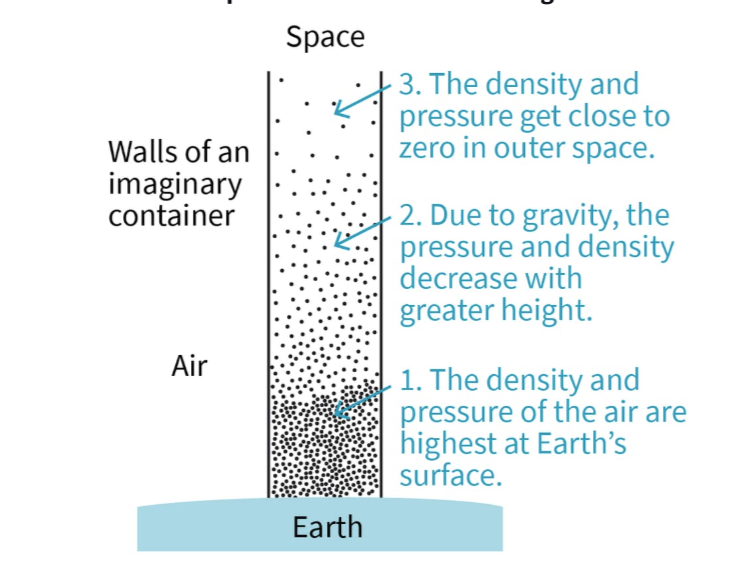
What are the variations of the atmospheric pressure relative to the height ?
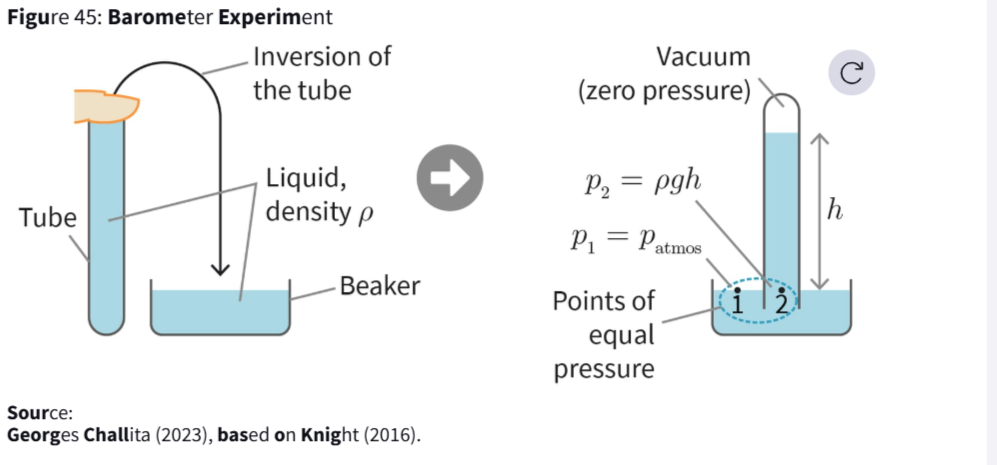
What is a barometer ? Describe the barometer experiment
device used to measure atmospheric pressure.
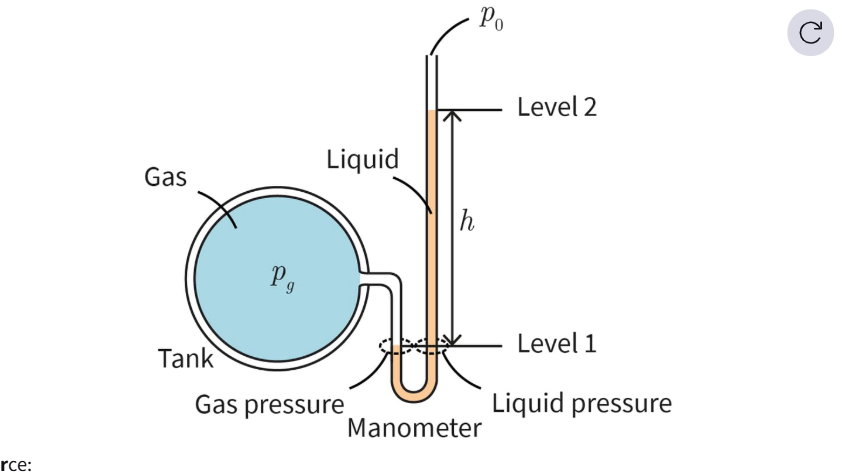
What is a Manometer ?
A manometer is a device consisting of an open U-shaped tube filled with a fluid and connected to a pressurized gas-filled tank.
It measures the gauge pressure of the gas.
What is gauge pressure ?
One defines the term “gauge pressure” Pg as the pressure measured relative to the atmospheric pressure
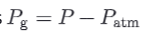
Is is the gauge pressure found with a manometer ? (“dormulas”

What does the Pascal’s Principles say about the forces on hydraulic lifters ?

About hydraulic lifters, what can you say about the liquid displacement ?
Since the liquid is incompressible, the downward displaced volume (input piston) is the same as the upward displaced volume (output piston)
resulting in a higher distance traveled by the input piston

What is the work done at the input & output cylinders for hydraulic lifters ?
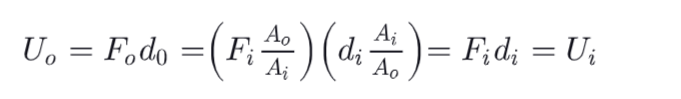
What is archimede’s principle ?
When a body is fully or partially submerged in a fluid, a buoyant force from the surrounding fluid acts on the body. The force is directed upward and has magnitude equal to the weight of the fluid that has been displaced by the body
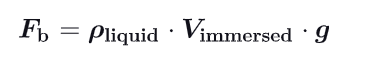
Give another formula for Fb :
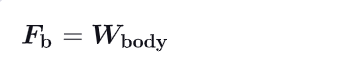
What is the apparent weight of a body ?
When an object in a liquid needs to be lifted, the lifting force only needs to overcome the apparent weight instead of the entire real weight.

WHat is viscosity ?
Viscosity is the resistance of a fluid against flow. It is analogous to friction for solids
What are the different types of “flow” ?
A flow is said to be “laminar” when the velocity at each point in the fluid is constant. The flow is smooth. It does not change or fluctuate.
Otherwise, the flow is “turbulent.”
What is an “ideal fluid” ?
Incompressible
exhibits non-viscous & laminar flow.
What is the equation of continuity ?

What is the volumetric flow rate formula ?
Q_v, m³/s
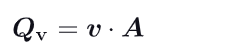
What is the mass flow rate formula ?
Q_m
