part 1: introduction to the global business environment
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Business management in a global context chapters 1, 2, 3.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Define globalization
Globalization is the shift towards a more integrated and interdependent world economy increasing the amount of cross-border trade.
Differentiate between the globalization of markets and the globalization of production.
globalization of markets - merging historically distinct and separate national markets into one huge global marketplace
globalization of production - sourcing of goods and services from locations around the globe taking advantage of national cost differnces (arbitrage)
What are the characteristics of globalization ?
increasing amounts of cross-border trade
rise of MNEs and increased competition for jobs between nations
erosion of differences among distinctive national cultures and identities
development of international bodies to try to deal with the increased interconnections
What are the four trends towards globalization?
changes in world output and world trade - the share of global economic activity of developed countries falling while the share of global economic activity of developing countries rises
foreign direct investment - investments by developing nations are on the rise while the FDI stock ( total cumulative value of foreign investments) by rich industrial countries is falling
types of companies - increase in the number of non-US multinational enterprises and a growth in the number of mini-multinationals due to advancements in technology and the internet
changes in world order- the collapse of russian communism, emergence of mexican and latin american markets, changes in government structures all create new opportunities and inward investment.
Define slowbalization
slowbalization is the process of slowing down, or even reversing, the trends of globalisation. It is an era of slouggish ness marked by cross-border investment, trade , bank loans and supply chaiuns shrinking or stangnating as part of world GDP
what are the reasons leading to slowbalisation ?
advantages of economies of scale and arbitrage from global sourcing has worn away
cost of moving goods stopped falling
protectionist poilicies continue to tighten
geopolitical rivalry grows
implications of slowbalisation
deeper links with regional blocs
supply chains are closer to home
tension between trading pattern and a global financial system
cannot fix climate change, migration, tax avoidance without global cooperation
how can companies take advantage of globalization trends ? ( what are the forces of globalization ?)
low barriers to trade and investment
companies can locate production facilities in the optimal location
production and sales take place in multiple markets creating interdependence between countries
technological change
advancements in communication information processing and transportation
the micro-processor facilitates high-power low-cost computing
the internet and e-commerce became a global equilizer lessening the constraints of scale, location, and time zones
transportation improvements
containerisation and development of super freighters (huge trains, trucks and ships) have facilitated the growth of glowbalization
What id Freideman’s hyperglobalist view ?
according to Friedeman (2005) globalization is accelerating and is flattening the world so that every nation will eventually be a part of a global marketplace that is shaped considerably by technological advancements increasing homogeneity in the world which means free cooperation and connection all over the world
- bonus -
world flatteners include :
fall of the berlin wall
increased outsourcing and offshoring
development of global supply chains
etc
What is Ghemwatt’s semi-globalist view ?
according to Ghemwatt (2001 ; 2017)companies consistently overestimate the attractiveness of foreign markets. The true amount of trade and investment between countries is affected by the geographical distance between countries ( there is an inverse relationship between countries’ distance and magnitude of trade)
What is Ghemwatt’s CAGE framework ?
the CAGE framework states that barriers of trade could form due to
Cultural distance - language, race , social norms, values
Administrative distance - political and institutional differences
Geographic distance - physical distance, size, climate
Economic distance - differnces in income, infrastructure, human talents
- bonus -
the law of distance states that international interactions are dampened by CAGE
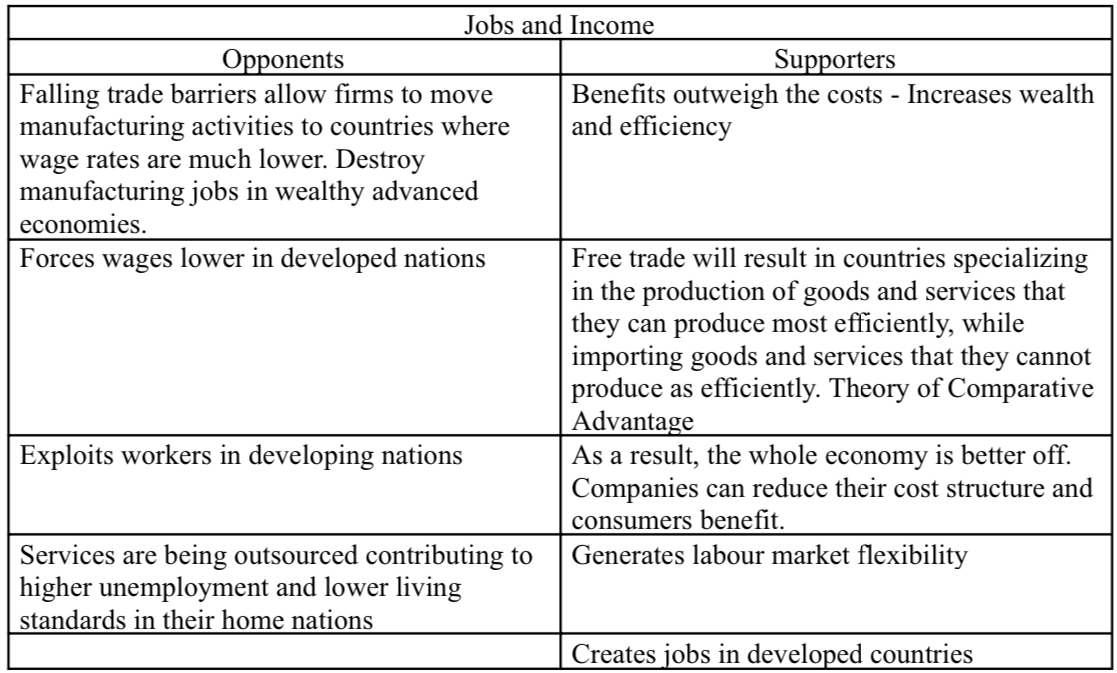
What are the globalization debates in jobs and income ?
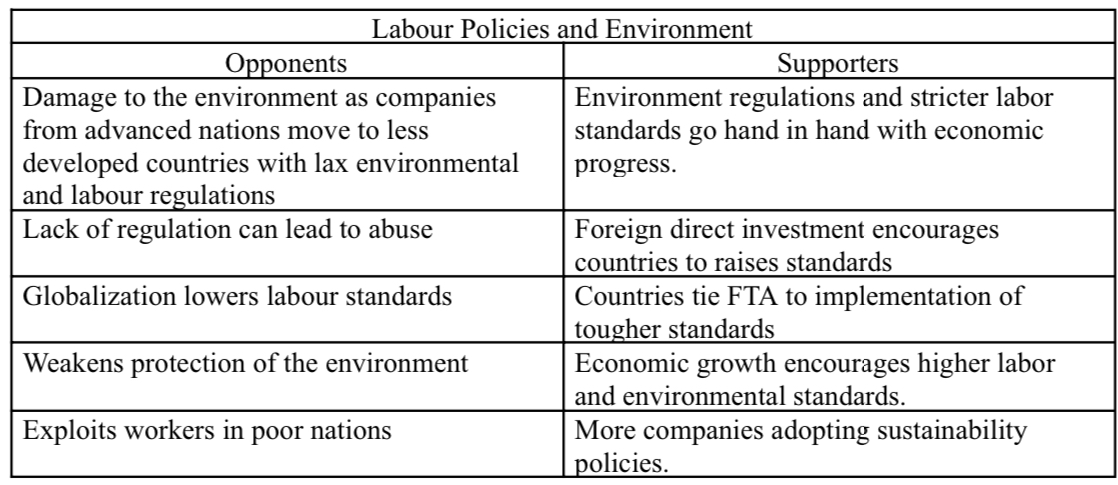
What are the globalization debates in terms of labor policies and environment?
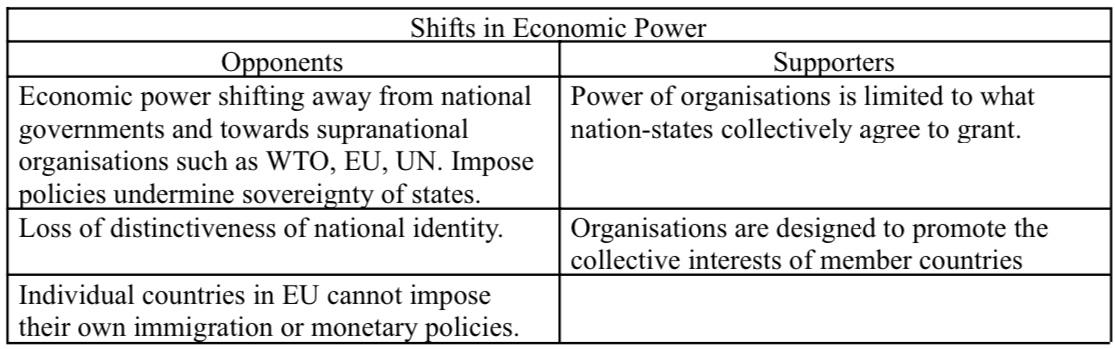
What are the globalization debates in shifts in economic power?
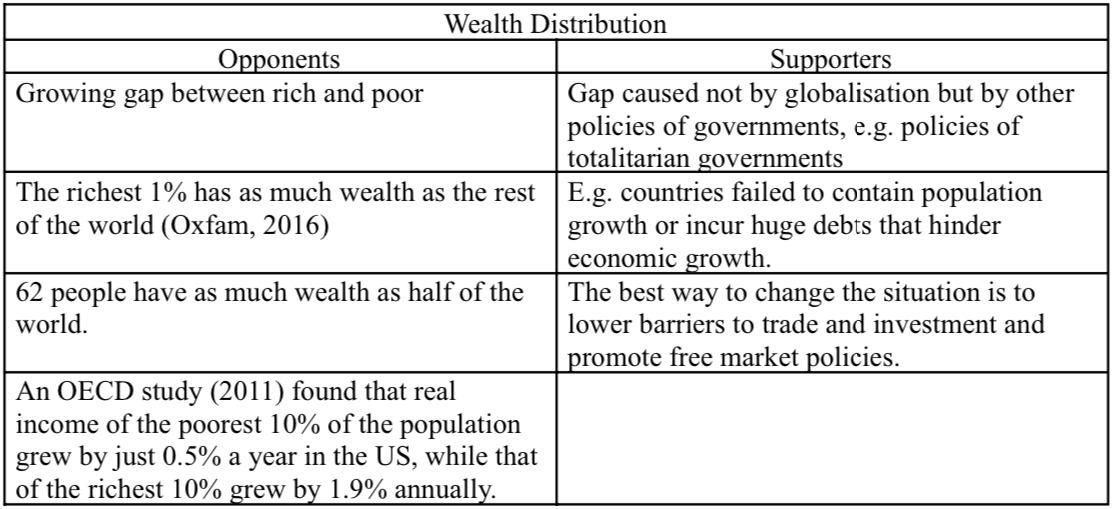
What are the globalization debates in wealth distribution ?
What are the key functions of institutions ?
to reduce uncertainty by limiting the range of acceptable actions
to reduce transaction costs from research and information,bargaining, policing and enforcement due to opportunistic behavior
Why do institutions matter to international businesses ?
managers and firms rationally pursue their interests and make choices withing formal and informal constraints
formal and informal institutions combine to govern firm behavior in situations where formal constrains fail, informal constraints play a larger role
what is a political system ?
A political system represents the rules of the game on how a country is governed politically and has 2 dimensions: the degree to which the emphasize collectivism vs individualism and the degree to which they are totalitarian or democratic
define collectivism
collectivism refers to a system that stresses the primacy of collective over individual goals ( the needs of society as a whole are viewed as more important than individual freedoms)
(Denmark tax and gov spending example)
define individualism
individualism is based on two concepts, : that individual freedoms and self expression are guaranteed and that people are allowed to pursue their own self interest within the rule of law and that will maximize society’s welfare