repeated measures ANOVAA
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Remember: ANOVA
• Comparing two or more groups
• Groups are independent
• Often used in experimental designs
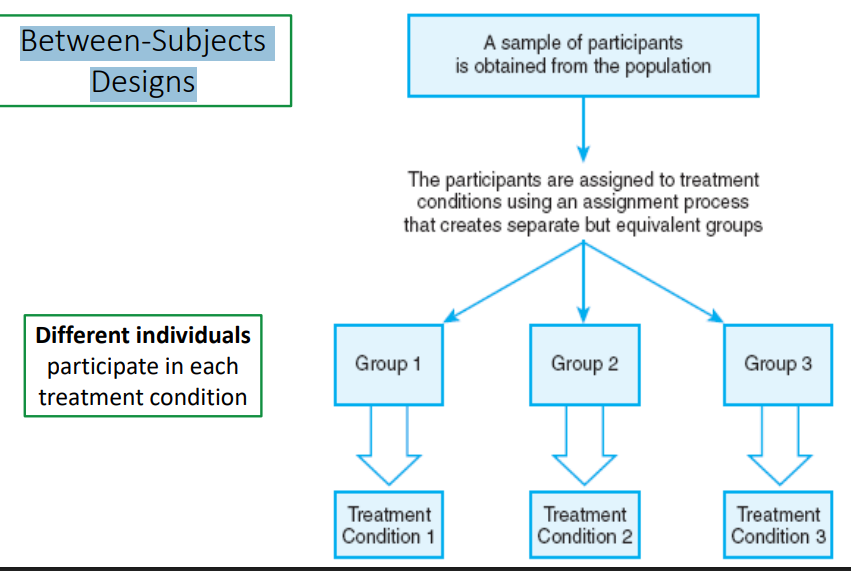
Between-Subjects Designs
Between-Subjects Designs
Within-Subjects Designs (repeated measures)
The same group of individuals participates in all treatment conditions
Note: to avoid a learning effect, different orders of treatments may be used (= counterbalancing)
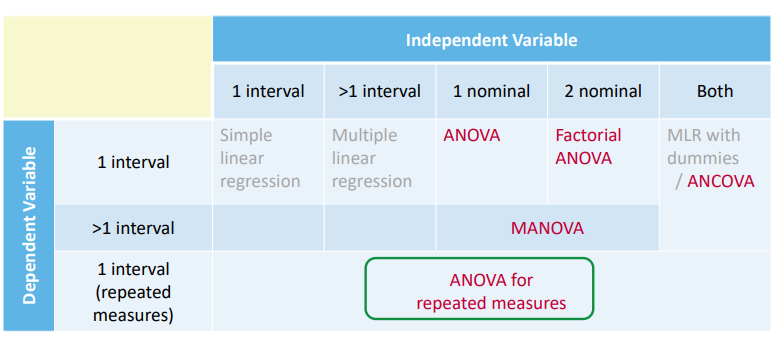
Overview of Module 2
What does a repeated measures (RM) design involve?
Within-subject measurements of the same dependent variable at
different time points (study changes over time)
under different conditions (differences between conditions)
What kind of dependency exists in repeated measures data? and how do you measure it
Measurements between time points are dependent.
analysis of different scores
advantages of RM ANOVA
More power to detect effects.
more economical because Fewer participants are needed.
The study develops over time.
Assumptions for ANOVA
• Random sample • Observations are independent • DV is normally distributed in each group (in the population) • Within-group variances are equal (in the population)
Assumptions for repeated measures ANOVA
1. Random sample
2. DV is normally distributed in each group (in the population)
3. A variation on the equal variance assumption: ▪ Assume the dependence between measurement moments is equal:
▪ Assume equal variances of the difference scores (Sphericity)
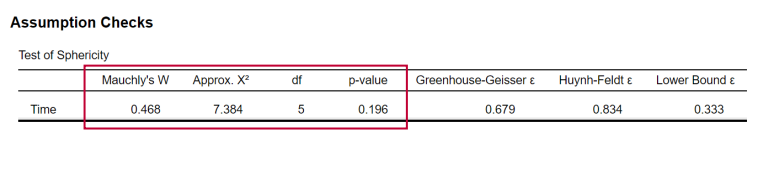
interpret this
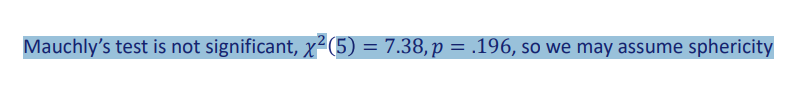
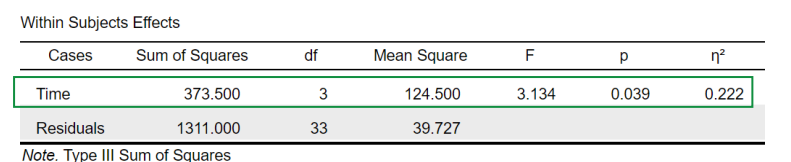
interpret
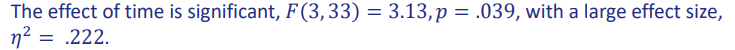
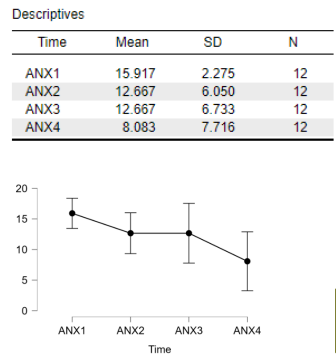
interpret
On average, children have highest anxiety level at time 1 and the lowest anxiety level at time 4
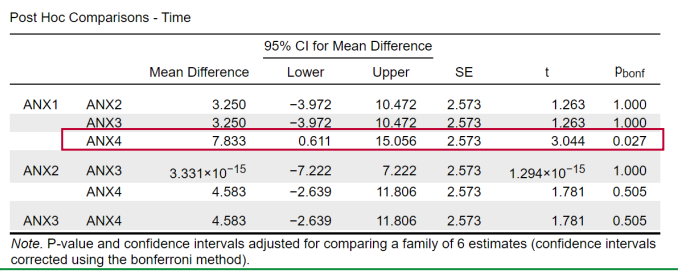
interpret
Only the Bonferroni corrected pairwise comparison between ANX1 and ANX4 is significant
• Interpretation example ANX1-ANX4: On average, children score 7.83 points lower on the anxiety scale at the fourth measurement than at the first measurement.
Mixed designs
At least 1 within-subjects factor
• At least 1 between-subjects factor
• Example – classical experimental design: ▪ control group and experimental group ▪ pre-test and post-test
Effects mixed design
▪ main effect(s) of within-subject factor(s)
▪ main effect(s) of between-subject factor(s)
▪ Interaction(s) of within- and between-subjects factor(s)
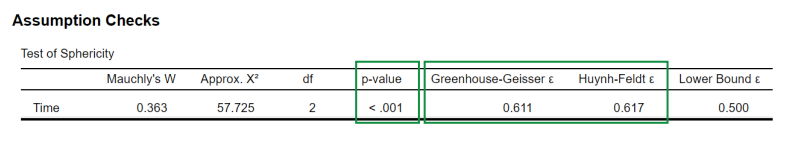
interpret and say the correction to use

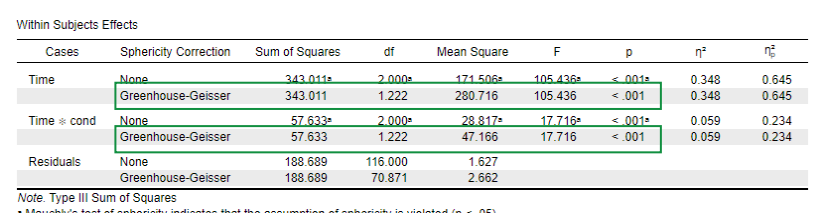
interpret the first row of time
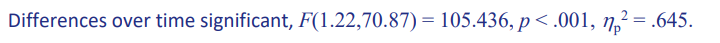
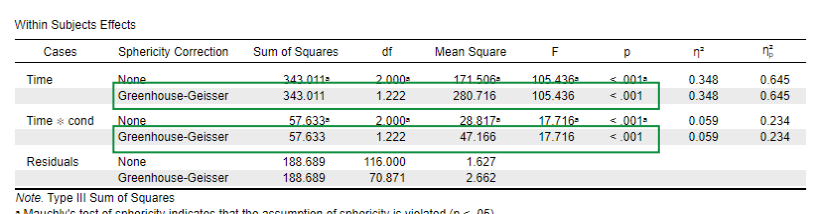
interpret interaction within-between
the mean changes over time for the counseling group are significantly different from the mean changes over time for the counseling & group therapy group
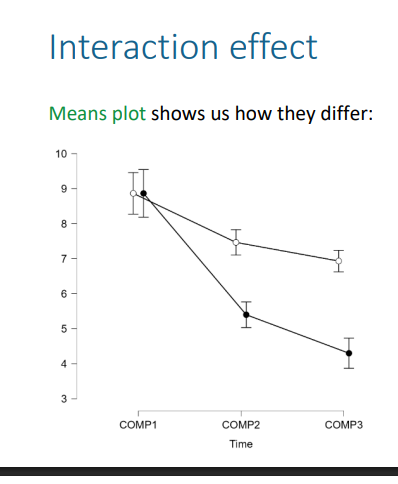
interpret

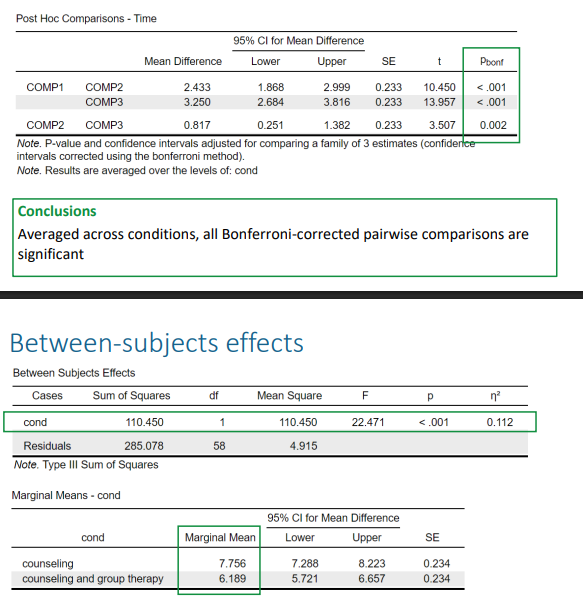
interpret
• Let’s suppose that we are only interested in the first two measurements: COMP1 & COMP2 • To compare OCD symptoms between the two groups on time point 2, we can control for differences on time point 1!When we only have two measurement moments, we can analyze the data using:
ANCOVA
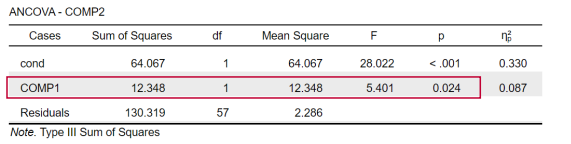
interpret
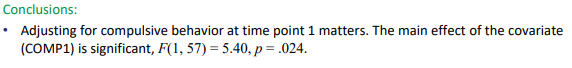
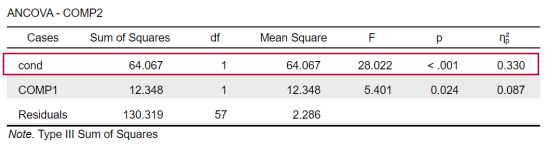
interpret

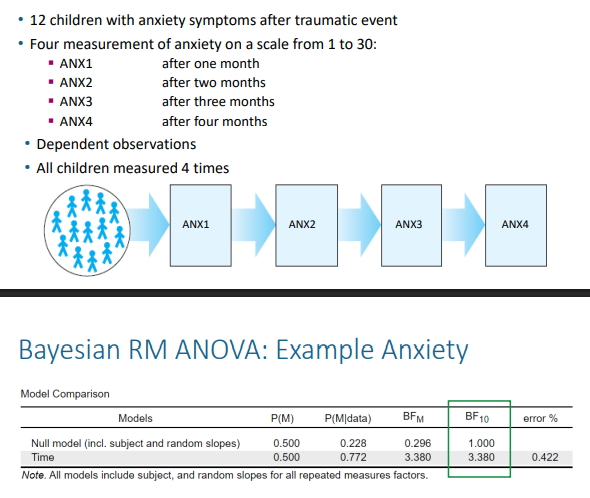
interpret
There is 3.38 times more support in the data for the alternative hypothesis (the mean scores change over time) than for the null hypothesis (the means do not change over time), 𝐵𝐹10 = 3.38 (moderate evidence).
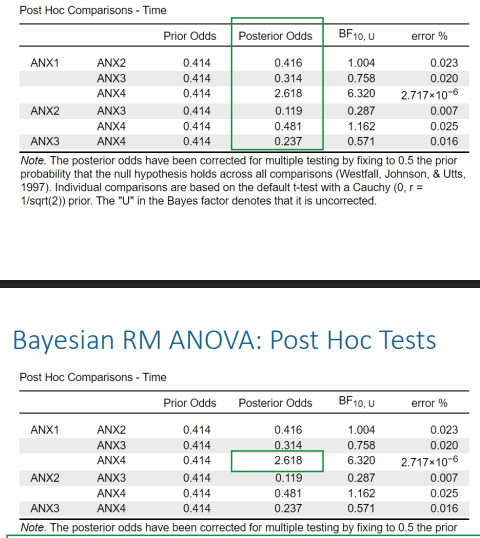
• The difference in anxiety level between time point 1 and 4 indicates moderate evidence for the alternative hypothesis, posterior odds = 2.62.
• All other posterior odds are either inconclusive (ANX1-ANX2; ANX2-ANX4) or indicate more support for H0 (ANX1-ANX3; ANX2-ANX3).
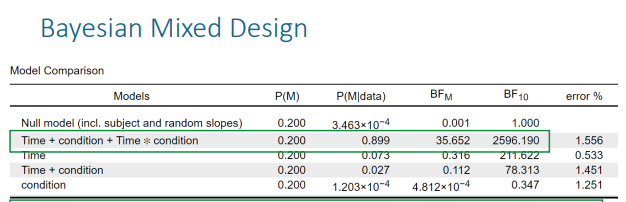
• The model with within-subject (time), between subject (condition), and interaction effect gets most support from the data over the null model (𝐵𝐹10 = 2596) • The effect that treatment has over time seems to differ between the two treatment conditions
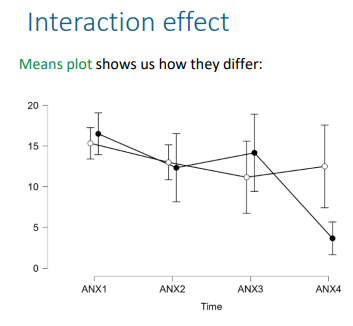
• In both conditions, the mean anxiety scores decline somewhat over time • Between time 1 and time 3, the scores are similar in both conditions
• The treatment condition shows a large reduction from time 3 to time 4, but the control condition does not