[BIO 120.11] Module 3 Part 1: Culturing Bacteria - Culture Media
1/166
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
167 Terms
Culture Media, Incubation Conditions
What are 2 of the growth requirements for culturing bacteria?
Growth, Reproduction
Culture media is essential for what bacterial processes?
TRUE
T/F: For bacteria, the primary indicator of growth is increase in number of cells
FALSE
T/F: For bacteria, the primary indicator of growth is increase in cell size
Culture Media
Source of energy and building blocks for the synthesis of new cell material
Micronutrients and Macronutrients
Culture media is the source of what nutrients?
Macronutrients
Nutrients required in large amounts
Protein (55%), RNA (20.5%)
The macromolecule that has the highest percent of dry weight (__) is ___, followed by ___ (__)
LPS is only found in outer membrane, 3.4%
Why is LPS only found in low concentrations in terms of % of dry weight? What is the %?
DNA, 3.1%
What macromolecule has the lowest % of dry weight? What is the % of dry weight?
50% C, 20% O, 14% N, 8% H, 3% P
What are the top 5 elemental composition of an E. coli cell in terms of dry weight?
TRUE
T/F: All macromolecules require Carbon
FALSE
T/F: Only carbohydrates require Carbon
Organic Polymers, Monomeric constituents of macromolecules
Source of carbon for heterotrophs?
CO2
Source of carbon for autotrophs?
Heterotroph will not grow
If you grow a heterotroph on a minimal media and place it near the window, what will happen to it?
Cyanobacteria (autotroph) will grow because it can fix CO2 from the air
If you grow cyanobacteria on a minimal media and place it near the window, what will happen to it?
TRUE
T/F: All macromolecules contain Oxygen
FALSE
T/F: Not all macromolecules contain Oxygen
Water
What is the source of oxygen for culture media?
Protein, Nucleic Acid, LPS
What 3 macromolecules contain Nitrogen?
Ammonia (NH3)
What is the source of Nitrogen for all microorganisms?
Nitrate (NO3-)
What is the source of Nitrogen for many microorganisms?
Nitrogen gas (N2)
What is the source of Nitrogen for nitrogen-fixing bacteria?
Organic polymers, Monomeric constituents of macromolecules
What are the sources of Nitrogen for heterotrophs?
The nitrogen fixers can still grow
If you leave a plate of nitrogen fixers on minimal media without any nitrogen source in an open space, what will be expected of their growth?
Tryptone, Beef Extract, Casein
Examples of medium ingredients that are rich in Nitrogen
FALSE
T/F: Nitrogen is needed by all macromolecules
TRUE
T/F: Nitrogen is only needed by select macromolecules
TRUE
T/F: Hydrogen is needed by all macromolecules
FALSE
T/F: Hydrogen is needed only in select macromolecules
TRUE
T/F: Phosphorus is needed only by select macromolecules
FALSE
T/F: Phosphorus is needed by all macromolecules
Water
What is the source of Hydrogen in a culture media?
Nucleic Acids, Phospholipids
What organic molecules require Phosphorus?
Inorganic phosphate compounds
What is the source of Phosphorus in a culture media?
TRUE
T/F: Sulfur is needed only for select macromolecules
FALSE
T/F: Sulfur is needed by all macromolecules
Inorganic S, Organic Sulfur Compounds
What are the 2 main sources of Sulfur in culture media?
Sulfate compounds, Sulfide compounds
What are two examples of inorganic S sources?
Vitamins (Thiamine, Biotin)
Amino acids (Cysteine, Methionine)
Lipoic Acid
What are three examples of organic sulfur compounds?
Micronutrients
Nutrients that are required in minute amounts
Trace Metals (Metals), Growth Factors (Organic Nutrients)
What are two types of micronutrients?
Micrograms
What is the unit used for micronutrients, given that they are required in very small amounts?
Stock solution then dilute
How do we prepare micronutrient solutions?
Defined Media, Complex Media
What are the 2 types of media based on composition?
Defined Media
Media Type - Composition: Prepared by adding precise amounts of highly purified inorganic or organic chemicals to distilled water
Highly purified
For defined media, the inorganic and organic chemicals that are added to distilled water must be in what condition?
Exact qualitative and quantitative composition
Describe Defined Media in terms of qualitative and quantitative composition
Simple Defined Media
The recipe shown in the image is an example of what kind of media?

Simple, Complex
What are the 2 types of Defined Media?
Simple Defined Media only have a single C source, Complex Defined Media have more than one C source
How do we differentiate between simple and complex media (under defined media)?
Complex Media
Media Type - Composition: Employ digests of microbial, animal, or plant products, or any of a number of other highly nutritious yet impure substances
Complex Media
The recipe shown in the image is an example of what kind of media?

Casein (milk), Beef extract, Peptone (protein hydrolysate), Tryptic soy broth (soybeans), Yeast extract
What are 5 examples of complex components found in complex media? [Pep CaBeTryYes]
Liquid Medium, Semi-solid Medium, Solid Medium
What are 3 Types of Culture Media Based on Fluidity or Consistency?
FALSE
T/F: Agar is both a solidifying and nutritional agent.
Agar will liquefy
If agar can be used by bacteria as a nutrient source, what is the expected result for the agar?
Broth
Alternative term for liquid media
0%
Percentage of agar in liquid medium
Propagation, Physiology studies
What are the 2 purposes for liquid media?
Liquid Medium
If we want to study gas production with a Durham tube, what kind of medium (based on consistency) should be used?
If you use liquid media, you just need to centrifuge. If you use solid medium, you will still need to scrape
Why is using broth or liquid media better for propagation studies?
0.2% to 0.5%
What is the percentage of solidifying agent in a semi-solid medium?
Motility, Oxygen Requirements, Swarming
What specific characteristics of bacteria can be studied using a semi-solid medium?
Aerobes on top, Anaerobes on bottom
If using a semi-solid medium for determining bacterial oxygen requirements, what results can be expected?
1.5% to 2%
What is the percentage of solidifying agent for solid media?
Morphology, Isolation, Enumeration
What can be studied or done using solid media? MIE
TRUE
T/F: We can use liquid medium or broth for enumeration.
FALSE
T/F: Only solid medium can be used for enumeration (i.e.: CFU)
TRUE
T/F: You can use liquid medium or broth for isolation
FALSE
T/F: Solid media is the only media type that can be used for isolation
Anaerobes
What kind of bacteria is best isolated using broth or liquid medium?
General Purpose, Enriched, Selective, Differential, Characteristic
What are the 5 types of media based on use? GESDC
General Purpose Media
Media Type - Use: Supports almost all microbial growth
TRUE
T/F: In General Purpose Media, there are no inhibitory substances
FALSE
T/F: We can put inhibitory substances in a General Purpose Media
Nutrient Agar
What is an example of General Purpose Media?
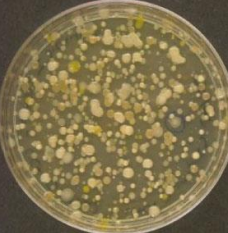
General Purpose Media
What is the media type shown in the image?
Enriched Media
Type of media (according to use) that involves the use of growth stimulants
Increase number of desired microorganisms to detectable level
What is the purpose of an enriched media?
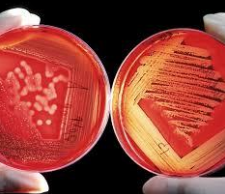
Enriched Media
What kind of media is shown in the image
FALSE
T/F: Enriched Media can suppress the growth of other bacteria
TRUE
T/F: Enriched media do not suppress the growth of other bacteria
Fastidious and Slow Growing Microorganisms
What kind of microorganisms work best for enriched media?
Fastidious Microorganisms
Microorganisms that have complex nutritional requirements
Blood Agar
What is an example of enriched media?
Growth Stimulant (serum, blood, other nutritious substances)
What is a key ingredient in enriched media?
TRUE
T/F: Enriched medium is recommended for slow-growing bacteria
FALSE
T/F: Enriched media is not recommended for slow-growing bacteria
TRUE
T/F: Enriched media does not make the isolation process of desired bacteria easier.
FALSE
T/F: Enriched media makes the isolation process of desired bacteria easier.
Selective Media
Media type (according to use) that can inhibit the growth of unwanted microorganisms and can encourage the growth of particular microorganisms.
TRUE
T/F: Aside from inhibiting the growth of unwanted microorganisms, selective media can also encourage the growth of particular organisms.
FALSE
T/F: Selective media can only inhibit the growth of unwanted microorganisms, but not enrich or encourage the growth of particular organisms
Inhibitors (antibiotics, dyes, toxic compounds, detergents)
What is a key ingredient for Selective Media
Mannitol Salt Agar
What is an example of selective media?
Staphylococcus aureus
A microorganism capable of fermenting Mannitol
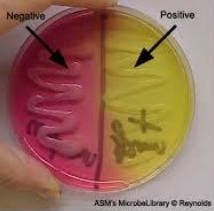
Selective Media
What is the category of the media shown in the image?
Characteristic Media
Media type (according to use) that functions for determination of metabolic activity, products, or growth requirements