Genetic Technologies in Molecular and Cellular Biology
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
103 Terms
Plasmids
Circular DNA molecules used in genetic engineering.
Antibiotic Resistance
Bacteria's ability to survive antibiotic treatment.
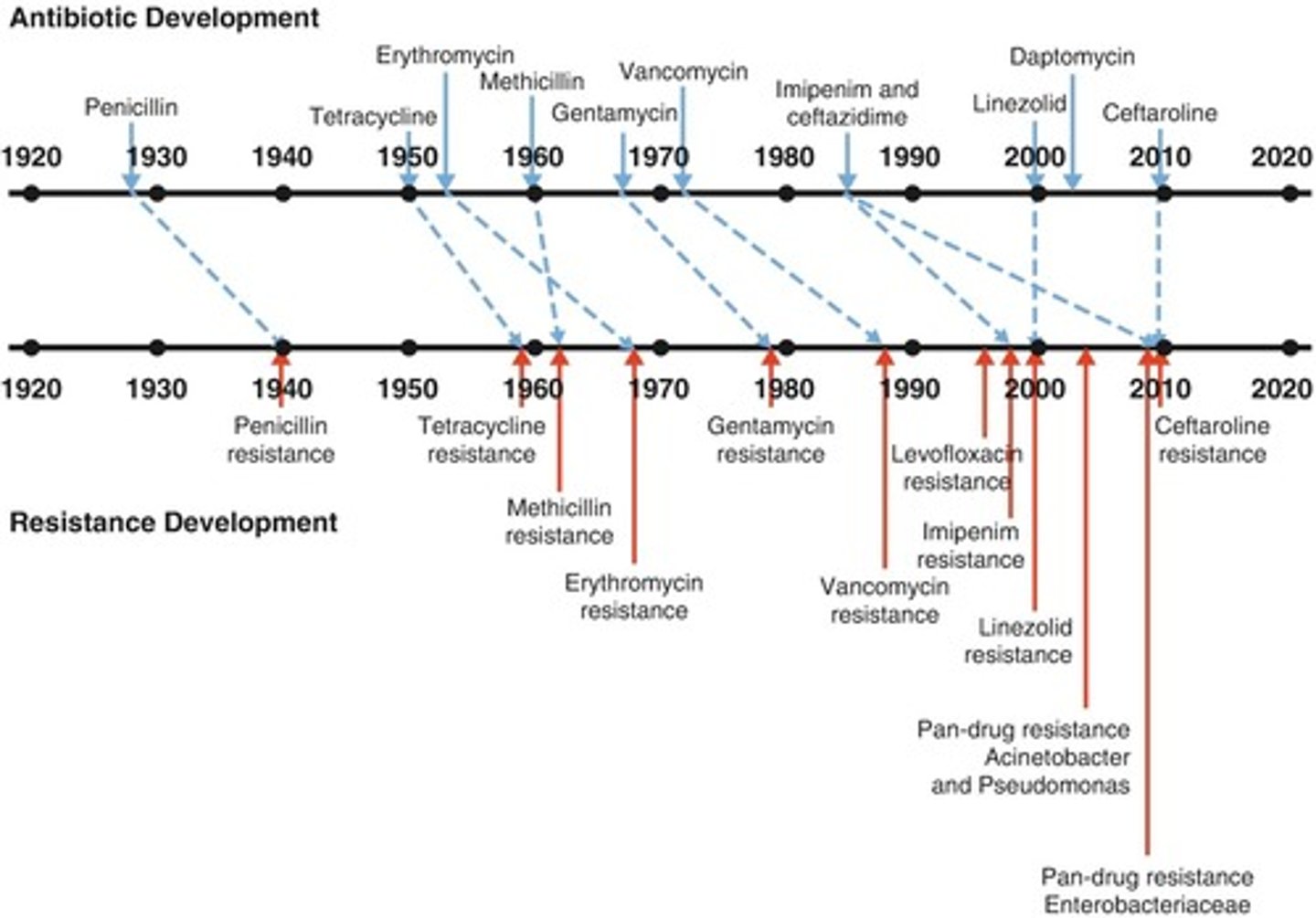
Penicillin
First antibiotic discovered by Alexander Fleming in 1928.
S. aureus
Bacteria with 90% resistance to penicillin today.
Vectors
Modified plasmids or phages for DNA transport.
Endonucleases
Enzymes that cut DNA at specific sites.
Restriction Endonucleases
Bacterial enzymes that degrade foreign DNA.
Recognition Sequences
Specific DNA sequences where restriction enzymes cut.
EcoRI
Restriction enzyme from E. coli.
SmaI
Restriction enzyme from S. marcescens.
Methylation
Modification of DNA to protect it from restriction enzymes.
Double-stranded DNA
DNA consisting of two complementary strands.
Recognition Sites
Specific sequences recognized by restriction enzymes.
Bacterial Genomes
Contain double-stranded DNA that can be cut.
Modification of Host DNA
Bacteria mark their DNA to avoid degradation.
Methylated DNA
DNA with added methyl groups at recognition sites.
Unmethylated DNA
DNA without methylation, susceptible to restriction enzymes.
Fungal Contaminant
Source of penicillin discovered accidentally.
Medical Problem
Antibiotic-resistant bacteria pose significant health risks.
Palindrome
Sequence reading same 5′-3′ on both strands.
Type II Restriction Enzymes
Most useful enzymes for genetic engineering.
Sticky Ends
Single-stranded overhangs after DNA cutting.
Blunt Ends
No overhangs; straight cuts in DNA.
Eco RI
Restriction enzyme producing sticky ends.
Eco RV
Restriction enzyme producing blunt ends.
BamHI
Restriction enzyme generating sticky ends.
Recombinant DNA
DNA fragments from different organisms combined.
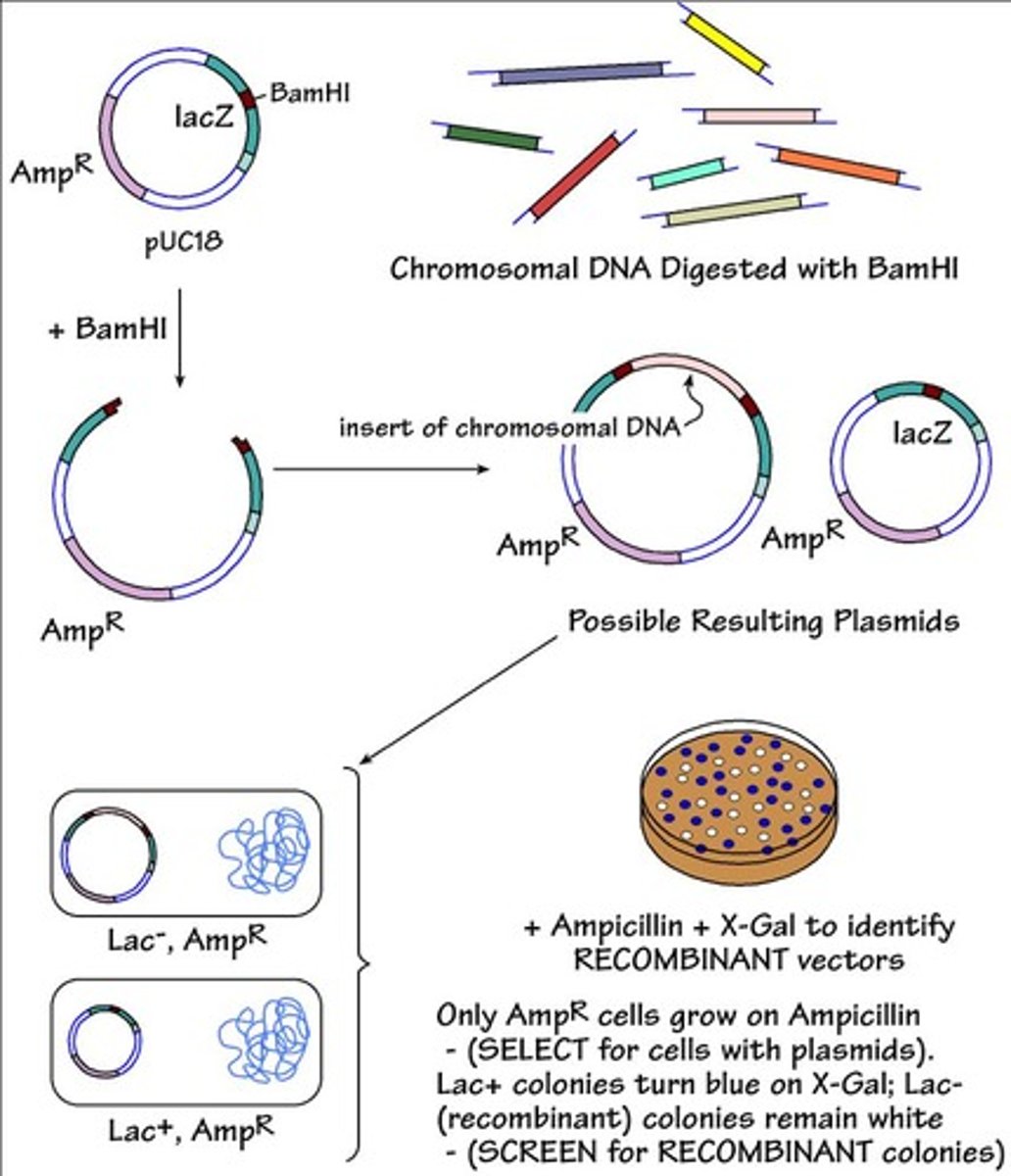
DNA Ligase
Enzyme sealing DNA fragments together.
Hybridization
Temporary base pairing of complementary sequences.
Complete Digestion
Cutting DNA into smaller fragments using enzymes.
Fragment Size Estimation
Predicting sizes based on enzyme cutting frequency.
Single-Stranded DNA
DNA with unpaired bases after a cut.
Double-Stranded DNA
DNA with paired bases on both strands.
Genomic DNA
Total DNA content within an organism's cells.
Restriction Site
Specific location on DNA recognized by enzymes.
DNA Fragmentation
Process of cutting DNA into smaller pieces.
Temporary Base Pairing
Short-lived pairing of complementary DNA sequences.
Gene Isolation
Extracting specific genes from larger DNA fragments.
Molecular Cloning
Creating copies of DNA fragments using enzymes.
Gene Cloning
Process of creating copies of a specific gene.
Plasmid Vector
Circular DNA used to transfer genes into cells.
ori
Origin of replication in plasmid vectors.
Polylinker
Collection of unique restriction sites in vectors.
Reporter Gene
Gene used to indicate successful cloning.
Antibiotic Resistance Gene
Gene providing resistance to antibiotics for selection.
Transformation
Process of introducing DNA into bacterial cells.
Transduction
DNA transfer into bacteria via bacteriophages.
Cell Clones
Identical cells derived from a single original cell.
Amplification
Increasing the quantity of DNA through cloning.
Genomic Library
Collection of DNA fragments representing an organism's genome.
Restriction Enzymes
Enzymes that cut DNA at specific sequences.
Ligate
Joining DNA fragments together using ligase.
E. coli
Bacterium commonly used in genetic cloning.
DNA Insert
Foreign DNA incorporated into a plasmid vector.
Cloning Experiment
Initial experiment to produce recombinant DNA.
Recombinant Vector
Vector containing foreign DNA inserted into it.
DNA Sequencing
Determining the nucleotide sequence of DNA.
Promoter
Region of DNA initiating transcription of a gene.
Introns
Non-coding segments of DNA within a gene.
Coding Regions
Parts of DNA that encode proteins.
Culture Volume
Amount of liquid medium used for bacterial growth.
Transformed Cell
Cell that carries a piece of foreign DNA.
Restriction Endonuclease
Enzyme that cleaves DNA at specific sequences.
Recombinant Plasmid
Vector containing inserted DNA fragment.
E. coli Host Strain
Bacterial strain used for DNA transformation.
cDNA Library
Collection of cloned cDNA representing expressed genes.
Reverse Transcriptase
Enzyme that synthesizes DNA from RNA template.
Processed mRNA
mRNA that has undergone splicing to remove introns.
DNA Polymerase
Enzyme that synthesizes DNA strands from templates.
Double-stranded cDNA
cDNA formed by complementary DNA synthesis.
PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction)
Technique to amplify specific DNA sequences.
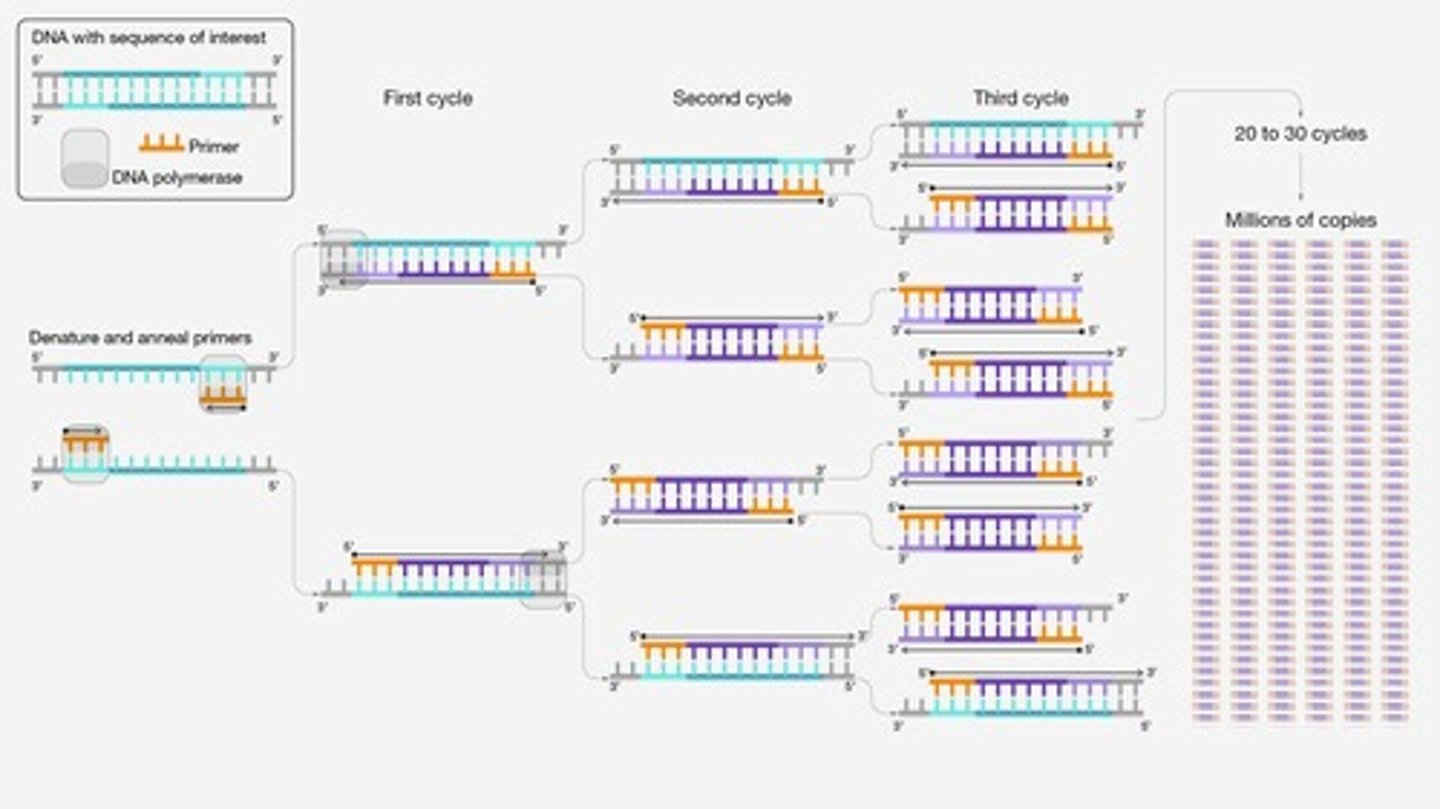
Flanking Sequences
Nucleotide sequences surrounding the target DNA.
Contaminating DNA
Unwanted DNA that may interfere with PCR results.
Library of Genomic Clones
Collection of cloned genomic DNA fragments.
Active Protein Production
Expression of proteins from specific genes in cells.
cDNA Insertion
Process of inserting cDNA into a vector.
Gene Expression
Process by which genes are transcribed and translated.
Tissue Harvesting
Collection of specific tissues for mRNA isolation.
Vector
DNA molecule used to deliver genetic material.
Limitations of Genomic Library
Includes introns; not suitable for protein production.
Advantages of PCR
Fast, easy, and minimizes experimental variables.
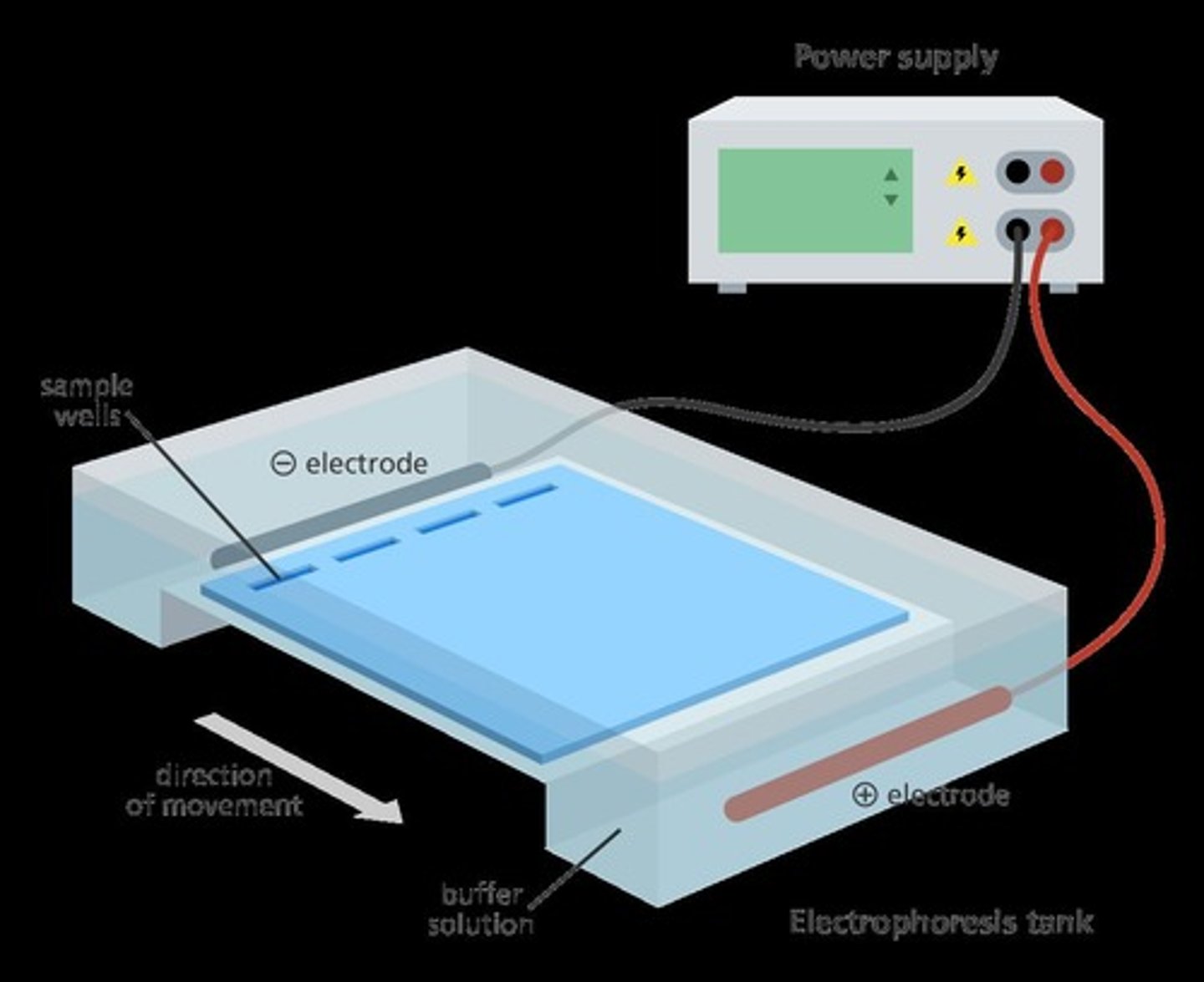
Gel Electrophoresis
Technique to separate DNA fragments by size.
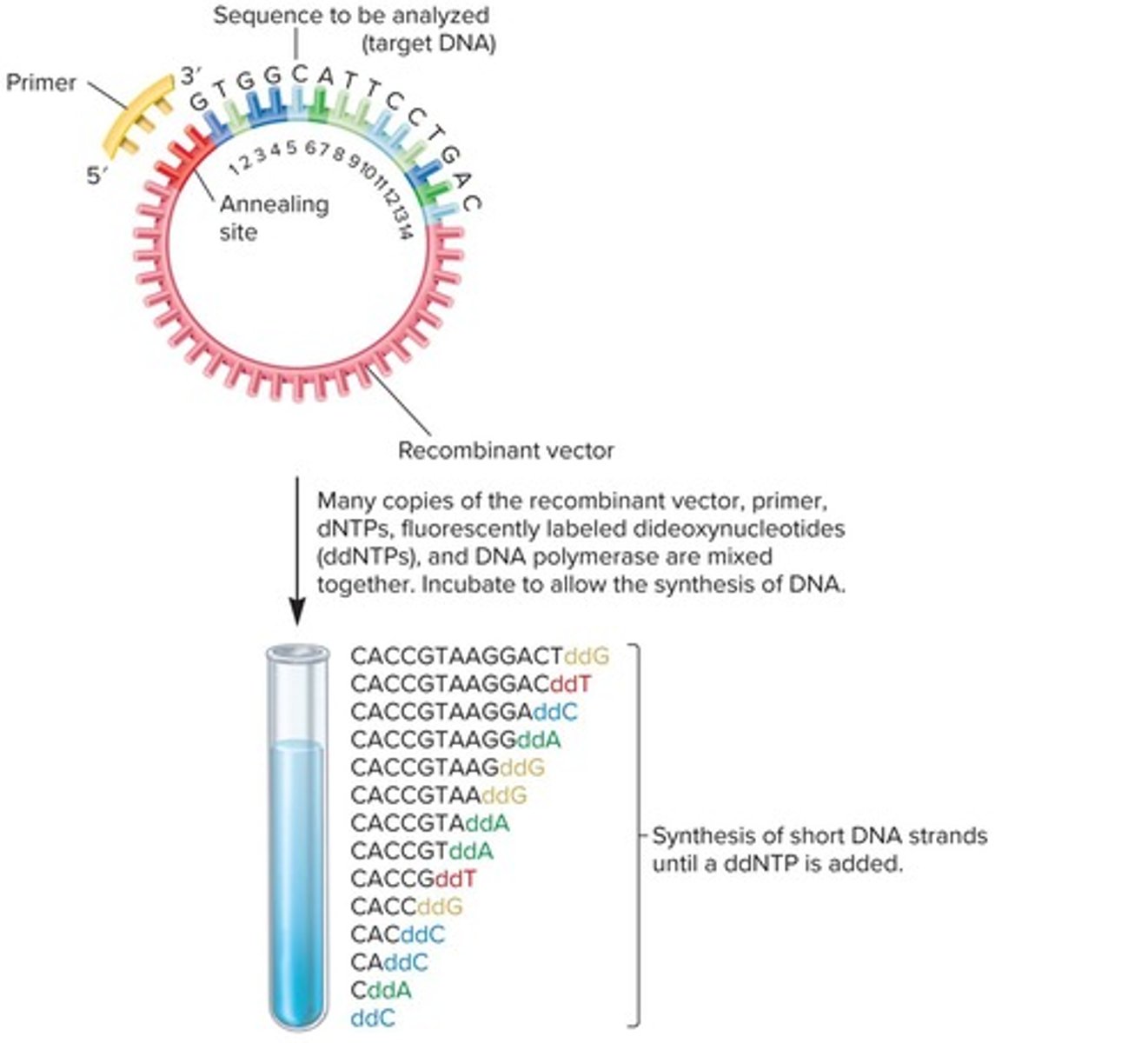
Dideoxy Chain Termination
Method for determining DNA sequences.
Transcriptome
Complete set of RNA transcripts in a cell.
Microarrays
Tools for analyzing gene expression levels.
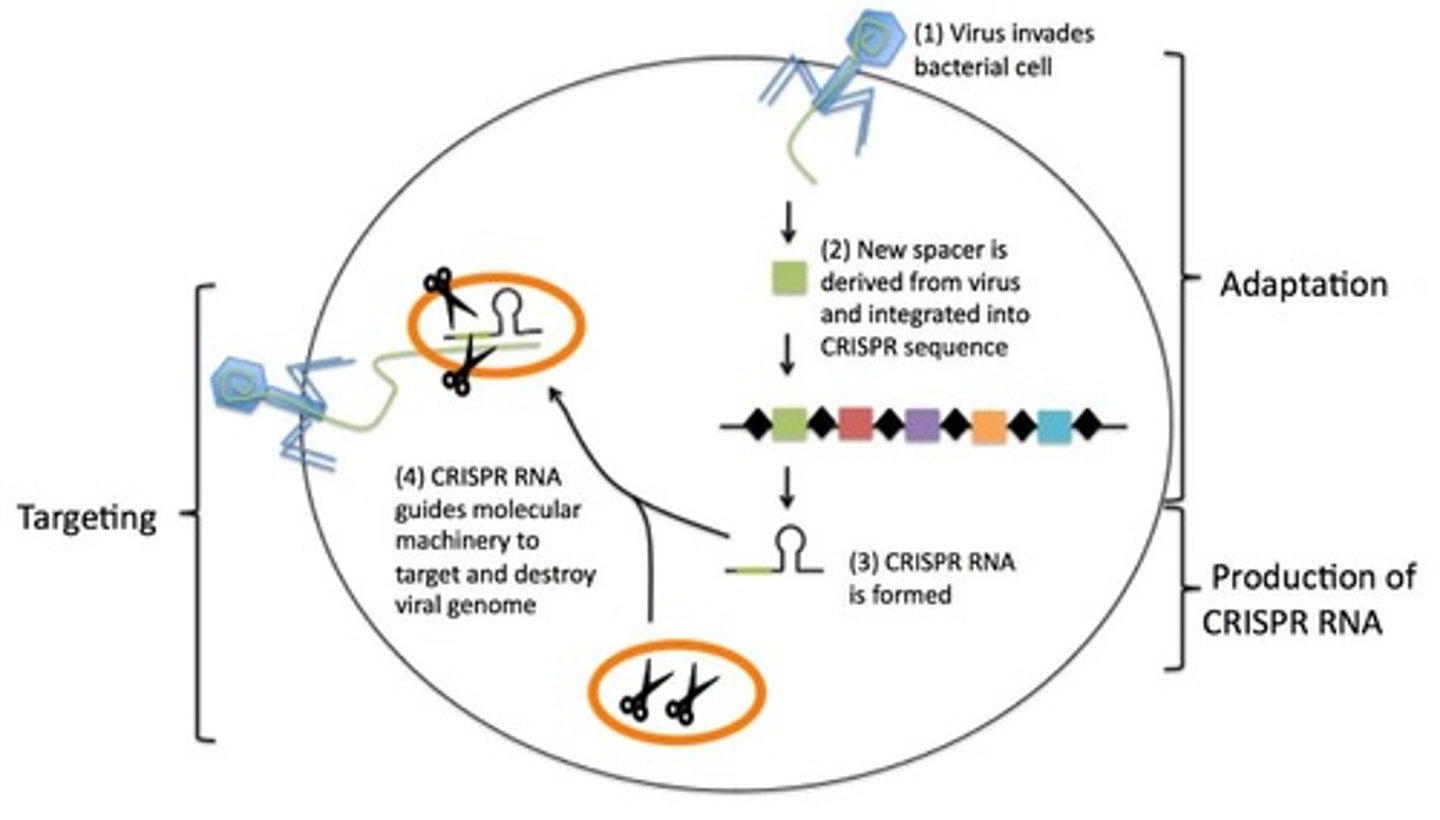
CRISPR-Cas9
Genome editing tool using guide RNA.
sgRNA
Single guide RNA directs Cas9 to target DNA.
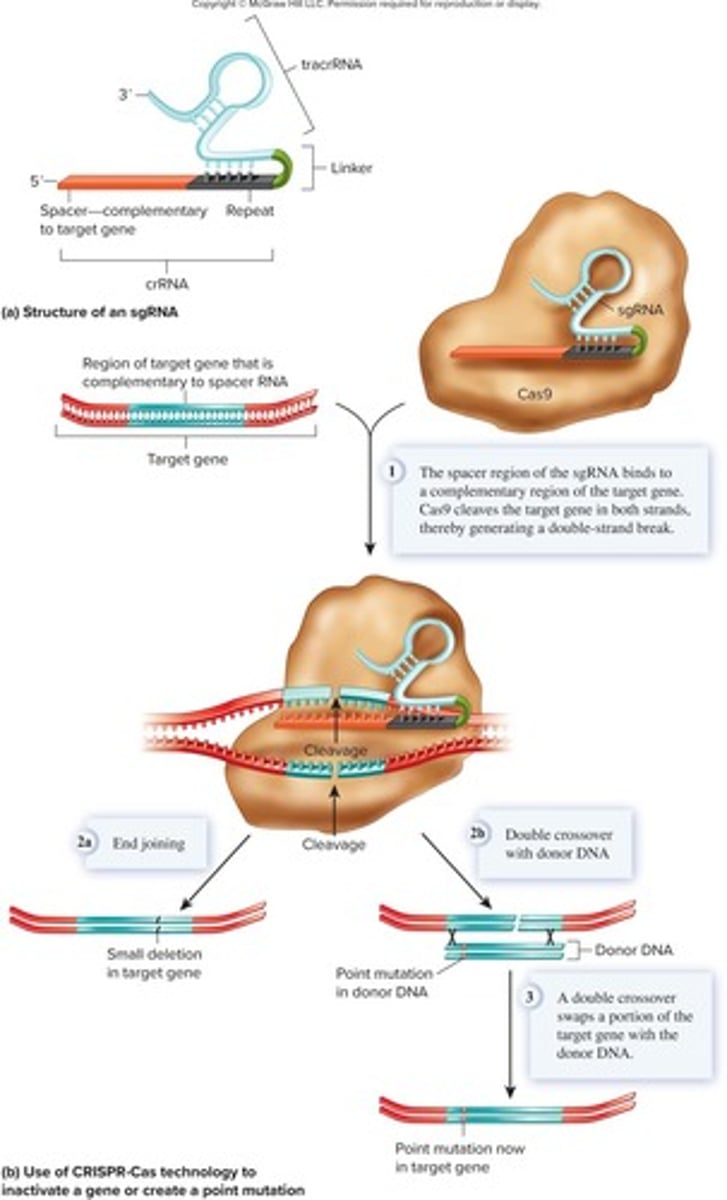
Natural Repair Systems
Cellular mechanisms to fix DNA breaks.
Gene Knockout
Disabling a gene to study its function.
Template Repair
Using a DNA copy to fix mutations.
Disease-causing Mutation
Genetic alteration leading to health issues.
Overactive Protein
Protein that functions excessively due to mutation.
Defective Protein
Non-functional protein resulting from genetic mutations.
Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2020
Awarded to Charpentier and Doudna for CRISPR.
Therapeutic Approaches
Strategies for treating genetic and chronic diseases.
Sickle-cell Anemia
Blood disorder caused by abnormal hemoglobin.
Thalassemia
Genetic blood disorder affecting hemoglobin production.
Leukemia
Cancer of blood-forming tissues, especially bone marrow.
Neurodegenerative Disorders
Conditions leading to progressive nerve cell degeneration.
Alzheimer's Disease
Progressive brain disorder affecting memory and cognition.