PHR912 SYNTHESIS & DEGRADATION OF AA
1/173
Earn XP
Description and Tags
block 3 week 3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
174 Terms
how many of the 11 nonessential-AA can be synthesized from glucose + nitrogen source?
10
What is tyrosine synthesized from?
Essential phenylalanine
Large amounts of these AA are needed in the diet:
Arginine
Phenylalanine
Methionine
These non-essential AA are produced from glucose via the intermediates of glycolytic pathway:
Ser
Gly
Cys
Ala
These non-essential AA are produced from intermediates of the TCA cycle:
Arg
Asparagine
aspartate
glutamate
glutamine
proline
Alpha-ketoglutarate is a precursor for what AA?
Glutamine
glutamate
proline
arginine
OAA is a precursor for what AA?
Asparagine (ASN)
Aspartic acid (ASP)
The fate of carbon of AA during the fasting state:
Carbon skeletons of AAs produce glucose, ketone bodies, and CO2
The fate of carbon skeletons in AA during the fed state:
Intermediates of AA metabolism are converted to glycogen and triacylglycerols (for storage in the adipose)
Only what organ contains all the pathways of AA synthesis and degradation?
Liver
Ser is generated from what?
3-Phosphoglycerate
Serine can go on to synthesize what amino acids?
Glycine
Cysteine
Alanine is produced via:
Transamination of pyruvate
Degradation of Ser, Gly, Cys, and Ala produce what?
Regenerate pyruvate
Glycolytic/ gluconeogenic pathway intermediates
Ser, Gly, Cys, and Ala can produce:
Glucose
get fully oxidized to CO2
Serine synthesis is increased by:
Induction of 3-phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase
Serine synthesis is decreaed by:
Feedback inhbition of phosphoserine phosphatase by serine
What two AA can serine produce?
Gly and Cys
Cys can get converted into what?
Pyruvate to make Ala
Glycine is produced from what via a reversible reaction involving what
Serine vis tetrahydrofolate
where is FH4 derived from?
folic acid
During the formation of Cys, what provides the carbons and nitrogen?
Ser
During the formatino of Cys, what is the sulfur provided by?
Met
Since the sulfur for CYS comes from MET, if there is a MET deficiency, it can be saved by?
An adequate source of CYS
PLP is the active form of what?
vitamin B6
PLP is the only route of what?
Homocycteine degradation
A deficiency of B6 / defect in cystathionine synthase leads to:
Homocysteinemia (accumulation of homocysteine)
PAPS
3 phosphoadenosine 5- phosphosulfate
what does PAPS do?
Sulfate donor in the degradation of cysteine
ALA is produced via:
Reversible transamination from pyruvate via alanine transaminase
Alanine is a major what amino acid?
Gluconeogenic amino acid for transport of carbon and nitrogen to the liver
Glutamate is derived from:
Alpha-ketoglutarate via transamination OR
Glutamate dehydrogenase
Alpha-ketoglutarate in the liver can form what?
Malate and via gluconeogenesis forms glucose
When histidine gets degraded by histidase, 5 of its carbons:
Ultimately form glutamate
FIGLU:
Formiimino-Glutamate
Transfer of 1 carbon of FIGLU to the tetrahydrogolate pool releases what?
NH4 and glutamate
When folate concentration is low, FIGLU is what?
Excreted in urine
Glutamine is produced from glutamate via:
Glutamine synthetase
What does glutamine synthetase do?
Add NH4 to carboxy group of side chain on glutamine, forming an amide
How does Glutamine → glutamate get catalyzed?
Glutaminase
Why is glutaminase very important in the kidney?
NH3 enters urine and decreases the acidity
What is a precursor AA for proline?
Glutamate
What is synthesized from glutamate via its semialdehyde?
Arginine
Arginine can be transaminated into:
Ornithine, a urea cycle intermediate
Urea cycle produces this amino acid:
Arginine
Arginine is not essential in adults, but is essential in:
Children
Arginine gets cleaved by what in the urea cycle to produce urea and ornithine?
Arginase
Excess ornithine in the urea cycle gets transaminated to:
Semialdehyde, oxidized to glutamate
Asp is produced via transamination of:
OAA
Asp ←> OAA is what?
Readily reversible reaction that can regenerate OAA
Asparagine is formed from what AA?
Aspartate
What enzyme catalyzes aspartate → asparagine?
Asparagine synthetase
asparagine be degraded back into what AA?
Aspartate, generating NH4
What enzyme catalyzes asparagine → aspartate?
Asparaginase
During the formation of asparagine, what provides the nitrogen for forming the amide group?
Glutamine
What statement is wrong about glutamate-5-semialdehyde?
All are correct
Which statement is wrong about arginine metabolism?
Arginine is converted to aspartate
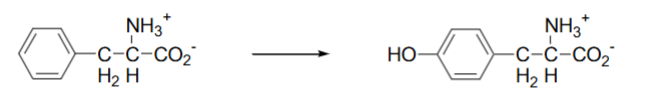
What statement is wrong about the following rxn?
Is readily reversible
What statemetn is wong about glycine and serine catabolism?
In the GCC-catalyzed reaction, one-carbon group from glyine is donated to THF to form methyl-THF
What statement is wrong about glutamate-5-semialdehyde?
All are correct
glutamate either is converted to or is derived from each of the following EXCEPT:
Leucine
The biosynthesis of what AA involves reactions which are also part of the urea cycle?
Arginine
Which statement is wrong about alanine metabolism
None
Which statement is incorrect about the synthesis of AA?
Alanine is synthesized from serine by a one-carbon rearrangement
What statements are correct about eniluracil and dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPD)?
DPD converts 5-FU to dihydro-5-FU
Eniluracil improves the efficacy of 5-FU
Thus, the combination therapy (5-FU + eniluracil) was developed for the treatment of solid tumors
Which is an incorrect pair?
Lysine : Butyrate
The folloiwng mammalian enzymes do not catalyze reactions that produce free ammonia (or ammonium ion):
None of the above
As AAs are degraded, their carbons are converted to:
CO2
compounds that generate glucose in the liver
pyruvate and tca cycle intermediates: alpha-ketogluatate, succinyl CoA, fumarate, OAA
Ketone bodies or their precursors: Acetoacetate, acetyl CoA
Glucogenic AA:
AAs if their carbons are converted to glucose
Ketogenic AA:
If carbons are converted to acetyl CoA or acetoacetate
Non-essential AAs are: (minus TYR)
Glucogenic
Tryptophan produces ____, which produces what?
Alanine, pyruvate
Met, Thr, Val, and Ile all form what?
Succintl CoA
Phe, after conversion to ____, forms ____
TYR, fumarate
Ketogenically, what does Trp, Thr, and Ile produce?
Acetyl CoA
Phe ketogenically produces what?
acetoacetate
what are the 2 essential AA that are exclusively ketogenic?
Lys, Leu
Alanine is
glucogenic
Arginine is
Glucogenic
Asparagine is
Glucogenic
Aspartate is
Glucogenic
CYS is
Glucogenic
Glutamate is
Glucogenic
Glutamine is
Glucogenic
glycine is
glucogenic
proline is
Glucogenic
serine is
glucogenic
tyrosine is
ketogenic and glucogenic
Histidine is
Glucogenic
Isoleucine is
glucogenic and ketogenic
leucine is
ketogenic
lysine is
ketogenic
methionine is
glucogenic
threonine
glucogenic and ketogenic
tryptophan is
ketogenic and glucogenic
valine is
glucogenic
phenylalanine is
ketogenic and glucogenic
serine is derived from ____ via ____
glucose, 3-PG
glycine and serine are:
Interchangeable
glycine and serine require ____ for interchangability
N5,N10-methylene THF