Genetics 311 Indiana University
1/236
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
237 Terms
Pseudoautosomal regions (PARs)
Homologous segments on the tips of the X and Y chromosomes that allow them to pair and recombine during meiosis. The two PARs contain about 30 genes total.
SRY
A protein that activates testes development and prevents the formation of ovaries. Sex determining region of Y.
Sex Reversal
(XX with SRY+ is male) and (XY with SRY- is female)
Sex Chromosomes
X(large amount of protien-coding genes) and Y(much smaller amount)
Thomas Hunt Morgan
Established a firm experimental base for the chromosome theory. (Specifc genes reside on specific chromosomes.
Crisscross inheritance
Males inherit eyecolor mutation from their mothers.
X-Linked
The gene is carried by the X chromosome and the Y chromosome carries no allele of the gene.
w+
normal / wild type allele
w
mutant allele
hemizygous
an individual who has only one member of a chromosome pair or chromosome segment rather than the usual two. Often used to describe X-linked genes in males who have only one X chromosome.
Nondisjunction
where the X chromsomes fail to seperate during meiosis in fmeales. Failure in chromsome segregation. Occurs in meiosis I or meiosis II.
All possible products of nondisjunction + fertilization
XXY
XXX
XO
OY (these die in embryonic development)
Kinetochore
A structure in the centromere region of each chromatid that is specialized for conveyance. Each kinetochore contains protein that enable the chromsome to slide along the microtubule.
Pedigree
A diagram of a family’s relevant genetic features, extending back through as many generations as possible.
Family pedigree diagram symbols
Squares = males
Circles = females
Diamonds = unspecified sex
Late-onset genetic trait
Symptoms are not present at birth and manifest themselves later in life. example = huntington disease
Incomplete Dominance
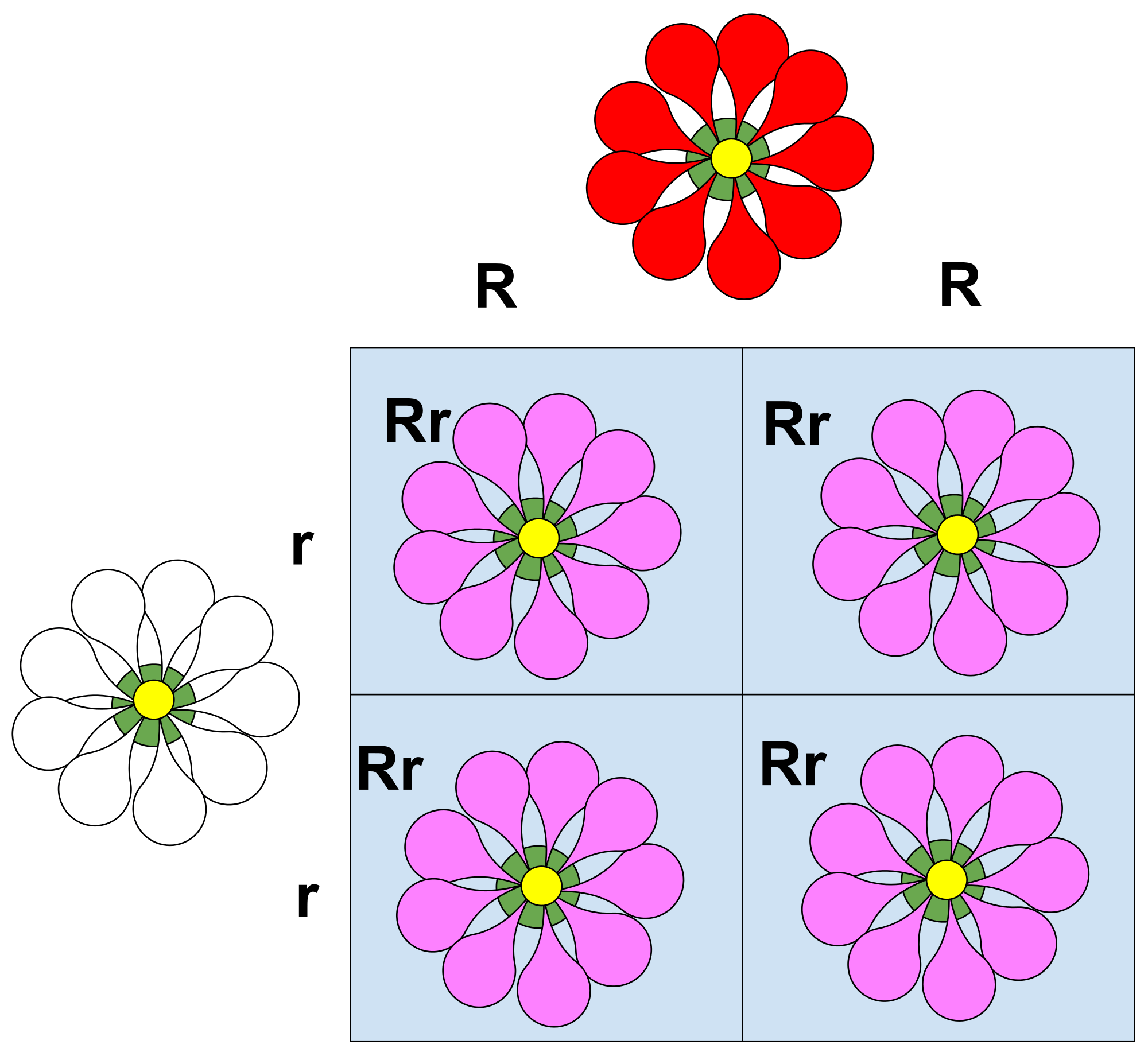
Codominance

Variable Expression
Incomplete penetrance

monohybrid
experiments involving hybrids for only a single trait. Cross of pure breeding parents that will always produce f1 hybrids that resemble one of their parents.
reciprocal cross
reversing the characteristics of the male and female parents, thus controlling whether a particular characteristic was transmitted via the eggs or sperm.
Dominant
characteristic that appears in all f1 hybrids
recessive
characteristic that remains hidden but reappears in F2
Punnet square
visual summary of a cross
principle of segregation
two identical alleles of pure breeding organism segregate during gamete formation. Each sperm or egg carries only one of each pair of parental alleles.
Hybrid
combining two different organisms with seperate characteristics. Offspring of parents that are genetically different.
F1
first generation of offspring
F2
second generation of offspring
phenotype
physical, visble, observable quality
genotype
pair of alleles present in an indivdual
gene
the heritable entity that determines a trait
alleles
alternate forms of a gene
homozygous
has two identical alleles of a given gene
heterozygous
two different alleles of the same gene
test cross
the cross of an individual of ambigous genotype with a homozygous recessive individual.
dihybrid cross
the seperation of the two alleles of a gene into different gametes
addition rule
mutually exclusive events (example is “or” events)
multiplication rule
independent events (example is “and” events)
somatic cells
non-reproductive body cells
germ cells
reproductive cells located in testes and ovaries.
Diploid
zygote carrying two matching sets of chromosomes
haploid
gametes of a diploid organism
mitosis
the nuclear division that apportion chromosomes equally to two daughter cells.
meiosis
chromosomes replicate once but the nucleus divides twice.
interphase
ongoing protein synthesis and cell growth
cytokinesis
this splits the nucleus and finally makes the identical daughter cells in mitosis
nuclear envelope
seperates nucleus from cytoplasm and protects the genetic material
nucleolus
responsible for synthesis of ribosomes
prophase (mitosis)
1.Chromsomes condense and become visible
centromeres move apart toward opposite poles and generate new microtubules
nucleoli begin to disappear
chromatid
the rods that make up chromosomes
centromere
holds chromosomes together.
1 chromosome = 1 centromere
0 centromere = no chromosome
metaphase (mitosis)
chromosomes align on the metaphase plate with sister chromatids facing opposite poles
mitotic spindle
microtubule based structure that segregates replicated chromosomes.
metaphase plate
the line where chromosomes align to eventually seperate in anaphase
anaphase (mitosis)
the connection between the centromers of the sister chromatids is severed.
The now seperated sister chromatids move to opposite poles
Prophase I (meiosis)
made of five stages, where homologues condense, pair, and crossing over occurs.
Stages:
Leptotene
Zygotene
Pachytene
Diplotene
Diakinesis
Metaphse I (meiosis)
Tetrads line up along the metaphase plate
Each chromosome of a homologous pair attaches to fibers from opposite pole
Sister chromatids attach to fibers from the same pole.
Leptotene
Chromosomes begin to condense
Centrosomes begin to move toward opposite poles
Zygotene
Homologus chromosomes enter synapsis
The synaptonemal complex forms
Pachytene
Synapis is complete
Crossing over, genetic exchange between nonsister chromatids of a homologous pair occurs.
Diplotene
A synaptonemal complex dissolves
A tetrad of four chromatids is visible
crossover points appear as chiasmata, holding nonsister chromatids together
meiotic arrest also occurs at this time in many species
Diakinesis
Chromatids thicken and shorten
The nuclear membrane breaks down and the spindle begins to form
Zygote
the cell formed by the fertilization of the egg by the sperm during sexual reproduction; in humans, eggs and sperm are haploid, and zygotes are diploid.
Anaphase I (meiosis)
sister centromeres remain connected to each other
the chiasmata dissolve
homologous chromosomes move to opposite poles
Synapsis (zipper = synaptonemal complex)
matching chromosomes are zipped together
Telophase I (meiosis)
The nuclear envelope reforms
Resultant cells have half the number of chromosomes, each consisting of two sister chromatids.
Cytokinesis seperates the daughter cells
Tetrad / bivalent
synapsed chrosome that contains four chromatids
synapsed chromosome that contains two chromatids
chiasmata
A point in which paired chromosomes remain in contact during the first metaphase of meiosis. Crossing over + exchange of genetic material occurs.
Sister chromatids
two identical DNA molecules that stay attached to centromere until cell replication.
Pedigree
an orderly diagram of a family’s relevant genetic features, extending through as many generations as possible
Pleiotropy
phenomenon in which a single gene determines a number of distinct and seemingly unrelated characteristics
Central dogma
flow of genetic information
Complementation test
if progeny are all wildtype = the strains had mutations in different genes (complementary)
if progeny are all mutant = the the strains had mutation in the same gene (not complementary)
Happloinsufficient
Abnormal phenotype shown because the level of gene activity is not enough to produce a normal phenotype
Polar body
small haploid cell asymmterical to the larger secondary oocytese
Epigenetic phenomena
heritable, self perpetuating changes in gene expression not caused by mutation in the base-pair sequence of DNA.
silenced
a promoter is repressed long term
cellular memory
transmission involves collaboration between
modified cytosine residues in DNA
Modified histone tail amino acids in chromatin
Small RNA molecules
Epigenetic information
the combination of molecular factors that determines whether a gene is “on” or “off”
DNA methylation
a biochemical modification of DNA in which a methyl group is added to the fifth carbon of the cystosine base in a 5’ CpG 3’ dinucleotide pair on one strand of the double helix.
DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs)
enzymes that catalyze the methylation of cytosines in CpG dinucleotides
CpG islands
DNA sequences that are hundreds to thousands of bp long where the frequency of CpG nucleotides is much higher than the rest of the genome. When unmethylated, the chromatin is open and the gene is transcriptionally active.
meCPs
repressors that bind to methylated CpG islands and close the chromatin
epistasis
a gene interaction in which the effects of alleles at one gene hide the effects of alleles at another gene
suppression
to inhibit a genes expression or activity, often by another gene or mechanism.
sex-limited
traits that are expressed only in one sex, even though both sexes carry the alleles responsible for the trait.
sex-influenced
traits that are expressed in both sexes but are influenced by the sex of the individual, often exhibiting different patterns of expression.
genetic anticipation
occurence of genetic disorder at progressively earlier ages in subsequent generations
genomic imprinting
the phenomenon in which a gene’s expression depends on the parent that transmits it; caused by sex-specific DNA methylation.
conditional mutation
A mutation that has the wild-type phenotype under certain (permissive) environmental conditions and a mutant phenotype under other (restrictive) conditions. Examples are temperature sensitive and nutritonal effect
acquired characteristics
the belief that traits influenced by environment can be passed on to offspring
chromosome or genetic map
a diagram showing the location of genes on a chromosome
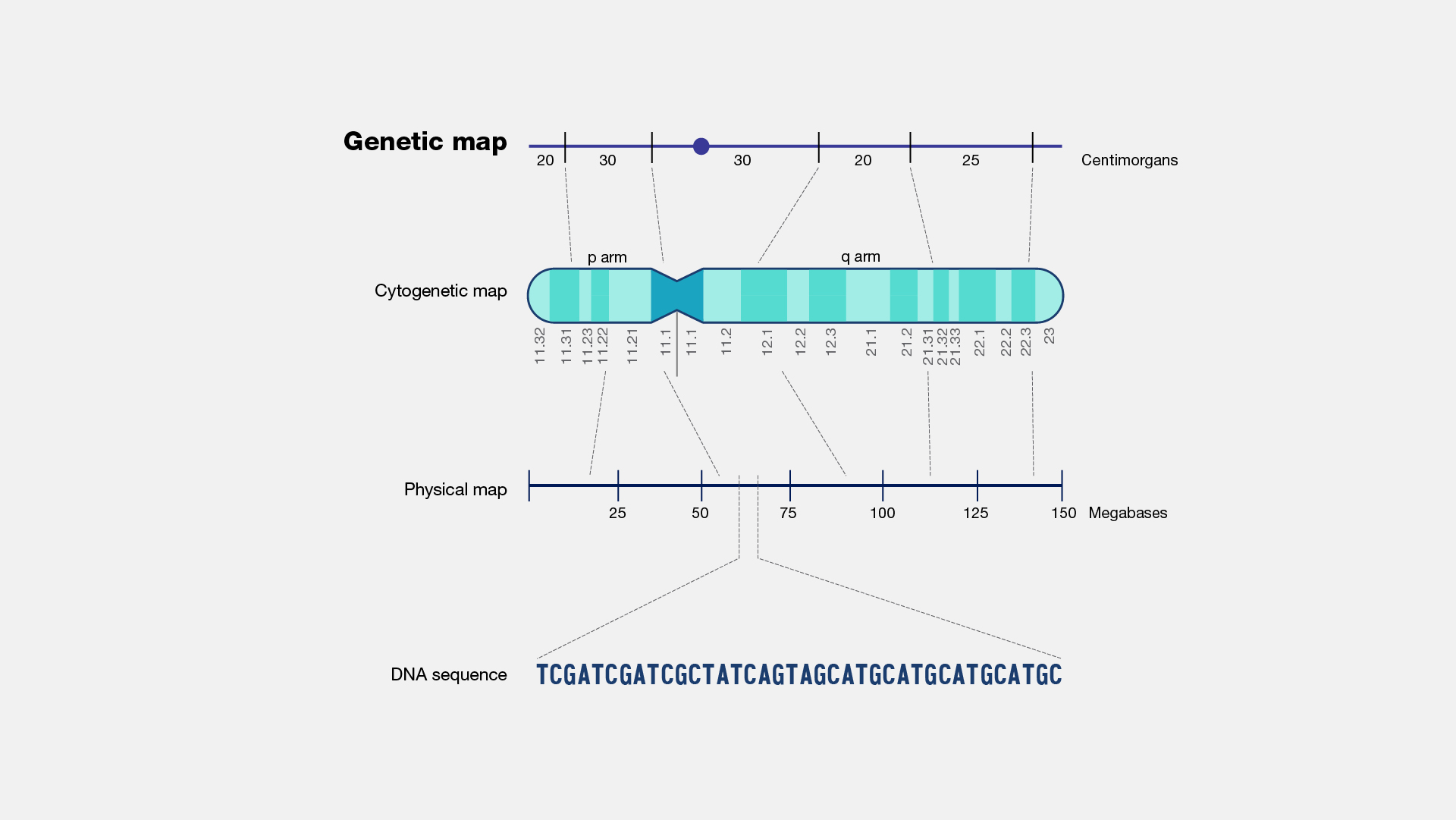
recombination
when crossover occurrs between genetic markers
crossover
exchange of corresponding chromosome segments between homologs
cis
the action of a dna site or an RNA molecule that acts only on the DNA or RNA to which it is connected physically
trans
the action of a protein or RNA that can bind to target sites on ANY DNA or RNA in the cell, connected or unconnected
parental
same combination of alleles found in parent’s chromosomes
nonparental
different combination of alleles from parents, i.e. recombinants
locus
a designated location on a chromosome; sometimes refers to a gene