b4 - community level systems (copy)
1/50
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
what are 4 examples of materials which are recycled through componenents of an ecosystem
water
carbon
nitrogen
oxygen
why is the recycling of nutrients important
if nutrients weren’t recycled they would all get used uo and there wouldn’t be any left for future organisms
describe the steps of the water cycle
water from lakes, rivers,oceans and soil evaporates into water vapour and rises into the atmosphere
water can also evaporate from plants through a process called transpiration
as the water vapour accumulates, it will can condense to form clouds
later the water will fall as rain which we call precipitation
the water will then seep into the soil , flow into rivers and lakes and be taken up by plants
the whole cycle then repeats over and over
in the water cycle what is evaporation
the process by which liquid water (in rivers, lakes etc) becomes gaseous water in the atmosphere
liquid water → gaseous water
in the water cycle what is condensation
the process by which gaseous water in the atmosphere becomes liquid water in clouds
gaseous water → liquid water
in the water cycle what is precipitation
the process by which liquid water falls from clouds as rain
what are the 5 stores of carbon
in the air (where its carbon dioxide)
in plants
in the soil
in fossil fuels
in animals
describe the steps of the carbon cycle
whole thing is powered by photosynthesis where green plants and algae take in the carbon dioxide from the atmosphere to make carbohydrates, fats and proteins
can then be passed on to animals by eating plants which passes the carbon compounds along to them
c02 is released into the atmosphere by plant and animal respiration
plants and animals die and decompose they are broken down by decomposers which release co2 back into the air through respiration
plant and animal products (e.g. wood and fossil furls) are burnt (combustion) which releases co2 back into the air
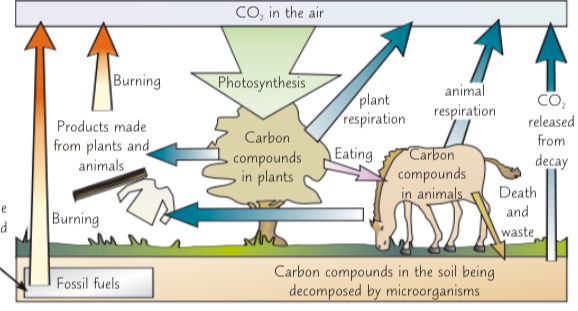
in the carbon cycle whihc process remove carbon dioxide from the atmopshere
photosynthesis
in the carbon cycle which 3 proccesses releease carbon dioxide back itno the atmosphere
respiration
decomposition
combustion
why is the nitrigen cycle important
There's lot of nitrogen in the air – about 78% of the air is nitrogen. Because nitrogen is so unreactive, it cannot be used directly by plants to make protein. Only nitrates are useful to plants, so we are dependent on other processes to convert nitrogen to nitrates in the soil.
how is nitrogen cycled through an ecosystem
nitrogen is fixed by lightning or nitrogen fixing bacteria
dentrifying bacteria release nitrogen back into the atmosphere
what are decomposers
microorganisms which break down or decay dead organic material as well as animal waste
what happens during decomposition
nutrients are released back into the soil to be recycled
what are some of the organisms that help in decomposition
bacteria and fungi
what are the three factors affecting decomposition rate
temperature
water
availability of oxygen
how does temperature affect the decomposition rate
Chemical reactions generally work faster in warmer conditions, but if it is too hot the enzymes in the bacteria can denature and stop decomposition.
how does water affect the decomposition rate
decomposing microorganisms need water for chemical processes
less water available, the slower these chemical processes will be
how does availability of oxyegn affect the decomposition rate
decomposers respire aerobically so lack of oxygen forces microorganisms to respire anaerobically
anaerobic decay is slower and less efficient
why does carbon need to be recycled
because theres only a set amount of carbon in the world
whats a community
the population of different species living in a habitat
whats a population
the number of a particular organism within an area
whats a habitat
a natural home or enviroment of an organism
whats an ecosystem
the interaction of a community of living organisms with the non living parts of the environment
whats distribution
how an organism is spread out in a given area
whats competition
an interaction between organisms or species in which they both try to use the same limited resources.
whats interdependance
idea that all organisms in an ecosystem depend upon one another
whats an abiotic factor
non living parts of an enviroment (e.g. soil PH)
whats a biotic fcator
living parts of an enviroment (e.g. snail)
whats a stable community
the species and environmental factors are in balance so that the population sizes remain fairly constant
what are the abiotic factors affecting communities
light intensity
temperature
moisture levels
soil ph and mineral content
how does light intensity affect communities
● Light is required for photosynthesis.
● The rate of photosynthesis affects the rate at which the plant grows.
● Plants can be food sources or shelter for many organisms.
how does temperature affect communities
temperature affects the rate of photosynthesus
how does moisture levels affect communties
Both plants and animals need water to survive
how does soil ph affect communities
Soil pH affects the rate of decay and therefore how fast mineral ions return to soil (which are then taken up by other plants).
what are biotic factors affecting communities
food availability
new diseases
new predators
how does food availability affect communties
more food means organisms can breed more successfully and therefore the population can increase in numbers
how do new predators affect communities
if the number of predatoes decreases, then the number of prey might increase because fewer of them will be eaten
how do new diseases affect communities
when a new pathogen arises the population has no resistance to it so they can be wiped out quickly
what are the 3 types of interdependence
mutualism
parasitism
predation
whats mutualism
when two species can interact and mutually benefit from each other
whats parasitism
rekationship between two organisms where in one organism (the parisite) thrives at the cost of the other (the host)
whats predation
where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey
what are 4 things animals compete for
mates
space
food
water
what are 4 things plants compete for
light
minerals
water
space
how is a food web different to a food chain
they are effectively multiple food chains combined
food webs show all interactions between the species in the community
what are producers
● E.g. plants and algae
● They make their own food by photosynthesis.
what are consumers
organisms that consume other organisms for their energy
what are primary consumers
consumers that eat producers
what is a secondary consumer
organisms that eat primary consumers.
what are tertiary consumers
organisms that eat secondary consumers
They have no predators and are at the top of the food chain