17 - Cortical Networks and Disconnection Syndromes
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
what is a disconnection syndrome?
behavioral effects that occur after the disconnection of cerebral connections.
in which case would more strange symptoms be expected: if two gray matter regions were damaged or if the white matter connection between them was damaged?
if the white matter connection is damaged
what are the three types of cerebral connections?
projection fibers, commissural fibers, and association fibers
what are projection fibers?
ascending and descending fibers (sup ←→ inf)
what are commissural fibers?
fibers that connect the two hemispheres (L ←→ R)
what are association fibers? describe both types.
long fiber bundles connect distant neocortical areas (ant ←→ post)
short fibers connect adjacent areas (U-shaped)
on DWI, what are the colors seen for each type of fiber bundle?
projection - blue
commissural - red
association - green
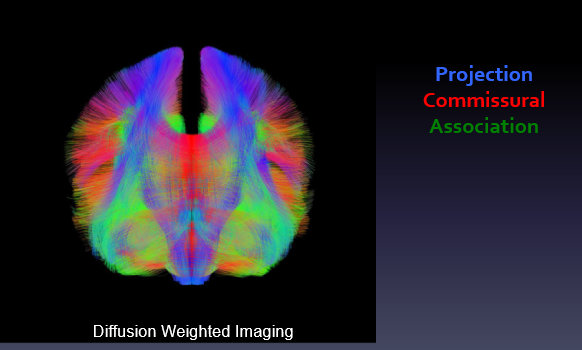
what type of fiber is the corticospinal tract + corona radiata?
projection fiber

the superior longitudinal fasciculus is a ___ connection
association
the inferior longitudinal fasciculus is a ___ connection
association
the uncinate fasciculus is a ___ connection
association
the cingulum is a ___ connection
association
the arcuate is a ___ connection
association
the corpus callosum is a ___ connection
commissural
the anterior commissure is a ___ connection
commissural
the hippocampal commissures (ventral and dorsal) are ___ connections
commussural
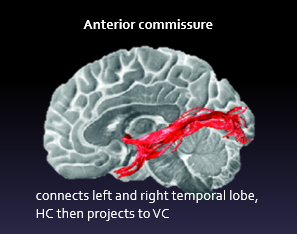
where does the anterior commissure connect?
it connects left and right temporal lobe/HC, then projects to visual cortex
what does corpus callosum translate to?
hard body
what area of the brain has very few connections to the corpus callosum?
the occipital lobes
the most anterior part of the corpus callosum is called the
genu
the most posterior part of the corpus callosum is called the
splenium
the genu has projections to the
prefrontal cortex
the splenium of the corpus callosum has projections to
inferior temporal gyrus, superior temporal gyrus, and visual cortex
how can you tell which side of the CC is anterior?
the posterior side (splenium) is more bulbous. also, the anterior commissure is closer to the anterior side
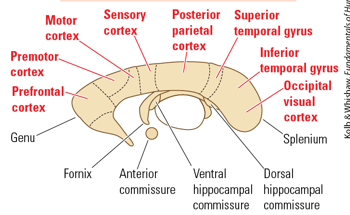
what does the body of the corpus callosum project to?
premotor, motor, somatosensory, posterior parietal cortex
what is the zipper hypothesis?
CC zips up the midline along the interhemispheric fissure
homotopic projections
connect homologous contralateral areas to each other
what is a commissurotomy?
severing of the corpus callosum
callosal agenesis
born without a corpus callosum
what are the outcomes of people with callosal agenesis and early transections?
enhanced conduction on remaining commissures, similar lateralization to normal population, some neuropsych test impairment (speed of processing, slight IQ differences)
the sense of ___ is not crossed, but there are fibers crossing the ___ that join this sense’s regions in each hemisphere
olfaction, anterior commissure
severing the anterior commissure has what effect on the senses?
inability of the right nostril to name odors, but can pick the odors out with the left hand
what happens if the visual system is disconnected?
cannot name what is presented to left visual field (right hemi), but can name what is presented to the right.
what happens when the somatosensory systems are disconnected?
cannot name what is felt in right hand
what happens when the auditory systems are disconnected?
dichotic listening tasks are impaired, but not completely (crossed + uncrossed)
which sensory system has both uncrossed and crossed fibers?
auditory
what happens when the motor systems are disconnected?
cannot perform verbal command with L hand (“touch your nose”). also left and right hands/parts dont know what the other is doing
a partial callosotomy preserves ___ side
posterior
___ transection of the corpus callosum results in motor disturbance
anterior
___ transection of the corpus callosum results in visual and somatosensory disturbance
visual and somatosensory
epilepsy received partial callosotomy, but seizures remained. what is the next treatment?
2nd surgery to complete callosotomy
Who wrote “Disconnection Syndromes in Animals and Man”?
Geschwind
What were the main findings of the article “Disconnection Syndromes in Animals and Man”?
certain behavioral deficits occur due to either inter-hemispheric disconnection, intra-hemispheric disconnection or both.
→ disconnection of regions may be cause of dysfunction instead of damage to the area itself
___ can occur from disconnection of visual association areas from perisylvian speech zone
agnosia and alexia
how can contralateral neglect be seen as a disconnection syndrome?
white matter damage in the R TPJ can lead to neglect, gray matter damage does not
what imaging shows the pathways between neural elements (nodes)
DTI
what is a node in a cortical network?
neural elements
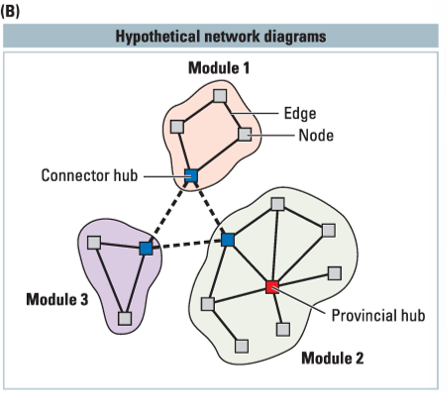
what is a edge in a cortical network?
pathways between nodes

nodes are connected to related nodes to form
functional modules
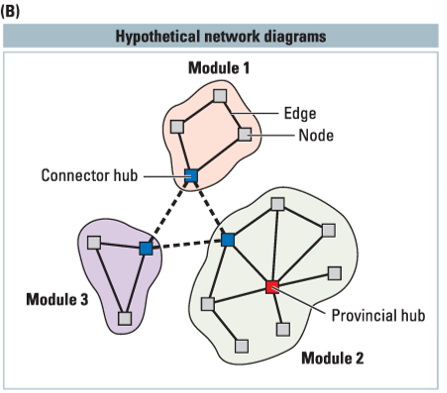
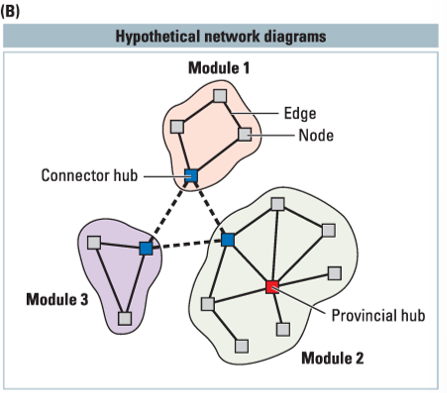
___ are connections between different nodes
hubs
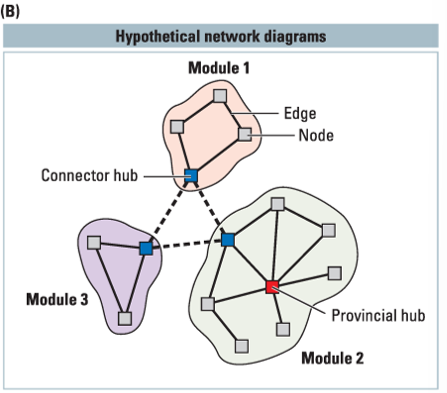
connector hubs vs provincial hubs
connector hubs interconnect between different modules. provincial hubs connect primarily to other nodes in the same module
hubs are important for
communication within the brain
what is a rich club?
hubs that are densely interconnected with other hubs
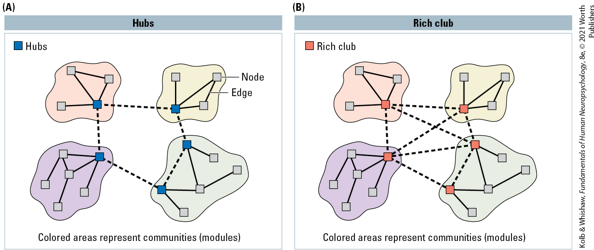
why are there modules that develop in networks?
having a majority of connections be short-distance minimizes the metabolic cost
what is functional integration in terms of neural networks and why is it important?
functional integration allows for the tendency to form connections that are distant from each other and perform distinct functions. this is important so that specific networks can result from interactions between specific modules
what are some examples of functional networks in the brain?
default mode network, salience network, dorsal and ventral visual streams, executive networks
Some studies suggest there are ___ that influence the development of different networks
epigenetic factors
what is the reasoning behind why disruption of networks can lead to disorders?
If normal brain function relies on interaction of separate networks, the disruption of these networks could lead to disorders
some research suggests that neurodegenerative disorders may start in ___ and spread to ___
one module (the “inital epicenter"), then spread to other modules along the rich club networks
spread of ___ in ___(disorder) mirrors the default mode network
spread of amyloid plaques/tau tangles in Alzheimer’s
what are some disorders that have patterns of abnormalities that mimic the network structure of the brain?
Parkinson’s, schizophrenia
___ (related to cortical networks) may explain the impaired levels of consciousness and awareness in traumatic brain injury
interruptions to the cortical hubs
how may childhood adversity and stress affect networks?
it may alter the networks, resulting in disorders