Interlude B - Sediments and Soils
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
physical weathering/mechanical weathering
breaks rocks into clasts (smaller grains or chunks)
examples of physical weathering
jointing - natural crack in a rock that can separate one piece of rock into two
frost wedging
salt wedging - dissolved salt in groundwater precipitates in open pore spaces in rocks
root wedging
thermal expansion - when heat of forest fire bakes a rock, the outer layer of a rock expands. when it cools, the layer contracts which breaks the outer part of the rock
chemical weathering
chemical reactions that alter or destroy minerals when a rock comes in contact with water solutions or air
types of chemical weathering
dissolution
hydrolysis
oxidation
hydration
dissolution
chemical weathering where water (a solvent) dissolves minerals as it flows through a rock (affecting mostly salts and carbonate minerals)
hydrolysis
chemical weathering where water reacts with minerals and breaks them down to form other minerals
oxidation
chemical weathering where reactions in rocks transform iron-bearing minerals into a rusty-brown mixture of various iron-oxide and iron-hydroxide minerals… rusts rocks
hydration
chemical weathering where the absorption of water into the crystal structure of minerals causes some minerals (like clay) to swell. this expansion weakens rock
how does soil form
chemical and physical weathering produce loose debris and ions in solution and the resulting detritus consists of mineral grains and new weathering products
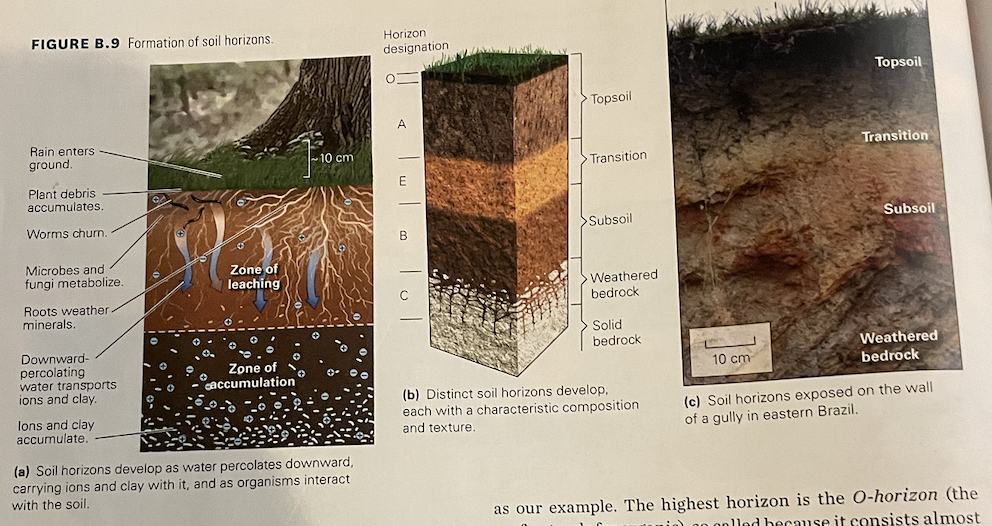
O and A horizons
dark grey to blackish topsoil, the fertile portion of soil that farmers till for planting crops - organic material
E horizon
in some places, the A-horizon grades downward into the E-horizon, which has undergone leaching but has not yet mixed with organic material
B horizon
ions and clay accumulate in the subsoil
C horizon
consists of the material derived from the substrate that’s been chemically weathered and broken apart, but hasn’t undergone leaching and accumulation. the C-horizon grades downward into unweathered bedrock or sediment
what is sediment?
consists of loose fragments of rocks or minerals broken off bedrock, mineral crystals that precipitate directly out of water, and shells or shell fragments
what is soil?
consists of rock or sediment that has been modified by physical chemical interaction with organic material, rainwater, and organisms at or just below the earth’s surface over time
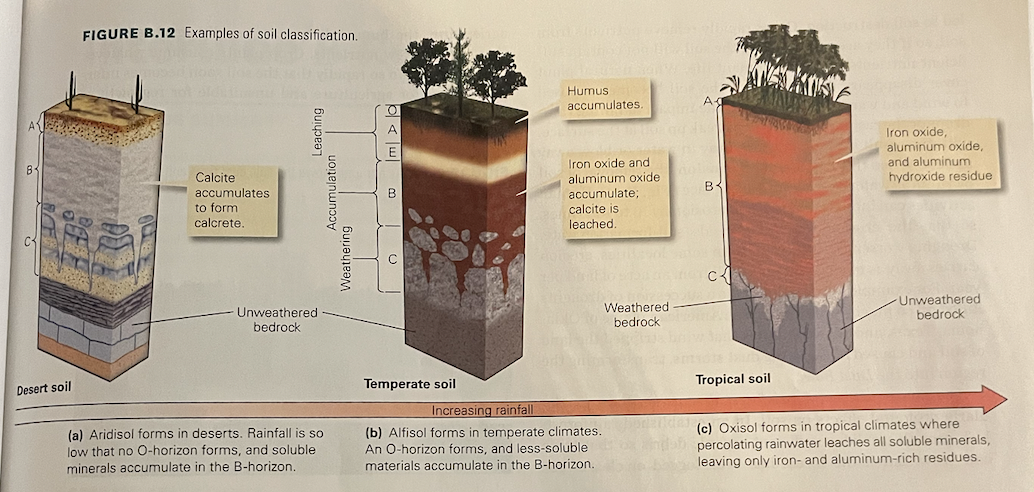
examples of soil classification
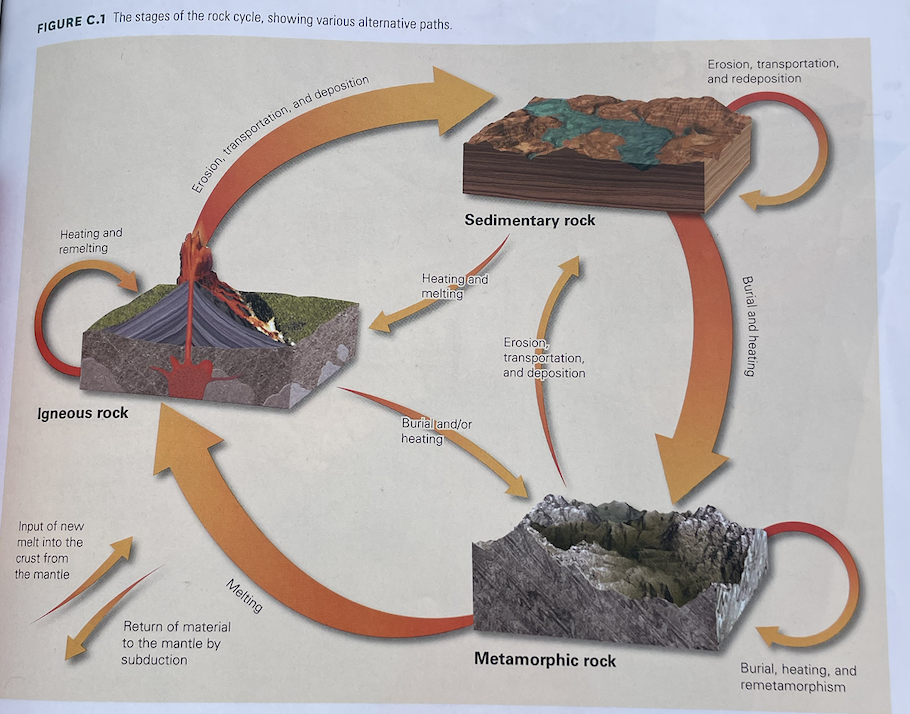
rock cycle