Ear Anatomy
5.0(2)Studied by 53 people
0%Unit 3: Sensation and Perception Mastery
0%Exam Mastery
Build your Mastery score
Supplemental Materials
Card Sorting
1/19
Last updated 2:12 PM on 3/23/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
1
New cards
What are hearing receptors?
cilia, hair-like structures on hair cells
2
New cards
Place Theory
"Different pitches stimulate different PLACES on basilar membrane" (due to difference in hair length between base and )
base = short/stiff hair cells = resonate with high frequencies
end = long/loose hair cells = resonate with low frequencies
base = short/stiff hair cells = resonate with high frequencies
end = long/loose hair cells = resonate with low frequencies
3
New cards
Frequency Theory
"At low pitches, neurons fire at the same rate as the sound's frequency"
ex. 75 Hz sound triggers neurons to fire 75 times per second
"At intermediate pitches (like human voices), GROUPS of neurons fire at the same rate as sound's frequency"
ex. 5,000 Hz sound triggers groups of 5 neurons to fire in rapid succession
ex. 75 Hz sound triggers neurons to fire 75 times per second
"At intermediate pitches (like human voices), GROUPS of neurons fire at the same rate as sound's frequency"
ex. 5,000 Hz sound triggers groups of 5 neurons to fire in rapid succession
4
New cards
Ossicles
Group of 3 bones in middle ear that amplify sound waves
5
New cards
Pinna
ear lobe
- focuses sound waves down ear canal
- focuses sound waves down ear canal
6
New cards
Cilia
- hair-like receptor cell
- when hair cells triggered on the organ of corti, it opens up mechanically gated sodium channels (generating a graded potential that could lead to an action potential)
- when hair cells triggered on the organ of corti, it opens up mechanically gated sodium channels (generating a graded potential that could lead to an action potential)
7
New cards
Timpone Membrane
eardrum
- membrane between outer and middle ear
- membrane between outer and middle ear
8
New cards
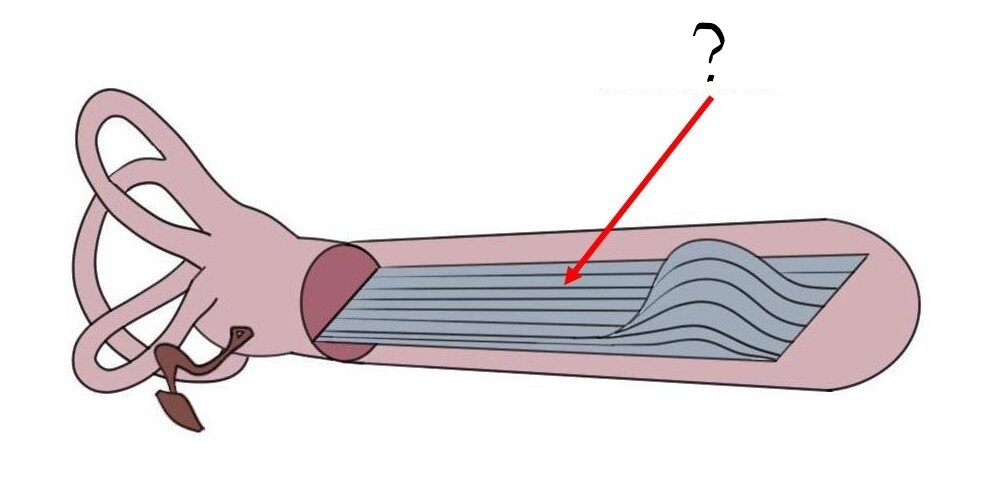
Basilar Membrane
- forms the base of the organ of Corti.
- Movement of the ______ in response to sound waves causes the depolarization of hair cells in the organ of Corti.
- The hair cells transduce auditory signals into electrical impulses
- diff. sections of the ____ respond to diff. frequencies of sound: high tones vibrate the region near the base, low tones vibrate the region near the apex
- Movement of the ______ in response to sound waves causes the depolarization of hair cells in the organ of Corti.
- The hair cells transduce auditory signals into electrical impulses
- diff. sections of the ____ respond to diff. frequencies of sound: high tones vibrate the region near the base, low tones vibrate the region near the apex
9
New cards
Oval Window
a membrane covering the entrance to the cochlea in the inner ear
is connected to stirrup
is connected to stirrup
10
New cards
Cochlea
spiral cavity of the inner ear filled with fluid
11
New cards
Volley Principle
the principle that individual fibers in an auditory nerve respond to one or another stimulus in a rapid succession of rhythmic sound stimuli, whereas other fibers in the nerve respond to the second, third, or nth stimulus. The result is that successive volleys of impulses are fired to match the inputs of stimuli, yet no single fiber is required to respond to every stimulus. Thus, a nerve can reflect a more rapid frequency of stimulation (e.g., 1000 Hz) than any individual fiber could follow
- this fixes the rebuttle of frequency theory where it is impossible to explain perception of sounds above 500 Hz since neuron's refractory period renders neruon incapable of firing above 500 impulses per second
- this fixes the rebuttle of frequency theory where it is impossible to explain perception of sounds above 500 Hz since neuron's refractory period renders neruon incapable of firing above 500 impulses per second
12
New cards
Organ of Corti
the receptor organ of the ear
- in the cochlea
- produces nerve impulses in response to sound vibrations
- contains receptor (hair) cells
- in the cochlea
- produces nerve impulses in response to sound vibrations
- contains receptor (hair) cells
13
New cards
Auditory Canal
passageway that leads from the outside of the head to the tympanic membrane, or eardrum membrane, of each ear
14
New cards
Auditory Nerve
intertwined axons of hair cells
- electrical impulses travel from organ of corti along __(this nerve)____ .
- electrical impulses travel from organ of corti along __(this nerve)____ .
15
New cards
Conduction Deafness
type of hearing loss that happens when sounds cannot get through the outer and middle ear (because they're damaged)
- hearing loss can be reduced with hearing aids that amplify sound waves
- hearing loss can be reduced with hearing aids that amplify sound waves
16
New cards
Perceptive Deafness
type of deafness that results from nerve damage in inner ear
- can be reduced by cochlear implants
- can be reduced by cochlear implants
17
New cards
Sound Localization
a listener's ability to identify the location or origin of a detected sound in direction and distance
18
New cards
Outer Ear
= collect sound waves
* ear lobe “pinna” funnels sound waves down the auditory canal
* ear lobe “pinna” funnels sound waves down the auditory canal
19
New cards
Middle Ear
= amplify sound waves
\
* defined by membranes on both sides
* ossicles: are all attached and get smaller, so the mechanical wave vibrations are amplified as they become more concentrated
* same frequency, but amplified amplitude (volume)
\
* defined by membranes on both sides
* ossicles: are all attached and get smaller, so the mechanical wave vibrations are amplified as they become more concentrated
* same frequency, but amplified amplitude (volume)
20
New cards
Inner Ear
= transduce sound waves
* cochlea
* basilar membrane
* cilia
* cochlea
* basilar membrane
* cilia