Chemistry - Group 7 and Covalent Bonding
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
What is group 7 called?
The halogens
The halogens are…
A group of reactive, non-metallic elements which are all diatomic molecules.
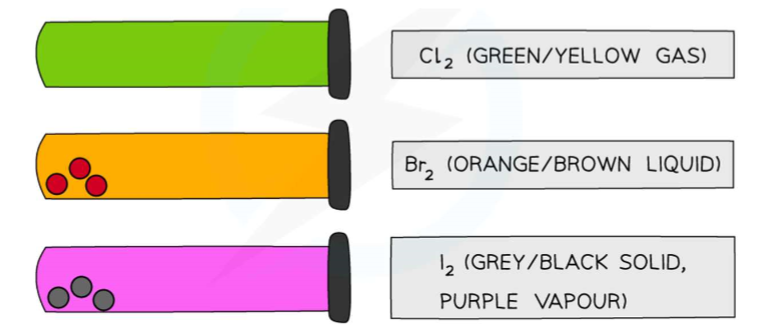
Colours and physical states of chlorine, bromine and iodine at room temperature:
The melting points and boiling points _______ as you go down the group.
increase
Why do the melting and boiling points increase as you go down the group?
This is due to increasing molecular forces as the atoms become larger, so more energy is required to overcome these forces.
Fluorine (F2) colour,state and reactivity:
A pale yellow gas - highly reactive
Astatine (At2) colour,state and reactivity:
A black solid - very unreactive
The reactivity _______ as you go down the group.
decreases
Explain the reactivity in group 7 in terms of electronic configuration:
All group 7 elements can gain one electron to obtain a full outer shell.
The easier it is for a halogen to attract an electron, the more reactive the halogen will be.
As you go down group 7, the extra electron becomes further away from the nucleus which makes it harder to attract.
This causes them to get less reactive as you go down the group.
Describe a test for chlorine:
It bleaches damp litmus paper white.
A more reactive halogen will displace a…
less reactive halogen.
What is a redox reaction?
Reduction/oxidation (gain or loss of oxygen)
However, it can sometimes refer to reactions involving the movement of electrons.
OIL RIG
Oxidation Is Loss of electrons.
Reduction Is Gain of electrons.
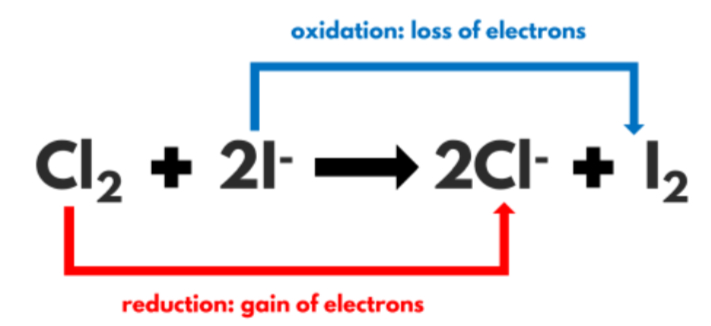
What is a halogen called when it becomes an ion?
A halide ion (Halogen-)
Halogens Reactivity: Most Reactive to least reactive
Chlorine
Bromine
Iodine
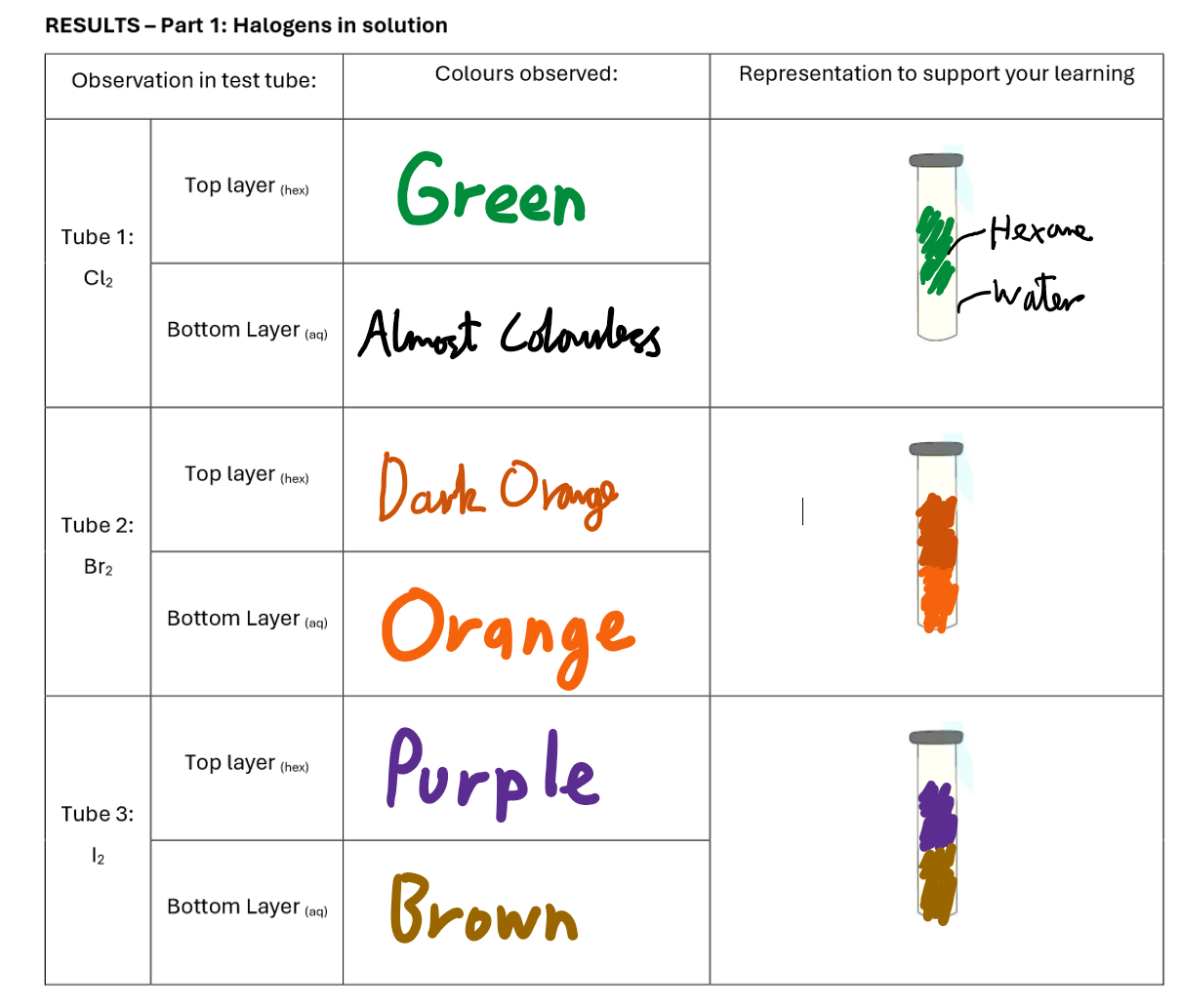
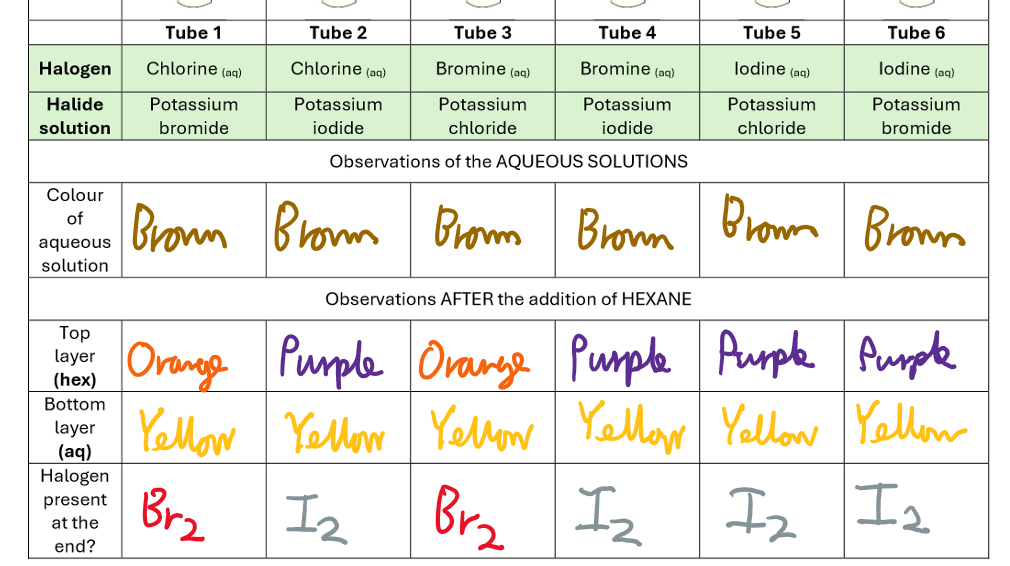
Halogens In Solution Results
Halogen Displacement Reactions Results
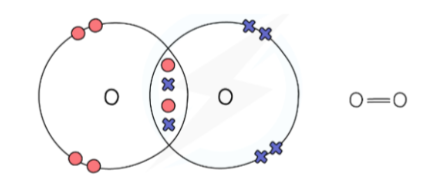
What is a covalent bond?
A shared pair of electrons between two neighbouring nuclei.
Are covalent bonds strong?
Yes
Covalent Bond Dot and Cross Diagram
What is the structure of covalent bonds called?
Simple molecular
Simple molecular structures have…
LOW melting and boiling points.
Weak intermolecular forces.
Why do they have low melting and boiling points?
There are only weak intermolecular forces which do not need much energy to overcome.
Allotropes of carbon
Diamond, Graphite and C60 Fullerene
Which of these have giant covalent structures?
Diamond and graphite
Giant covalent structures have…
High melting points.
Why do Giant Covalent Structures have high melting points?
Because lots of energy is requires to break the many strong covalent bonds.
Do covalent compounds usually conduct elctricity?
No, as they have no delocalised electrons.
Graphite is an exception.
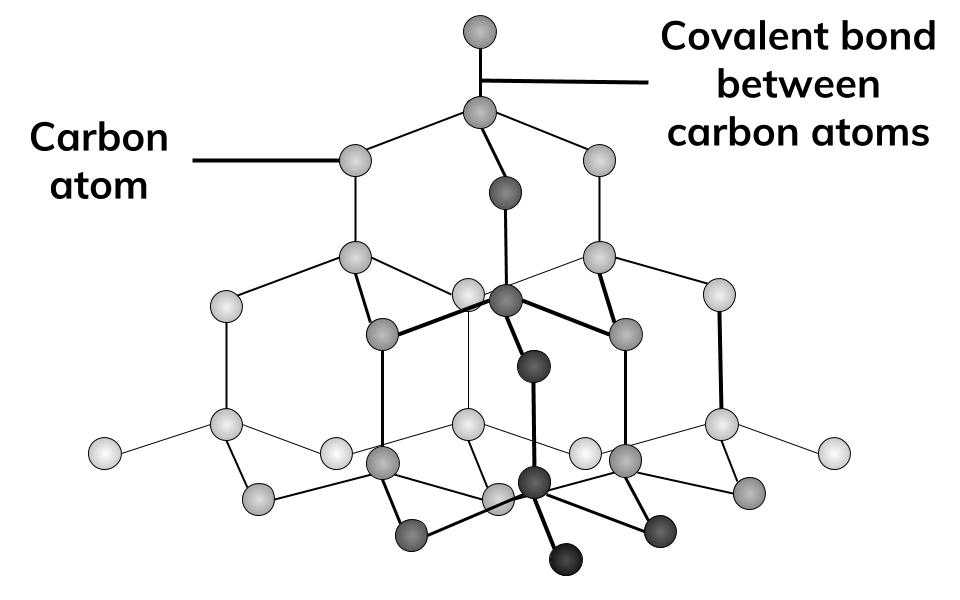
Structure of Diamond
Giant Lattice
Diamond is very hard because:
Each carbon atom is contently bonded to four other carbon atoms.
The Covalent bonds are very strong.
Diamond does not conduct electricity because…
Each atom is using all of its electrons to form four covalent bonds, so there are no delocalised electrons.
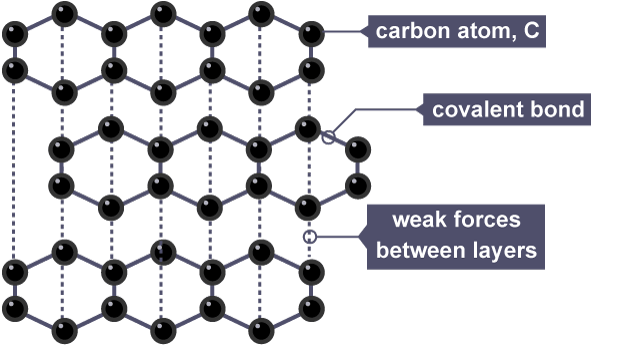
Graphite is…
Soft and slippery.
What is the structure of graphite?
Giant Lattice
Graphite forms in layers that are free to slide over each other because there are only weak forces between the layers.
Graphite can…
Conduct electricity and heat.
Graphite can conduct electricity and heat because…
Each carbon atom only forms three bonds. This leaves some delocalised electrons which are free to move and carry charge.
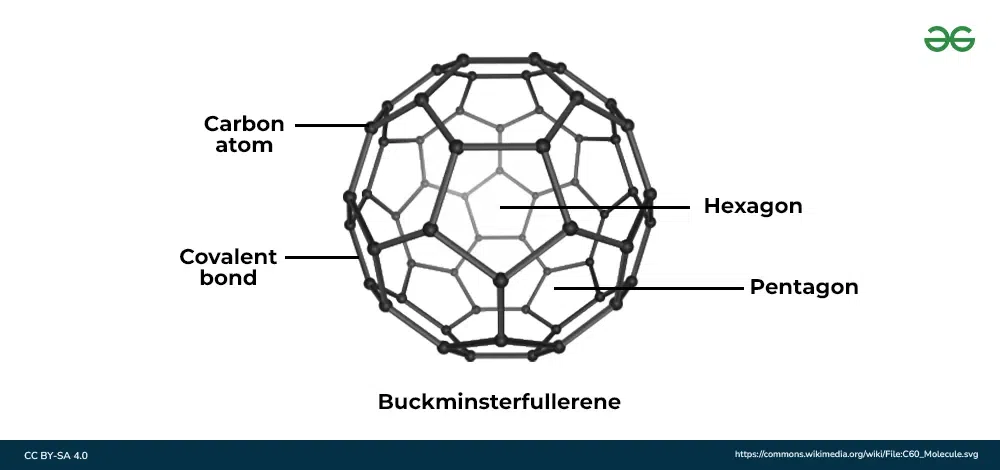
C60 Fullerne Structure
Simple molecular structure.
C60 Fullerne has…
A low melting and boiling point because there are only weak intermolecular forces which require little energy to overcome.
C60 Fullerene is also…
Soft and slippery
Use of C60 Fullerne:
Drug delivery due to its hollow structure.
Graphite information
Giant Lattice Structure (layers)
3 covalent bonds formed by each carbon atom plus 1 weak attraction between the layers of carbon atoms
Soft, shiny, grey
Conducts electricity
High melting and boiling point
Diamond Information:
Giant Lattice Structure
4 covalent bonds per carbon atom
Very high boiling and melting point
Hard, transparent
Can not conduct electricity (no delocalised electrons)
Each carbon atom bonds in a tetrahedral shape
C60 Fullerene Information:
Simple molecular structure
Each carbon atom is bonded to 3 others
High melting and boiling point
Bonds between molecules are weak
Can not conduct electricity (no delocalised electrons)
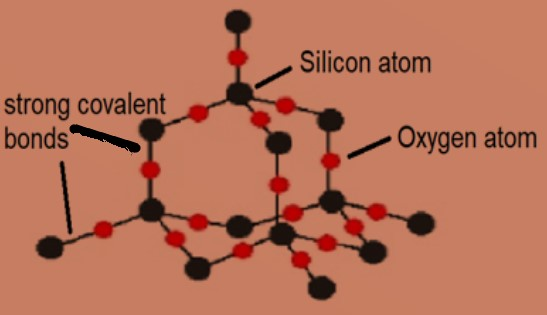
Silicon Dioxide
Silicon forms 4 covalent bonds and oxygen forms 2 covalent bonds
Giant Structure
High melting and boiling point
Can not conduct electricity (no delocalised electrons)