Accounting equations and key terms
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
accounting equations
assets = liabilities + shareholders equity
expanded accounting equation
a = l + s/c + re + rev - expenses - dd
end common shares
beg c/s + new owners - stock repurchase
end re
beg re + ni - div declared
NI
rev - exp
book value
E
current ratio
current assets/ current liabilities
end a/r (accounts receivable)
beginning a/r + credit sales - cash collection
insurance purchase
prepaid insurance beginning + new purchase + new rent payment - use of insurance - use of rental space
end a/p (accounts payable)
beginning a/p + beg a/p + credit purchase - cash
end inventory
purchases + beg inventory - cogs
market value
#of common share outstanding traded x stock price
t account
title
LS: debit
RS: credit
working capital
= current assets - current liabilities
debt to total assets
total liabilities / total assets
basic EPS (basic earnings per share)
income avail to common shareholders/weighted avg of number of shares
higher is better
PE ratio (price-earnings)
market price per share/basic EPS
higher is better
historical cost
we use the assets and liabilities recorded at original acquisition cost cca
accrual basis accounting
revenue and expense recognition - revenues and expenses are recorded when they are earned or incurred, not when the cash is exchangedevr
rev recognization
when merch is sold and delivered or when service is performed
matching principle
expenses match revenues, they should be reported in the same period
deferred rev
cash received and recorded as liabilities before rev is earned
prepaid expenses
expenses paid in cash & recorded as assets before use
Initially recorded as assets because they provide future benefits
Expire over time or through usage
accrued expenses
incurred for which cash has yet to be paid and that have yet to be recorded through journal entries
accrued revenues
revenues earned for which cash has yet to be received and that have tet to be recorded through journal entries
depreciation
process of allocating cost over estimated useful life
asset * month/year(period)
temporary accounts
revenue accounts
expense accounts
dividends declared
temporary use of accounts to record activity
restarts for the year - not carried over
permanent accounts
all asset accounts
all liability accounts
s/h/e accounts
closing entries
close all rev accounts to income summary (new temp acct set up help w closing process)
close all exp accts to income summary
close all income summary to retained earnings
close div declared to RE
normal debit balance
expense
asset
div declared
normal credit balance
liability
revenue
s/c and RE
gross profit
sales - cogs
income loss before tax
gross profit - operating exp
net income (loss)
income (loss) before tax - income tax expense
inventory purchase
dr) inventory cr) cash, payables
freight costs fob destination
ownership of the goods remains with the seller until it reaches buyer. seller pays the freight costs
freight costs fob shipping point
shipping is on the buyer and the onus is on the buyer when the carrier accepts the goods from the seller
purchase returns
return goods for credit or cash depending on how sale was made
In both cases, a decrease (credit) is made to the inventory account to reflect the decrease in cost of goods purchased (COGS is dr)
purchase allowance
may choose to keep merch if seller grants a reduction
In both cases, a decrease (credit) is made to the inventory account to reflect the decrease in cost of goods purchased (COGS is dr)
goods are sold
dr) cash, a/r, deferred rev cr)sales revenue
sales rev - cogs = gross profit
inc in equity
expense recognition
dr) cogs cr) inventory
inc in net assets
inc in cash/ar or reduction in deferred rev>reduction in inventory
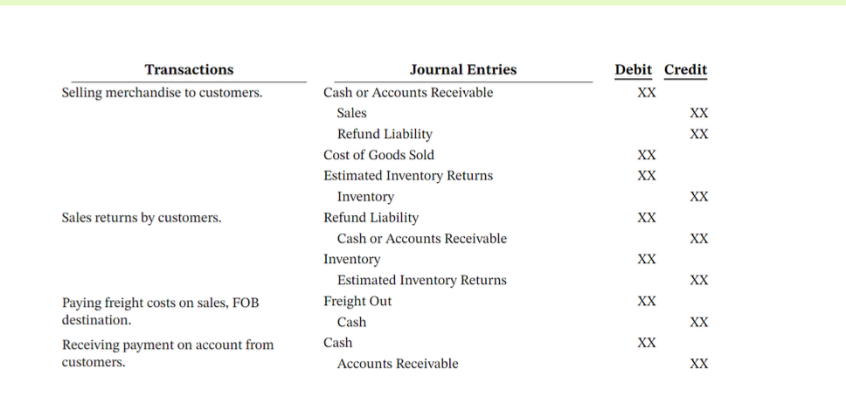
summary of sales transactions
multistep I/s presentation
Shows many steps in determining income before tax
Gross profit = sales – COGS
Income from operations = gross profit – operating expenses
Income before income tax = income from operations + non-operating revenue – non-operating expenses
Net income = income before income tax – income tax expense
nature classification
expenses are reported according to their natural classification
function
expenses are reported according to the activity for which they were incurred
GPM (gross profit margin)
gross profit/sales
generally better to have a higher number
PM (profit margin)
net income/sales
ending inventory
beginning inv + net purchases - COGS
NRV
selling price - cost needed to make goods ready for sale
adjust to the lower amount - cost vs NRV
inventory turnover
cogs/avg inventory
average inventory
(beginning inventory/ending inventory)/2
days in inventory
365 days/inventory turnover