1/2/3. Intro to Study Design & Descriptive Studies & Analytical Cross-Sectional Studies
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
study designs are broadly classified into what 2 types?
observational
experimental/intervention
describe observational studies.
One or more groups are observed.
Characteristics about the observed are recorded, described and analyzed
describe experimental/intervention studies.
investigator controlled intervention/exposure allocation (treatment, procedure or drug therapy)
Investigator analyzes effect of intervention/exposure on the study outcome
what are the 2 types of observational studies?
descriptive
analytical
What kind of study?
Investigator observes the patterns of the exposure and the other variables in the study
descriptive (observational)
what are examples of descriptive (observational) studies?
case study/report
case-series
cross-sectional (descriptive survey studies)
what kind of study are cross-sectional studies?
can be descriptive as well as analytical (observational)
what are descriptive studies helpful for?
observing trends/patterns for main variable of interest + covariates
generating research hypotheses for larger studies
t/f: in descriptive studies, investigators observes and collects info on variables of interest.
true
do investigators change study aspects in descriptive studies?
no
describe the who, where, and when of descriptive studies
who →exposure group
where → population source/location
when → time period
(all in relation to the what/outcome)
what kind of studies are used to measure the relationship between exposure and outcome?
descriptive studies
can a direction of relationship be determined from descriptive studies?
no
what are examples of analytical studies?
cross sectional (analytical can estimate odds ratios)
case control studies (retrospective)
cohort studies (prospective or longitudinal)
what is the hierarchy of evidence?
1. Systematic reviews and meta-analyses
2. Randomized controlled trials
3. Cohort studies
4. Case-control studies
5. Cross-sectional studies
6. Case reports or case series
7. Expert opinion
8. Anecdote
the main group of interest in a study are called…?
observational studies → cases
experimental studies → treatment or intervention group
the comparison group in a study are called…?
controls (aka non-cases)
in experimental studies, also called non-treatment or control group
what is the term representing the result or effect of interest in the study?
outcome (eg. presence of disease, health status, success of treatment)
t/f: some studies may have multiple outcomes and multiple exposures
true
what is the term for Characteristic of the individual (age, gender, weight) or a variable related to environment (air pollution), lifestyle (smoking, exercise), social status (poverty or income level) or participant’s background (education level, race/ethnicity)?
exposure (or risk factor)
what are 2 types of experimental/interventional studies?
controlled trials (most common)
trials with no controls or external controls
what type of study?
trials that include an experimental group and a control/comparison group.
EXPERIMENTAL/INTERVENTIONAL STUDIES (controlled trials)
what are examples of controlled trials?
randomized vs non-randomized
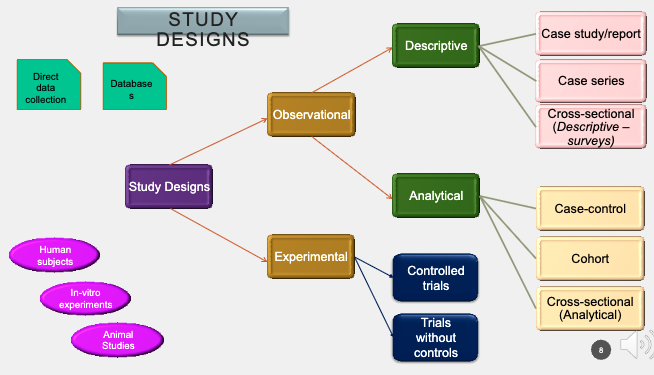
what type of study?
Characteristics of a patient are recorded and published in a report
case study (descriptive, observational)
what are some key characteristics of case study?
no control is used
usually short duration of study
precursor to future studies (hypothesis generating)
what type of study?
Characteristics of a series of patients are recorded and published in a report.
Looking at same condition or treatment in a series of patients to observe trends or patterns
case series (descriptive, observational)
what are some key characteristics of case series?
no controls used (rarelt comparison set of pts included)
short duration of study
precursor to larger studies (hypothesis generating)
(similar to case study)
what are the advantages of case report/series?
easy to conduct
short duration
inexpensive
useful for generating hypotheses for larger studies
what are the disadvantages of case report/series?
cannot evaluate associations
generalizability is an issue
what type of study?
Useful in describing the characteristics of a population at one point in time (a slice of time to see what is happening).
Useful in describing the characteristics such as knowledge, attitude and practices in the population
Descriptive cross-sectional studies (observational)
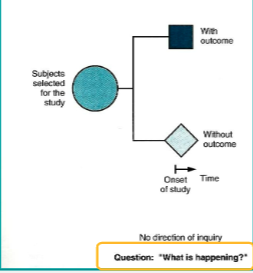
Descriptive cross-sectional studies (observational) are sometimes referred to as…?
prevalence studies (can be used to examine prevalence of disease/condition)
what is the duration of cross sectional studies?
can be short or long duration
Descriptive cross-sectional studies can be precursors to what type of studies?
cohort and case-control studies
incidence or mortality studies often use what type of study design?
cross-sectional design (to study incidence patterns or mortality rates over a period of time)
what are the advantages of Descriptive cross-sectional studies?
convenient
less time consuming
large samples
can be done with limited resources
what are the disadvantages of Descriptive cross-sectional studies?
cannot evaluate causal association
participation bias (surveys/interviews)
interview/reporting bias
slice of time may not be representative of full picture
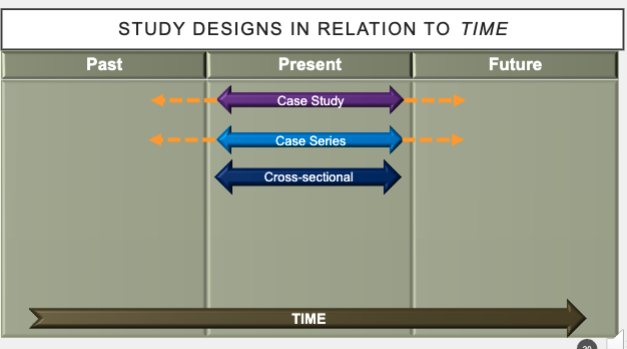
what type of study?
test the research hypothesis about the exposure-outcome relationship that is under investigation
analytical studies
what 2 things can be measured/evaluated in analytical studies?
association (between exposure and outcome)
magnitude (off association between exposure and outcome)
what type of study design?
Does smoking status (never, past and current) have an effect on periodontal disease status (yes/no)?
analytical
what are examples of analytical studies?
cross sectional
case control
cohort studies
what type of study?
Association between exposure and outcome at one point in time is evaluated
analytical cross-sectional study
in analytical cross-sectional study, ________ of relationship is estimated but not ________.
magnitude; direction
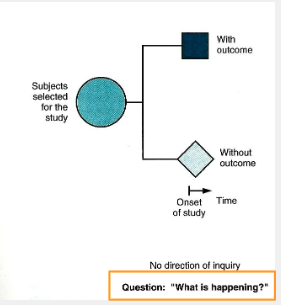
what are advantages of cross sectional sutdies?
easy to conduct
commonly describe burden of disease, disease trends, behavioral patterns, etc.
correlation betwen variable determined and cross-sectional relationships analyzed
what are disadvantages of cross sectional sutdies?
need large sample size
need time, money, resources
cannot establish causal association
cannot establish time sequence/temporality
descriptive vs analytical cross-sectional study designs:
Overall disease burden can be described in large populations.
Disease patterns can be described with this design.
Can be utilized to generate research question or hypothesis for future studies.
descriptive
descriptive vs analytical cross-sectional study designs:
In addition to describing disease burden, disease patterns and trends, relationship between exposure and outcome can be analyzed.
Research hypothesis/research question can be evaluated statistically
Odds ratios for the relationship between exposure and outcome can be estimated
analytical