CHEM 2510 / Topic 7: MS
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
What are the three universal functions of MS?
> Prod ions.
> Sep ions.
> Det ions.
(Mass spectrum shows abundance vs. mass/charge of ions)
• What is m/z?
• What is abundance?
> mass of a given ion divided by # of elem charge
> signal intensity of every m/z valu.
Define the ff.:
Base peak
Product ions.
Molecular ion.
Precursor ion.
base peak: p w/ greatest intensity (may/may not be molecular ion).
product ions: ions prod from precursor dissoc (aka fragment/daughter ions).
molecular ion: ion prod by removal from (positive ions) or addition of (negative ions) a molecule of one/more e- w/o frag of mol struc.
precursor ion: ion that dissoc to form prod ions (may/may not be molecular ion).
Define the ff.:
atomic mass
molecular mass
nominal mass
atomic mass: weighted avg of masses of isotopes of an element (use Da = 1/12 mass of single 12C).
molecular mass: sum of unified atomic mass unites of a molecule or ion (use u = unified atomic mass unit).
nominal mass: integer mass of most abundant isotope of each element in an ion/molecule.
What are the ways that analytes are usually introduced into the first stage of MS?
chromatog.
direct insertion probe (when MM of one X is required).
In GC, ionization of gaseous X is at low pressures. In HPLC and CE,
What are the five ionization modes?
Electron ionization.
Chemical ionization.
Field ionization.
Field desorption.
Plasma ionization.
How does EI work?
e-’s are emitted from a heated filament w/ energy of 70 eV.
Neutral X molecules enter the ion source orthogonal to beam of e-.
Molecules are bombarded w/ the e- beam → ionized.
(Less than 0.1% of neutral molecules are ionized).
What drives ionization in EI?
Why does EI use 70 eV?
Which electrons ionize first?
Why does EI cause fragmentation?
ionization energy (min energy to remove e- from gaseous mol).
70 eV >> typical molecular IE (e- loss is easy).
lowest IE e- (nonbonding < π < σ).
xs from 70 eV stays in ion = int E → bonds vibrate → mol fragments.
Why M+• often weak/absent in EI?
Why is EI a “hard” ionization technique?
xs E → rapid fragmentation.
high-E e- beam → extensive fragmentation (softer ionization tech (CI) can be employed).
How does CI work?
Reagent gas ionized.
Reagent ions form.
X ionized.
(Lower int E transferred w/ little frag)
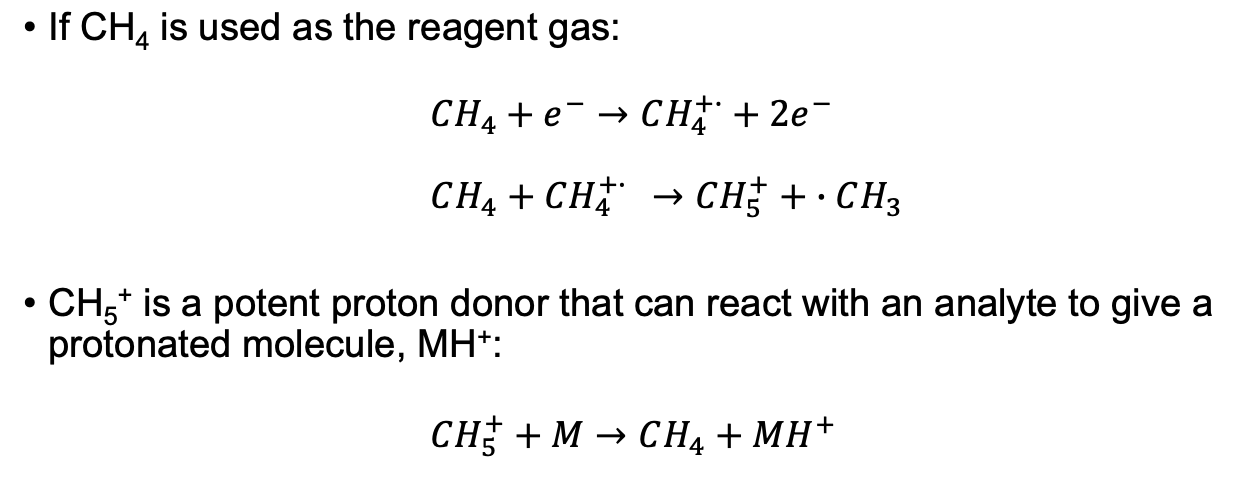
What are other ionization modes?
Electrospray ionization.
Atmospheric pressure chemical ionization.
Matrix-assisted laser desorption.
How does ESI ionize?
> high V sprays liquid → charged droplets.
> solv evaporates → gas-phase ions (often [M+H]⁺ / [M−H]⁻, multicharged).
How does APCI ionize?
> nebulized + heated liquid → gas.
> Reagent ions prod.
> proton transfer to X (usually single-charge ions).
How does MALDI ionize?
> Laser hits M + X.
> M absorbs E.
> X desorbs & ionizes.
> big biomolecules, minimal frag.
What are mass analyzers?
part of MS-mer separating ions by m/z.
For the second stage, why do mass analyzers operate at very low pressure?
Maximize mean free path → fewer ion-molecule collisions → accurate m/z separation (mean free path ≈ 1/P).
What are six types of mass analyzers?
quadrupole.
ion trap.
magnetic sector.
time of flight.
orbitraps.
ion cyclotron resonance.
Define the ff.:
Mass range.
Resolution.
Mass accuracy.
Scan rate.
Resolving power.
mass range: range over which the MS-meter analyzer can operate.
mass accuracy: how close the value determined is to the true value.
scan rate: speed at which an analyzer can scan (typically reported in decades/sec; decade = m/z 100 to m/z 1000).
resolution (∆m): how well a mass analyzer separates ions of different mass / smallest difference in m/z values that can be detected as separate peaks.
resolving power (R): how good the instrument is at separating close peaks.
(Good = big R and small ∆m.)
What are the two common approaches to defining R?
Valley approach: Measure ∆(m/z) b/w the centres of two neighbouring peaks, ensuring valley b/w them = 10% of peak height.
Full-width at half-maximum: Measure width of one peak at half max height (smaller w = better res).
What are the equations for determining R for valley approach and FWHM?
R_{valley}=\frac{\left(\frac{m}{z}\right)}{\Delta\left(\frac{m}{z}\right)}
R_{FWHM}=\frac{\left(\frac{m}{z}\right)}{\left(\frac{m}{z}\right)_{\frac12}}
Why does scan speed matter?
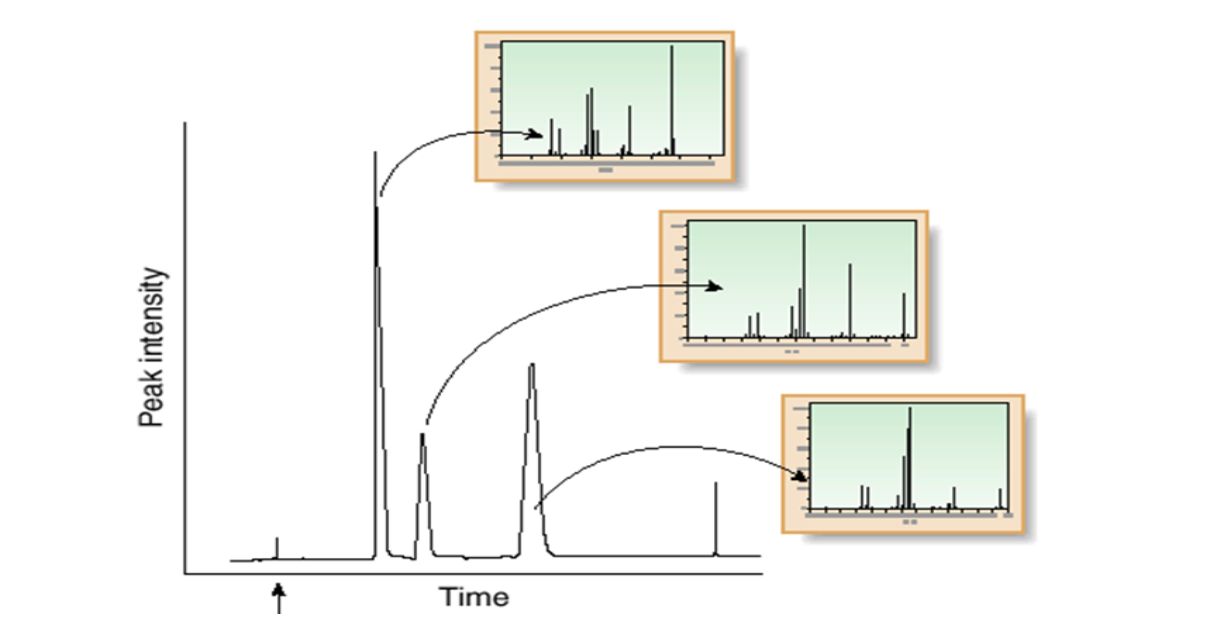
Chromatographic peaks are short-lived.
You need multiple spectra per peak to define it (more scans → better peak shape + quant).
GC peaks ~6–10 s → need fast scans. LC peaks ~10–20 s → can use slower scans. Goal: ~7–10 scans per chromatographic peak.
How does a full scan work?
Choose m/z range.
Instrument scans that range over and over (each sweep = one MS-rum).
How does a selected ion monitoring work?
pre-select specific m/z values / not scan everything → only small # of ions (m/z values characteristic of X) = usually strong/high intensity.
better DL b/c focused on smaller range.
What’s the advantage for SIM when compounds co-elute?
same tr but different m/z → sepped by mass resolution, not chromatog.
How do QqQ and QTOF differ?
QqQ: Q1 selects precursor → Q2 fragments → Q3 selects product (best for targeted quant, high sens).
QTOF: quadrupole selects ion → TOF measures exact m/z (best for ID + accurate mass, high resolution).
What is product/daughter ion scan used for? How does it work?
Used for structure elucidation.
Q1: Selects ONE parent (precursor) ion
Q2: Fragments the selected parent ion by CID.
Q3: Scans ALL daughter (product) ions
Many peaks = many daughters from one parent
What is precursor/parent ion scan used for? How does it work?
Used to link specific fragment ions w/ parent ion & det if peak present from desired cpd / interfering cpd.
Q1: Scans ALL parent (precursor) ions
Q2: Fragments each parent ion by CID.
Q3: Selects ONE daughter (product) ion.
Many peaks = many parents that produce the same daughter.
What is multiple reaction monitoring used for? How does it work?
Used for highly selective and sensitive quantitative analysis of known target analytes.
Q1: Selects ONE parent (precursor) ion.
Q2: Fragments the selected parent ion by CID.
Q3: Selects ONE daughter (product) ion.
One signal per parent → daughter transition.
(In MRM, the mass spectrometer rapidly cycles through predefined precursor–product ion transitions to monitor specific fragmentation reactions.)
What are the two types of MS detectors?
Faraday cup.
electron multiplier.
What are the six desirable features of a detector?
fast response time.
low electronic noise.
high collection efficiency.
same response for all m/z values.
large dynamic range.
long-term stability.