Bio Exam 3 / Final Exam Review
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/123
Earn XP
Last updated 4:56 PM on 12/6/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
124 Terms
1
New cards
What is bioinformatics?
Computational techniques for solving
biological problems
biological problems
2
New cards
What is biotechnology?
the use of biological agents for technological advancement.
3
New cards
What are the fields of biotechnology?
Medicine, agriculture, fermentation, oil spill treatments, production of biofuels
4
New cards
What are proteomics
The study of entire set of proteins in a given organism
5
New cards
What is genomics?
the study of entire genomes
6
New cards
Why was the discovery of DNA so important?
understand DNA replication, allows scientists to find genetic diseases
7
New cards
Why clone DNA?
target genes and find cures
8
New cards
What type of diseases has technology led us to study? (cloning)
Pulmonary Fibrosis
9
New cards
How do you interpret a BLAST output?
Give info on all sequences that have been found and stored in NCBI; most (top to least)
10
New cards
What does the percent sequence identity mean?
How identical the two strands are across the nucleic and amino acid sequence
11
New cards
How are protein and gene sequences represented in Computational Biology?
Amino acids represented using strings of alphabets; DNA = ATCG
12
New cards
What is the plasma membrane?
phospholipid bilayer/fluid mosaic model; defines borders and keeps cells functional by being selectively permeable; allows some materials to enter
13
New cards
What are the principal components of plasma membrane?
Lipids, carbohydrates, proteins
14
New cards
Why is the cell surface important?
It provides protection by controlling what enters and leaves the cell like recognizing foreign cells (like facial features); glycoproteins and glycolipids found
15
New cards
What is active transport?
require the cell’s energy, low to high concentration, works against diffusion

16
New cards
What is passive transport?
does not require cell energy, high to low concentration, diffusion

17
New cards
What is endocytosis?
cell membrane engulfs external substances and brings them into the cell
18
New cards
What are the different types of endocytosis?
Phagocytosis (cell "eating" = large) and pinocytosis (cell "drinking" = small )
19
New cards
What is exocytosis?
vesicles containing substances fuse with the plasma membrane and the contents are released to the exterior of the cell
20
New cards
How many cells are in the human body?
37.2 trillion
21
New cards
What is the difference between integral and peripheral proteins?
Integral proteins integrate into membrane structure vs peripheral proteins found on the exterior and interior surfaces of the membrane (attach)
22
New cards
What are examples of integral proteins?
Transport proteins, channel proteins, carrier protein, aquaporins
23
New cards
What are examples of peripheral proteins?
Glycoproteins
24
New cards
What is cell signaling and why is it important?
- part of any communication process that governs basic activities of cells and coordinates all cell actions.
- Errors in signaling interactions and cellular info processing are responsible for diseases (cancer, diabetes, autoimmunity)
- Diseases treated more effectively and theoretically, artificial tissues maybe created
- Errors in signaling interactions and cellular info processing are responsible for diseases (cancer, diabetes, autoimmunity)
- Diseases treated more effectively and theoretically, artificial tissues maybe created
25
New cards
What is the process of cell signaling as it occurs in receptor tyrosine kinases?
- Signaling molecules bind to receptor
- Receptors dimerize
- Tyrosine resides are phosphorylated
- Triggers a downstream cellular response
- Receptors dimerize
- Tyrosine resides are phosphorylated
- Triggers a downstream cellular response
26
New cards
What is phosphorylation?
addition of a phosphate group
27
New cards
What are second messengers?
molecule that helps activate something (specific termination)
28
New cards
What is phospholipase C?
an enzyme that facilitates the breakdown of PIP2 and DAG, which are both second messengers
29
New cards
What are some responses to cell signals?
Gene expression (transcription of RNA), increase in cellular metabolism (muscle cells), cell growth (cell divison ), cell death (apoptosis), termination of signal cascade
30
New cards
What is Respiration?
molecular process that breaks down glucose, produces waste products, and energy
31
New cards
What is ATP and how is it used by the cell as an energy source?
makes energy and provides fuel for the body
32
New cards
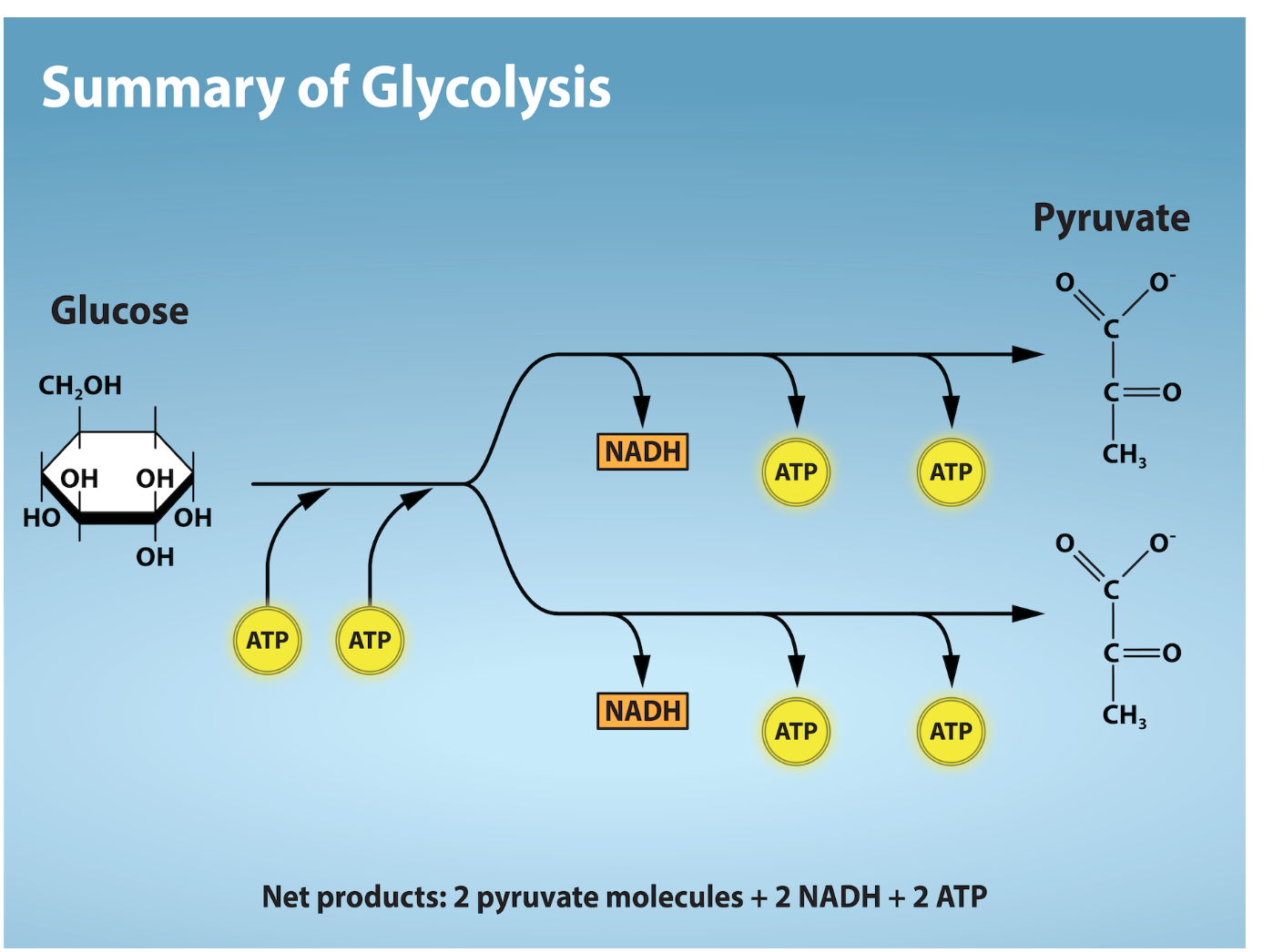
What is glycolysis?
breakdown of glucose by enzymes, releasing energy and pyruvic acid
33
New cards
What are the two phases of glycolysis?
Step 1: (energy required) uses two ATP molecules in the phosphorylation of glucose, which is then split into three-carbon molecules
Step 2: (energy releasing) involved phosphorylation without ATP investment and produces two NADH and four ATP molecules per glucose
Step 2: (energy releasing) involved phosphorylation without ATP investment and produces two NADH and four ATP molecules per glucose
34
New cards
What is the outcome of glycolysis?
4 new ATP molecules and 2 molecules of NADH
35
New cards
What is
a rate-limiting enzyme?
a rate-limiting enzyme?
an enzyme that regulates the rate of a metabolic pathway
36
New cards
What are some examples of a rate-limiting enzyme?
phosphofructokinase, pyruvate kinase
37
New cards
What is the electron transport chain?
series of electron transported embedded in inner mitochondrial membrane that shuttles electrons from NADH and FADH2 to molecular oxygen
38
New cards
What is lactic fermentation?
method used by animals and certain bacteria like yogurt
39
New cards
What is metabolism?
All the chemical reactions that take place inside cells including those that use energy and release energy
40
New cards
What is a metabolic pathway?
Series of interconnected biochemical reactions that convert a substrate molecule(s), step-by-step, through series of metabolic intermediates, eventually yielding a final product(s)
41
New cards
What happens during the glycolysis cycle?
breakdown of glucose in order to obtain ATP
42
New cards
What happens during the oxidative phosphorylation cycle?
disposal of electrons released by glycolysis and citric acid cycle
43
New cards
What happens during the krebs cycle / citric acid cycle?
acetyl-CoA oxidation in order to obtain GTP and valuable intermediates
44
New cards
What is an enzyme?
substance that lowers the activation energy of a reaction, but does not change the free energy of the reaction
45
New cards
What is a coenzyme?
small organic molecule which enhances activity of an enzyme; ex: vitamins
46
New cards
What is a cofactor?
non-protein channel chemical compound / metallic ion that is required for an enzymes activity
47
New cards
What is a substrate?
chemical reactants to which an enzyme binds
48
New cards
What is energy coupling?
transfer of energy from catabolism to anabolism / transfer of energy from exergonic process to endergonic process
49
New cards
What is activation energy?
energy required for a reaction to proceed, and it's lower if reaction catalyzed
50
New cards
What is kinetic energy?
energy associated w/ objects in motion; ex: airplane in flight
51
New cards
What is potential energy?
potential to do work
52
New cards
What is chemical energy?
providing living cells w/ energy from food; the release of energy is brought by breaking molecular bonds w/in fuel molecules (stored)
53
New cards
What are some examples of kinetic energy?
Moving water from a waterfall, an airplane in flight, a speeding bullet, a walking person, rapids molecule movement in the air, and electromagnetic radiation
54
New cards
What are some examples of potential energy?
suspended wrecking ball, water behind a dam
55
New cards
What are some examples of chemical energy?
The molecules in gasoline
56
New cards
What are the primary functions of the respiratory system?
deliver oxygen to cells of the body's tissue and remove carbon dioxide, a cell waste product
57
New cards
What are the structural components of the respiratory system?
nasal cavity, the trachea, and lungs
58
New cards
Why is hemoglobin so important?
carries oxygen to cells and carbon dioxide to lungs
59
New cards
What is the role of circulation within the immune system?
carries immune cells to destinations
60
New cards
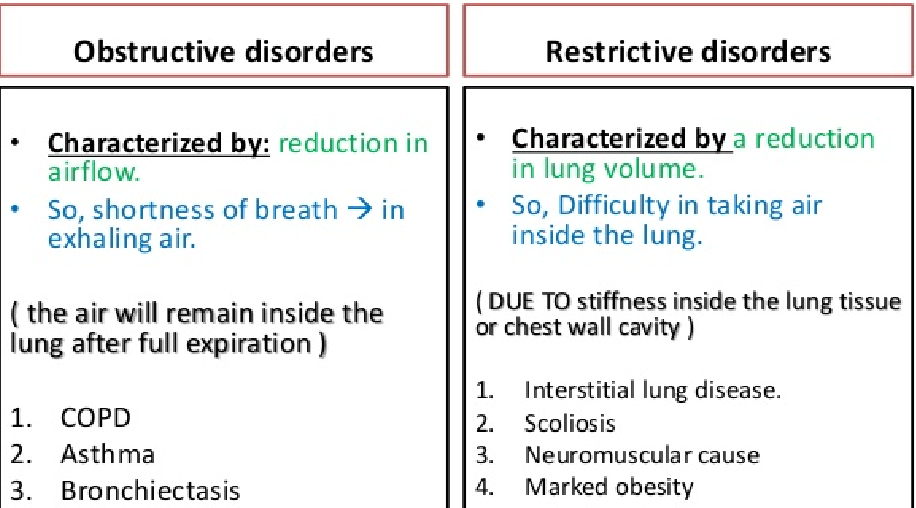
What are examples of obstructive lung diseases?
COPD, Asthma, Bronchiectasis
61
New cards
What are examples of restrictive lung diseases?
Intestinal lung disease, scoliosis, neuromuscular cause, marked obesity
62
New cards
What is the difference between obstructive and restrictive lung diseases?
obstruction is reduction in airflow vs restrictive is reduction in lung volume
63
New cards
What is the process of blood flow to the heart and to the body?
Blood is pushed through by pumping the heart.
First the aorta --> blood travels ---> arteries --> arterioles
--> capillary beds
First the aorta --> blood travels ---> arteries --> arterioles
--> capillary beds
64
New cards
What are the differences between arteries, veins, and capillaries?
Arteries take blood away from the heart.
Veins are blood vessels that bring blood black to the heart.
Capillaries connect veins and arteries and smallest.
Veins are blood vessels that bring blood black to the heart.
Capillaries connect veins and arteries and smallest.
65
New cards
Which organisms use diffusion as a means of obtaining oxygen?
Human circulatory system
66
New cards
What are the types of circulatory systems?
systemic, pulmonary, and coronary circuits
67
New cards
What are examples of organisms that have circulatory systems?
Fish, amphibians, reptiles, mammals/birds
68
New cards
All of the DNA within a genome encodes protein.
False
69
New cards
What major development in 1988 became the starting point for curating bioinformatic resources?
NCBI
70
New cards
For the purposes of Bioinformatics, a single strand of DNA can be thought of as a string of bases comprised of A, T, C, and P.
False
71
New cards
Cells build their protein from __ different amino acids.
20
72
New cards
Books and articles are considered important types of databases.
False
73
New cards
An organism's genome contains genes
True
74
New cards
Which of the following contains instructions for making proteins?
Genes
75
New cards
Which plasma membrane component can be either found on its surface or embedded in the membrane structure?
Protein
76
New cards
Which of the following is not an example of an energy transformation?
Turning on a light switch
77
New cards
Which transport mechanism can bring whole cells into a cell?
phagocytosis
78
New cards
What happens to the membrane of a vesicle after exocytosis?
It fuses with and becomes part of the plasma membrane.
79
New cards
Which of the following statements about the control of enzyme activity by phosphorylation is correct?
Phosphorylation of an enzyme results in a conformational change.
80
New cards
In what important way does receptor-mediated endocytosis differ from phagocytosis?
It brings in only a specifically targeted substance.
81
New cards
Which of the following enzyme catalyzes the first step of glycolysis?
Hexokinase
82
New cards
Which of the following is not true about enzymes:
They increase delta G of reactions.
83
New cards
Which of the following statements about the regulation of a metabolic pathway is correct?
Most metabolic pathways are regulated.
84
New cards
Which of the following statements about the control of enzyme activity by phosphorylation is correct?
Phosphorylation of an enzyme results in a conformational change.
85
New cards
Which type of metabolic fuel is utilized for generating glucose under conditions of severe starvation?
Amino Acids
86
New cards
Which of the following plasma membrane receptors activate signaling pathways usually by forming molecular dimers that result in protein phosphorylation reactions upon binding of their specific ligand?
Receptor tyrosine kinases
87
New cards
Enzymes lower the reaction's activation energy but do not change the reaction's free energy.
True
88
New cards
In the capillaries and veins, the blood pressure continues to decrease but velocity increases.
True
89
New cards
What condition was discussed in class as arising during prolonged exposure to high altitude such as in aviation?
hypoxia
90
New cards
Boyle's law states that pressure and ratio are inversely related.
False
91
New cards
Which of the following correctly lists the 3 circuits of the mammalian circulatory system?
systemic, pulmonary and coronary
92
New cards
Cilia move mucus and particles out of the bronchi and bronchioles back up to the throat where it is swallowed and eliminated via the esophagus.
True
93
New cards
Animals and Fungi have specialized connective tissues.
False
94
New cards
Arteries and capillaries consist of three layers, while veins consist of a single layer.
False
95
New cards
As we discussed in lecture and based on your understanding of the relationship between animal body size and activity level, which animal has the fastest metabolic rate?
Mouse
96
New cards
What is ATP?
Source of energy for use by cells
97
New cards
Pulmonary fibrosis is an obstructive disease.
False
98
New cards
Asthma is a restrictive disease.
False
99
New cards
Which of the following is not a feature common to most animals?
asexual reproduction
100
New cards
Which of the following animal has the simplest circulatory system?
Fish